Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Chapter 6
Tutorial Chapter 6
Uploaded by
Ee Hong BinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Chapter 6
Tutorial Chapter 6
Uploaded by
Ee Hong BinCopyright:
Available Formats
BT10903 1-2020/2021
TUTORIAL 6
Chapter 6 (Matrix Algebra)
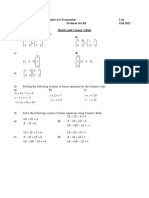
1. Find the transpose, 𝐴𝑇 of matrix 𝐴.
2 5 −3 0
6 −3
a) 𝐴 = [ ] c) 𝐴 = [0 3 6 2]
2 4
7 8 −2 1
−2 3 0
b) 𝐴 = [2 4 6 8] d) 𝐴 = [ 3 4 5]
0 5 −6
2. Compute the indicated matrices if:
2 1 −6 −5 −2 −1 0 0
𝐴=[ ] 𝐵=[ ] 𝐶=[ ] 0=[ ]
3 −3 2 −3 −3 3 0 0
a) 3𝐶 − 2𝐵 c) 3(2𝐴 − 3𝐵)
b) 𝐴 − 2𝐵 + 3𝐶 d) 1/3𝐴 + 3(2𝐵 + 5𝐶)
3. Compute the indicated matrices if:
1 2
1 3 1 0 1 2 −1
𝐴 = [0 −1] 𝐵=[ ] 𝐶=[ ] 𝐷=[ ]
4 −1 1 2 1 0 2
7 0
a) 3𝐴 + 𝐷 𝑇 c) 𝐴 + 𝐷 𝑇 − 𝐵
b) (𝐵 − 𝐶)𝑇 d) (𝐷 − 2𝐴𝑇 )𝑇
4. Perform the indicated operations.
−2 1 1 −2
1 2 2 0 1
a) [1 −4] [ 0 1] c) [ ] ([ ] [2 1 ])
3 4 1 0 −2
5 0 3 0
−1 1 3 4 8 9 2 3
1 −2 d) 2 [ ] + 7 ([ ][ ])
b) [ 0 4] [ ] 5 6 0 1 4 5
3 4
2 1
5. A company with two different outlets manufactures musical instruments. Outlet 1
manufactures 10 guitars, 25 flutes and 15 violins per month. Outlet 2 manufactures 15
guitars, 15 flutes and 20 violins per month. If the monthly production cost for each guitar
is $48, each flute is $69, and each violin is $73, use suitable matrix operations to find the
total production costs for both outlets.
You might also like
- Form 5 Mathematics Chapter 4 MatricesDocument9 pagesForm 5 Mathematics Chapter 4 MatricesGan J Xin100% (1)
- Linear Algebra and Its Applications 5th Edition by Lay McDonald Test BankDocument17 pagesLinear Algebra and Its Applications 5th Edition by Lay McDonald Test BankvalgorbNo ratings yet
- Schonemann Trace Derivatives PresentationDocument82 pagesSchonemann Trace Derivatives PresentationGiagkinis GiannisNo ratings yet
- Exercises From Linear Algebra, Signal Processing, and Wavelets. A Unified Approach. Python VersionDocument71 pagesExercises From Linear Algebra, Signal Processing, and Wavelets. A Unified Approach. Python VersionAfsaneh ShakeriNo ratings yet
- Guia 1 AlgebraDocument3 pagesGuia 1 AlgebraCarlos Edward Garces ArriagadaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Classes 1-3 MatricesDocument3 pages2023 Classes 1-3 Matricesgugercin80No ratings yet
- Case Based MCQS: 1. Amit, Biraj and Chirag Were Given The Task of Creating A Square Matrix of Order 2Document19 pagesCase Based MCQS: 1. Amit, Biraj and Chirag Were Given The Task of Creating A Square Matrix of Order 2stiwari638859No ratings yet
- Mathematics-I, Sem-I Practice Questions On All ModulesDocument12 pagesMathematics-I, Sem-I Practice Questions On All Modulesaditya2189rdNo ratings yet
- Corporacion Universitaria Uniminuto Ingenieria Civil Algebra LinealDocument2 pagesCorporacion Universitaria Uniminuto Ingenieria Civil Algebra LinealjuanguiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 EMS 112-1Document2 pagesTutorial 1 EMS 112-1Liberatus MpetaNo ratings yet
- Matrix Algebra Slides Class Notes V5 S010 Week 13 B Apr 8Document22 pagesMatrix Algebra Slides Class Notes V5 S010 Week 13 B Apr 8Taylor BeautrandNo ratings yet
- MTA Practice Questions - 2023Document3 pagesMTA Practice Questions - 2023Priyam DasNo ratings yet
