Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2023 Paul N 106
2023 Paul N 106
Uploaded by
Crystal ValdezThe document lists several respiratory and cardiovascular conditions that can cause dyspnea (shortness of breath). For each condition, it describes key signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, medical and surgical treatment options, and relevant nursing interventions. Respiratory conditions discussed include asthma. Cardiovascular conditions discussed include coronary artery disease. For each condition, specific clinical features, diagnostic tests, medical management strategies, possible surgical procedures, and nursing interventions are detailed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Comprehensive Critical Care UltrasoundDocument692 pagesComprehensive Critical Care UltrasoundRonei Renato RubboNo ratings yet
- V.courtney Broaddus MD (Editor), Joel D Ernst MD (Editor), Talmadge E King JR MD (Editor), Stephen C. Lazarus MD (Editor), Kathleen F. Sarmiento MD (Editor), Lynn M. Schnapp MD (Editor), Renee DDocument3,317 pagesV.courtney Broaddus MD (Editor), Joel D Ernst MD (Editor), Talmadge E King JR MD (Editor), Stephen C. Lazarus MD (Editor), Kathleen F. Sarmiento MD (Editor), Lynn M. Schnapp MD (Editor), Renee DKazuto Kath Torres100% (2)
- FAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN - AsthmaDocument1 pageFAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN - AsthmaJULIANNE BAYHON80% (5)
- 118A - Chapter 1 - CRITICAL CARE NURSING LEC (EDITED) Handout #1Document14 pages118A - Chapter 1 - CRITICAL CARE NURSING LEC (EDITED) Handout #1Joanna Taylan100% (5)
- Heart Failure Review QuestionsDocument33 pagesHeart Failure Review Questionszbestgurl100% (2)
- TB NCPDocument1 pageTB NCPPatricia JuatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperienceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperiencePauline GarciaNo ratings yet
- HSNS 264 - Part BDocument9 pagesHSNS 264 - Part BHarshana Sandaruwan SomarathneNo ratings yet
- Silliman University: Syllabus OnDocument5 pagesSilliman University: Syllabus OnAisen Denniel NeriNo ratings yet
- NAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen DATE: Oct. 7, 2019: Subjective: DXDocument2 pagesNAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen DATE: Oct. 7, 2019: Subjective: DXTyn TynNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 1Document10 pagesNCP 1 1Samantha VeraNo ratings yet
- Iac RT ObstructionDocument7 pagesIac RT Obstructionia.sumbillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP On URTIDocument8 pagesDrug Study and NCP On URTIRomhea MatmyrNo ratings yet
- University of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesUniversity of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANNo ratings yet
- Name: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaDocument2 pagesName: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaMae Therese B. MAGNONo ratings yet
- Qst. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDocument5 pagesQst. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindicati ONS Common Side Effects Nursing Considerations Generic NameDocument1 pageMechanism of Action Indication Contraindicati ONS Common Side Effects Nursing Considerations Generic NamegraceNo ratings yet
- Caballero NSTPDocument7 pagesCaballero NSTPClairyssa Myn D CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Final Thyroid Storm NCPDocument6 pagesFinal Thyroid Storm NCPoguitekim1No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument18 pagesNursing Care PlanLayo, Ivy L.No ratings yet
- ABADINGO-Pedia Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesABADINGO-Pedia Nursing Care PlanAndrea Abadingo100% (1)
- Careplan 2 NSG 434 CCDocument8 pagesCareplan 2 NSG 434 CCapi-509642710No ratings yet
- NCP Drug Study KriziaDocument5 pagesNCP Drug Study KriziaAlexia AlbaniaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternKimberly T. CaballeroNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 (N3A) - Bronchial Asthma Case Presentation ManusDocument39 pagesGROUP 2 (N3A) - Bronchial Asthma Case Presentation ManusMariane ViterboNo ratings yet
- Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center Inc.: College of NursingDocument6 pagesRamon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center Inc.: College of NursingJona Joyce JunsayNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning ASTHMADocument4 pagesDischarge Planning ASTHMANadja JamilahNo ratings yet
