Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ISA 701 MindMap
ISA 701 MindMap
Uploaded by
Ali HaiderOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ISA 701 MindMap
ISA 701 MindMap
Uploaded by
Ali HaiderCopyright:
Available Formats
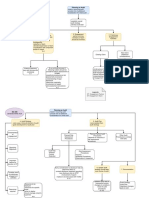
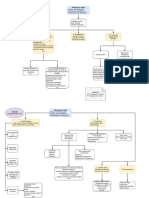
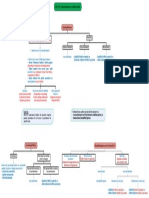
ISA 701: Key Audit Matter
When to include KAM Section How to determine KAM How to draft KAM Section
Audit of Complete Set of General Other Audit Engagements Definition Factors in determining significance Examples Main Heading (Key Audit Matters)
Purpose Financial Statements of Listed – Introductory Language
Entity – Statement depending on existence of KAM, and type of opinion
"We have determined the matters described below to be Key Audit
– Not required. – Most significant – Higher Risk 1. Goodwill, Intangible Assets, Deferred Tax. Matters to communicate in our report."
– Allowed if auditor decides or law requires. – Current Period – Judgments and Complexity involved 2. Valuation of assets and liabilities.
Required (except in Disclaimer of Opinion) – Communicated with TCWG – Expert involved 3. Change in accounting policies.
– Significant Event/transactions 4. Areas where work of Expert or Component
– Significant Accounting Policies auditor is used. Sub-heading (individual KAM)
5. Acquisition and disposals of business units.
6. Restructuring of business.
7. Significant number of litigations, and tax
contingencies. What Why How
Additional Concepts 8. Significant related party transactions.
Matter + Reference Justification Addressed
– How many KAMs (no lengthy list, 2-3) (Procedures, Outcome, Observation)
– No KAM
– When KAM not reported
– KAM from previous year or other clients
– Modified Opinion alongwith KAM
– Original information to be provided by
management Exam Tip: Drafting of KAM is like drafting of Risk Assessment Question.
You might also like
- IncomeTax Banggawan2019 Ch14Document12 pagesIncomeTax Banggawan2019 Ch14Noreen Ledda0% (1)
- Verification of Cash Payment To SubscriptionDocument2 pagesVerification of Cash Payment To SubscriptionAlexNo ratings yet
- Ukff3083 Financial Statement AnalysisDocument4 pagesUkff3083 Financial Statement AnalysisChong Jk100% (1)
- Principles of Deductions: Exercise Drill No. 1Document37 pagesPrinciples of Deductions: Exercise Drill No. 1cyken100% (2)
- Infographic FIN346 Chapter 5Document2 pagesInfographic FIN346 Chapter 5AmaninaYusri100% (2)
- Requirement: Prepare Journal Entries in The Books of The Home Office and in The Books of The Branch Office ForDocument2 pagesRequirement: Prepare Journal Entries in The Books of The Home Office and in The Books of The Branch Office ForvonnevaleNo ratings yet
- CAF 08 Chapter 4 MindMapDocument3 pagesCAF 08 Chapter 4 MindMapShahaer MumtazNo ratings yet
- ISA 800 MindMapDocument1 pageISA 800 MindMapA R AdILNo ratings yet
- Aars Isa 300 Series Flowcharts by Sir Jamshaid AkhtarDocument13 pagesAars Isa 300 Series Flowcharts by Sir Jamshaid AkhtarahmadNo ratings yet
- Audit and Assurance PrincipleDocument2 pagesAudit and Assurance PrincipleIsabell CastroNo ratings yet
- Alur Proses Operational AuditDocument8 pagesAlur Proses Operational AuditEvelina Debora DamanikNo ratings yet
- Dividend Decision Class NotesDocument18 pagesDividend Decision Class NotesSphamandla MakalimaNo ratings yet
- CAF 08 Chapter 4 MindMapDocument3 pagesCAF 08 Chapter 4 MindMapArslan AhmadNo ratings yet
- CE TrainingDocument44 pagesCE TrainingAzizzulHassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Cost & Management AccountingDocument30 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Cost & Management AccountingJiajia MoxNo ratings yet
