Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Object
Object
Uploaded by
Rachana Reddy SunkiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Joins in SQLDocument13 pagesJoins in SQLabcd efghNo ratings yet
- Dental Clinic DBMS Chapter IIDocument4 pagesDental Clinic DBMS Chapter IICristian Rhoide Villato ParillaNo ratings yet
- 100 Fundamentals of JsDocument14 pages100 Fundamentals of JsMohan Lal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bismil La JavascriptDocument13 pagesBismil La JavascriptSoya BeanNo ratings yet
- Dot NotationDocument2 pagesDot NotationCOD PIRATESNo ratings yet
- Java Script ObjectDocument40 pagesJava Script ObjectNida khanNo ratings yet
- Objects in JSDocument6 pagesObjects in JSShreyas GowdaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number - 2.3: Aim of The Experiment - 7.1Document15 pagesExperiment Number - 2.3: Aim of The Experiment - 7.1Sakshi RaiNo ratings yet
- JavaScript ObjectsDocument11 pagesJavaScript Objectswittol2iNo ratings yet
- OODP - Week 3Document23 pagesOODP - Week 3vinith gomezNo ratings yet
- 100 Conceitos JavascriptDocument28 pages100 Conceitos Javascriptberseker_oneNo ratings yet
- JavaScript PDFDocument18 pagesJavaScript PDFamitfegade121No ratings yet
- Java ConstructorsDocument5 pagesJava ConstructorsJeniffer MakalintalNo ratings yet
- Modern JavaScript Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesModern JavaScript Cheat Sheetmukta.sairatna1No ratings yet
- JavaScript ObjectsDocument7 pagesJavaScript ObjectsMuhammad AmirNo ratings yet
- Web Developer Bootcamp (Notes) (Code Comented)Document6 pagesWeb Developer Bootcamp (Notes) (Code Comented)Henry G.No ratings yet
- HTML NoteDocument6 pagesHTML Notepc651719No ratings yet
- AIT-Open University: Part ADocument23 pagesAIT-Open University: Part AAmoako Mante HenryNo ratings yet
- Interview - Js - Questions PreviewDocument29 pagesInterview - Js - Questions PreviewArun PandeyNo ratings yet
- ES6 - Cheat SheetDocument12 pagesES6 - Cheat Sheetlemaguinchristian2004No ratings yet
- JavaScript Int QsDocument9 pagesJavaScript Int QsdxtraviNo ratings yet
- A. C++ Provides Built Objects For Input/output Operations Inside Iostream.hDocument23 pagesA. C++ Provides Built Objects For Input/output Operations Inside Iostream.hudi969No ratings yet
- JS FAQ MozillaDocument49 pagesJS FAQ Mozillachaitu215No ratings yet
- Accessors: Properties Are Named Members of Classes, Structures, and Interfaces. Member Variables or Methods in A Class orDocument6 pagesAccessors: Properties Are Named Members of Classes, Structures, and Interfaces. Member Variables or Methods in A Class orDiveshDuttNo ratings yet
- Javascript BasicsDocument2 pagesJavascript BasicsvenkiNo ratings yet
- 3rdchapter C++Document17 pages3rdchapter C++sagar dhitalNo ratings yet
- MongooseDocument22 pagesMongoosesicario01No ratings yet
- s30 DiscussionDocument5 pagess30 DiscussionMark KelvinNo ratings yet
- Module 3 CPP NewDocument21 pagesModule 3 CPP NewA 18No ratings yet
- ITEW2 WEEK 5 Objects - The BasicsDocument48 pagesITEW2 WEEK 5 Objects - The BasicsMOON CAKENo ratings yet
- 12.1 Next-Gen-Js-Summary PDFDocument8 pages12.1 Next-Gen-Js-Summary PDFBenefitsNo ratings yet
- Let & Const: - FunctionDocument8 pagesLet & Const: - FunctionRajiv PunjabiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument66 pagesUntitledTony StarkNo ratings yet
- Web Technology 4Document36 pagesWeb Technology 4kskchariNo ratings yet
- C Unit-3Document12 pagesC Unit-3BHARATHI TNo ratings yet
- JsoppsnotesDocument10 pagesJsoppsnotesBhanu ChouhanNo ratings yet