- Asthma WorksheetDocument5 pagesAsthma WorksheetÀi ZìjǐNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyCris SolisNo ratings yet
- Should Patients With Mild Asthma Use Inhaled SteroidsDocument5 pagesShould Patients With Mild Asthma Use Inhaled Steroidstsiko111No ratings yet
- Case # 4 Difficulty of BreathingDocument6 pagesCase # 4 Difficulty of BreathingGrace TanajuraNo ratings yet
- Ah HvdshjefkwrDocument10 pagesAh HvdshjefkwrArabella MostalesNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDocument5 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoNo ratings yet
- NCP Skills LabDocument6 pagesNCP Skills LabJunnie Rose IsiderioNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaBerina ŠarićNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaNurliyana GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short TermDocument7 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short TermOUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Go NCP IneffectivebreathingpatDocument7 pagesGo NCP IneffectivebreathingpatSAMANTHA T. MODESTONo ratings yet
- Respiratory Asthma: Common Signs and Symptoms of Asthma IncludeDocument18 pagesRespiratory Asthma: Common Signs and Symptoms of Asthma IncludeAen Panda BebeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationSam PothNo ratings yet
- ACCP Ambulatory CareDocument50 pagesACCP Ambulatory CareJim DansNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyNygie HaudarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearancemaxynezolayvarNo ratings yet
- FNCP FinalDocument5 pagesFNCP FinalGewel Bardaje AmboyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- FNCP AhitoDocument3 pagesFNCP AhitoHazel Grace AhitoNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Activity (NCP, Drug)Document25 pagesGroup 2 - Activity (NCP, Drug)christelNo ratings yet
- As Ma 2Document6 pagesAs Ma 2api-3728652No ratings yet
- NCP FDAR DS of Covid 19Document18 pagesNCP FDAR DS of Covid 19Lyka Shane Pineda AngalaNo ratings yet
- Ventolin DrugstudyDocument1 pageVentolin DrugstudyMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation ManingasDocument7 pagesCase Presentation ManingasestimojervsNo ratings yet
- Asthma 2.0Document5 pagesAsthma 2.0Pranjal SrivastavNo ratings yet
- NCP-Bronchial Asthma Without EvalDocument2 pagesNCP-Bronchial Asthma Without EvalTrisha Lapid MatulaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanRachelleNo ratings yet
- Independent:: Melanie Claire Torillo Bsn2 LeiningerDocument12 pagesIndependent:: Melanie Claire Torillo Bsn2 LeiningermelanieclairetorilloNo ratings yet
- Case-Scenario Respiratoty Disease During Pregnancy NCPDocument4 pagesCase-Scenario Respiratoty Disease During Pregnancy NCPChristianne CapuaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Cough: General Topics: Chapter 6Document3 pagesTreatment of Cough: General Topics: Chapter 6Martijn JohanNo ratings yet
- NCP Pagalanan PablicoDocument15 pagesNCP Pagalanan PablicoRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeRammiel Saylo CarlosNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Map of Nursing Roles and FunctionsDocument3 pagesConceptual Map of Nursing Roles and FunctionsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Burnett Rediscovered: Clinical Strategies of the Great Homeopath for Modern Practice – Line of Action of Remedies – Organ Remedies – Pathological Similimum – VaccinosisFrom EverandBurnett Rediscovered: Clinical Strategies of the Great Homeopath for Modern Practice – Line of Action of Remedies – Organ Remedies – Pathological Similimum – VaccinosisNo ratings yet
- Saint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing: Dumaguete City 2 Semester, Academic Year 2022-2023Document52 pagesSaint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing: Dumaguete City 2 Semester, Academic Year 2022-2023Crystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Paying For Them Immediately Upon Delivery. (POWER) : The Nature and Functions of CreditDocument2 pagesPaying For Them Immediately Upon Delivery. (POWER) : The Nature and Functions of CreditCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Politics and Political BehaviorDocument27 pagesPolitics and Political BehaviorCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan Topic: Psychotheraphy Education Date: Participants: Venue: Goal: at The End of The SessionDocument2 pagesHealth Teaching Plan Topic: Psychotheraphy Education Date: