Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M2 Learner-Centered Psychological Principles
M2 Learner-Centered Psychological Principles
Uploaded by
Galang RoxanneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M2 Learner-Centered Psychological Principles
M2 Learner-Centered Psychological Principles
Uploaded by
Galang RoxanneCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 2 The successful learner can link new information
with existing knowledge in meaningful ways.
LEARNER-CENTERED PSYCHOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES 4. Strategic Thinking
The successful learner can create and use a
1. Cognitive and Metacognitive Factors repertoire of thinking and reasoning strategies to achieve
2. Motivational and Affective Factors complex learning goals.
3. Developmental and Social Factors
5. Thinking about thinking
4. Individual Differences Factors Higher order strategies for selecting and monitoring
mental operations facilitate creative and critical thinking.
6. Context of Learning
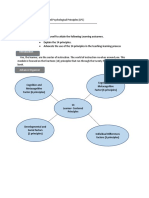
The Learner-Centered Psychological Principles
Learning is influenced by environmental factors,
(The 14 Principles)
including culture, technology, and instructional practices.
The principles were put together by APA(American
Psychological Association). The following 14 psychological
Motivational and Affective Factors
Principles pertain to the learner and the teaching process.
7. Motivational and Emotional influences on learning.
The 14 Principles have the following aspects:
What and how much is learned is influenced by the
learner’s motivation. Motivation to learn, in turn, is
● They focus on psychological Factors that are influenced by the individual’s emotional states, beliefs,
primarily internal to and under the control of the interests and goals and habits of thinking.
learner rather than conditioned habits or
8. Intrinsic Motivation to learn
physiological factors. However, the principles The learner’s creativity, the order thinking, and
also attempt to acknowledge external natural curiosity all contribute to motivation to learn. Intrinsic
environment or contextual factors that interact motivation is stimulated by tasks of optimal novelty and
with these internal factors. difficulty, relevant to personal interests, and providing for
personal choice and control.
● The principles are intended to deal holistically
with learners in the context of real-world 9. Effects of Motivation on Efforts.
learning situations. Thus, they are best Acquisition of complex knowledge and skills
requires extended learner effort and guided practice.
understood as an organized set of principles;
Without learner’s motivation to learn, the willingness to exert
no principle should be viewed in isolation. this effort is unlikely without coercion.
● The principles are divided into those referring to
Developmental and Social Factors
(1) Cognitive and Metacognitive (2)
Motivational and Affective (3) 10. Developmental influences on learning
Developmental and Social (4) Individual As individuals develop, there are different
Differences Factors in influencing learners opportunities and constraints for learning. Learning is most
and learning. effective when differential development within and across
physical, intellectual, emotional, and social domains is taken
● The Principles are intended to apply to all into account.
learners- from children, to teachers, to
11. Social influences on learning
administrators, to parents, and to community Learning is influenced by social interactions,
members involved in our educational system. interpersonal relations, and communication with others.
Cognitive and Metacognitive Factors
Individual Differences Factors
1. Nature of the Leaning Process
The Learning of complex subject matter is most 12. Individual differences in Learning
effective when it is an intentional process of constructing Learner’s have different strategies, approaches,
meaning from information and experience. and capabilities for learning that are a function of prior
2. Goals of the Learning Process experience and heredity.
The successful learner, over time and with support
and instructional guidance, can create meaningful, coherent 13. Learning and Diversity
representations of knowledge.
3. Construction of Knowledge
Learning is most effective when differences in
learners’ linguistic, cultural, and social backgrounds are
taken into account.
14. Standards and Assessment
Setting appropriately high and challenging
standards and assessing the learner as well as learning
progress- including diagnostic, process, and outcome
assessment- are integral parts of the learning process.
Alexander and Murphy gave a summary of the 14
principles
● The knowledge base. One’s existing knowledge
serves as the foundation of all future learning. The
learner’s previous knowledge will influence new
learning specifically on how he represents new
information, makes associations and filters new
experiences.
● Strategic processing and control. Learners can
develop skills to reflect and regulate their thoughts
and behaviors in order to learn more
effectively(Metacognition).
● Motivation and Affect. Factors such as intrinsic
motivation(from within), reasons for wanting to
learn, personal goals and enjoyment of learning
tasks all have a crucial role in the learning process.