- C++ Learn: Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument6 pagesC++ Learn: Object Oriented ProgrammingHarish MNo ratings yet
- Chap 7: Structure and PointerDocument43 pagesChap 7: Structure and PointerZulfaqih JainiNo ratings yet
- C Chapter-5Document10 pagesC Chapter-5SANJAY MAKWANANo ratings yet
- Reactjs Final NotesDocument10 pagesReactjs Final Notesamitfegade121100% (1)
- OOP Lab Report-8Document13 pagesOOP Lab Report-8Talha TufailNo ratings yet
- Main PDF Lesson 4Document26 pagesMain PDF Lesson 4onecarloscruz111No ratings yet
- Oop Lect 2Document19 pagesOop Lect 2Muhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Objects and ClassesDocument70 pagesObjects and ClassesfarqaleetaliNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 OODPDocument43 pagesUnit 2 OODPpk6048No ratings yet
- Dot Net LokendraDocument15 pagesDot Net Lokendranishanmainali56No ratings yet
- Properties (C# Programming Guide) - Microsoft DocsDocument14 pagesProperties (C# Programming Guide) - Microsoft DocsperexwiNo ratings yet
- Basic JsDocument4 pagesBasic JssailormuneluneNo ratings yet
- Labs CS201: Lab # 12 Problem StatementDocument31 pagesLabs CS201: Lab # 12 Problem StatementSikandar AbbasNo ratings yet
- ExceptionsDocument1 pageExceptionskidusbelete019No ratings yet
- Intro To JavaScript SlidesDocument25 pagesIntro To JavaScript SlidesPadmaja BhogadiNo ratings yet
- JspracDocument29 pagesJspracAyush ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Node CollateDocument110 pagesNode CollatePERLUESNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document9 pagesLab 6JAWERIA ASLAMNo ratings yet
- Javascript Notes by Siddharth DoshiDocument43 pagesJavascript Notes by Siddharth DoshiSiddharth DoshiNo ratings yet
- ConstructorDocument13 pagesConstructorsiddhant kudesiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document15 pagesAssignment 1Pakmedic incNo ratings yet
- JavaScript CheatsheetsDocument17 pagesJavaScript CheatsheetsHaLiff BostamanNo ratings yet
- JavaScript CheatsheetDocument17 pagesJavaScript CheatsheetSowmyaNo ratings yet
- TypeScript CheatsheetsDocument10 pagesTypeScript CheatsheetsMiliNo ratings yet
- 3rd - Week 10Document12 pages3rd - Week 10bdxqffcdq2No ratings yet
- Tinyvers AssignmentDocument3 pagesTinyvers AssignmentRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Avesta CoverDocument1 pageAvesta CoverRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- 1858022-Javscript Object PDFDocument7 pages1858022-Javscript Object PDFRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- ArrayDocument3 pagesArrayRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Each Aspect: Edigtn Ual SysbmDocument3 pagesEach Aspect: Edigtn Ual SysbmRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument3 pagesFunctionsRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument3 pagesStringsRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Java 3Document21 pagesJava 3Rachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Oen Onder: de Patce DeteoninaDocument8 pagesOen Onder: de Patce DeteoninaRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Java ProgramsDocument4 pagesJava ProgramsRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 10, 2021Document4 pagesAdobe Scan Jul 10, 2021Rachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- The Entity-Relationship Model: Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1Document18 pagesThe Entity-Relationship Model: Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1Anonymous WuZ9bYkuNo ratings yet
- Tm1 API GuideDocument453 pagesTm1 API GuideMoataz DeiabNo ratings yet