Participants: Venue: Goal: at The End of The SessionCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Group 4Document19 pagesMacroeconomics Group 4Crystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Usb GrayDocument3 pagesUsb GrayCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- A Case Study No.1 LeadershipDocument5 pagesA Case Study No.1 LeadershipCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Oral Business PresentationDocument1 pageOral Business PresentationCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Daftar Penyakit Telinga Hidung Tenggorok-Kepala Leher Menurut Icd 10Document10 pagesDaftar Penyakit Telinga Hidung Tenggorok-Kepala Leher Menurut Icd 10LA ODE ULU MAJIDNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rajendran'S Institute of Medical Education: Cvs - Anatomy (45 MCQS)Document15 pagesDr. Rajendran'S Institute of Medical Education: Cvs - Anatomy (45 MCQS)suckeydluffyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyFirst SnowNo ratings yet
- Management of Lower Extremity Pain From Chronic Venous Insufficiency: A Comprehensive ReviewDocument30 pagesManagement of Lower Extremity Pain From Chronic Venous Insufficiency: A Comprehensive Reviewangeline chandraNo ratings yet
- 16-K-Ca ImbalanceDocument11 pages16-K-Ca Imbalanceمصطفى محمد جواد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Moonlight RadiologyDocument40 pagesMoonlight RadiologyOJ Alexander NadongNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Mark K NotesDocument131 pagesNCLEX Mark K NotesRhika Mae ObraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case 1Document37 pagesDrug Study Case 1Maria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Application Details: About YouDocument11 pagesApplication Details: About YouMarius LixandruNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft CabgsurgeryDocument26 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Graft Cabgsurgeryfatha100% (1)
- HIpertensiDocument28 pagesHIpertensiasna tuppangNo ratings yet
- Log Book (Eng)Document10 pagesLog Book (Eng)revanth kallaNo ratings yet
- Summary of HyperthyroidismDocument8 pagesSummary of HyperthyroidismAbedinego MalukaNo ratings yet
- What Is CPR?Document7 pagesWhat Is CPR?Harshal AachrekarNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSIONDocument24 pagesHYPERTENSIONCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Tadano Hydraulic Crane Ar 1000m 1 p2 1ej Parts Catalog EnjpDocument22 pagesTadano Hydraulic Crane Ar 1000m 1 p2 1ej Parts Catalog Enjprachelharrison091289kdj100% (106)
- Drug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument18 pagesDrug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsJenica ManuntagNo ratings yet
- Cagayan Valley Medical Center Department of Surgery: Clinical Case DiscussionDocument60 pagesCagayan Valley Medical Center Department of Surgery: Clinical Case DiscussionVISHWAKARMA RAJATNo ratings yet
- Normal Ecg - EkgDocument2 pagesNormal Ecg - Ekgsonew89No ratings yet
- Osler-Weber-Rendu Disease - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument4 pagesOsler-Weber-Rendu Disease - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfanaNo ratings yet
- Obesity in Adults: Drug TherapyDocument36 pagesObesity in Adults: Drug TherapyGerman Barrientos CabreraNo ratings yet
- Anterior Cerebral Artery StrokeDocument9 pagesAnterior Cerebral Artery StrokeAlin CiubotaruNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Urinary SystemDocument26 pagesAnatomy of The Urinary Systemglenian560No ratings yet
- DM DFU Foot Assessment Form DraftDocument3 pagesDM DFU Foot Assessment Form DraftikhlaslivingNo ratings yet
- 022 PTSD & StrokeDocument2 pages022 PTSD & Strokejim912No ratings yet
- Acyanotic CHDDocument83 pagesAcyanotic CHDmrinmayee deshmukhNo ratings yet
2023 Paul N 106
2023 Paul N 106
Uploaded by
Crystal Valdez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views10 pagesThe document lists several respiratory and cardiovascular conditions that can cause dyspnea (shortness of breath). For each condition, it describes key signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, medical and surgical treatment options, and relevant nursing interventions. Respiratory conditions discussed include asthma. Cardiovascular conditions discussed include coronary artery disease. For each condition, specific clinical features, diagnostic tests, medical management strategies, possible surgical procedures, and nursing interventions are detailed.
