Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Secret Lay Lay PDF
Secret Lay Lay PDF
Uploaded by
HAMAD MOIZ CHODHRYOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Secret Lay Lay PDF
Secret Lay Lay PDF
Uploaded by
HAMAD MOIZ CHODHRYCopyright:
Available Formats
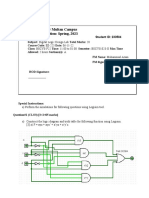
Asset Ab visk is (lo x SoH) x (40x Jooth) + 10% (5% x50)+ 10% 2S+ foe (of 2.8) = $4025 = 27S (ef) Informatio asset B is ant internal personnel database behind a firetaalll- Industry reparts indicate a | percerrt chance ___ of am attack . The information Secuyity and IT departments a report that if the oganixation js attacked , the attacle has a_/o percent chane of sucess. The assetis valuec ____ at ascre of 25 on a scale of 0 40 foo, and informah: ______ Seeurity and IT Staff expect that sd percent of theasr= assumptiats and dota are 90 percent accurate = Asset BS visk is_( (x 10%) x (asxg0%) + [0 = (0.1% xX/2-5)+ 10% = 0/25 + lo (of 0.125) 0./254 0.0/2£ 701375 _ 4) Documenting the Results f Risk. Assessment ~The final) summarized document is the ranked Vulnerability risk Warkshest” ~ Risk identification and assessment deliverables (Table $-/0, pads) Ginformation asset chossification werksheet (figure $7, p27/) @biwighted criteria analysis worksheet Cable £2, Prey @ Ranked yulnerabifity risk loaksheet (Table £9, Posey i 4 _ ORisk Cntrol Strategies 7 Once the ranked vulnerability worksheet has been crealed , one of Five basic strategies +o cat) must be chosen 3 defend, tansfer, _ mitigate , accept, and terminate . Defend — Te prevent the exploitation of the vidnerabidity > Prefered approach and accomplished by means ef courterivta threads, removing vulnerabilities in assets . Limiting acess to assets, and adding protective safeguards. _ — 3 Commo methods used. to defend + D AppPicottion of policy 2 To mandedp thet Certain procedures are abicoys followed ces) A Shict Policy om requiring passiwards ®@ Training and educection & Awareness, +roining » and eduction ave essential if emplyees are to exibit safe and cartrolfed behavior. ® Aepbication of technolesy ¢ Technical solutions are often reguired to assure that risk is reduced (2) Transfer ~ Joattempt to shift yisk to otler assets, other processes , ar other organi zations ~ Accomplished by rethinking how Services are offered » yeyising deployment models , outsourcing to other organisations , Purchasing insurance , or implementing Service cortracts with providers , — Focus ener94 and resources om g@hat they do best whige velyilg on cosuttants or contractoys or other types of expertise, ~ Ensure tat the disaster vecovery veguirements of the attsourcing Gortoct are Sufficient and have been met befwe they ave needed for vecovery efforts |) Mitigede — To attempt to yedu { hough planing and pepevation | © Incident response plan a [ers recovery plan Je See ir + caused by the exploitation of vulne' 12_(p2 5) Figuve (2 Business Coitinuity plan 7 — Mitigation begins with the early detection of ant atlack and. “abil ty fo vespad quickly , efficiently » and effectively. (Accept coy oo a _ — Todo ricthing to potect a a. uidnevabidity and +p accept the outcone Of its exploitation. eee a ~ This strategy is based on the conclusion sat the cosh of protecting - an asset does not Sustify the security expenditure. _ (5) Terminate $ to avoid those business activities that intoduce uncattyailed visks © Selecting a Risk Cotto) Strategy RanuEnuanioes - — Risk cortrol invellves selecting one of the five visk coryal strategies Por __ each vulierabifity =? Risk handding decision points (See Fig. 5/2, P27?) ~ Feasibifity Stuclies + Al the economic and yaieconontic consequences of the vuhuerabidity must be explored. — Got benefit analysis (CBA) (or economic feasibility study) ® Gisider the ecoiomic feasibility of implementing information securrty cortrofs and Sefequaids MME coct op Odevelopnent or acquisition Staining fees @inplementakiar @sewice Oraintenance - ~ Benefit is the value tat an ovgatizetint realizes by using cnrtrols Pprevert fosses associated with a specific vulnerability. + i | $ I - SLE = asset value x EF —_ r s that ooulld Single Joss expectancy _ ____emposure factor s expected percentage of Dass thar Sle fe fica accu frm @ particuler entack an attack (£9) Avoebsite_ has an estimatid value of $ 1,000,000 and o deliberate act of sabotage oy vandalism Scenario indicaled thet jo f the website would be damaged or destroyed => SLE= asset value x EF = 47,000,000 x 0./ = 4 /00,000 — Te ascertain how rivch foss is expected from a singhe empected athack, amd how often ese atkacks occur > AME = SLE x ARO _ annuolized Toss expectance Annualized rote of occurrence : aa ~~ sD occur abut once every tue Yeors > ARO= 0.5(=50%) (€9) ALE = SLE x ARO = _$/00,000%0.