Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MECH-OF-DEFORMABL-BODIES-EVALuation 2
MECH-OF-DEFORMABL-BODIES-EVALuation 2
Uploaded by
Joshua OrcalesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MECH-OF-DEFORMABL-BODIES-EVALuation 2
MECH-OF-DEFORMABL-BODIES-EVALuation 2
Uploaded by
Joshua OrcalesCopyright:
Available Formats
REVIEW EVALUATION 4
Mechanics of Deformable Bodies
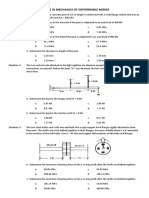
Situation 1: The two steel 9. Determine the decrease in length of the post.
shafts each with one end built a. 1.56 mm
into a rigid support have b. 1.18 mm
flanges rigidly attached to c. 1.78 mm
their free ends. The shafts are d. 1.93 mm
to be bolted together at their
flanges. However, initially there is a 6° mismatch in the location of the Situation 5: The two vertical rods
bolt holes. Use G = 83 GPa and neglect deformations of the bolts and attached to the light rigid bar are
flanges. identical except for length. Assume that
all the connections are pinned. Before
1. Determine the maximum shearing stress in the 1-m long shaft after the load W was attached, the bar was
the shafts are bolted together horizontal, and the rods were stress-
a. 99.05 MPa free.
b. 108.65 MPa
c. 43.48 MPa 10. Determine the load in the longer rod if W = 8 kN.
d. 165.14 MPa a. 5.45 kN
b. 8.57 kN
2. Determine the maximum shearing stress in the 2-m long shaft after c. 2.86 kN
the shafts are bolted together d. 7.27 kN
a. 165.14MPa
b. 99.05 MPa 11. Determine the load in the shorter rod if W = 8 kN
c. 43.48 MPa a. 2.86 kN
d. 108.65 MPa b. 7.27 kN
c. 8.57 kN
Situation 2: During a stress-strain test, the unit deformation at a stress d. 5.45 kN
of 78 MPa was observed to be 189 x 10-6 and at a stress of 165 MPa,
the unit deformation was observed to be 650 x 10-6. Situation 6: The two pieces of wood are glued together along the
plane that is at an angle α with the longitudinal dimension. Allowable
3. What is the modulus of elasticity? shear stress is 1.468 MPa while for the allowable normal stress it is
a. 529.89 GPa 0.456 MPa. Use α = 30°.
b. 199.99 GPa
c. 188.72 GPa 12. What should be the dimension w so that the allowable shear stress
d. 431.67 GPa will not be exceeded?
a. 130 mm
4. What is the strain corresponding to a stress of 91 MPa b. 110 mm
a. 257.89 x 10-6 c. 90 mm
b. 339.45 x 10-6 d. 150 mm
c. 412.34 x 10-6
d. 501.76 x 10-6 13. What should be the dimension w so that the allowable normal
stress will not be
5. What is the length of a member that elongates 300 mm when exceeded?
subjected to a stress of 100 MPa a. 130 mm
a. 1163.31 m b. 110 mm
b. 461.54 m c. 90 mm
c. 981.76 m d. 150 mm
d. 1587.30 m
14. What should be the value of angle α so that the shear stress is
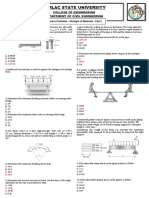
Situation 3: A steel cable is used to lift a load, W. maximum?
Given: W (Total load including weight of cable) = 175 kN a. 90°
Properties of the Steel Cable: b. 30°
Diameter = 30 mm c. 45°
Length = 12 m d. 60°
Modulus of Elasticity = 200 GPa
15. It is the constant of proportionality that defines linear relationship
6. Find the elongation (mm) of the cable as it lifts the load W. between stress and strain.
a. 12 a. Modulus of Elasticity
b. 15 b. Elasticity
c. 20 c. Hooke’s Law
d. 18 d. Elastic limit
7. What is the resulting strain (mm/mm) in the cable as it lifts the load 16. It is the unit strength of material.
W? a. strain
a. 0.00300
b. stress
b. 0.00085
c. 0.00207 c. pascal
d. 0.00124 d. deformation
8. Due to a very heavy load, the steel cable breaks. The recorded 17. Property of the material upon the removal of applied load it will not
diameter at failure is 27.5 mm. Calculate the ductility (%) of the go back to its original size and shape.