Original Description:
Original Title
2023 PAUL N 106 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document lists several respiratory and cardiovascular conditions that can cause dyspnea (shortness of breath). For each condition, it describes key signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, medical and surgical treatment options, and relevant nursing interventions. Respiratory conditions discussed include asthma. Cardiovascular conditions discussed include coronary artery disease. For each condition, specific clinical features, diagnostic tests, medical management strategies, possible surgical procedures, and nursing interventions are detailed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views10 pages2023 Paul N 106
2023 Paul N 106
Uploaded by
Crystal ValdezThe document lists several respiratory and cardiovascular conditions that can cause dyspnea (shortness of breath). For each condition, it describes key signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, medical and surgical treatment options, and relevant nursing interventions. Respiratory conditions discussed include asthma. Cardiovascular conditions discussed include coronary artery disease. For each condition, specific clinical features, diagnostic tests, medical management strategies, possible surgical procedures, and nursing interventions are detailed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
PAUL N 106 - PROBLEM BASED LEARNING
In the Emergency Department (ED) or Emergency Room (ER), patient usually seek medical intervention because of dyspnea.
List down all diseases that will cause DYSPNEA. Please categorize according to system.
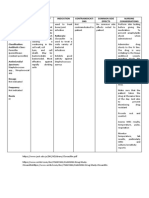
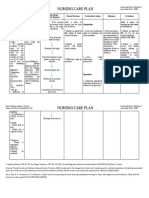
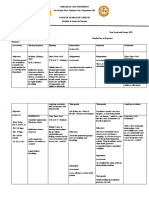
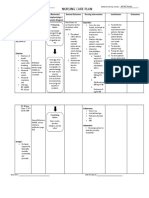
System Illness/Disease Signs/ Diagnostics/Labs Medical Surgical Nursing
Symptoms Management Managemen Intervention
(at least 6 t
clinical features)
Respirator Asthma Shortness Spirometry Medical Bronchial 1. Assess
y of breath. Peak flow management thermoplast respiratory
Cough. meter tests includes y status by
Chest Exhaled bronchodilators closely
tightness nitric oxide like beta-2 evaluating
or pain. test agonists and breathing
Wheeze (a Methacholin muscarinic patterns and
whistling e challenge antagonists monitoring
sound Imaging (salbutamol and vital signs.
when you tests ipratropium 2. Administer
breathe). Allergy bromide prescribed
breathing testing respectively) and medications,
faster. anti- such as
exhaustion inflammatories bronchodilato
or such as inhaled rs, anti-
dizziness. steroids (usually inflammatori
beclometasone es, and
but steroids via antibiotics.
any route will be 3. Promote
helpful). adequate
oxygenation
and a normal
breathing
pattern
4. Explain the
possible use
of
hyposensitiza
tion therapy
5. Help the
child cope
with poor
self-esteem
by
encouraging
him to
ventilate
feelings and
concerns.
Listen
actively as
the child
speaks, focus
on the child’s
strengths,
and help him
to identify the
positive and
negative
aspects of his
situation.
6. Discuss the
need for
periodic PFTs
to evaluate
and guide
therapy and
to monitor
the course f
the illness.
7. Provide child
and family
teaching.