- Ocjp 6Document8 pagesOcjp 6Umakant BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Fazil e JobsDocument54 pagesFazil e JobsFazil Puthussery FzlNo ratings yet
- It8076 ST Unit IiDocument37 pagesIt8076 ST Unit Iinmaheshkumar EEE-HICETNo ratings yet
- Upwork TestDocument22 pagesUpwork TestRam50% (2)
- Broadvest Corporate Advisories - DeVELOPMENT PlanDocument19 pagesBroadvest Corporate Advisories - DeVELOPMENT PlanTom Mwashi MoongaNo ratings yet
- Utility Computing: Midhun.S.H S7 Cse 7114Document23 pagesUtility Computing: Midhun.S.H S7 Cse 7114Puspala ManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Lab Iconics Lab Informatics & Compliance Solutions - BrochureDocument12 pagesLab Iconics Lab Informatics & Compliance Solutions - BrochureRaveeNo ratings yet
- QUESTION BANK - DbmsDocument8 pagesQUESTION BANK - Dbmssumeetkhatri2501No ratings yet
- Configuração Do Sentora Durante A InstalaçãoDocument1 pageConfiguração Do Sentora Durante A InstalaçãoThiago CabralNo ratings yet
- Exchange Server 2016 ArchitectureDocument9 pagesExchange Server 2016 ArchitectureNavneetMishraNo ratings yet
- Azure Cosmos DBDocument54 pagesAzure Cosmos DBrajasekhardulamNo ratings yet
- FWD 2972 Shiwani PRM7010 Agile Methodologies in The Digital Business EnvironmentDocument13 pagesFWD 2972 Shiwani PRM7010 Agile Methodologies in The Digital Business EnvironmentSoumyadeep BoseNo ratings yet
- Learn SQL Quickly Using 30 ScenariosDocument107 pagesLearn SQL Quickly Using 30 ScenariosDrum CodeNo ratings yet
- SAP-C S4FCF 2021 OtroDocument30 pagesSAP-C S4FCF 2021 OtroRossy CondeNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence and Analytics ToolsDocument4 pagesBusiness Intelligence and Analytics ToolsBryan CapulongNo ratings yet
- HDF Nifi SecurityDocument50 pagesHDF Nifi SecuritymanishNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 8Document3 pagesAssignment No 8bakwas idNo ratings yet
- TIF SIF 401 Week 01Document66 pagesTIF SIF 401 Week 01Damar Alam RejaNo ratings yet
- BRKPRG 1816Document148 pagesBRKPRG 1816Ta-Jen HsuNo ratings yet
- MSBI Online Training PDFDocument8 pagesMSBI Online Training PDFNagesh KhandareNo ratings yet
- Logcat CSC Compare LogDocument1,997 pagesLogcat CSC Compare LogEmanuel BoteoNo ratings yet
- Dam301 Data Mining and Data Warehousing Summary 08024665051Document48 pagesDam301 Data Mining and Data Warehousing Summary 08024665051Temiloluwa IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Panherkar O. Laravel Rest API Made Easy. Learn To Write Fluent Laravel API 2023Document51 pagesPanherkar O. Laravel Rest API Made Easy. Learn To Write Fluent Laravel API 2023Karoly SoosNo ratings yet
- Cs604 - Final Term Subjective With Reference Solved by Umair SaulatDocument29 pagesCs604 - Final Term Subjective With Reference Solved by Umair SaulatchiNo ratings yet
- Functional Specification: Author: Akanksha Jain Date: 4 Jan, 2011Document4 pagesFunctional Specification: Author: Akanksha Jain Date: 4 Jan, 2011AkankshaNo ratings yet
- Sample Project PlanDocument4 pagesSample Project PlanWallace YeungNo ratings yet
Object
Object
Uploaded by
Rachana Reddy SunkiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Object
Object
Uploaded by
Rachana Reddy SunkiCopyright:
Available Formats
Objects in detail
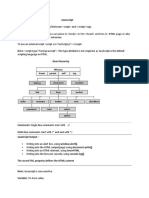
Creating an Object
const person = {
firstName: "Shubham",
lastName: "Kadam",
age: 23,
car: {
brand: "Mercedes",
year: 2020,
},
};
The first block of code shows how to create a new object using object literal syntax. An object literal is a list of key-value pairs enclosed in curly braces {} . The keys
are represented by strings, and the values can be any data type (strings, numbers, arrays, etc).