- Excercise Ch1 MatrixDocument7 pagesExcercise Ch1 MatrixDucnghia DaoNo ratings yet
- Excercise Ch1 MatrixDocument7 pagesExcercise Ch1 MatrixDucnghia DaoNo ratings yet
- Excercise Ch1 MatrixDocument7 pagesExcercise Ch1 MatrixDucnghia DaoNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument5 pagesMatrices[T3A] Siti najihah mansorNo ratings yet
- LinearAI DS FinalCh1-8,10!13!2021S2 DR - OmarDocument13 pagesLinearAI DS FinalCh1-8,10!13!2021S2 DR - OmarRasheed ZawahrehNo ratings yet
- Hw1 - AlgebraDocument3 pagesHw1 - AlgebraTrần Đức ThuậnNo ratings yet
- ECON1101Document4 pagesECON1101Helen ToNo ratings yet
- Matrices&Determinants RLTDocument16 pagesMatrices&Determinants RLTRahul JunejaNo ratings yet
- E20214 Math Econ 03 Matrix and Cramer's RuleDocument3 pagesE20214 Math Econ 03 Matrix and Cramer's RuleJohn ChanNo ratings yet
- Math 013 PHW1Document2 pagesMath 013 PHW1dummy accoutNo ratings yet
- 1st Lesson EconometricsDocument21 pages1st Lesson Econometricsjovanamarceta89No ratings yet
- Taller 1: Preliminares: Ejercicios 1.8Document11 pagesTaller 1: Preliminares: Ejercicios 1.8Daniel Fernando Diaz PitaNo ratings yet
- Grade Xii - A Assignment (Maths)Document3 pagesGrade Xii - A Assignment (Maths)Jegadheesvaran MNo ratings yet
- Assignment Mathematics IDocument12 pagesAssignment Mathematics IAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Matrices and DeterminantsDocument2 pagesQuiz - Matrices and Determinantskuukuacobbina2005No ratings yet
- Introduction To Matrices Practice StripsDocument1 pageIntroduction To Matrices Practice StripsUnique AquaNo ratings yet
- Roots International Schools: Mathematics (60) Final Exam, Grade, 9, 2021 PAPER: 01Document3 pagesRoots International Schools: Mathematics (60) Final Exam, Grade, 9, 2021 PAPER: 01Ali Shakeel KashmiriNo ratings yet
- # 3 LinearDocument3 pages# 3 LinearCindy TorreonNo ratings yet
- # 2 & 3 LinearDocument3 pages# 2 & 3 LinearCindy TorreonNo ratings yet
- 28 (A) Quadratic Equation SolutionDocument2 pages28 (A) Quadratic Equation SolutionNyan Lin SettNo ratings yet
- Guía de Ejercicios Unidad 4: 1) Realice Las Siguientes PotenciasDocument4 pagesGuía de Ejercicios Unidad 4: 1) Realice Las Siguientes PotenciasFranco JofreNo ratings yet
- Maths - Matrices Assignment 1Document3 pagesMaths - Matrices Assignment 1Amit Sharma100% (1)
- Exercise - 1Document2 pagesExercise - 1Subbu SuniNo ratings yet
- Maths Assignment 1Document6 pagesMaths Assignment 1VidomikNo ratings yet
- Zenbaki ArrazionalakDocument3 pagesZenbaki ArrazionalakIsaak Boutalha Mohamed - LamiñeNo ratings yet
- Calcul Algebric Descompuneri În Factori Utilizând Reguli de Calcul În 2. Descompunerea În Factori Utilizând Formule de Calcul PrescurtatDocument2 pagesCalcul Algebric Descompuneri În Factori Utilizând Reguli de Calcul În 2. Descompunerea În Factori Utilizând Formule de Calcul PrescurtatAsiu Mihaela Rodica50% (2)
- Palt Dbm20023Document5 pagesPalt Dbm20023Farish AzraeiツNo ratings yet
- Eem3213 - 13052020 Take Home Final Exam Question PaperDocument4 pagesEem3213 - 13052020 Take Home Final Exam Question PaperSaranya DeviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Tutorial)Document5 pagesChapter 1 (Tutorial)Zikri KiNo ratings yet
