Professional Documents
Culture Documents
S&P Block PDF
S&P Block PDF
Uploaded by
vrtbhgmngfOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
S&P Block PDF
S&P Block PDF
Uploaded by
vrtbhgmngfCopyright:
Available Formats
706 s and p-Block Elements
(5) Solubility in liquid NH 3
(10) Complex ion formation : A metal shows complex formation
(i) These metals dissolve in liquid NH to produce blue coloured 3
only when it possesses the following characteristics, (i) Small size (ii)
solution, which conducts electricity to an appreciable degree. High nuclear charge (iii) Presence of empty orbitals in order to accept
(ii) With increasing concentration of ammonia, blue colour starts electron pair ligand. Only Lithium in alkali metals due to small size forms a
changing to that of metallic copper after which dissolution of alkali metals few complex ions Rest all alkali metals do not possess the tendency to form
in NH ceases. complex ion.
3
(iii) The metal atom is converted into ammoniated metal in i.e. M +
Anomalous behaviour of Lithium
(NH ) and the electron set free combines with NH molecule to produce Anomalous behaviour of lithium is due to extremely small size of
3 3
ammonia solvated electron. lithium its cation on account of small size and high nuclear charge, lithium
exerts the greatest polarizing effect out of all alkali metals on negative ion.
Na (x y)NH 3 [ Na( NH 3 )x ] [e(NH 3 )y ] Consequently lithium ion possesses remarkable tendency towards solvation
Ammoniated cation Ammoniated electron and develops covalent character in its compounds. Li differs from other
(iv) It is the ammoniated electron which is responsible for blue alkali metals in the following respects,
colour, paramagnetic nature and reducing power of alkali metals in (1) It is comparatively harder than other alkali metals. Li can’nt be
ammonia solution. However, the increased conductance nature of these stored in kerosene as it floats to the surface, due to its very low density. Li
metals in ammonia is due to presence of ammoniated cation and ammonia is generally kept wrapped in parrafin wax.
solvated electron. (2) It can be melted in dry air without losing its brilliance.
(v) The stability of metal-ammonia solution decreases from Li to Cs. (3) Unlike other alkali metals, lithium is least reactive among all. It
(vi) The blue solution on standing or on heating slowly liberates can be noticed by the following properties,
hydrogen, 2M + 2NH 2MNH + H . Sodamide (NaNH ) is a waxy solid,
3 2 2 2 (i) It is not affected by air. (ii) It decomposes water very slowly to
used in preparation of number of sodium compounds. liberate H . (iii) It hardly reacts with bromine while other alkali metals react
2
(6) Nitrates : Nitrates of alkali metals (MNO ) are soluble in water 3
violently.
and decompose on heating. LiNO decomposes to give NO and O and rest 3 2 2
(4) Lithium is the only alkali metal which directly reacts with N to 2
all give nitrites and oxygen. form Lithium nitride (Li N) 3
2MNO 3
2MNO + O (except Li)
2 2
(5) Lithium when heated in NH forms amide, Li NH while other 3 2
metals form amides, MNH .
4 LiNO 2Li O + 4NO + O 2
(6) When burnt in air, lithium form Li O sodium form Na O and
3 2 2 2
(7) Sulphates
2 2
Na O other alkali metals form monoxide, peroxide and superoxide.
2 2
(i) Alkali metals’ sulphate have the formula M SO . 2 4
(7) Li O is less basic and less soluble in water than other alkali
2
(ii) Except Li SO , rest all are soluble in water.
2 4 metals.
(iii) These sulphates on fusing with carbon form sulphides, M SO + 2 4 (8) LiOH is weaker base than NaOH or KOH and decomposes on
4C M S + 4CO 2
heating.
(iv) The sulphates of alkali metals (except Li) form double salts with 2 LiOH Li 2 O H 2O
the sulphate of the trivalent metals like Fe, Al, Cr etc. The double sulphates
crystallize with large number of water molecules as alum. e.g. KSO . Al (SO ) . 24 2 4 2 4 3
(9) LiHCO is liquid while other metal bicarbonates are solid.
3
HO.
2
(10) Only Li CO decomposes on heating
2 3
(8) Reaction with non-metals Li 2 CO 3 heat
Li 2 O CO 2 .
(i) These have high affinity for non-metals. Except carbon and
Na CO , K CO etc. do not decompose on heating.
nitrogen, they directly react with hydrogen, halogens, sulphur, phosphorus 2 3 2 3
etc. to form corresponding compounds on heating. (11) LiNO and other alkali metal nitrates give different products on
3
heating
300 0 C
2Na + H 2
2NaH ; 2K + H 2
2KH 4LiNO = 2Li O+4NO + O ; 2NaNO = 2NaNO + O
3 2 2 2 3 2 2
2Na + Cl 2
2NaCl ; 2K + Cl 2
2KCl (12) LiCl and LiNO are soluble in alcohol and other organic 3
solvents. These salts of other alkali metals are, however, insoluble in organic
2Na + S Na S ; 2K + S KS
2 2
solvents.