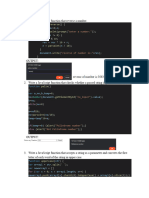
The Dot and Square Notation
// Dot notation
const person = {
firstName: "Shubham",
};
person.dog = {
name: "fluffy",
age: 2,
};
person.age = 23; // Age is being added in person object
console.log(person.dog.age); // 2
// Square bracket notation
const property = "age";
console.log(person[property]); // 23
The above code demonstrates two ways to access and modify the properties of an object: dot notation and square bracket notation.
With dot notation, you can access or set a property of an object using a dot ( . ) followed by the property name. For example, person.age = 23 sets the age
property of the person object to 23.
With square bracket notation, you can access or set a property using a string inside square brackets ( [] ). For example, person['age'] = 23 sets the age property
of the person object to 23.
const dog = {
name: "Fluffy",
bark: () => {
console.log("woof,woof");
},
};
dog.bark(); // woof,woof
// this keyword
const car = {
name: "Lambo",
model: 2019,
Details: function () {
console.log(this.name, this.model);
},
};
car.Details(); // Lambo 2019
this notation is useful when you need to access a property whose name is stored in a variable.
Methods
// Object.keys() creates an array containg the keys of an object.
// Intialize an object
const employee = {
boss: "Shubham",
secretary: "Samarth",
sales: "John",
accountant: "Oscar",
};
// Let's say we want to see all the positions(keys) in the employee object
const positions = Object.keys(employee);
console.log(positions); // [ 'boss', 'secretary', 'sales', 'accountant' ]
// Object.values() creates an array containg the values of an object.
const session = {
id: 1,
time: `26-July-2022`,
device: "Mobile",
browser: "Chrome",
};
const sessionInfo = Object.values(session);
console.log(sessionInfo); // [ 1, '26-July-2022', 'Mobile', 'Chrome' ]
// Object.entries() creates an array containg the key/value of an object.
const operatingSystem = {
name: "Ubuntu",
version: "20.04",
license: "Open Source",
};
const entries = Object.entries(operatingSystem);
console.log(entries); // [
[ 'name', 'Ubuntu' ],
[ 'version', '20.04' ],
[ 'license', 'Open Source' ]
]
// Intialize an object
const user = {
username: "Shubham",
password: "12345",
};
const admin = Object.freeze(user);
user.username = "Samarth"; // Trying to overwrite the object username
console.log(user.username); // Shubham (remains the same);
// Object.seal() prevents new properties
// from being added to an object,
// but allows the modification of existing properties
// Intialize an object
const user = {
username: "Shubham",
password: "12345",
};
const newUser = Object.seal(user);
const newUser = Object.seal(user);
newUser.username = "Samarth"; // The username will be changed
newUser.age = 23; // the age property will not be added because we applied Object.seal()
console.log(user);// { username: 'Samarth', password: '12345' }
The above block of code demonstrates four methods that are built into JavaScript: Object.keys() , Object.values() , Object.entries() , and
Object.freeze() .
Object.keys() creates an array containing the keys (property names) of an object.
Object.values() creates an array containing the values of an object.
Object.entries() is a built-in JavaScript method that returns an array of an object's own enumerable string-keyed property [key, value] pairs, in the same
order as that provided by a for...in loop (the difference being that a for-in loop enumerates properties in the prototype chain as well).