- CFAS SemiFinalDocument4 pagesCFAS SemiFinalJoy CastillonNo ratings yet
- 419 Reviewer MIDTERMSDocument12 pages419 Reviewer MIDTERMSGatungay JanessaNo ratings yet
- CA Final Audit of Banks Revision CA SJDocument15 pagesCA Final Audit of Banks Revision CA SJmsanjib920No ratings yet
- Planning An Audit ISA 300: EP: Engagement Partner ET: Engagement TeamDocument2 pagesPlanning An Audit ISA 300: EP: Engagement Partner ET: Engagement TeamMuhammad AslamNo ratings yet
- Capital Maintenance: Let's Tackle The Difficult QuestionsDocument20 pagesCapital Maintenance: Let's Tackle The Difficult QuestionsJeremiah OjimaduNo ratings yet
- Treasury Process FlowchartDocument7 pagesTreasury Process FlowchartNarayan KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Materiality, Misstatements and Reporting Part I: ISA Implementation Support ModuleDocument14 pagesMateriality, Misstatements and Reporting Part I: ISA Implementation Support ModulelloydNo ratings yet
- Cfas Reviewer Chapter 1 5 CompressDocument5 pagesCfas Reviewer Chapter 1 5 CompressabetomelyprincessNo ratings yet
- Standards and The Conceptual Framework Underlying Financial AccountingDocument26 pagesStandards and The Conceptual Framework Underlying Financial AccountingLodovicus LasdiNo ratings yet
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument25 pagesRoot Cause AnalysisJonathan WenNo ratings yet
- ConceptDocument35 pagesConcepts2022100196No ratings yet
- Open Customer PortfolioDocument1 pageOpen Customer PortfolioRam Mohan MishraNo ratings yet
- Intensive Basic AccountingDocument4 pagesIntensive Basic AccountingMaryll Cyan Magnaye100% (2)
- Shailesh CVDocument3 pagesShailesh CVSuryakant AgrawalNo ratings yet
- PDF Memo 5a and 5b Ocean Manufacturing Inc DLDocument5 pagesPDF Memo 5a and 5b Ocean Manufacturing Inc DLnaura syahdaNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTING REVIEWER Accounting Priciples and AssumptionsDocument2 pagesACCOUNTING REVIEWER Accounting Priciples and AssumptionsMary Ingrid Arellano RabulanNo ratings yet
- Commerce and Accountancy SyllabusDocument2 pagesCommerce and Accountancy SyllabusRituraj BoruahNo ratings yet
- Informed Maintenance PlanningDocument14 pagesInformed Maintenance PlanningArdelean PaulNo ratings yet
- Far NotesDocument4 pagesFar NotesMikasa AckermanNo ratings yet
- The New Auditor's Report: Overview of The New and Revised Auditor Reporting Standards and Related Conforming AmendmentsDocument26 pagesThe New Auditor's Report: Overview of The New and Revised Auditor Reporting Standards and Related Conforming AmendmentsAndhika Suhud Meliora SitumorangNo ratings yet
- CA Inter Accounting Revision NotesDocument106 pagesCA Inter Accounting Revision NoteskalyanikamineniNo ratings yet
- Stra Ma ReviewerDocument2 pagesStra Ma ReviewerRosario, MarissaNo ratings yet
- Far 1-2Document3 pagesFar 1-2Marjorie UrbinoNo ratings yet
- Ifrs 17 - Operational Implications: Martyn Van Wensveen, Partner EY Malaysia IFRS 17 Implementation Lead (APAC)Document21 pagesIfrs 17 - Operational Implications: Martyn Van Wensveen, Partner EY Malaysia IFRS 17 Implementation Lead (APAC)Sulist SulistNo ratings yet
- Credit Analysis and Framewok - MODULE 1Document9 pagesCredit Analysis and Framewok - MODULE 1Boci & Company Services LimitedNo ratings yet
- ISA 510 MindMapDocument1 pageISA 510 MindMapA R AdILNo ratings yet
- MBP InsuranceDocument22 pagesMBP InsuranceMurtuza SadikotNo ratings yet
