Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 1.3
Unit 1.3
Uploaded by
nashwah mahomed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesRAM is a computer's short-term memory that is used to store active programs and data that is currently being worked on due to its fast access speeds. Storage devices like hard drives are the computer's long-term memory for permanently storing large amounts of data and programs. ROM is read-only memory that stores the computer's basic input/output system (BIOS) instructions which are protected from accidental deletion and allow the computer to function.
Original Description:
Original Title
Unit 1.3.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRAM is a computer's short-term memory that is used to store active programs and data that is currently being worked on due to its fast access speeds. Storage devices like hard drives are the computer's long-term memory for permanently storing large amounts of data and programs. ROM is read-only memory that stores the computer's basic input/output system (BIOS) instructions which are protected from accidental deletion and allow the computer to function.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesUnit 1.3
Unit 1.3
Uploaded by
nashwah mahomedRAM is a computer's short-term memory that is used to store active programs and data that is currently being worked on due to its fast access speeds. Storage devices like hard drives are the computer's long-term memory for permanently storing large amounts of data and programs. ROM is read-only memory that stores the computer's basic input/output system (BIOS) instructions which are protected from accidental deletion and allow the computer to function.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
16 February 2021
Unit 1.3 – Memory as part of a computer system
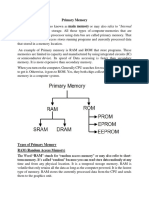
A computer has three important types of memory:
RAM (short-term memory)
storage devices (long-term memory)
ROM (read-only memory).
ROM
◊ the read-only memory (or ROM) stores the computer’s BIOS.
◊ your computer’s read-only memory can only be retrieved but not overwritten or
deleted during normal operation. This prevents the accidental deletion of the
instructions needed to use the computer.
◊ As the ROM cannot be changed normally, the settings are saved on a tiny piece of
memory connected to the ROM called the CMOS.
◊ Unlike the ROM, the CMOS needs to have power to keep its data. To ensure that the
CMOS continues to store the BIOS settings (even when the computer is turned off
and disconnected from power) the CMOS is connected to a small battery.
RAM
all active programs and data that is currently being worked on is stored in its RAM.
Since the RAM is closely connected to your CPU and has very high read and write
speeds, it can ensure that your CPU has access to all the data it needs when it needs
the data. Without RAM, your computer would need to read and write all data it is
using to your hard drive, which is much slower than the RAM.
As a result, your CPU would spend a lot of time waiting for data to be loaded.
Examples of data stored in RAM include:
information currently shown on the screen.
applications running in the background.
instructions the computer is busy with.
instructions the computer might need next.
data the computer might need next.
Since RAM is only used for short-term memory storage, it is cleared the moment
you turn off your computer.
Temporary and permanent Storage
Temporary storage includes:
16 February 2021
RAM is electronic memory and comprises of a combination of capacitors and
transistors to store data.
Cache memory is also called CPU memory. It Is very fast and works directly with the
CPU to store small amounts of information that may be needed by the CPU.
Disk cache memory: Instead of the CPU having to wait for data to be stored on a slow
hard disk, it sends the information to be saved to the disk cache memory. From the
disk cache, the data is written to the hard drive, which stores it permanently.
Permanent storage includes:
Magnetic tape and hard disk drives use magnetic properties to store and retrieve
information. This allows large amounts of information and programs to be stored
permanently, although the devices take longer to write and read the information than
RAM.
SSD (Solid State Drives): As with RAM, SSDs store data on a chip, which means
that it uses electricity to store data rather than magnetism like conventional hard
drives or lasers like DVD drives. However, unlike RAM, SSDs can store data
permanently. SSDs are faster but more expensive than a hard disk drive.
Flash drives use the same technology as SSD’s but usually have a smaller capacity
and are designed to be a portable form of storage.
Optical storage media: CD, DVD and Blu-ray disks are cheap, portable media that can
be used to store data. While these disks can have a high capacity, they are slower to
read from and write to than all the previous storage types.
Differences between RAM, storage devices and ROM
You might also like
- Unit1 Computer MemoryDocument5 pagesUnit1 Computer Memorylandofbooks2021No ratings yet
- Memoryfunction Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week2Document43 pagesMemoryfunction Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week2somerandomhedgehogNo ratings yet
- Unit III RAM-ROM-CACHE-HDD-FLOPPY-CDDocument12 pagesUnit III RAM-ROM-CACHE-HDD-FLOPPY-CDxagal74444No ratings yet
- Memory Units of A ComputerDocument16 pagesMemory Units of A ComputerRaghav MadanNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory: Is An Essential Element of A Computer. Without Its Memory, A Computer Is of HardlyDocument10 pagesComputer Memory: Is An Essential Element of A Computer. Without Its Memory, A Computer Is of HardlyVivek NambiarNo ratings yet
- Memory." and Primary Storage. All Those Types of Computer Memories That AreDocument6 pagesMemory." and Primary Storage. All Those Types of Computer Memories That Aregargib07No ratings yet