- Maths - Matrices - Matrices Multiplication - Assingment - 9 June 2020Document2 pagesMaths - Matrices - Matrices Multiplication - Assingment - 9 June 2020Amit SharmaNo ratings yet
- ALG 2 Teoría de Exponentes Ejercicios PropuestosDocument3 pagesALG 2 Teoría de Exponentes Ejercicios Propuestosdaycorcas10No ratings yet
- Ch.2: Inverse Trigonometry: Youtube Channel "Anurag Chauhan Maths"Document4 pagesCh.2: Inverse Trigonometry: Youtube Channel "Anurag Chauhan Maths"madhav bhallaNo ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinant DPPDocument14 pagesMatrices and Determinant DPPrathode robinNo ratings yet
- 12 TH M Holiday ASS NEDocument5 pages12 TH M Holiday ASS NEgunapranes15No ratings yet
- Taller 1 Algebra Lineal Viveros Morales Jesus EduardoDocument23 pagesTaller 1 Algebra Lineal Viveros Morales Jesus Eduardojesus viverosNo ratings yet
- Matrix Det eDocument1 pageMatrix Det eMcSudul HasanNo ratings yet
- Practica - de - Matrices - y - Determinantes Solucion DefinitivoDocument9 pagesPractica - de - Matrices - y - Determinantes Solucion DefinitivoCopycentro 2No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Maths IDocument1 pageAssignment 2 Maths I2023kucp1012No ratings yet
- Akshat Chaudhary 0445Document12 pagesAkshat Chaudhary 0445sahil2110877No ratings yet
- Workshop I September 16 - 1002Document2 pagesWorkshop I September 16 - 1002David Perdomo PeñaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1Document2 pagesAssignment No.1globalnetwork.4488No ratings yet
- Mathematics D - 1Document2 pagesMathematics D - 1Aditya GhoseNo ratings yet
- Engineering Problem Solving With Matlab and Maple: April 2019Document24 pagesEngineering Problem Solving With Matlab and Maple: April 2019JOYPRAKASH GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Answers Ch2.3-2.5Document5 pagesAnswers Ch2.3-2.5ntokozocecilia81No ratings yet
- Ejercicio 4A Tarea 1 Algebra LinealDocument5 pagesEjercicio 4A Tarea 1 Algebra LinealHenry BritoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 L and H Sec-1Document2 pagesAssignment 1 L and H Sec-1Roopa TadurNo ratings yet
- Practice ProblemDocument1 pagePractice ProblemElly John ReliquiasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 With SolutionsDocument14 pagesTutorial 1 With SolutionsTanmaysainiNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 9Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 9Ee Hong BinNo ratings yet
- Uj00102 WC1 S11Document4 pagesUj00102 WC1 S11Ee Hong BinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 8Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 8Ee Hong BinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 7Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 7Ee Hong BinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 5Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 5Ee Hong BinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 4Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 4Ee Hong BinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 3Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 3Ee Hong BinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document1 pageTutorial 2Ee Hong BinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document2 pagesTutorial Chapter 1Ee Hong BinNo ratings yet