material. a. flexibility
a. 18 b. plasticity
b. 24 c. elasticity
c. 16 d. ductility
d. 20
18. The stress beyond which the material is no longer elastic.
Situation 4: The 250 mm x 375 mm concrete post a. Proportional Limit
of 3.5 m length is reinforced with a wide flange b. Elastic Limit
section that has an area of 600π mm2. Ec = 25 c. Yield Point
GPa and Est = 200 GPa. d. Elastic Range
9. Determine the stress in the concrete if the post is 19. The ratio of lateral strain to axial strain.
subjected to an axial load of 900 kN. a. Hooke’s ratio
a. 8.42 MPa b. Strain ratio
b. 5.99 MPa
c. Poisson’s ratio
c. 6.45 MPa
d. Young’s ratio
d. 7.63 MPa
20. In the equation of virtual work, following force is neglected
8. Determine the stress in the steel if the post is subjected to an axial
a. reaction of any smooth surface with which the body is in contact
load of 900 kN.
b. reaction of a rough surface of a body which rolls on it without
a. 81.2 MPa
slipping.
b. 71.0 MPa
c. reaction at a point or an axis, fixed in space, around which a body is
c. 67.3 MPa
constrained to turn.
d. 59.4 MPa
d. all of the above
You might also like
- Astm E606 - E606m-21Document16 pagesAstm E606 - E606m-21Tamara Silvana CárcamoNo ratings yet
- 2020 WTS 12 Work, Energy & PowerDocument22 pages2020 WTS 12 Work, Energy & PowerThabelo NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Official Preboard Structural Engineering and ConstructionDocument7 pagesOfficial Preboard Structural Engineering and ConstructionDexter Dote0% (2)
- Dehumidification Calculation 2 PDFDocument4 pagesDehumidification Calculation 2 PDFdokundot100% (1)
- ISO 16345-2014 Water-Cooling Towers-Testing and Rating of Thermal PerformanceDocument159 pagesISO 16345-2014 Water-Cooling Towers-Testing and Rating of Thermal PerformanceErick VargasNo ratings yet
- Aero Technology Easa Module 8 Basic Aerodynamics QuestionsDocument42 pagesAero Technology Easa Module 8 Basic Aerodynamics QuestionsAnoop singh100% (1)
- Rigid Pipeline DesignDocument123 pagesRigid Pipeline DesignAditya Prasad100% (1)
- QuizDocument2 pagesQuizTheod VilaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam in Strength of Materials Nov2023 ReviewDocument6 pagesEvaluation Exam in Strength of Materials Nov2023 ReviewSharmaine FajutaganaNo ratings yet
- 94 - Strength of Materials Refrehser SetDocument4 pages94 - Strength of Materials Refrehser SetJ O M A RNo ratings yet
- Review Problems in Strength of MaterialsDocument10 pagesReview Problems in Strength of MaterialsJenesis de Guzman50% (2)
- STDocument1 pageSTJea Clarie Mendioro EspinasNo ratings yet
- Supplementary RCDDocument1 pageSupplementary RCDBenjie MorenoNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test: Subject Code: MT1Document3 pagesMastery Test: Subject Code: MT1Jaslyn MagtanongNo ratings yet
- Examination 1 Answer KeyDocument1 pageExamination 1 Answer KeyEngr Amethyst RiegoNo ratings yet
- Compre AS2 and AS3Document6 pagesCompre AS2 and AS3kimberlyjoyregaladoNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IiDocument3 pagesAssignment - IichritNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials With AnswersDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials With AnswersNathaniel Pascua100% (1)
- Assignment - IiDocument5 pagesAssignment - IichritNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 StructuralDocument20 pagesExam 2 StructuralMs. Engr100% (1)
- Strength of Materials Refrehser SetDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials Refrehser SetGracielle Nebres67% (3)
- Strenght of Materials Day 3Document3 pagesStrenght of Materials Day 3anjago824No ratings yet
- Structural 1Document3 pagesStructural 1eufemiorodolfoNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Strema Part 3Document3 pagesPractice Problems - Strema Part 3Meverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- 5 Design Nov 2013 KeyDocument6 pages5 Design Nov 2013 KeyKenneth PadunanNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Review NotesDocument6 pagesStrength of Materials Review NotestristanryanmNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Document4 pagesDiagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Yoshjordan LambNo ratings yet
