Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Coulombs Law HTML Guide - en
Coulombs Law HTML Guide - en
Uploaded by
Jaenewton LimaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Coulombs Law HTML Guide - en
Coulombs Law HTML Guide - en
Uploaded by
Jaenewton LimaCopyright:
Available Formats
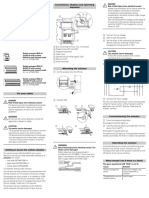
Tips for Teachers Coulomb’s Law
Macro Scale Screen
Visualize the electrostatic force that two charges exert on each other, and adjust the charge magnitude
and separation to see how they affect the force.
SEE the forces in
the system
MEASURE the
distance between
charges
VIEW forces in
standard or
scienti c notation
Atomic Scale Screen
Explore electrostatic attraction and repulsion at the atomic scale, and build a Hydrogen atom.
DRAG charges
apart or together SHOW/HIDE
force magnitude
OBSERVE the
distance scale
Rouinfar, November 2021
fi
Model Simpli cations
• The color of the charge represents its sign (blue = negative, red = positive, gray = no charge). The
saturation of the color represents the magnitude of the charge.
• The Force Values checkbox displays the magnitude of the forces, and is therefore always positive.
• The vector arrows represent the direction of the force, and scale with its magnitude. Due to the large
range of possible values, the force vectors do not scale linearly, and are meant to be a qualitative
representation.
• The gures attached to the charges are displayed to help students understand why the objects stay in
place, despite their attraction or repulsion. When the force is attractive, the gures
will pull on the masses. When the force is repulsive, the gures will push against the
masses. The gures will take a deeper stance to indicate that the force exerted on
the charge it is holding has increased. However, the gures are massless and do not
contribute to the forces in the system.
• The gures on the Atomic Scale screen appear to be built out of a ball-and-stick modeling kit to help
cue the scale differences between the screens.
Suggestions for Use
Sample Challenge Prompts
• Identify two ways you can change the amount of electrostatic force that the charges experience. How
could you increase electrostatic force using each factor? How could you decrease electrostatic force
using each factor?
• Select two different values for charge 1 and charge 2. How does the force that the smaller charge
exerts on the larger charge compare to the force that the larger charge exerts on the smaller charge?
• Predict what happens to the electrostatic force as the distance between the charges is doubled.
• Explain the difference between attractive and repulsive forces.
• On the Atomic Scale Screen, measure the electrostatic force in a Hydrogen atom.
• Pick an independent variable to manipulate and design an experiment to determine what happens to
the electrostatic force as this variable is changed. What do you observe?
• Design an experiment to determine the equation that describes the relationship between the
electrostatic force, the charges, and the distance between the charges. Plot your data and choose an
appropriate trend line.
Explore Inverse Square Laws
Use Gravity Force Lab to investigate the gravitational force.
• Determine the similarities and differences between the gravitational and electrostatic forces.
• Compare the magnitudes of the gravitational and electrostatic forces in the hydrogen atom.
See all published activities for Coulomb’s Law here.
For more tips on using PhET sims with your students, see Tips for Using PhET.