- CA Intermediate Accounting Marathon Handwritten Summary NotesDocument133 pagesCA Intermediate Accounting Marathon Handwritten Summary Notesadsa100% (1)
- CAPE Accounting Unit 1 Module 1 The Nature and Scope of AccountingDocument11 pagesCAPE Accounting Unit 1 Module 1 The Nature and Scope of AccountingRhea Lee Ross100% (1)
- RutgersDocument9 pagesRutgersupasanauvicNo ratings yet
- Final Audit CA SJ Short Notes Audit of BanksDocument15 pagesFinal Audit CA SJ Short Notes Audit of BankssimranNo ratings yet
- Marathon Batch Final With Cover and Index PDFDocument106 pagesMarathon Batch Final With Cover and Index PDFChandreshNo ratings yet
- UNVEILING-Analysis of KAM (Final) PDFDocument20 pagesUNVEILING-Analysis of KAM (Final) PDFBmjannah MasturaNo ratings yet
- 00 Tapovan Advanced Accounting Fasttrack 2024 BenchmarkDocument210 pages00 Tapovan Advanced Accounting Fasttrack 2024 Benchmarklakshmibhavani.2808No ratings yet
- Impact of Reliability Centered: Maintenance ProgramDocument11 pagesImpact of Reliability Centered: Maintenance ProgramCepi Sindang KamulanNo ratings yet
- McframeéVtraining Purchasing, Inspection, Inventory (L) 7.0.3.0 R00-EnDocument106 pagesMcframeéVtraining Purchasing, Inspection, Inventory (L) 7.0.3.0 R00-EnKerr PalaranNo ratings yet
- Important Concepts For Case Studies: Partial Compliance With AFRF Is Not Allowed E.G. "Financial Statements Are in Substantial Compliance With I FRS"Document2 pagesImportant Concepts For Case Studies: Partial Compliance With AFRF Is Not Allowed E.G. "Financial Statements Are in Substantial Compliance With I FRS"Raees aliNo ratings yet
- Webinar ACCA AFA IAPI IAI-What You Need To Know About Implementing KAM - NS Presentation FinalDocument21 pagesWebinar ACCA AFA IAPI IAI-What You Need To Know About Implementing KAM - NS Presentation FinalRiri BariNo ratings yet
- Sept Dec 2018 Darjeeling CoDocument6 pagesSept Dec 2018 Darjeeling Conajihah zakariaNo ratings yet
- 768760870587security Frameworks NIST CSF As An Enabler and Incident Response ApproachDocument33 pages768760870587security Frameworks NIST CSF As An Enabler and Incident Response ApproachggcvbcNo ratings yet
- Aan 4560Document22 pagesAan 4560ompatelNo ratings yet
- BABOK v2 Study MaterialDocument129 pagesBABOK v2 Study MaterialNg FlongNo ratings yet
- 00 Tapovan Advanced Accounting Free Fasttrack Batch BenchmarkDocument144 pages00 Tapovan Advanced Accounting Free Fasttrack Batch BenchmarkDhiraj JaiswalNo ratings yet
- ObjectiveDocument10 pagesObjectiveKaren QVNo ratings yet
- Ambit - IIM Calcutta Job Description FormDocument2 pagesAmbit - IIM Calcutta Job Description Formdeepakcool208No ratings yet
- ISA 706 MindmapDocument1 pageISA 706 MindmapAli HaiderNo ratings yet
- Performance Highlights FY20Document5 pagesPerformance Highlights FY20RahulNo ratings yet
- Slides 4Document45 pagesSlides 4Paulina CohalionNo ratings yet
- ACCTG ReviewerDocument13 pagesACCTG ReviewerAnn Christine C. ChuaNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Reports in British Columbia: The Strata Lots Owners Guide to Selecting Your Provider and Understanding Your ReportFrom EverandDepreciation Reports in British Columbia: The Strata Lots Owners Guide to Selecting Your Provider and Understanding Your ReportNo ratings yet
- Practice Set (Questions) - IFRS 5 PDFDocument2 pagesPractice Set (Questions) - IFRS 5 PDFAli Haider100% (2)
- CFAP 1 AFR Winter 2022Document5 pagesCFAP 1 AFR Winter 2022Ali HaiderNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance - Summary Notes by Mannar Siddiqui - Advanced Corporate Laws (CFAP-02) - 1Document6 pagesCorporate Governance - Summary Notes by Mannar Siddiqui - Advanced Corporate Laws (CFAP-02) - 1Ali HaiderNo ratings yet