Object.freeze() is a method in JavaScript that prevents an object from being modified. It makes the object's properties and values read-only, and prevents
new properties from being added, removed, or modified. Once an object is frozen, you can no longer change its properties or values, and you cannot add or
remove properties from the object.
You might also like
- Joins in SQLDocument13 pagesJoins in SQLabcd efghNo ratings yet
- Dental Clinic DBMS Chapter IIDocument4 pagesDental Clinic DBMS Chapter IICristian Rhoide Villato ParillaNo ratings yet
- 100 Fundamentals of JsDocument14 pages100 Fundamentals of JsMohan Lal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bismil La JavascriptDocument13 pagesBismil La JavascriptSoya BeanNo ratings yet
- Dot NotationDocument2 pagesDot NotationCOD PIRATESNo ratings yet
- Java Script ObjectDocument40 pagesJava Script ObjectNida khanNo ratings yet
- Objects in JSDocument6 pagesObjects in JSShreyas GowdaNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number - 2.3: Aim of The Experiment - 7.1Document15 pagesExperiment Number - 2.3: Aim of The Experiment - 7.1Sakshi RaiNo ratings yet
- JavaScript ObjectsDocument11 pagesJavaScript Objectswittol2iNo ratings yet
- OODP - Week 3Document23 pagesOODP - Week 3vinith gomezNo ratings yet
- 100 Conceitos JavascriptDocument28 pages100 Conceitos Javascriptberseker_oneNo ratings yet
- JavaScript PDFDocument18 pagesJavaScript PDFamitfegade121No ratings yet
- Java ConstructorsDocument5 pagesJava ConstructorsJeniffer MakalintalNo ratings yet
- Modern JavaScript Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesModern JavaScript Cheat Sheetmukta.sairatna1No ratings yet
- JavaScript ObjectsDocument7 pagesJavaScript ObjectsMuhammad AmirNo ratings yet
- Web Developer Bootcamp (Notes) (Code Comented)Document6 pagesWeb Developer Bootcamp (Notes) (Code Comented)Henry G.No ratings yet
- HTML NoteDocument6 pagesHTML Notepc651719No ratings yet
- AIT-Open University: Part ADocument23 pagesAIT-Open University: Part AAmoako Mante HenryNo ratings yet
- Interview - Js - Questions PreviewDocument29 pagesInterview - Js - Questions PreviewArun PandeyNo ratings yet
- ES6 - Cheat SheetDocument12 pagesES6 - Cheat Sheetlemaguinchristian2004No ratings yet
- JavaScript Int QsDocument9 pagesJavaScript Int QsdxtraviNo ratings yet
- A. C++ Provides Built Objects For Input/output Operations Inside Iostream.hDocument23 pagesA. C++ Provides Built Objects For Input/output Operations Inside Iostream.hudi969No ratings yet
- JS FAQ MozillaDocument49 pagesJS FAQ Mozillachaitu215No ratings yet
- Accessors: Properties Are Named Members of Classes, Structures, and Interfaces. Member Variables or Methods in A Class orDocument6 pagesAccessors: Properties Are Named Members of Classes, Structures, and Interfaces. Member Variables or Methods in A Class orDiveshDuttNo ratings yet
- Javascript BasicsDocument2 pagesJavascript BasicsvenkiNo ratings yet
- 3rdchapter C++Document17 pages3rdchapter C++sagar dhitalNo ratings yet
- MongooseDocument22 pagesMongoosesicario01No ratings yet
- s30 DiscussionDocument5 pagess30 DiscussionMark KelvinNo ratings yet
- Module 3 CPP NewDocument21 pagesModule 3 CPP NewA 18No ratings yet
- ITEW2 WEEK 5 Objects - The BasicsDocument48 pagesITEW2 WEEK 5 Objects - The BasicsMOON CAKENo ratings yet
- 12.1 Next-Gen-Js-Summary PDFDocument8 pages12.1 Next-Gen-Js-Summary PDFBenefitsNo ratings yet
