Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mariano, Luis Sidney N. - Discussion Points For Topic 6
Mariano, Luis Sidney N. - Discussion Points For Topic 6
Uploaded by
Sidney Mariano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageThe document discusses two multilateral institutions, the World Bank and IMF, and their influence on national policies. It describes how the World Bank was unwilling to support industrial projects that could help countries become self-sufficient. It also notes that World Bank loans required repayment by purchasing goods from industrialized nations. The document then summarizes that the IMF was founded to promote monetary cooperation and balance of payments adjustments. It explains that the IMF has power through members' contributions and expertise in financial stability, making countries reliant on their advice.
Original Description:
Original Title
Mariano, Luis Sidney N._Discussion Points for Topic 6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses two multilateral institutions, the World Bank and IMF, and their influence on national policies. It describes how the World Bank was unwilling to support industrial projects that could help countries become self-sufficient. It also notes that World Bank loans required repayment by purchasing goods from industrialized nations. The document then summarizes that the IMF was founded to promote monetary cooperation and balance of payments adjustments. It explains that the IMF has power through members' contributions and expertise in financial stability, making countries reliant on their advice.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageMariano, Luis Sidney N. - Discussion Points For Topic 6
Mariano, Luis Sidney N. - Discussion Points For Topic 6
Uploaded by
Sidney MarianoThe document discusses two multilateral institutions, the World Bank and IMF, and their influence on national policies. It describes how the World Bank was unwilling to support industrial projects that could help countries become self-sufficient. It also notes that World Bank loans required repayment by purchasing goods from industrialized nations. The document then summarizes that the IMF was founded to promote monetary cooperation and balance of payments adjustments. It explains that the IMF has power through members' contributions and expertise in financial stability, making countries reliant on their advice.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Multilateral Institutions and Its Influence in National
Decision and Policy Making: The World Bank (WB) and
the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
The reading “The Creation of the Bretton Woods Institutions” by Eric
Toussaint (2007) was an eye-opener to the United States' (U.S.) behavior
throughout history as a leading power. What it seems to me—the U.S.
together with colonial powers designed a system wherein developing
countries are intended to fail and suffer. For instance, the World Bank was
observed to be disapproving or unwilling to loan industrial-related projects
that would help a developing country satisfy its domestic affairs and soon
after rely on its own. Additionally, the loans given to developing countries
must be paid back by purchasing goods and services from industrialized
countries or the North. Although this can be seen as “justified” or “normal”
payback because the money they used was mostly from the contributions of
first-world countries, the policy would have been more inclusive and
charitable if debtors could use what they earned to pay it forward to less
developed countries while still repaying their loans to the WB.
Barnett and Finnemore (2004) in “Expertise and Power at the International
Monetary Fund” explained all the basic information about the IMF, such as
its mission, structure, and autonomy. Firstly, the IMF is known to be founded
on the purposes of monetary cooperation, stability of globalization, and
balance-of-payments adjustments. Secondly, the IMF is designed for power
to reside on state members and not on a central group representative of a
lone country’s interest—power depends on the size of a country’s wealth and
prosperity. Thirdly, the IMF is independent in resources and does not have
to rely on governments or organizations—this means that when members
join the IMF, they contribute a one-time “quota” and additional costs are
only going to be paid if that member is interested. Essentially, the IMF banks
on its expertise and knowledge (i.e., great emphasis on staff and financial
stability), making it the primary reason why countries rely on them for
financial aspects.
Bibliography
Barnett, M., & Finnemore, M. (2004). Rules for the World: International Organizations in Global Politics. Cornell University Press.
Toussaint, E. (2007). The World Bank: A Critical Primer.
MARIANO, LUIS SIDNEY N.