- ICAP Past Exams (Solutions) - IAS 19Document6 pagesICAP Past Exams (Solutions) - IAS 19Ali HaiderNo ratings yet
- ISA 600 MindMapDocument2 pagesISA 600 MindMapAli HaiderNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Planning The EnterpriseDocument15 pagesEntrepreneurship Planning The Enterprisecharlie besabellaNo ratings yet
- This Project Is Done by Karthik SP Based On Cash Flow Analysis For Union Bank of IndiaDocument105 pagesThis Project Is Done by Karthik SP Based On Cash Flow Analysis For Union Bank of IndiaKarthik Sp100% (1)
- Laravel: Name Position Office Age Start Date SalaryDocument2 pagesLaravel: Name Position Office Age Start Date SalaryMạnh Quang ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Lippo 2022Document2 pagesLippo 2022Suryati indrianiNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Subject-Accountancy For Class-12th Examination 2024-25Document53 pagesQuestion Paper Subject-Accountancy For Class-12th Examination 2024-25AFRAH JALEELANo ratings yet
- Basic Corporate Law OutlineDocument59 pagesBasic Corporate Law Outlinedylthethrill100% (2)
- 2004 ACE Limited (NYSE: ACE) 10-KDocument149 pages2004 ACE Limited (NYSE: ACE) 10-KACELitigationWatchNo ratings yet
- Effect of Foreign Institutional Investors On Corporate Board Attributes A Literature ReviewDocument7 pagesEffect of Foreign Institutional Investors On Corporate Board Attributes A Literature ReviewRiya CassendraNo ratings yet
- Role of Suspended Directors in Committee of CreditorsDocument7 pagesRole of Suspended Directors in Committee of CreditorsMohitNo ratings yet
- Reporting & Interpreting Investments in Other CorporationsDocument52 pagesReporting & Interpreting Investments in Other CorporationsMichaelNo ratings yet
- Sox PDFDocument10 pagesSox PDFRajesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Lifting of Corporate VeilDocument6 pagesLifting of Corporate VeilSamiksha Pawar100% (1)
- Eric &philipDocument4 pagesEric &philipKing MacunatNo ratings yet
- Sampa Video Case Analysis Submission by Abhishek Ojha EPGP 04B 003 Saurabh Singh EPGP 04B 102 and Toban Varghese EPGP 04B 116Document11 pagesSampa Video Case Analysis Submission by Abhishek Ojha EPGP 04B 003 Saurabh Singh EPGP 04B 102 and Toban Varghese EPGP 04B 116hernandezc_joseNo ratings yet
- Model Portfolios: TD E-Series Funds: For Illustration Purposes OnlyDocument2 pagesModel Portfolios: TD E-Series Funds: For Illustration Purposes OnlypenisfuckerNo ratings yet
- CORPORATE LAW II - Part A & B (Q)Document4 pagesCORPORATE LAW II - Part A & B (Q)Ravi VarmaNo ratings yet
- Suzlon Energy: Previous YearsDocument15 pagesSuzlon Energy: Previous YearsSorav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (Accounting Problems)Document11 pagesQuestion Bank (Accounting Problems)Abhishek MohantyNo ratings yet
- Method NIFTY Equity IndicesDocument126 pagesMethod NIFTY Equity IndicesShubham JainNo ratings yet
- Joint Stock CompanyDocument26 pagesJoint Stock CompanyPratik ShahNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pages2nd Quarter Exam Entrepreneurshipjeo nalugon100% (1)
- Pro-Forma Journal EntriesDocument4 pagesPro-Forma Journal EntriesAdam CuencaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Common Stock ValuationDocument7 pagesChapter 10: Common Stock ValuationJhela HemarNo ratings yet
- Gearing Ratio - Lecture PDFDocument1 pageGearing Ratio - Lecture PDFDivineDavisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Introduction To Regular Income TaxDocument18 pagesChapter 7 Introduction To Regular Income TaxDANICKA JANE ENERONo ratings yet