- Let & Const: - FunctionDocument8 pagesLet & Const: - FunctionRajiv PunjabiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument66 pagesUntitledTony StarkNo ratings yet
- Web Technology 4Document36 pagesWeb Technology 4kskchariNo ratings yet
- C Unit-3Document12 pagesC Unit-3BHARATHI TNo ratings yet
- JsoppsnotesDocument10 pagesJsoppsnotesBhanu ChouhanNo ratings yet
- C++ Learn: Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument6 pagesC++ Learn: Object Oriented ProgrammingHarish MNo ratings yet
- Chap 7: Structure and PointerDocument43 pagesChap 7: Structure and PointerZulfaqih JainiNo ratings yet
- C Chapter-5Document10 pagesC Chapter-5SANJAY MAKWANANo ratings yet
- Reactjs Final NotesDocument10 pagesReactjs Final Notesamitfegade121100% (1)
- OOP Lab Report-8Document13 pagesOOP Lab Report-8Talha TufailNo ratings yet
- Main PDF Lesson 4Document26 pagesMain PDF Lesson 4onecarloscruz111No ratings yet
- Oop Lect 2Document19 pagesOop Lect 2Muhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Objects and ClassesDocument70 pagesObjects and ClassesfarqaleetaliNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 OODPDocument43 pagesUnit 2 OODPpk6048No ratings yet
- Dot Net LokendraDocument15 pagesDot Net Lokendranishanmainali56No ratings yet
- Properties (C# Programming Guide) - Microsoft DocsDocument14 pagesProperties (C# Programming Guide) - Microsoft DocsperexwiNo ratings yet
- Basic JsDocument4 pagesBasic JssailormuneluneNo ratings yet
- Labs CS201: Lab # 12 Problem StatementDocument31 pagesLabs CS201: Lab # 12 Problem StatementSikandar AbbasNo ratings yet
- ExceptionsDocument1 pageExceptionskidusbelete019No ratings yet
- Intro To JavaScript SlidesDocument25 pagesIntro To JavaScript SlidesPadmaja BhogadiNo ratings yet
- JspracDocument29 pagesJspracAyush ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Node CollateDocument110 pagesNode CollatePERLUESNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document9 pagesLab 6JAWERIA ASLAMNo ratings yet
- Javascript Notes by Siddharth DoshiDocument43 pagesJavascript Notes by Siddharth DoshiSiddharth DoshiNo ratings yet
- ConstructorDocument13 pagesConstructorsiddhant kudesiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document15 pagesAssignment 1Pakmedic incNo ratings yet
- JavaScript CheatsheetsDocument17 pagesJavaScript CheatsheetsHaLiff BostamanNo ratings yet
- JavaScript CheatsheetDocument17 pagesJavaScript CheatsheetSowmyaNo ratings yet
- TypeScript CheatsheetsDocument10 pagesTypeScript CheatsheetsMiliNo ratings yet
- 3rd - Week 10Document12 pages3rd - Week 10bdxqffcdq2No ratings yet
- Tinyvers AssignmentDocument3 pagesTinyvers AssignmentRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Avesta CoverDocument1 pageAvesta CoverRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- 1858022-Javscript Object PDFDocument7 pages1858022-Javscript Object PDFRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- ArrayDocument3 pagesArrayRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Each Aspect: Edigtn Ual SysbmDocument3 pagesEach Aspect: Edigtn Ual SysbmRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument3 pagesFunctionsRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument3 pagesStringsRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Java 3Document21 pagesJava 3Rachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Oen Onder: de Patce DeteoninaDocument8 pagesOen Onder: de Patce DeteoninaRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Java ProgramsDocument4 pagesJava ProgramsRachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 10, 2021Document4 pagesAdobe Scan Jul 10, 2021Rachana Reddy SunkiNo ratings yet