- Possible, and Determine Whether Row Interchanges Are NecessaryDocument78 pagesPossible, and Determine Whether Row Interchanges Are NecessaryNhân HồNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics-Ii: C. Lakshmi Vara PrasadDocument73 pagesApplied Mathematics-Ii: C. Lakshmi Vara PrasadC L V PrasadNo ratings yet
- HadamandDocument25 pagesHadamandullisrinuNo ratings yet
- Definition of MatrixDocument1 pageDefinition of MatrixFlora FloraNo ratings yet
- CS 4731: Computer Graphics Lecture 8: 3D Affine Transforms: Emmanuel AguDocument28 pagesCS 4731: Computer Graphics Lecture 8: 3D Affine Transforms: Emmanuel AgumaheshNo ratings yet
- LA Assignment 3 PDFDocument4 pagesLA Assignment 3 PDFvinayNo ratings yet
- Gate Mathematics PDFDocument150 pagesGate Mathematics PDFjfhmjmhfcnjcnNo ratings yet
- Column Vectors Questions MMEDocument7 pagesColumn Vectors Questions MMErajhdishadNo ratings yet
- Mathematics II (MTH163)Document6 pagesMathematics II (MTH163)NazmaNo ratings yet
- MATH 211 Quiz 1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesMATH 211 Quiz 1 SolutionsAbdulrahman AlhammadiNo ratings yet
- Matrix Analysis For ScientistDocument172 pagesMatrix Analysis For Scientistdialneira7398No ratings yet
- 4.1 - 4.2 DiagonalizationDocument13 pages4.1 - 4.2 DiagonalizationNor adilahNo ratings yet
- Chap16 Schur ComplementsDocument9 pagesChap16 Schur ComplementsYAAKOV SOLOMONNo ratings yet
- S S S 3 Fur Maths 1ST Term E-Note 2017Document64 pagesS S S 3 Fur Maths 1ST Term E-Note 2017Gabriel OnalekeNo ratings yet
- Vidyasthali Public School: General InstructionsDocument5 pagesVidyasthali Public School: General InstructionsrhafedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document14 pagesLecture 10Noreen KanwalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics For Business: Chapter 7: MatricesDocument23 pagesMathematics For Business: Chapter 7: MatricesoverkilledNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 - Matrices: Advance Engineering Math (Tcie 3-1)Document5 pagesQuiz 2 - Matrices: Advance Engineering Math (Tcie 3-1)mileygeniusNo ratings yet
- Algebra of Matrices: Previous Eamcet BitsDocument10 pagesAlgebra of Matrices: Previous Eamcet BitseamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Vko WGDocument50 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Vko WGhitesh mahoreNo ratings yet
- The Matrix Cookbook: Kaare Brandt Petersen Michael Syskind Pedersen Version: January 5, 2005Document43 pagesThe Matrix Cookbook: Kaare Brandt Petersen Michael Syskind Pedersen Version: January 5, 2005Vanessa SSantosNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic MatricesDocument8 pagesHyperbolic Matricesbikash bayanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Important Questions Matrices: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 25Document25 pagesCBSE Class 12 Mathematics Important Questions Matrices: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 25Syed AhmedNo ratings yet
- LINEAR ALGEBRA USING PYTHON - Sheet1Document5 pagesLINEAR ALGEBRA USING PYTHON - Sheet1KAUSHIK MOURYANo ratings yet
- Tut 3-1Document2 pagesTut 3-1Sadhin SaleemNo ratings yet
- Inverse of A 3x3 Matrix.Document2 pagesInverse of A 3x3 Matrix.rodwellheadNo ratings yet