Assist the
child and
family to
name signs
and
symptoms of
an acute
attack and
appropriate
treatment
measures
8. Refer the
family to
appropriate
community
agencies for
assistance.
Coronary Artery Chest pain Coronary The goals of Corona Monitor blood
Disease or Angiography medical ry pressure,
Cardiovas discomfort Echocardiog management are angiopl apical heart
cular (angina) ram (ECHO) to decrease the asty rate, and
Weakness Electrocardi oxygen demands and respirations
light- ogram (ECG of the stent every 5
headednes or EKG) myocardium and placem minutes
s Stress to increase the ent. during an
nausea Echocardiog oxygen supply Corona anginal
(feeling ram through ry attack.
sick to Stress pharmacological artery Maintain
your Thallium therapy and risk bypass continuous
stomach), Test factor control graft ECG
or a cold Chest X-ray surger monitoring or
sweat. y obtain a 12-
Pain or (CABG) lead ECG, as
discomfort . directed,
in the arms monitor for
or arrhythmias
shoulder. and ST
Shortness elevation.
of breath. Place patient
in
comfortable
position and
administer
oxygen, if
prescribed, to
enhance
myocardial
oxygen
supply.
Identify
specific
activities
patient may
engage in
that are
below the
level at which
anginal pain
occurs.
Reinforce the
importance of
notifying
nursing staff
whenever
angina pain
is
experienced.
Encourage
supine
position for
dizziness
caused by
antianginals.
Be alert to
adverse
reaction
related to
abrupt
discontinuati
on of beta-
adrenergic
blocker and
calcium
channel
blocker
therapy.
These drug
must be
tapered to
prevent a
“rebound
phenomenon”
; tachycardia,
increase in
chest pain,
and
hypertension.
Explain to
the patient
the
importance of
anxiety
reduction to
assist to
control
angina.
Teach the
patient
relaxation
techniques.
Review
specific
factors that
affect CAD
development
and
progression;
highlight
those risk
factors that
can be
modified and
controlled to
reduce the
risk.
Gastrointe Ulcerative Colitis Frequent Barium Treatments can Procto Promote
stinal diarrhea enema be broadly colecto nursing care
throughout Colonoscopy considered as my of the client
the day Stool those used to and who is
(usually analysis induce remission Brooke receiving
occurring 3 (at diagnosis or ileosto nothing by
or more for a subsequent my. mouth,
times) flare), such as 5- Abdom receiving oral
Headaches. aminosalicylic inal fluids, or on
Body acid (5-ASA) colecto total
aches. agents, my parenteral
Bloody or corticosteroids and nutrition
mucus- and biologics, and ilcorect during an
filled bowel those used for al acute
movement. long-term anasto exacerbation.
Mild fever. maintenance of mosis. Assess for
Nausea remission such as Procto fluid and
and 5-ASA agents, colecto electrolyte
vomiting. biologics and my imbalance.
thiopurines. and Administer IV
Kock fluids and
pouch. electrolytes
Restor as indicated.
ative Encourage a
procto low-residue,
colecto high-protein,
my high-calorie
with diet with
ileal supplemental
pouch- vitamin
anal therapy and
anasto iron
mosis replacement.
(IPAA). Implement
measures to
treat diarrhea
or
constipation.
Address and
mediate the
client’s pain.
Promote
intermittent
rest periods
and bed rest
when the
client has
acute
exacerbations
.
Endocrine Hyperthyroidism
Circulatory Arrhythmia Pounding in Electrocardiogr •
your chest. am (ECG or
Dizziness or EKG)
feeling Ambulatory
lightheaded. monitors
Shortness of Stress test
breath. Cardiac
Chest catheterization
discomfort. Echocardiogra
Weakness or m
fatigue Electrophysiolo
(feeling very gy study (EPS)
tired). Tilt tables test
Weakening of
the heart
muscle or low
ejection
fraction.