- The Entity-Relationship Model: Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1Document18 pagesThe Entity-Relationship Model: Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1Anonymous WuZ9bYkuNo ratings yet
- Tm1 API GuideDocument453 pagesTm1 API GuideMoataz DeiabNo ratings yet
- Ocjp 6Document8 pagesOcjp 6Umakant BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Fazil e JobsDocument54 pagesFazil e JobsFazil Puthussery FzlNo ratings yet
- It8076 ST Unit IiDocument37 pagesIt8076 ST Unit Iinmaheshkumar EEE-HICETNo ratings yet
- Upwork TestDocument22 pagesUpwork TestRam50% (2)
- Broadvest Corporate Advisories - DeVELOPMENT PlanDocument19 pagesBroadvest Corporate Advisories - DeVELOPMENT PlanTom Mwashi MoongaNo ratings yet
- Utility Computing: Midhun.S.H S7 Cse 7114Document23 pagesUtility Computing: Midhun.S.H S7 Cse 7114Puspala ManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Lab Iconics Lab Informatics & Compliance Solutions - BrochureDocument12 pagesLab Iconics Lab Informatics & Compliance Solutions - BrochureRaveeNo ratings yet
- QUESTION BANK - DbmsDocument8 pagesQUESTION BANK - Dbmssumeetkhatri2501No ratings yet
- Configuração Do Sentora Durante A InstalaçãoDocument1 pageConfiguração Do Sentora Durante A InstalaçãoThiago CabralNo ratings yet
- Exchange Server 2016 ArchitectureDocument9 pagesExchange Server 2016 ArchitectureNavneetMishraNo ratings yet
- Azure Cosmos DBDocument54 pagesAzure Cosmos DBrajasekhardulamNo ratings yet
- FWD 2972 Shiwani PRM7010 Agile Methodologies in The Digital Business EnvironmentDocument13 pagesFWD 2972 Shiwani PRM7010 Agile Methodologies in The Digital Business EnvironmentSoumyadeep BoseNo ratings yet
- Learn SQL Quickly Using 30 ScenariosDocument107 pagesLearn SQL Quickly Using 30 ScenariosDrum CodeNo ratings yet
- SAP-C S4FCF 2021 OtroDocument30 pagesSAP-C S4FCF 2021 OtroRossy CondeNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence and Analytics ToolsDocument4 pagesBusiness Intelligence and Analytics ToolsBryan CapulongNo ratings yet
- HDF Nifi SecurityDocument50 pagesHDF Nifi SecuritymanishNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 8Document3 pagesAssignment No 8bakwas idNo ratings yet
- TIF SIF 401 Week 01Document66 pagesTIF SIF 401 Week 01Damar Alam RejaNo ratings yet
- BRKPRG 1816Document148 pagesBRKPRG 1816Ta-Jen HsuNo ratings yet
- MSBI Online Training PDFDocument8 pagesMSBI Online Training PDFNagesh KhandareNo ratings yet
- Logcat CSC Compare LogDocument1,997 pagesLogcat CSC Compare LogEmanuel BoteoNo ratings yet
- Dam301 Data Mining and Data Warehousing Summary 08024665051Document48 pagesDam301 Data Mining and Data Warehousing Summary 08024665051Temiloluwa IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Panherkar O. Laravel Rest API Made Easy. Learn To Write Fluent Laravel API 2023Document51 pagesPanherkar O. Laravel Rest API Made Easy. Learn To Write Fluent Laravel API 2023Karoly SoosNo ratings yet
- Cs604 - Final Term Subjective With Reference Solved by Umair SaulatDocument29 pagesCs604 - Final Term Subjective With Reference Solved by Umair SaulatchiNo ratings yet
- Functional Specification: Author: Akanksha Jain Date: 4 Jan, 2011Document4 pagesFunctional Specification: Author: Akanksha Jain Date: 4 Jan, 2011AkankshaNo ratings yet
- Sample Project PlanDocument4 pagesSample Project PlanWallace YeungNo ratings yet