II - B PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION
PA 103 - MWZ
You might also like
- Philippine Public DebtDocument20 pagesPhilippine Public Debtmark genove100% (3)
- Spotify Strategig Possining and Product Life Cycle Four Basic Stages.Document5 pagesSpotify Strategig Possining and Product Life Cycle Four Basic Stages.Jorge YeshayahuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To International Development CH10Document20 pagesIntroduction To International Development CH10snowdave1997No ratings yet
- Escaping PovertyDocument26 pagesEscaping PovertyMădălina NistorNo ratings yet
- 2008 Usaid Enhancing Governement Effectiveness in YemenDocument30 pages2008 Usaid Enhancing Governement Effectiveness in YemenYemen ExposedNo ratings yet
- HHRG 112 BA19 WState PKlein 20120508Document16 pagesHHRG 112 BA19 WState PKlein 20120508Eric GarrisNo ratings yet
- Canova 2015Document32 pagesCanova 2015HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Sovereignty, Developing Countries and International Financial Institutions: A Reply To David WilliamsDocument6 pagesSovereignty, Developing Countries and International Financial Institutions: A Reply To David Williamsimdad ullahNo ratings yet
- Summary of Anderson and Kukucha Chapter 9: The World Bank and International DevelopmentDocument3 pagesSummary of Anderson and Kukucha Chapter 9: The World Bank and International DevelopmentFria SumitroNo ratings yet
- Escaping Poverty Leeson PDFDocument26 pagesEscaping Poverty Leeson PDFNico BicannNo ratings yet
- Dambisa Moyos Dead Aid A Critical Review PDFDocument25 pagesDambisa Moyos Dead Aid A Critical Review PDFscribd00com50% (2)
- No. 25 - Safeguarding Prosperity in A Global Financial System: The Future International Financial ArchitectureDocument91 pagesNo. 25 - Safeguarding Prosperity in A Global Financial System: The Future International Financial ArchitecturebowssenNo ratings yet
- Preempting Postcolonial GrowthDocument26 pagesPreempting Postcolonial GrowthrteehaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 What Is MoneyDocument6 pagesAssignment 4 What Is MoneyMuhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- MFG en Paper The Commercialization of Microfinance in Latin America Apr 2009 PDFDocument129 pagesMFG en Paper The Commercialization of Microfinance in Latin America Apr 2009 PDFVICTOR TERANNo ratings yet
- A Critique of The Recession of 1920Document32 pagesA Critique of The Recession of 1920Zerohedge100% (1)
- Evolution of Banking FinalDocument7 pagesEvolution of Banking FinalDouglasNo ratings yet
- Primer On 21st Century Free Trade AgreementsDocument132 pagesPrimer On 21st Century Free Trade AgreementsSasha FierceNo ratings yet
- Marta Arias José María VeraDocument28 pagesMarta Arias José María VeraVictor Nasser ValadezNo ratings yet
- Defying Bureaucratic Malfeasance: The IMF's Push For Good GovernanceDocument12 pagesDefying Bureaucratic Malfeasance: The IMF's Push For Good GovernanceoheokharisNo ratings yet
- Microfinance Introduction Evolution NotesDocument5 pagesMicrofinance Introduction Evolution NotesMIRADOR ACCOUNTANTS KENYANo ratings yet
- Differ IMF and World BankDocument11 pagesDiffer IMF and World BankVipin MohanNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The Role of States' in Face of A Global PandemicDocument7 pagesAnalyzing The Role of States' in Face of A Global PandemicISHA HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- 2000 DoJ Memo About USAID and Terrorism Finance From 9/11commission FilesDocument25 pages2000 DoJ Memo About USAID and Terrorism Finance From 9/11commission Files9/11 Document Archive100% (1)
