Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6 - The Integral Test Solutions PDF
6 - The Integral Test Solutions PDF
Uploaded by
I am SmoothieCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 2015b Mat271b Exa MemoDocument9 pages2015b Mat271b Exa MemoMduduzi Magiva Mahlangu100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4Izzati AtirahNo ratings yet
- Improper Integrals: DX X FDocument12 pagesImproper Integrals: DX X FEric GokNo ratings yet
- 3.8 Derivatives of Inverse Trig Functions: Lewis and Clark Caverns, MontanaDocument9 pages3.8 Derivatives of Inverse Trig Functions: Lewis and Clark Caverns, MontanaSelina LeeNo ratings yet
- 2019 YIJC Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsDocument14 pages2019 YIJC Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsGeorge ChooNo ratings yet
- Math Suggestion2Document22 pagesMath Suggestion211polash68emonNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus - Definite IntegralsDocument3 pagesIntegral Calculus - Definite IntegralsPaul BrownNo ratings yet
- Differentiation - Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument6 pagesDifferentiation - Hyperbolic FunctionsTbos ThabisoNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 End of Chapter TestDocument6 pagesCh. 5 End of Chapter TestOld NewbornNo ratings yet
- FSC Derivative Integration FormulasDocument2 pagesFSC Derivative Integration Formulasمحمد اليافعيNo ratings yet
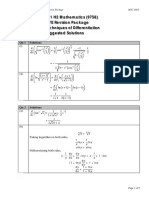
- H2 MYE Revision Package Techniques of Differentiation SolutionsDocument5 pagesH2 MYE Revision Package Techniques of Differentiation SolutionsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Improper Integrals and The Integral Test - GDLCDocument11 pagesImproper Integrals and The Integral Test - GDLCWarda JoryNo ratings yet
- 2016b Mat271b Exb Memo v1 Main ExamDocument10 pages2016b Mat271b Exb Memo v1 Main ExamMduduzi Magiva MahlanguNo ratings yet
- 39 Ext 12Document1 page39 Ext 12api-3706821No ratings yet
- Alg2 Formula SheetDocument4 pagesAlg2 Formula SheetbrdshnNo ratings yet
- Integration 2Document30 pagesIntegration 2Peter WambuorNo ratings yet
- DX X F DX X F: 2.2 Integrals Whose Integrands Become InfiniteDocument12 pagesDX X F DX X F: 2.2 Integrals Whose Integrands Become InfiniteEric GokNo ratings yet
- Calculus II - MTHN003 - Solutions of Previous Mid Term ExamsDocument37 pagesCalculus II - MTHN003 - Solutions of Previous Mid Term ExamsMahmoud shendyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Self Review SolutionsDocument2 pagesLecture 4 Self Review SolutionsGareth WongNo ratings yet
- The Uniform Distribution From A To B: Continuous DistributionsDocument71 pagesThe Uniform Distribution From A To B: Continuous Distributionsمروان الحاسيNo ratings yet
- Lesson 07 Differentiation of Inverse Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument2 pagesLesson 07 Differentiation of Inverse Hyperbolic FunctionsMUSIIWA LIGAVHANo ratings yet
- tp2 SolnDocument11 pagestp2 SolnMrinmay Dev SarmaNo ratings yet
- Math AA HL 2Document6 pagesMath AA HL 2Aryan Waghdhare100% (1)
- Num Int 1 DDocument32 pagesNum Int 1 DAhmad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Integration by SubstitutionDocument4 pagesIntegration by SubstitutionMacrine GraceNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review: 1 A 1 B Intersection Point ADocument16 pagesChapter Review: 1 A 1 B Intersection Point AnasehaNo ratings yet
- 2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test (Solutions)Document14 pages2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test (Solutions)Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- 0775 Further Maths 2021 MG p2Document6 pages0775 Further Maths 2021 MG p2Théophile MbameNo ratings yet
- AEM-Chapter01 (PD Orde 1)Document57 pagesAEM-Chapter01 (PD Orde 1)Achmad FauziNo ratings yet
- MYE Timed Trial 2 - SolutionsDocument13 pagesMYE Timed Trial 2 - SolutionsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Integration of Rational Functions by Partial FractionDocument22 pagesIntegration of Rational Functions by Partial FractionRitzz ThakurNo ratings yet
- Exercises: 1.1 - Volumes Using Cross-SectionsDocument9 pagesExercises: 1.1 - Volumes Using Cross-SectionsRodrigo TorresNo ratings yet
- Integration Notes PDFDocument7 pagesIntegration Notes PDFLim Lester Yu JunNo ratings yet
- TRIAL MATHEMATICS T 2021 Kluang Q P2Document2 pagesTRIAL MATHEMATICS T 2021 Kluang Q P2ZurainiNo ratings yet