3Na + P Na P ; 3K + P
3
KP 3
(13) LiCl is deliquescent while NaCl, KBr etc. are not. Lithium
(ii) Li reacts, however directly with carbon and nitrogen to form chloride crystals contain two molecules of water of crystallisation ( LiCl.
carbides and nitrides. 2H O). Crystals of NaCl KBr, KI etc do not conation water of crystallisation.
2
2Li + 2C LiC ; 6Li + 2N 2 Li N 2 2 3
(14) Li SO does not form alums like other alkali metals.
2 4
(iii) The nitrides of these metals on reaction with water give NH . 3 (15) Li reacts with water slowly at room temperature Na reacts
M N + 3H O 3MOH + NH
3 2 3
vigorously Reaction with K. Rb and Cs is violent.
(9) Reaction with acidic hydrogen : Alkali metals react with acids (16) Li reacts with Br slowly. Reaction of other alkali metals with Br 2 2
and other compounds containing acidic hydrogen (i.e, H atom attached on is fast.
F,O, N and triply bonded carbon atom, for example, HF, H O, ROH, RNH , 2 2
(17) Li CO Li C O , LiF , Li PO are the only alkali metal salts which are
2 3 2 2 4 3 4
CH CH) to liberate H . 2
insoluble or sparingly soluble in water.
1 1 Diagonal Relationship of Li with Mg
M H 2O MOH H2 ; M HX MX H2 Due to its small size lithium differs from other alkali metals but
2 2
resembles with Mg as its size is closer to Mg Its resemblance with Mg is
1 1 known as diagonal relationship. Generally the periodic properties show
M ROH ROH H2 ; M RNH 2 RNHNa H2
2 2 either increasing or decreasing trend along the group and vice versa along
You might also like
- Alkali and Alkali Earth Metals - SRDocument20 pagesAlkali and Alkali Earth Metals - SRMuzahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- S Block PDFDocument22 pagesS Block PDFRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- 7 PDFDocument1 page7 PDFRishabhNo ratings yet
- (Ix) Hydrides: (1) (2) (Ix) Hydrides: (1) : Behaviour of Lithium Different From Other Alkali MetalsDocument1 page(Ix) Hydrides: (1) (2) (Ix) Hydrides: (1) : Behaviour of Lithium Different From Other Alkali MetalsRishabhNo ratings yet
- Jee S BlockDocument129 pagesJee S BlockAmirtha RajNo ratings yet
- CH 10 ExerciseDocument24 pagesCH 10 ExerciseTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Group 1-2Document22 pagesGroup 1-2Gudia kumariNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Jan11 Chapter 10 The S Block ElementsDocument16 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Jan11 Chapter 10 The S Block Elementserfgtrgv vfvvvNo ratings yet
- Sblock NotesDocument22 pagesSblock NotesLaukikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 S Block Elements NCERT Class 11 SolutionsDocument20 pagesChapter 10 S Block Elements NCERT Class 11 SolutionsZagreus OfficialNo ratings yet
- X DZaa ZQAr X1 PA9 EUG2 R MDocument22 pagesX DZaa ZQAr X1 PA9 EUG2 R MSubhashakti BeheraNo ratings yet
- Book (Complete)Document63 pagesBook (Complete)Aditi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 01 S and P Block Elements Theory Final E 1Document17 pages01 S and P Block Elements Theory Final E 1gnkstarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document63 pagesChapter 18Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Elements Unit 3.1 8Document45 pagesChemistry of Elements Unit 3.1 8Zyra Erylle Rodriguez CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Representive ElementsDocument26 pagesChemistry of Representive ElementsNatish JaglanNo ratings yet
- S BlockDocument53 pagesS BlockhappyNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Study Materials English MediumDocument13 pages11th Chemistry Study Materials English Mediumprathiksha6660No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument30 pagesChemistrybhupesh mahapatroNo ratings yet
- S - Block Elements, Class 11Document13 pagesS - Block Elements, Class 11Ashish kumarNo ratings yet
- S&P Block PDFDocument1 pageS&P Block PDFvrtbhgmngfNo ratings yet
- The S-Block ElementsDocument20 pagesThe S-Block Elements97 science Saurav Pratap singhNo ratings yet
- DF CompleteDocument11 pagesDF Completeranaharshit994No ratings yet
- Scientific Reasons XII Inorganic ChemistryDocument2 pagesScientific Reasons XII Inorganic Chemistrynazish kiranNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 4: Metals: by Team Meow Meow (Halimeow and 3 Headed Creature)Document3 pagesChemistry Chapter 4: Metals: by Team Meow Meow (Halimeow and 3 Headed Creature)Bren Jousef BayhonNo ratings yet