- EC304 Essay 1Document9 pagesEC304 Essay 1Ashley ConnerNo ratings yet
- EC304 Essay 1Document10 pagesEC304 Essay 1Ashley ConnerNo ratings yet
- M2T2 Detalo BSEM2 TCWDocument5 pagesM2T2 Detalo BSEM2 TCWLoren Mae DetaloNo ratings yet
- Πρόταση για χρέη στο ΔΝΤDocument24 pagesΠρόταση για χρέη στο ΔΝΤnbnewsNo ratings yet
- Braun - Koddenbrock - Three Phases of Financial-Sector PowerDocument34 pagesBraun - Koddenbrock - Three Phases of Financial-Sector PowerEmiliaNo ratings yet
- The Rotten Roots of The IMF and The World Bank - The NationDocument9 pagesThe Rotten Roots of The IMF and The World Bank - The NationZallan KhanNo ratings yet
- 2-CSO Accountability and National Coordination-VietnamDocument36 pages2-CSO Accountability and National Coordination-VietnamLinh ChiNo ratings yet
- Social Capital and Civil SocietyDocument19 pagesSocial Capital and Civil SocietyAlexandre SkarsgårdNo ratings yet
- Public FinancesDocument5 pagesPublic Financesteebone747100% (1)
- Maniago, Aizel D. Annotation No. 4Document9 pagesManiago, Aizel D. Annotation No. 4Aizel ManiagoNo ratings yet
- Universal Basic Income PowerpointDocument12 pagesUniversal Basic Income Powerpointsamocamo 123No ratings yet
- Basic Income in Times of Grave Economic CrisisDocument10 pagesBasic Income in Times of Grave Economic Crisismoebius70No ratings yet
- MG214-s11152110 - Assignment 2Document5 pagesMG214-s11152110 - Assignment 2Pedro De Suarez RooneyNo ratings yet
- Harry Wilson Pensions White PaperDocument53 pagesHarry Wilson Pensions White PaperCeleste KatzNo ratings yet
- Frieden - Brettonwoods - Dec2017 (1) .PDF-WT - SummariesDocument4 pagesFrieden - Brettonwoods - Dec2017 (1) .PDF-WT - SummariesGagan AnandNo ratings yet
- Group6 ClassE20 - 1930's Economic Crisis in USADocument3 pagesGroup6 ClassE20 - 1930's Economic Crisis in USAHồng VyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Global Economy Market IntegrationDocument17 pagesChapter 23 Global Economy Market IntegrationFLORENCE DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Imf and World BankDocument5 pagesImf and World BankAhmad Waqas DarNo ratings yet
- The World Bank and The Privatization of Public Education - A Mexican PerspectiveDocument33 pagesThe World Bank and The Privatization of Public Education - A Mexican Perspectivehumb_santosNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter For Puplic EnterpriseDocument84 pagesFull Chapter For Puplic Enterprise0913314630No ratings yet
- Proposition of ValueDocument11 pagesProposition of ValueyonoidNo ratings yet
- MGT of Financial MKT & Instu CH-1Document6 pagesMGT of Financial MKT & Instu CH-1fitsumNo ratings yet
- Financial Literacy, Financial Education and Economic OutcomesDocument42 pagesFinancial Literacy, Financial Education and Economic OutcomesManuel GanglNo ratings yet
- Powell 20200519 ADocument8 pagesPowell 20200519 Ajack venitraNo ratings yet
- Working Paper: On What Terms Is The IMF Worth Funding?Document35 pagesWorking Paper: On What Terms Is The IMF Worth Funding?Saima FaqeerNo ratings yet
- Ponzi Finance and Global Liquidity Meltdown: Lessons From MinskyDocument13 pagesPonzi Finance and Global Liquidity Meltdown: Lessons From MinskyJames PatelNo ratings yet
- Midterm Module ContempDocument11 pagesMidterm Module Contempotherpurposes496No ratings yet
- Imf WB How Do They DifferDocument15 pagesImf WB How Do They DifferRiya DasNo ratings yet
- Case Study Solution: Future of World Bank and IMFDocument5 pagesCase Study Solution: Future of World Bank and IMFJithu Jose ParackalNo ratings yet
- Common Criticisms FINALDocument10 pagesCommon Criticisms FINALAtish KissoonNo ratings yet