- Plate 4Document33 pagesPlate 4sammy lopez100% (1)
- STREMADocument1 pageSTREMAIcon Byl P. VergaraNo ratings yet
- Final Preboard Design 2021Document2 pagesFinal Preboard Design 2021Vic NairaNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgC6RSwXitvNxv5doXAP4XkxEcDPev5JBWgWWpjIm48Kf0i - FaBwWf5y5kx8AAr2V HM5a9QynzxGonhZ - 17VAFd4bS5yAMOvRzRG5YDbIPKku0 YMNrF340S3 D7Kt3Xg8BwvwMGVVSFmnnDocument2 pagesACFrOgC6RSwXitvNxv5doXAP4XkxEcDPev5JBWgWWpjIm48Kf0i - FaBwWf5y5kx8AAr2V HM5a9QynzxGonhZ - 17VAFd4bS5yAMOvRzRG5YDbIPKku0 YMNrF340S3 D7Kt3Xg8BwvwMGVVSFmnnMark Christian HerreraNo ratings yet
- E 93 EecDocument4 pagesE 93 Eecjos manaoisNo ratings yet
- Excellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsDocument3 pagesExcellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsGlaiza Marie100% (1)
- Smat Latest HandoutsDocument4 pagesSmat Latest HandoutsKyle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1Document3 pagesAssignment - 1chritNo ratings yet
- UT25Document2 pagesUT25mike reyesNo ratings yet
- RefM 08 - Basic Structural Engineering (Part 02)Document1 pageRefM 08 - Basic Structural Engineering (Part 02)usueNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory Refresher Set PDFDocument6 pagesStructural Theory Refresher Set PDFezer joseph bacoNo ratings yet
- Refresher Set Sec-6: Review InnovationsDocument4 pagesRefresher Set Sec-6: Review InnovationsJerome YangaNo ratings yet
- F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review CenterDocument3 pagesF.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Centermateojullieanne100% (1)
- F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review CenterDocument3 pagesF.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review CenterAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Structural AnalysisDocument14 pagesStructural AnalysisPrincess Gupo Tañas100% (1)
- 1st Preboard Design PDocument13 pages1st Preboard Design PHarf MirandaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Strema Part 1Document4 pagesPractice Problems - Strema Part 1Meverlyn RoqueroNo ratings yet
- Tsu m19 Practice Problems Smat2Document1 pageTsu m19 Practice Problems Smat2Mark Lester ValdozNo ratings yet
- Mechanics (Finals)Document6 pagesMechanics (Finals)Sherwin ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Mech. 322 Quiz No. D 2Document3 pagesMech. 322 Quiz No. D 2jtitularNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Reinforced Concrete Design)Document4 pagesModule 3 (Reinforced Concrete Design)Glaiza MarieNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam StructDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Exam StructJejomar MotolNo ratings yet
- Steel DesignDocument5 pagesSteel DesignLYNSER CORONEL ABANZADONo ratings yet
- Instruction: Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Answer Sheet Box Provided in A Separate FileDocument2 pagesInstruction: Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Answer Sheet Box Provided in A Separate FileFernan FalogmeNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Set 2Document6 pagesPractice Problem Set 2Dion Adrian GenilNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 2 - Set ADocument2 pagesQuiz No 2 - Set AMayoune Nasinopa Galvez100% (1)
- Ced 225 - Final QuizDocument3 pagesCed 225 - Final QuizErvin Jhon BogaNo ratings yet
- Psad - 14Document2 pagesPsad - 14SamNo ratings yet
- Module in Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument5 pagesModule in Mechanics of Deformable BodiesPamela SanchezNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 DesignDocument7 pagesPreboard 2 DesignApril Benosa100% (1)
- Steel Design v2Document4 pagesSteel Design v2Benjie MorenoNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets (Pre-Stressed) PDFDocument2 pagesProblem Sets (Pre-Stressed) PDFleanne DespaNo ratings yet
- Exam No 1Document10 pagesExam No 1Yedda M IlaganNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 2 - Set DDocument2 pagesQuiz No 2 - Set DMayoune Nasinopa GalvezNo ratings yet
- Slu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetDocument9 pagesSlu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetJonathan Basilio100% (1)