- Computer Assignment 3Document5 pagesComputer Assignment 3hudanasir183No ratings yet
- Memory and Its TypesDocument4 pagesMemory and Its TypesNikku100% (2)
- Unit 3 Memory OrganisationDocument23 pagesUnit 3 Memory Organisation586ayushNo ratings yet
- Storage DevicesDocument11 pagesStorage DevicesHuma aliNo ratings yet
- Performing Mensuration Q3Document10 pagesPerforming Mensuration Q3Janice Agbuya TamondongNo ratings yet
- What Random Access Memory Is Used For: OS Processor HDD SSDDocument7 pagesWhat Random Access Memory Is Used For: OS Processor HDD SSDTushiro K. HimuraNo ratings yet
- Computer Memor1Document12 pagesComputer Memor1kschauhan8007No ratings yet
- Memory Unit - 5 Coa PDFDocument18 pagesMemory Unit - 5 Coa PDFArun KrishNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Microprocessor Architecture and Operations.pptxDocument18 pagesUNIT 2 Microprocessor Architecture and Operations.pptxkinjalbenanilbhaisolankiNo ratings yet
- Data StorageDocument9 pagesData Storage2027dpatel.studentNo ratings yet
- Memory: Prepared By: Kevin D. CaratiquitDocument38 pagesMemory: Prepared By: Kevin D. CaratiquitKevin Dela Fuente CaratiquitNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument8 pagesComputer MemoryTakudzwa TapaNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory: Is An Essential Element of A Computer. Without Its Memory, A Computer Is of HardlyDocument3 pagesComputer Memory: Is An Essential Element of A Computer. Without Its Memory, A Computer Is of HardlyArap ChitoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Storage DeviceDocument10 pagesWhat Is A Storage Devicexy.xyloneNo ratings yet
- Storage Devices or Memory Units of A Computer - General Awareness and Knowledge - Bank Exams PDF DownloadDocument4 pagesStorage Devices or Memory Units of A Computer - General Awareness and Knowledge - Bank Exams PDF DownloadDavuluri Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Memory and Its TypesDocument29 pagesMemory and Its Typesneelneel89No ratings yet
- Here Is An Example of A Machine With 1GB of RAMDocument6 pagesHere Is An Example of A Machine With 1GB of RAMaguslizarNo ratings yet
- CSC113 AssignmentDocument3 pagesCSC113 AssignmentAlphus DavidNo ratings yet
- Different Types of MemoryDocument26 pagesDifferent Types of MemorySayani Chandra100% (1)
- Two Basic Categories of Computer Memory:: Primary Storage and Secondary StorageDocument7 pagesTwo Basic Categories of Computer Memory:: Primary Storage and Secondary StorageRahul ShrivasNo ratings yet
- MEMORYDocument6 pagesMEMORYniharboyka912No ratings yet
- Memory and Its TypesDocument36 pagesMemory and Its TypesAaruni100% (1)
- MemoryDocument28 pagesMemorydeadlyzephyrNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory: Prepared By: Avanthika Krishnan, XI DDocument17 pagesComputer Memory: Prepared By: Avanthika Krishnan, XI DAvanthikaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document16 pagesLesson 3SHEALA LADERANo ratings yet
- Storage Devices: RAM (Random Access Memory)Document13 pagesStorage Devices: RAM (Random Access Memory)Narmina MamedovaNo ratings yet
- Memory Unit 1Document4 pagesMemory Unit 1Naina KumariNo ratings yet
- Ram and RomDocument3 pagesRam and RomMEENA J RCBSNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument12 pagesComputer MemoryErmin Sehic100% (1)
- CDCA 2203 Ram & RomDocument11 pagesCDCA 2203 Ram & RomMUHAMAD AMMAR SYAFIQ BIN MAD ZIN STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument22 pagesComputer MemoryasiNo ratings yet
- Data StorageDocument62 pagesData StorageManahilNo ratings yet
- Types of MemoryDocument3 pagesTypes of MemoryVenkatareddy Mula0% (1)
- MemoryDocument6 pagesMemoryderry6271No ratings yet
- Livin in The It Era Module 3Document2 pagesLivin in The It Era Module 3Obeña Grecia Joy T.No ratings yet
- Computer Memory: Types of RamDocument3 pagesComputer Memory: Types of RamJose Ric Catarus Bataluna Jr.No ratings yet
- CF Notes - Unit 3Document16 pagesCF Notes - Unit 3Md ZamanNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument5 pagesMemoryKanika DarochNo ratings yet
- 2.BCI Unit2 R19Document16 pages2.BCI Unit2 R19chariNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory PDFDocument9 pagesComputer Memory PDFShweta Kakumanu0% (1)
- MemoryDocument9 pagesMemoryFazrul RosliNo ratings yet
- Name: Sanam Khan Mpa-Ii Assignment #1Document4 pagesName: Sanam Khan Mpa-Ii Assignment #1Sanam KhanNo ratings yet
- What Is RAMDocument2 pagesWhat Is RAMWill AsinNo ratings yet
- Storage DevicesDocument8 pagesStorage Devicesyehiam807No ratings yet
- INTERNAL MEMORY Ram/romDocument10 pagesINTERNAL MEMORY Ram/romRon NokwareNo ratings yet
- Differentiate Between RAM and ROM: Random Access Memory (RAM)Document7 pagesDifferentiate Between RAM and ROM: Random Access Memory (RAM)Kunwer TaibaNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument26 pagesUnit IIPriyanshu VermaNo ratings yet
- What Is ComputerDocument30 pagesWhat Is Computerasw.priyasinghNo ratings yet
- Examples of Primary and Secondary Storage DevicesDocument2 pagesExamples of Primary and Secondary Storage DevicesGenevaNo ratings yet
- Rom Ram RDocument10 pagesRom Ram RSul SyaNo ratings yet
- I Ram M: Nstallation of OdulesDocument14 pagesI Ram M: Nstallation of Odulesanshuman singhNo ratings yet
- The Role of Memory in The ComputerDocument6 pagesThe Role of Memory in The ComputerabcdNo ratings yet
- Beginner's Guide for Cybercrime InvestigatorsFrom EverandBeginner's Guide for Cybercrime InvestigatorsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Unit 1.4Document2 pagesUnit 1.4nashwah mahomedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1nashwah mahomedNo ratings yet
- IT Practical LB Gr11 WEB PDFDocument252 pagesIT Practical LB Gr11 WEB PDFnashwah mahomedNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument2 pagesMemorynashwah mahomedNo ratings yet