Rouinfar, November 2021
fi
fi
fi
fi
fi
fi
fi
You might also like
- USITT 07 Lighting Plot Standards PDFDocument1 pageUSITT 07 Lighting Plot Standards PDFBenji ArrigoNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Homework 4: Problem 1 (15 Points)Document15 pagesSolutions To Homework 4: Problem 1 (15 Points)joa91189100% (1)
- 9.2 Engaged Discussion: TorqueDocument14 pages9.2 Engaged Discussion: TorqueMischelle BeerbaumNo ratings yet
- Eaton Guide To Circuit Protection & ControlDocument72 pagesEaton Guide To Circuit Protection & ControlGuruxyzNo ratings yet
- 4PH0 - 1P - Que - 20170112 (Q5 I-V Graph, Circuit)Document3 pages4PH0 - 1P - Que - 20170112 (Q5 I-V Graph, Circuit)superpooh-1No ratings yet
- Massve Fermion-Pk ApriDocument17 pagesMassve Fermion-Pk ApriKhanin LaylasNo ratings yet
- Q. Derive Lorentz Force EquationDocument11 pagesQ. Derive Lorentz Force EquationRakesh SNo ratings yet
- Solid State - Sample MaterialDocument41 pagesSolid State - Sample MaterialMukund BachankarNo ratings yet
- AtomicDocument31 pagesAtomicJanith100% (1)
- RF PropogationDocument3 pagesRF PropogationShubham RastogiNo ratings yet
- Musical Instrument With One (Or More) Button(s)Document11 pagesMusical Instrument With One (Or More) Button(s)Vanissa LawNo ratings yet
- Physicsproject 220603105851 C42bd1efDocument14 pagesPhysicsproject 220603105851 C42bd1efashwin sNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7: Pulsed Lasers: You Can Download and Read Reading Materials PDFDocument25 pagesLecture 7: Pulsed Lasers: You Can Download and Read Reading Materials PDFLethargic AzadhirachtaNo ratings yet
- DielectDocument15 pagesDielect조성철No ratings yet
- Coil Resistance FormulaDocument5 pagesCoil Resistance FormulaMarudhasalamMarudhaNo ratings yet
- 1003 0720 Modelación y Simulación 2 - Libro Averill M Law - Simulation Modeling and Analysis - Solutions of Select ExercisesDocument285 pages1003 0720 Modelación y Simulación 2 - Libro Averill M Law - Simulation Modeling and Analysis - Solutions of Select ExercisesSaul ObandoNo ratings yet
- Mcr3U Unit #7: Trigonometric Functions Section Numbers HomeworkDocument18 pagesMcr3U Unit #7: Trigonometric Functions Section Numbers HomeworkpersonNo ratings yet
- 4ph1-1p-Que-20231117 (Q10 Parallel Circuit)Document2 pages4ph1-1p-Que-20231117 (Q10 Parallel Circuit)superpoohNo ratings yet
- Axon Guide To ElectrophysiologyDocument117 pagesAxon Guide To ElectrophysiologyMarciMolnárNo ratings yet
- Discrete Solitons en BEECDocument1 pageDiscrete Solitons en BEECPamela Catalán ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Waves: Physics WallahDocument4 pagesWaves: Physics Wallahsrijit227No ratings yet
- Study Unit Thirteen ForecastingDocument9 pagesStudy Unit Thirteen ForecastingrachelNo ratings yet
- Switch Actuator REG-K/x230/16 With Current Detection and Manual ModeDocument2 pagesSwitch Actuator REG-K/x230/16 With Current Detection and Manual ModeOrlando SantofimioNo ratings yet
- IB Physics IA Investigation of InterfereDocument16 pagesIB Physics IA Investigation of InterfereFarah ShaikhNo ratings yet
- SM CoursesDocument2 pagesSM CoursesJerome JeitanyNo ratings yet
- RF and EMC Formulas and Charts: Conversions for 50Ω Environment Antenna Equations www.arworld.usDocument1 pageRF and EMC Formulas and Charts: Conversions for 50Ω Environment Antenna Equations www.arworld.usamirNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 PDFDocument14 pagesLecture5 PDFante mitarNo ratings yet
- L22 RANS ModelsDocument11 pagesL22 RANS ModelsShamik MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Poster Ecoc Rimini 030921Document1 pagePoster Ecoc Rimini 030921Jaya Kumar KbNo ratings yet