- (Done) The Microfinance PromiseDocument105 pages(Done) The Microfinance PromiseVadimNo ratings yet
- Toc Aff v.1Document13 pagesToc Aff v.1Sully MrkvaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 8551982735374377674Document8 pagesInbound 8551982735374377674Ryan austriaNo ratings yet
- Esr Assignmt 1nov11Document12 pagesEsr Assignmt 1nov11hashimhafiz10% (1)
- IMF Governance and The Issue On PoliticizationDocument2 pagesIMF Governance and The Issue On PoliticizationAmmar KattoulaNo ratings yet
- Notes1 2 21Document20 pagesNotes1 2 21Sidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- (POLSC11) CH1-4 Revision Notes (Sir's Version)Document7 pages(POLSC11) CH1-4 Revision Notes (Sir's Version)Sidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Mariano, Luis Sidney N. - Discussion Points For Topic 3Document1 pageMariano, Luis Sidney N. - Discussion Points For Topic 3Sidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Mariano, Luis Sidney N. - Discussion Points For Topic 5Document1 pageMariano, Luis Sidney N. - Discussion Points For Topic 5Sidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Politics Notes 2 17Document16 pagesPolitics Notes 2 17Sidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Congress of The Philippines: (Epublic CT ODocument4 pagesCongress of The Philippines: (Epublic CT OSidney MarianoNo ratings yet
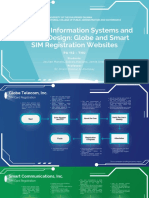
- Manalo, Mariano, Unas - Designing Information Systems and Content DesignDocument11 pagesManalo, Mariano, Unas - Designing Information Systems and Content DesignSidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Mariano LuisSidney WW2Document2 pagesMariano LuisSidney WW2Sidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Mariano, Luis Sidney N. - Discussion Points For Topic 2Document1 pageMariano, Luis Sidney N. - Discussion Points For Topic 2Sidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Mariano LuisSidney WW4Document3 pagesMariano LuisSidney WW4Sidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Mariano LuisSidney WW1Document4 pagesMariano LuisSidney WW1Sidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Community Profile and Narrative ReportDocument61 pagesCommunity Profile and Narrative ReportSidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- The Feasibility of Aquaponics in T.L.E. Garden of Sto. Tomas de Villanueva Parochial SchoolDocument61 pagesThe Feasibility of Aquaponics in T.L.E. Garden of Sto. Tomas de Villanueva Parochial SchoolSidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Group1 PETA2Document44 pagesGroup1 PETA2Sidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Community Profile and Narrative ReportDocument66 pagesCommunity Profile and Narrative ReportSidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Flood in Brgy. 293, Binondo, Manila Through Waste ManagementDocument55 pagesPrevention of Flood in Brgy. 293, Binondo, Manila Through Waste ManagementSidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Name: Mariano, Luis Sidney N. Date: NOVEMBER 16, 2020 Yr.& Section: 12-HUMSS 2 POSCDocument7 pagesName: Mariano, Luis Sidney N. Date: NOVEMBER 16, 2020 Yr.& Section: 12-HUMSS 2 POSCSidney MarianoNo ratings yet
- Guaranty and Suretyship CasesDocument82 pagesGuaranty and Suretyship Cases001nooneNo ratings yet
- Annexure-10b) MA5620 & MA5626 Product Description PDFDocument52 pagesAnnexure-10b) MA5620 & MA5626 Product Description PDFFares DamNo ratings yet
- Brigada Solicitation and InvitationDocument3 pagesBrigada Solicitation and Invitationguendolyn templadoNo ratings yet
- Appendix 2 Works ListDocument18 pagesAppendix 2 Works ListAnonymous 4BZUZwNo ratings yet