- Refresher 4 MDSPDocument11 pagesRefresher 4 MDSPKira YagamiNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 04 Footing DesignDocument29 pages04 Footing DesignJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- Bmyo 2019 CBLDocument7 pagesBmyo 2019 CBLJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics ModuleDocument7 pagesEngineering Mechanics ModuleJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Atterberg LimitsDocument4 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Atterberg LimitsJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering (Soil Properties)Document7 pagesGeotechnical Engineering (Soil Properties)Joshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures With AnswersDocument17 pagesTheory of Structures With AnswersJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- 05 Professional &practical Skiils in IT EraDocument16 pages05 Professional &practical Skiils in IT EraJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- 02.1 Computer & Computer SystemsDocument24 pages02.1 Computer & Computer SystemsJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- 03 WWW & InternetDocument24 pages03 WWW & InternetJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- 01.1 Review On Computer FundamentalsDocument18 pages01.1 Review On Computer FundamentalsJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Group 4 Ce4aDocument5 pagesLab 5 Group 4 Ce4aJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Group 4 Liquid LimitDocument4 pagesLab 4 Group 4 Liquid LimitJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- CH-8 Complex StressesDocument21 pagesCH-8 Complex Stressesمحمد خريبطNo ratings yet
- 2 Marathon MAD PDFDocument12 pages2 Marathon MAD PDFsrey sNo ratings yet
- Calculation ReportDocument229 pagesCalculation ReportDarioNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Performance of Heat Pump Using R32 and HFO-mixed ReDocument11 pagesEvaluation of Performance of Heat Pump Using R32 and HFO-mixed ReCypresDelaCruzSalvadorNo ratings yet
- Energetics QPDocument11 pagesEnergetics QPKarim WaelNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Helium Method To Measure PorosityDocument6 pagesLab 3 Helium Method To Measure PorosityRichard OwusuNo ratings yet
- Ata 21 TrsonDocument160 pagesAta 21 TrsonTam Ho100% (1)
- Snap Hook: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.4Document18 pagesSnap Hook: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.4venalum90No ratings yet
- PHYS 1421-11 (Nov) - 08Document14 pagesPHYS 1421-11 (Nov) - 08yassin mashalyNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy Problems Worksheet 2Document3 pagesConservation of Energy Problems Worksheet 2Balkis MungurNo ratings yet
- 2-Real Gases LectureDocument38 pages2-Real Gases Lecturemahmoud50% (2)
- CalorDocument4 pagesCalorAlex AngelNo ratings yet
- Construction 1: SWELL: Soil Increases in Volume When Loose / ExcavatedDocument27 pagesConstruction 1: SWELL: Soil Increases in Volume When Loose / ExcavatedAaron Buckle100% (2)
- Activate 1 SBDocument9 pagesActivate 1 SBAntvan JesudassNo ratings yet
- Etabs 19.1Document2 pagesEtabs 19.1Esraa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Post-Tensioned Slabs: Published by VSL International LTDDocument44 pagesPost-Tensioned Slabs: Published by VSL International LTDSyedNo ratings yet
- Superficial ExpansionDocument10 pagesSuperficial ExpansionLakshayaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Document4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Michael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump DesignDocument6 pagesCentrifugal Pump DesignJAy PatelNo ratings yet
- Slab Raft Foundation PresentationDocument25 pagesSlab Raft Foundation PresentationOsarieme Osakue100% (1)
- Stress Concentration FactorDocument18 pagesStress Concentration FactorAmisha ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Ce3100 STR Lab July Nov 2014Document37 pagesCe3100 STR Lab July Nov 2014GTSNo ratings yet
- Jirka 1994 Turbulence in Open Channel FlowsDocument3 pagesJirka 1994 Turbulence in Open Channel FlowsJoão Paulo Mendes FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Heatexchanger PDDocument29 pagesHeatexchanger PDbhavinaNo ratings yet