£= $ $9000 indiatis that unfess the organization increases the Level of security on its Website» it can expect to lose $50,000 per yew — CBA = ALE (prior) — ALE Cpost) — ACS annualized cost of the safeguard ~ Evaluation, assessment, and maintenance of yisk corirals tthe strategy and its accompanying cortrals qust be enitored and reevaluated on an orgows basis te determine their effectiveness, and +p cafeulate mone accurately the estimated residual) visk. (See Fig, S-/4 Risk Gutred Gcle, P306) |, © Guartitative versus Qualitative Risk Cortvel Practices = ( Guoititotive assessment : uses actual valyes oy estimates (63) previous Work Qualitative assessment ¢ USES chayacteristics thet do net use numerical measures €€3) Sanyfe Scales 2fnote, no chonce , (hao, mediuel, high , very high , alsiast certain} A-zZ, 0-10, I-5, © 0-20 DNetric-based measure g Comparison based on mmeric stondords , suchas # of successful attacks , \ (ote ) 0 Metric: Sef -fowrs Spent on System protection, $ spent an protection, tof security persamel $2 QOhocess-based measure § fess punber-frcused and wore Strategic re af = ji ivi indhiv ic performs in pursuit of i48 Se a Paus im ee Seiad ne ‘sania eee to accamphish o particular process’ ~ asing scales relieves the organization fam the difficulty of determining exact values. ~ | © Benchmarking and Best Practices — “Benchmarking” is the process of seeking out aid studying the practices used in other orgaiizactiaS that produce yesults you would Like ty duphiaid in your organization a 7 _ _ _ ~ Chen benchmarking, an organization typically uses oe of two types of ‘measures to Compare practices ig ed measures oY _process-bhasec as weosures ~ The difference between ani organizatiars measures and Hse of others is_ often referred fo as aperfomance gap” Performance gps_ provide iisight inte the areas that an organization should creyk on to improve its Secwity postures and defenses. _ ~ “Best business practices” (or ” best practices”) are security efferts that Seek te provide a superior Sevell of performance in the protection of informacion, Best security practices ore “hese security efforts that aye amarg the bes In he Industry , palancing the need for access - inrformection zorth adepuacts protection ~ Benchnorking best practices is accomplished by means of the metric -based ov process-based measures described earlier (Sauce) yy), Cert, org» Hue. Micreseft . om /en-ys [Security / defulk,as; » © Applying Best Practices ~ dohen coisidering est practices fey adoptia, consider the folowing 2 © Does your organization resemble the identified target organizedion coith the best practice under carsiderccticn ? I $3 | @ Can your organizetion expend vesurces simifay to these identified with the best practice ? @ Is yeur organization in a sinlar threat envivonnent as that proposed inthe best practice 2 _ - = ablloms with he application of benchmarking and best practices 3 _ © Organizatiots dort talk to each other . > Beouise valuable Lessos ave nat receded , disseminated and ccluatel, the entire industry suffers. @ No +o organizations are identical % Specific informatio may nc opply in other corterts._ Thus, Seek Lessors anid eKampfes yatfer than specific technolegies . @ Best practices are moving target. _ ® Simphy researching information Secuvity benchmarking deesn't necessarily prepare & practitioner-fiy shot todo next Safeguard against new challenges + com © BaseLining — ~ A “baseline” is a value ov profile of a performance metric against ahich Changes in the performance metric can be usefully compared . — “Boselining” is +he analysis of measures agaist establiched standards - Tn information Security, basefining is Hie comparisar of security activities and events against the organization's Sidure performance , ~ Ina sense, basefining can provide the foundatiot for internal benchmarking. The information gathered for an organization's first visk assessment beames the baseline for firture conparisms . Therefre, iti is. important that the initial baseline be accurate, - © er Results su __=dhen the orgaiization is pursuing an overall yisk management program, it pequires_a Systematic report thet enynerates the opportuilittes for contrWin: risk — This_report documents. a Series. of “pepesed. corrals, ei Ff cohich c tas been justified by ore o more feasibility or yakiondlizaction approaches. = Ato minimums each information asset - threat t pales should have ice papesed “Shateay ine been executed.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- PDF 6Document6 pagesPDF 6HAMAD MOIZ CHODHRYNo ratings yet
- PDF 3Document36 pagesPDF 3HAMAD MOIZ CHODHRYNo ratings yet
- PDF 2Document59 pagesPDF 2HAMAD MOIZ CHODHRYNo ratings yet
- Raw Build LogDocument1 pageRaw Build LogHAMAD MOIZ CHODHRYNo ratings yet
- DLD Lab Mid ExamDocument5 pagesDLD Lab Mid ExamHAMAD MOIZ CHODHRYNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 CN - OdtDocument3 pagesLab 2 CN - OdtHAMAD MOIZ CHODHRYNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document PDFDocument1 pageUntitled Document PDFHAMAD MOIZ CHODHRYNo ratings yet
- ATM ProjectDocument7 pagesATM ProjectHAMAD MOIZ CHODHRYNo ratings yet