● Development and Individual Differences.
Learning is a unique journey for each person
because each learner has his own unique
combination of genetic and environment factors that
influence him.
● Situation or context. Learning happens in the
context of a society as well as within an individual.
END OF MODULE 2
You might also like
- Prof Ed 1 Lecture 1 Learner Centered PrinciplesDocument65 pagesProf Ed 1 Lecture 1 Learner Centered PrinciplesDee Em87% (52)
- Play and Social Development Checklist PDFDocument4 pagesPlay and Social Development Checklist PDFLiezel Cauilan100% (2)
- The Child and Adolescent LearnersDocument179 pagesThe Child and Adolescent LearnersMyla Guab100% (1)
- Unit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersDocument8 pagesUnit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersMyla GuabNo ratings yet
- Learner: Motivational and Affective Factors (3 Principles) Cognitive and Metacognitive Factor (6 Principles)Document3 pagesLearner: Motivational and Affective Factors (3 Principles) Cognitive and Metacognitive Factor (6 Principles)Sherwin Gipit100% (3)
- Module 2 LearnerDocument9 pagesModule 2 LearnerJayson PalmaNo ratings yet
- Zero To FiveDocument17 pagesZero To FiveparparcitaNo ratings yet
- SReYA ManualDocument22 pagesSReYA Manualalemblessie75% (16)
- Reviewer To Sir Jolly PalomeraDocument14 pagesReviewer To Sir Jolly PalomeraJoanna Marie de LunaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document21 pagesUnit 1Jinzel Kaye CristobalNo ratings yet
- Prelim ModuleDocument34 pagesPrelim ModuleKyla Jelinne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner - Centered TeachingDocument21 pagesFacilitating Learner - Centered TeachingRicamae BalmesNo ratings yet
- LCP Advanced ReferenceDocument2 pagesLCP Advanced ReferenceAmaiEdenNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1Document13 pagesThe Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1Rea Jane OrnedoNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological Principles Lesson 1Document26 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological Principles Lesson 1Trixie Mae Issobelle Remoroza100% (1)
- Educ 1Document2 pagesEduc 1Guenevere EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Pec102Document18 pagesGroup 1 Pec102Alyzza Maree MacuhaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Facilitating LearnerDocument9 pagesWeek 2 Facilitating LearnerNoemi PachocoNo ratings yet
- Learner - Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument24 pagesLearner - Centered Psychological PrinciplesAngelica Cortes Bustamante100% (3)
- PED6 ChildAdolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument6 pagesPED6 ChildAdolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesJoshua Elizon DomingoNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document22 pagesGroup 5Rhoevy DavilaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Document22 pagesUNIT 1: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Princess Olalia100% (2)
- Written Report Unit 2 Bsed Fil 1aDocument13 pagesWritten Report Unit 2 Bsed Fil 1aaira mambagNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Document24 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Jeson A. LongnoNo ratings yet
- Educ 101Document35 pagesEduc 101Cyrell Joshua Salas100% (1)
- 14 Learning Principles: - Erica Miles BarrientosDocument6 pages14 Learning Principles: - Erica Miles BarrientosERICAMILES BARRIENTOSNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Nov. 25Document15 pagesLesson 2 - Nov. 25riza velascoNo ratings yet
- 14 Learners Psychological PrinciplesDocument49 pages14 Learners Psychological PrinciplesUnknown UnknownNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document8 pagesModule 5Franz Simeon ChengNo ratings yet
- 14 Learner - CenteredDocument32 pages14 Learner - Centereddarel medeza100% (2)
- Tcallp ReviewerDocument15 pagesTcallp ReviewerCamela SorianoNo ratings yet
- Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument31 pagesLearner Centered Psychological PrinciplesvaflorjvNo ratings yet
- Learnered Center PriciplesDocument26 pagesLearnered Center PriciplesArselia RubanteNo ratings yet
- Module2.practice (Answer)Document2 pagesModule2.practice (Answer)Jezzel Joy LaboraNo ratings yet
- Module 2 LCPDocument25 pagesModule 2 LCPJohn Conrad OrlinaNo ratings yet
- Fourteen Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument9 pagesFourteen Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesKimay DanielNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer (Educ 1)Document8 pagesMidterm Reviewer (Educ 1)Nicaela EstarejaNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent Development Siena College of TigaonDocument25 pagesChild and Adolescent Development Siena College of TigaonRyukireiiNo ratings yet