Lymphatic Lymphoma Painless Physical exam
swelling of Removing a
lymph nodes lymph node for
in your neck, testing
armpits or Blood tests
groin Removing a
Persistent sample of bone
fatigue marrow for
Fever testing
Shortness of Imaging tests
breath
Unexplained
weight loss
Itchy skin
You might also like
- Comprehensive Critical Care UltrasoundDocument692 pagesComprehensive Critical Care UltrasoundRonei Renato RubboNo ratings yet
- V.courtney Broaddus MD (Editor), Joel D Ernst MD (Editor), Talmadge E King JR MD (Editor), Stephen C. Lazarus MD (Editor), Kathleen F. Sarmiento MD (Editor), Lynn M. Schnapp MD (Editor), Renee DDocument3,317 pagesV.courtney Broaddus MD (Editor), Joel D Ernst MD (Editor), Talmadge E King JR MD (Editor), Stephen C. Lazarus MD (Editor), Kathleen F. Sarmiento MD (Editor), Lynn M. Schnapp MD (Editor), Renee DKazuto Kath Torres100% (2)
- FAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN - AsthmaDocument1 pageFAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN - AsthmaJULIANNE BAYHON80% (5)
- 118A - Chapter 1 - CRITICAL CARE NURSING LEC (EDITED) Handout #1Document14 pages118A - Chapter 1 - CRITICAL CARE NURSING LEC (EDITED) Handout #1Joanna Taylan100% (5)
- Heart Failure Review QuestionsDocument33 pagesHeart Failure Review Questionszbestgurl100% (2)
- TB NCPDocument1 pageTB NCPPatricia JuatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperienceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lorma Colleges Con Template Related Learning ExperiencePauline GarciaNo ratings yet
- HSNS 264 - Part BDocument9 pagesHSNS 264 - Part BHarshana Sandaruwan SomarathneNo ratings yet
- Silliman University: Syllabus OnDocument5 pagesSilliman University: Syllabus OnAisen Denniel NeriNo ratings yet
- NAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen DATE: Oct. 7, 2019: Subjective: DXDocument2 pagesNAME: Kristyn Joy D. Atangen DATE: Oct. 7, 2019: Subjective: DXTyn TynNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 1Document10 pagesNCP 1 1Samantha VeraNo ratings yet
- Iac RT ObstructionDocument7 pagesIac RT Obstructionia.sumbillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP On URTIDocument8 pagesDrug Study and NCP On URTIRomhea MatmyrNo ratings yet
- University of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesUniversity of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANNo ratings yet
- Name: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaDocument2 pagesName: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaMae Therese B. MAGNONo ratings yet
- Qst. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDocument5 pagesQst. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindicati ONS Common Side Effects Nursing Considerations Generic NameDocument1 pageMechanism of Action Indication Contraindicati ONS Common Side Effects Nursing Considerations Generic NamegraceNo ratings yet
- Caballero NSTPDocument7 pagesCaballero NSTPClairyssa Myn D CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Final Thyroid Storm NCPDocument6 pagesFinal Thyroid Storm NCPoguitekim1No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument18 pagesNursing Care PlanLayo, Ivy L.No ratings yet
- ABADINGO-Pedia Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesABADINGO-Pedia Nursing Care PlanAndrea Abadingo100% (1)
- Careplan 2 NSG 434 CCDocument8 pagesCareplan 2 NSG 434 CCapi-509642710No ratings yet
- NCP Drug Study KriziaDocument5 pagesNCP Drug Study KriziaAlexia AlbaniaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternKimberly T. CaballeroNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 (N3A) - Bronchial Asthma Case Presentation ManusDocument39 pagesGROUP 2 (N3A) - Bronchial Asthma Case Presentation ManusMariane ViterboNo ratings yet
- Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center Inc.: College of NursingDocument6 pagesRamon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center Inc.: College of NursingJona Joyce JunsayNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning ASTHMADocument4 pagesDischarge Planning ASTHMANadja JamilahNo ratings yet