- S BlockDocument6 pagesS BlockSora RoseNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes The S-Block ElementsDocument40 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes The S-Block ElementsNair SidharthNo ratings yet
- 11th All Batch Assignment-01, S-Block 03-02-22 - 827032Document2 pages11th All Batch Assignment-01, S-Block 03-02-22 - 827032sanket pawarNo ratings yet
- The S-Block Elements - Shobhit NirwanDocument14 pagesThe S-Block Elements - Shobhit NirwanAadarsh PandeyNo ratings yet
- AlkalinemetalsDocument9 pagesAlkalinemetalsKunwarNo ratings yet
- S and P Block ElementsDocument47 pagesS and P Block ElementsDhruv SainiNo ratings yet
- S - Block Elements Unit - 10: Group I Elements: Alkali MetalsDocument15 pagesS - Block Elements Unit - 10: Group I Elements: Alkali MetalsVivan TNo ratings yet
- Watermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFDocument15 pagesWatermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFMeerab ShahNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Short NotesDocument71 pagesInorganic Short NotesSUNIL VODELANo ratings yet
- Subject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: The S-Block Elements Top ConceptsDocument10 pagesSubject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: The S-Block Elements Top ConceptsRISHI KEJRIWALNo ratings yet
- S-Block Elements & Compounds: Group - IDocument46 pagesS-Block Elements & Compounds: Group - Iविशाल जायसवालNo ratings yet
- Sunyzz - Unit 4 Chemistry TestDocument1 pageSunyzz - Unit 4 Chemistry TestAmiel DonqueNo ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument16 pagesS Block Elementsyashvir.lko4963No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 EdetDocument46 pagesChapter 5 EdetHabtamu mullu BiadgoNo ratings yet
- VIII Chemistry The S-Block Elements IIT Material (30.11.2022)Document9 pagesVIII Chemistry The S-Block Elements IIT Material (30.11.2022)Jameer ShaikNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes - The S-Block ElementsDocument21 pages11 Chemistry Notes - The S-Block ElementsAishwary yadav100% (1)
- Adobe Scan Mar 06, 2024Document8 pagesAdobe Scan Mar 06, 2024SPCET.FY.24No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 09 Feb 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 09 Feb 2023Puspen PalNo ratings yet
- 11 NCERT Solutions Chemistry ChapterDocument20 pages11 NCERT Solutions Chemistry ChapterSandeep Kumar Anand (SUSBS Assistant Professor)No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 The S-Block ElementsDocument18 pagesChapter 10 The S-Block ElementsYash PlayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes (Metals)Document4 pagesChemistry Notes (Metals)Teo Jia Ming Nickolas75% (4)
- SblockkkkDocument3 pagesSblockkkkKisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- S Block 11Document28 pagesS Block 11Simranpreet Singh KhalsaNo ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument31 pagesS Block ElementsMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: The S-Block ElementsDocument13 pagesChapter 10: The S-Block Elementsgyogi1989No ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Metals and Non - MetalsDocument4 pagesChapter - 3 Metals and Non - MetalsJohnny MurrayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14.1: Metals Introduction.: How Are The Properties of Metals Related To Their Structure?Document5 pagesChapter 14.1: Metals Introduction.: How Are The Properties of Metals Related To Their Structure?Lixue's PoyaiNo ratings yet
- S Block-1Document46 pagesS Block-1Jeevan KumarNo ratings yet
- The Group 1 Elements: The Alkali Metals: "Read in The Name Your God Who Created " Chemistry of ElementsDocument44 pagesThe Group 1 Elements: The Alkali Metals: "Read in The Name Your God Who Created " Chemistry of ElementsFajar Sa'bandiNo ratings yet
- New Fou 1&2 Nagratoli S - BlockDocument19 pagesNew Fou 1&2 Nagratoli S - BlockAnamikaNo ratings yet
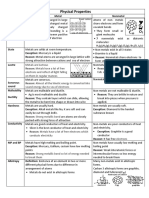
- M&NM-TABLE - Phy and Chem PropDocument3 pagesM&NM-TABLE - Phy and Chem PropanjanaNo ratings yet
- Iron Metabolism: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical ConsequencesFrom EverandIron Metabolism: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical ConsequencesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingFrom EverandCorrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingNo ratings yet