- Falt Beed Flores Activity 1 PsychologicalDocument1 pageFalt Beed Flores Activity 1 PsychologicalRANIELLA FLORESNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document5 pagesModule 1Dhaze OjanoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument22 pagesModule 2 - Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesJanzen A. GabioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 EDUC121 Learner Centered Psychological Principles PDFDocument21 pagesChapter 1 EDUC121 Learner Centered Psychological Principles PDFDaryll QuilantangNo ratings yet
- Mam RoseDocument2 pagesMam RoseAngielyn Montibon JesusNo ratings yet
- Cognitive and Metacognitive FactorsDocument2 pagesCognitive and Metacognitive Factorsrobert babidaNo ratings yet
- Learners-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument4 pagesLearners-Centered Psychological PrinciplesAmbita CherylNo ratings yet
- Ed 1 Introduction LCPDocument27 pagesEd 1 Introduction LCPJimeniah Ignacio RoyoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Module 1 FLCT The Learning Principles.Document6 pagesActivity 1 Module 1 FLCT The Learning Principles.Juedy Lala PostreroNo ratings yet
- Child Growth Development 2023Document81 pagesChild Growth Development 2023Hanima S. DaudNo ratings yet
- Lesson No. 1Document3 pagesLesson No. 1Hezel CabunilasNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument8 pagesThe Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesMarny Pangandian MasiglatNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument37 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesJanny DiezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersDocument8 pagesUnit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersMyla GuabNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - The Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Document31 pagesMODULE 1 - The Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Tintin Llauderes LloricoNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of The Physical Cognitive An Socio-Emotional Development of Pre-SchoolersDocument6 pagesSynthesis of The Physical Cognitive An Socio-Emotional Development of Pre-SchoolersGerome Anthon BritonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Ed123Document7 pagesLesson 5 Ed123Julie Ann Arenasa PiscosNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP) : Ma'Am Yen CeledonDocument9 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP) : Ma'Am Yen CeledonDan Jezreel EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Acilitating: University of Mindanao Tagum CampusDocument25 pagesAcilitating: University of Mindanao Tagum CampusClara ArejaNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Document19 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Rosie GoldNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument4 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesHariette Mae OnofreNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document23 pagesModule 2Frances Bea Abarado100% (1)
- From Struggle to Success: Practical Study Techniques for Every StudentFrom EverandFrom Struggle to Success: Practical Study Techniques for Every StudentNo ratings yet
- Noliandelfili 220125031105Document30 pagesNoliandelfili 220125031105Galang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Semi Block FormatDocument3 pagesSemi Block FormatGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- 6 230126032521 64d9c397 1Document33 pages6 230126032521 64d9c397 1Galang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Resume - 2023 02 28 095447 1 1 2 2Document3 pagesResume - 2023 02 28 095447 1 1 2 2Galang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- ARTAPP AGBON PPT - 051041 (Copy)Document9 pagesARTAPP AGBON PPT - 051041 (Copy)Galang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Purcom M 10 Business LettersDocument11 pagesPurcom M 10 Business LettersGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- GALANGDocument2 pagesGALANGGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- ClauDocument26 pagesClauGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- MAPEH Animation LPDocument6 pagesMAPEH Animation LPGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Ink 2014 4 1 8Document5 pagesInk 2014 4 1 8Galang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- 6 230126032521 64d9c397Document25 pages6 230126032521 64d9c397Galang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Bodong Powerpoint 1Document9 pagesBodong Powerpoint 1Galang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- The Power of Never Giving UpDocument2 pagesThe Power of Never