- Asthma WorksheetDocument5 pagesAsthma WorksheetÀi ZìjǐNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyCris SolisNo ratings yet
- Should Patients With Mild Asthma Use Inhaled SteroidsDocument5 pagesShould Patients With Mild Asthma Use Inhaled Steroidstsiko111No ratings yet
- Case # 4 Difficulty of BreathingDocument6 pagesCase # 4 Difficulty of BreathingGrace TanajuraNo ratings yet
- Ah HvdshjefkwrDocument10 pagesAh HvdshjefkwrArabella MostalesNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDocument5 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoNo ratings yet
- NCP Skills LabDocument6 pagesNCP Skills LabJunnie Rose IsiderioNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaBerina ŠarićNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaNurliyana GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short TermDocument7 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short TermOUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY COLLEGENo ratings yet
- Go NCP IneffectivebreathingpatDocument7 pagesGo NCP IneffectivebreathingpatSAMANTHA T. MODESTONo ratings yet
- Respiratory Asthma: Common Signs and Symptoms of Asthma IncludeDocument18 pagesRespiratory Asthma: Common Signs and Symptoms of Asthma IncludeAen Panda BebeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationSam PothNo ratings yet
- ACCP Ambulatory CareDocument50 pagesACCP Ambulatory CareJim DansNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyNygie HaudarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearancemaxynezolayvarNo ratings yet
- FNCP FinalDocument5 pagesFNCP FinalGewel Bardaje AmboyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- FNCP AhitoDocument3 pagesFNCP AhitoHazel Grace AhitoNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Activity (NCP, Drug)Document25 pagesGroup 2 - Activity (NCP, Drug)christelNo ratings yet
- As Ma 2Document6 pagesAs Ma 2api-3728652No ratings yet
- NCP FDAR DS of Covid 19Document18 pagesNCP FDAR DS of Covid 19Lyka Shane Pineda AngalaNo ratings yet
- Ventolin DrugstudyDocument1 pageVentolin DrugstudyMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation ManingasDocument7 pagesCase Presentation ManingasestimojervsNo ratings yet
- Asthma 2.0Document5 pagesAsthma 2.0Pranjal SrivastavNo ratings yet
- NCP-Bronchial Asthma Without EvalDocument2 pagesNCP-Bronchial Asthma Without EvalTrisha Lapid MatulaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanRachelleNo ratings yet
- Independent:: Melanie Claire Torillo Bsn2 LeiningerDocument12 pagesIndependent:: Melanie Claire Torillo Bsn2 LeiningermelanieclairetorilloNo ratings yet
- Case-Scenario Respiratoty Disease During Pregnancy NCPDocument4 pagesCase-Scenario Respiratoty Disease During Pregnancy NCPChristianne CapuaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Cough: General Topics: Chapter 6Document3 pagesTreatment of Cough: General Topics: Chapter 6Martijn JohanNo ratings yet
- NCP Pagalanan PablicoDocument15 pagesNCP Pagalanan PablicoRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeRammiel Saylo CarlosNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Map of Nursing Roles and FunctionsDocument3 pagesConceptual Map of Nursing Roles and FunctionsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Burnett Rediscovered: Clinical Strategies of the Great Homeopath for Modern Practice – Line of Action of Remedies – Organ Remedies – Pathological Similimum – VaccinosisFrom EverandBurnett Rediscovered: Clinical Strategies of the Great Homeopath for Modern Practice – Line of Action of Remedies – Organ Remedies – Pathological Similimum – VaccinosisNo ratings yet