- Brochure SP Option Plus UK HDDocument2 pagesBrochure SP Option Plus UK HDkentNo ratings yet
- Jatka JIjIIJDocument1 pageJatka JIjIIJMiroNo ratings yet
- TransmitDocument18 pagesTransmit조성철No ratings yet
- Balloon Pop ExtravaganzaDocument8 pagesBalloon Pop Extravaganzaapi-381674437No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 IGCSEDocument18 pagesChapter 9 IGCSEeminnayal.enNo ratings yet
- Green SCGxworkshop Poster v2Document1 pageGreen SCGxworkshop Poster v2Anonymous FtU8ya4ru1No ratings yet
- Fully Convolutional Networks For Semantic Segmentation: Jonathan Long Evan Shelhamer Trevor Darrell UC BerkeleyDocument10 pagesFully Convolutional Networks For Semantic Segmentation: Jonathan Long Evan Shelhamer Trevor Darrell UC BerkeleyUnaixa KhanNo ratings yet
- 2015 May 20 Q9 (Edexcel 4PH0 FBI)Document2 pages2015 May 20 Q9 (Edexcel 4PH0 FBI)superpooh-1No ratings yet
- Lab 10 - Superposition and Standing WavesDocument6 pagesLab 10 - Superposition and Standing WavesArfa MubashirNo ratings yet
- Gravity Force Lab HTML Guide - enDocument3 pagesGravity Force Lab HTML Guide - endedirusadi277No ratings yet
- Solids & Semiconductors (Theory)Document25 pagesSolids & Semiconductors (Theory)Avi KedarrNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Materials Themed Issue: Please Take A Look at The Issue 2 2011 To Access Other Reviews in This Themed IssueDocument60 pagesHybrid Materials Themed Issue: Please Take A Look at The Issue 2 2011 To Access Other Reviews in This Themed IssueAlejandro Rubio MartinezNo ratings yet
- Essential Satellite CommunicationsDocument2 pagesEssential Satellite CommunicationsJacobNo ratings yet
- Automation Mind MapDocument1 pageAutomation Mind MapDanieleNo ratings yet
- Column Cleaning and Storage: Together, We Can Do MoreDocument1 pageColumn Cleaning and Storage: Together, We Can Do MoreAdjieDarmawanNo ratings yet
- Nice Epmb Eplb Photocells ManualDocument2 pagesNice Epmb Eplb Photocells ManualMFANo ratings yet
- Amc El 2022 NM C SectionDocument1 pageAmc El 2022 NM C SectionRahul ChandraNo ratings yet
- Instrumnets For KTDocument2 pagesInstrumnets For KTKousik AmancharlaNo ratings yet
- A3 - IUP - Village Boundary MapDocument1 pageA3 - IUP - Village Boundary MapAbdullah KhimarNo ratings yet
- Incorporation of A Fault Factor Into TheDocument35 pagesIncorporation of A Fault Factor Into TheCARLOS OSIEL SEBASTIÁN VALDÉSNo ratings yet
- FlyerDocument1 pageFlyerSuman ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Extragalactic EmpiricismDocument4 pages1.3 Extragalactic EmpiricismSHAM painNo ratings yet
- Alilean, Special & General Relativity: Física Del Cosmos: Lecture IDocument24 pagesAlilean, Special & General Relativity: Física Del Cosmos: Lecture IGuillermo Martínez RamónNo ratings yet
- My Physics MTG 2024Document473 pagesMy Physics MTG 2024arunarajeshwaryNo ratings yet
- Sec17d (DustySurfaceCharging Arcing) - Compressed PDFDocument13 pagesSec17d (DustySurfaceCharging Arcing) - Compressed PDFGerardo ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Wipers and WashersDocument82 pagesWipers and WashersWilli RinconNo ratings yet
- 一步之遥 总谱-1Document33 pages一步之遥 总谱-1gimbirriNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering, The University of TokyoDocument1 pageDepartment of Civil Engineering, The University of TokyoaseNo ratings yet
- Physics EEDocument23 pagesPhysics EESatyam GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2011 Jun q17 (Radioactivity, Fission & Fusion)Document5 pages2011 Jun q17 (Radioactivity, Fission & Fusion)superpoohNo ratings yet