- Importance of Assessment of Intelligence in Clinical PsychologyDocument1 pageImportance of Assessment of Intelligence in Clinical PsychologyKimberly AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Script of The Discussion of The Agenda ItemsDocument2 pagesScript of The Discussion of The Agenda Itemsapi-326200277No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Metabolism Adapted From Zhihong Li Material - May 2024Document79 pagesNucleic Acid Metabolism Adapted From Zhihong Li Material - May 2024Black RavenoidNo ratings yet
- Systematix Sona BLW Initiates CoverageDocument32 pagesSystematix Sona BLW Initiates Coveragejitendra76No ratings yet
- Magnetic Systems Specific Heat$Document13 pagesMagnetic Systems Specific Heat$andres arizaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Oral Cryotherapy in Preventing Chemotherapy Induced Oral Stomatitis Among Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDocument10 pagesEffect of Oral Cryotherapy in Preventing Chemotherapy Induced Oral Stomatitis Among Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaIjahss JournalNo ratings yet
- 13 3friedman PDFDocument20 pages13 3friedman PDFfreedownloads1No ratings yet
- Dial Plan Implementation: Introducing Call RoutingDocument180 pagesDial Plan Implementation: Introducing Call RoutingGuillermo Ex TottiNo ratings yet
- Hasil To SBMPTN Gratis 7Document129 pagesHasil To SBMPTN Gratis 7MauzNo ratings yet
- HRM Project On Engro FoodsDocument20 pagesHRM Project On Engro FoodsSaad MughalNo ratings yet
- Oops (Object Oriented Programming Structure)Document10 pagesOops (Object Oriented Programming Structure)MANOJ SNo ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Klien Dengan Pasca Operasi Hernia Inguinalis Di Lt.6 Darmawan Rs Kepresidenan Rspad Gatot Soebroto Jakarta Tahun 2019Document7 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Klien Dengan Pasca Operasi Hernia Inguinalis Di Lt.6 Darmawan Rs Kepresidenan Rspad Gatot Soebroto Jakarta Tahun 2019Ggp Kristus Raja SuliNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Coronation NightDocument8 pagesFinancial Statement Coronation NightRuel Gapuz ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Problem StatementDocument15 pagesProblem Statementcabamaro100% (3)
- American Cinematographer - March 1969Document98 pagesAmerican Cinematographer - March 1969daniel boronat rubioNo ratings yet
- Installing Wonderware InTouch 2014 R2 DevelopmentDocument12 pagesInstalling Wonderware InTouch 2014 R2 DevelopmentARMANDO GALENONo ratings yet
- Bowthorpe News May 2017Document36 pagesBowthorpe News May 2017Anonymous AySEIwycNo ratings yet
- Backward Calculation For Bearing Capacity Estimation of Geogrid Reinforced Foundation by Finite Element MethodDocument13 pagesBackward Calculation For Bearing Capacity Estimation of Geogrid Reinforced Foundation by Finite Element MethodFoolad GharbNo ratings yet
- Mail Delivery SubsystemDocument9 pagesMail Delivery SubsystemLu GuessaNo ratings yet
- The Eternal VeritiesDocument81 pagesThe Eternal VeritiesDr Jacquelyn PY SooNo ratings yet
- KPSEA NominalRoll SCHDocument3 pagesKPSEA NominalRoll SCHjared odhiamboNo ratings yet
- MODULEDocument8 pagesMODULEFrances Nicole SegundoNo ratings yet
- Mortality RateDocument5 pagesMortality Rateamit kumar dewanganNo ratings yet
- RA 020 Risk Assessment - Risk Assessment - Installation of Cables in Ducts & TrenchesDocument11 pagesRA 020 Risk Assessment - Risk Assessment - Installation of Cables in Ducts & Trenchesthomson100% (2)
- Igc Code Implemented in DNV RulesDocument123 pagesIgc Code Implemented in DNV Ruleslearsipi061No ratings yet