- Saint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing: Dumaguete City 2 Semester, Academic Year 2022-2023Document52 pagesSaint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing: Dumaguete City 2 Semester, Academic Year 2022-2023Crystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Paying For Them Immediately Upon Delivery. (POWER) : The Nature and Functions of CreditDocument2 pagesPaying For Them Immediately Upon Delivery. (POWER) : The Nature and Functions of CreditCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Politics and Political BehaviorDocument27 pagesPolitics and Political BehaviorCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan Topic: Psychotheraphy Education Date: Participants: Venue: Goal: at The End of The SessionDocument2 pagesHealth Teaching Plan Topic: Psychotheraphy Education Date: Participants: Venue: Goal: at The End of The SessionCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Group 4Document19 pagesMacroeconomics Group 4Crystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Usb GrayDocument3 pagesUsb GrayCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- A Case Study No.1 LeadershipDocument5 pagesA Case Study No.1 LeadershipCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Oral Business PresentationDocument1 pageOral Business PresentationCrystal ValdezNo ratings yet
- Daftar Penyakit Telinga Hidung Tenggorok-Kepala Leher Menurut Icd 10Document10 pagesDaftar Penyakit Telinga Hidung Tenggorok-Kepala Leher Menurut Icd 10LA ODE ULU MAJIDNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rajendran'S Institute of Medical Education: Cvs - Anatomy (45 MCQS)Document15 pagesDr. Rajendran'S Institute of Medical Education: Cvs - Anatomy (45 MCQS)suckeydluffyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyFirst SnowNo ratings yet
- Management of Lower Extremity Pain From Chronic Venous Insufficiency: A Comprehensive ReviewDocument30 pagesManagement of Lower Extremity Pain From Chronic Venous Insufficiency: A Comprehensive Reviewangeline chandraNo ratings yet
- 16-K-Ca ImbalanceDocument11 pages16-K-Ca Imbalanceمصطفى محمد جواد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Moonlight RadiologyDocument40 pagesMoonlight RadiologyOJ Alexander NadongNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Mark K NotesDocument131 pagesNCLEX Mark K NotesRhika Mae ObraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case 1Document37 pagesDrug Study Case 1Maria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Application Details: About YouDocument11 pagesApplication Details: About YouMarius LixandruNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft CabgsurgeryDocument26 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Graft Cabgsurgeryfatha100% (1)
- HIpertensiDocument28 pagesHIpertensiasna tuppangNo ratings yet
- Log Book (Eng)Document10 pagesLog Book (Eng)revanth kallaNo ratings yet
- Summary of HyperthyroidismDocument8 pagesSummary of HyperthyroidismAbedinego MalukaNo ratings yet
- What Is CPR?Document7 pagesWhat Is CPR?Harshal AachrekarNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSIONDocument24 pagesHYPERTENSIONCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Tadano Hydraulic Crane Ar 1000m 1 p2 1ej Parts Catalog EnjpDocument22 pagesTadano Hydraulic Crane Ar 1000m 1 p2 1ej Parts Catalog Enjprachelharrison091289kdj100% (106)
- Drug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument18 pagesDrug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsJenica ManuntagNo ratings yet
- Cagayan Valley Medical Center Department of Surgery: Clinical Case DiscussionDocument60 pagesCagayan Valley Medical Center Department of Surgery: Clinical Case DiscussionVISHWAKARMA RAJATNo ratings yet
- Normal Ecg - EkgDocument2 pagesNormal Ecg - Ekgsonew89No ratings yet
- Osler-Weber-Rendu Disease - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument4 pagesOsler-Weber-Rendu Disease - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfanaNo ratings yet
- Obesity in Adults: Drug TherapyDocument36 pagesObesity in Adults: Drug TherapyGerman Barrientos CabreraNo ratings yet
- Anterior Cerebral Artery StrokeDocument9 pagesAnterior Cerebral Artery StrokeAlin CiubotaruNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Urinary SystemDocument26 pagesAnatomy of The Urinary Systemglenian560No ratings yet
- DM DFU Foot Assessment Form DraftDocument3 pagesDM DFU Foot Assessment Form DraftikhlaslivingNo ratings yet
- 022 PTSD & StrokeDocument2 pages022 PTSD & Strokejim912No ratings yet
- Acyanotic CHDDocument83 pagesAcyanotic CHDmrinmayee deshmukhNo ratings yet