- Activity Guide - Filtering Data: Data Set: Female State LegislatorsDocument3 pagesActivity Guide - Filtering Data: Data Set: Female State LegislatorsWilliam QiuNo ratings yet
- Fusion PosterDocument1 pageFusion PosterGreg SonnenfeldNo ratings yet
- 30th International Physics OlympiadDocument5 pages30th International Physics OlympiadelsewhereNo ratings yet
- Rockets Projectile LabDocument4 pagesRockets Projectile Labsyed.imam100% (1)
- Questions On Resonance in AC CircuitsDocument35 pagesQuestions On Resonance in AC Circuitskibrom atsbha100% (2)
- Study Material Chemistry-1 PDFDocument340 pagesStudy Material Chemistry-1 PDFYash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- c251 PDFDocument8 pagesc251 PDFMagpie 2023No ratings yet
- V Imp ExampleDocument24 pagesV Imp ExamplealiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Work Done by A Constant ForceDocument9 pagesUnit 4: Work Done by A Constant ForceYabetse GirmaNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Af e F I DDocument5 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology: Af e F I DJack SoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Pakistan Ordnance Factory Wah Cantt: Electrical EngineeringDocument11 pagesIntroduction of Pakistan Ordnance Factory Wah Cantt: Electrical EngineeringNusrat Abbas AwanNo ratings yet
- First Law of Thermodynamics, Energy Transfer and General Energy AnalysisDocument22 pagesFirst Law of Thermodynamics, Energy Transfer and General Energy AnalysisdenyNo ratings yet
- Kbic-120 ManualDocument7 pagesKbic-120 ManualrwdeboltNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering 2nd Sem AktuDocument6 pagesElectrical Engineering 2nd Sem AktuNerdy TechNo ratings yet
- An Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010 )Document32 pagesAn Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010 )joshua humirangNo ratings yet
- Compact DIN Rail Mount Power Supply: Single-Phase Switching Power Supply 120-230 Vac Output Power 500 WDocument1 pageCompact DIN Rail Mount Power Supply: Single-Phase Switching Power Supply 120-230 Vac Output Power 500 WnaderjsaNo ratings yet
- Bescom GSTN No: 29Aaccb1412G1Z5Document2 pagesBescom GSTN No: 29Aaccb1412G1Z5sivakumar.tNo ratings yet
- Frequency Measurement ExperimentDocument4 pagesFrequency Measurement ExperimentKEDARISETTY SAISREENo ratings yet
- BBRBDocument3 pagesBBRBKrishnan Mudaliar BopalanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 7 - MDL - 3Q - NTS112 Chemistry 2Document53 pagesWEEK 1 7 - MDL - 3Q - NTS112 Chemistry 2Ashley Marie TrajadaNo ratings yet
- Training Machines2, Homework in Electrical MachinesDocument5 pagesTraining Machines2, Homework in Electrical MachinesNGOUNENo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) BHEL Exam PaperDocument3 pages(WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) BHEL Exam Paperavuma22No ratings yet
- AIIMS Physics Sample EbookDocument42 pagesAIIMS Physics Sample Ebookmisostudy0% (1)
- Energy MetersDocument30 pagesEnergy MetersBilal Javed100% (1)
- ELEX9 Energy Conversion CC GoodDocument6 pagesELEX9 Energy Conversion CC Goodultron gajgajgjkgagaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cycle BraytonDocument15 pagesBasic Cycle BraytonMarin Andreea100% (2)
- ELEGO VI 6KW Dual Output SettingDocument5 pagesELEGO VI 6KW Dual Output SettingmahmoodNo ratings yet
- Electric PotentialDocument12 pagesElectric PotentialCable PadcalNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic NiDocument22 pagesThermodynamic NiJm BejaNo ratings yet
- 11.guarded Plate ApparatusDocument4 pages11.guarded Plate ApparatusManoj Kumar.SNo ratings yet