Giving UpGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- M5 VygotskyDocument1 pageM5 VygotskyGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Child and AdolesenceDocument16 pagesChild and AdolesenceGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement GalangDocument2 pagesAcknowledgement GalangGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Development of Infacy Toddler5 180609022138Document17 pagesCognitive Development of Infacy Toddler5 180609022138Galang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- The Amazing History of CamiguinDocument3 pagesThe Amazing History of CamiguinGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Good Morning Everyone Group 1Document44 pagesGood Morning Everyone Group 1Galang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson PlanGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Conflict Resolution Education ReportDocument13 pagesConflict Resolution Education ReportGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReportDocument36 pagesEntrepreneurship ReportGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument23 pagesEntrepreneurshipGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Sir Basco ENCODEDDocument3 pagesSir Basco ENCODEDGalang RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Sibling Relations and Their Impact On Childrens DevelopmentDocument8 pagesSibling Relations and Their Impact On Childrens DevelopmentSzimonetta VukNo ratings yet
- Senarai RujukanDocument4 pagesSenarai RujukanMel KierraNo ratings yet
- TRB Caregiving NC IIDocument39 pagesTRB Caregiving NC IIPaul Mark PilarNo ratings yet
- بچوں کی نشوونما - آزاد دائرۃ المعارف، ویکیپیڈیاDocument23 pagesبچوں کی نشوونما - آزاد دائرۃ المعارف، ویکیپیڈیاnomanhassan932No ratings yet
- Bachelor of Pyschology in Honours: HDPS1203 Child Behaviour ManagementDocument16 pagesBachelor of Pyschology in Honours: HDPS1203 Child Behaviour ManagementSI LEE BEE Moe100% (1)
- Cdi ManualDocument50 pagesCdi ManualJosue CuzcanoNo ratings yet
- Cara 1 ExamDocument10 pagesCara 1 ExamRODELIZA FEDERICONo ratings yet
- Issues and Recent Studies On Learners Growth and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesIssues and Recent Studies On Learners Growth and DevelopmentShawn Henry CepedaNo ratings yet
- Ece497 - Week 2 Assignment Early ChildhoodDocument1 pageEce497 - Week 2 Assignment Early Childhoodapi-408918735No ratings yet
- Developmental DelayDocument15 pagesDevelopmental DelayYian FaustoNo ratings yet
- Influence of Parenting Styles On Development ofDocument6 pagesInfluence of Parenting Styles On Development ofMeta Dwi FitriyawatiNo ratings yet
- BES-121 Childhood and Growing UpDocument57 pagesBES-121 Childhood and Growing UpPulkesh PulakNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Gender-Fluid Parenting On Child Development A Quantitative StudyDocument10 pagesThe Impact of Gender-Fluid Parenting On Child Development A Quantitative Studydeadkill55512No ratings yet
- Documentary Report On Middle Childhood DevelopmentDocument8 pagesDocumentary Report On Middle Childhood DevelopmentJamila AbdulganiNo ratings yet
- Adepoju - Failure To ThriveDocument37 pagesAdepoju - Failure To ThriveAdepoju Victor AbiolaNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Early Childhood Care Education Teaching Decce T 1Document5 pagesDiploma in Early Childhood Care Education Teaching Decce T 1HuzefaNo ratings yet
- West LA College - ScheduleDocument93 pagesWest LA College - ScheduleDushtu_HuloNo ratings yet
- Piaget's Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentDocument13 pagesPiaget's Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentSultraDemo TV100% (1)
- The Physical Self 1Document37 pagesThe Physical Self 1DELA CRUZ Janelle F.No ratings yet
- MED SyllabusDocument67 pagesMED SyllabusDigbi's CreationNo ratings yet
- Sociocultural Theory and Education: Students, Teachers, and KnowledgeDocument10 pagesSociocultural Theory and Education: Students, Teachers, and KnowledgeShaziaNo ratings yet
- Family Engagement Plan: Suggested ActivitiesDocument11 pagesFamily Engagement Plan: Suggested Activitiesapi-609545195No ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies Gold Assessment Touring GuideDocument36 pagesTeaching Strategies Gold Assessment Touring Guideapi-384820029No ratings yet
- TheoriesDocument16 pagesTheorieserika garcelisNo ratings yet
- Learning Through Play Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesLearning Through Play Literature Reviewafmzswxbbbbitf100% (1)
- Ece 20 Soc Study m2 To PrintDocument5 pagesEce 20 Soc Study m2 To PrintDiana Jane GareNo ratings yet
- Development in Down SyndromeDocument30 pagesDevelopment in Down SyndromeRoilan MarlangNo ratings yet