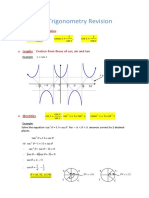
- A2 Level Trigonometry Revision: Three Further Trig RatiosDocument7 pagesA2 Level Trigonometry Revision: Three Further Trig RatiosLauren ChikwehwaNo ratings yet
- Gen Math - LESSON-4-RATIONAL-FUNCTIONDocument39 pagesGen Math - LESSON-4-RATIONAL-FUNCTIONJhade Layug ManatigaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 02 Limits and DerivativeDocument67 pagesLecture - 02 Limits and Derivativezjn1816333625No ratings yet
- Differential Equations 2Document16 pagesDifferential Equations 2LNo ratings yet
- TP 2Document7 pagesTP 2Mrinmay Dev SarmaNo ratings yet
- S5 Further Calculus 4 Integration 1-2Document6 pagesS5 Further Calculus 4 Integration 1-2isaiahseruyangeNo ratings yet
- Higher Maths: Revision NotesDocument26 pagesHigher Maths: Revision NotesAsep sunaryaNo ratings yet
- 7.8 Improper IntegralsDocument17 pages7.8 Improper Integralsمصطفى احمدNo ratings yet
- 01 Indefinate IntegrationDocument8 pages01 Indefinate IntegrationKalp JethaniNo ratings yet
- Integation (Without Ans) 13.05 PDFDocument49 pagesIntegation (Without Ans) 13.05 PDFDhruv ModiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document35 pagesLecture 6eustachebimenyimanaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Random VariableDocument24 pagesContinuous Random VariableEriick He'No ratings yet
- Sma 201 - 2007Document154 pagesSma 201 - 2007Paul LoyapanNo ratings yet
- 3 Continuous DistributionsDocument9 pages3 Continuous DistributionszzaanNo ratings yet
- Test 22B IntegrationDocument2 pagesTest 22B IntegrationHa MinhNo ratings yet
- 7 Bernoullis Equation NotesDocument6 pages7 Bernoullis Equation NotesOjit QuizonNo ratings yet
- Improper IntegralsDocument46 pagesImproper IntegralsLiliana Amp0% (1)
- BP (A)Document11 pagesBP (A)zoe yinzNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 IntegrationDocument88 pagesChapter7 Integrationhyacinth4eveNo ratings yet
- Integration #2Document57 pagesIntegration #2Chinaidine Petit-FrereNo ratings yet
- Differential CalculasDocument15 pagesDifferential CalculasShamim RahmatNo ratings yet
- Integrace 3Document1 pageIntegrace 3simcasromovaNo ratings yet
- Materi Minggu Ke-6Document26 pagesMateri Minggu Ke-6Qod RiyaNo ratings yet
- INPS-DEFINITE INTEGRAL-Study-MaterialDocument16 pagesINPS-DEFINITE INTEGRAL-Study-MaterialSps BloggerNo ratings yet
- Elementary Exercise Motion SolutionDocument4 pagesElementary Exercise Motion Solutionnainaradhey24No ratings yet
- 2 - Sequences Solutions PDFDocument11 pages2 - Sequences Solutions PDFI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- 1 - SequencesDocument4 pages1 - SequencesI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- 3 - Infinite SeriesDocument3 pages3 - Infinite SeriesI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Book-CH 3 PDFDocument48 pagesChemistry Book-CH 3 PDFI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- 5 - The Integral TestDocument2 pages5 - The Integral TestI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Updated PDFDocument91 pagesChapter 4 Updated PDFI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Transient Response RL & RCDocument23 pagesChapter 7 - Transient Response RL & RCI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Ch12 Ch13 ALL ProblemsDocument18 pagesCh12 Ch13 ALL ProblemsI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Ch9 Ch10 ALL ProblemsDocument32 pagesCh9 Ch10 ALL ProblemsI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Ch8 ALL ProblemsDocument92 pagesCh5 Ch8 ALL ProblemsI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Simple Resistive CircuitsDocument2 pagesChapter 3 - Simple Resistive CircuitsI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Inductance and CapacitanceDocument7 pagesChapter 6 - Inductance and CapacitanceI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Circuit ElementsDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - Circuit ElementsI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Techniques of Circuit AnalysisDocument31 pagesChapter 4 - Techniques of Circuit AnalysisI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
6 - The Integral Test Solutions PDF
6 - The Integral Test Solutions PDF
Uploaded by
I am SmoothieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6 - The Integral Test Solutions PDF
6 - The Integral Test Solutions PDF
Uploaded by
I am SmoothieCopyright:
Available Formats
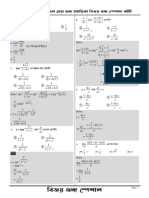
10.
3 THE INTEGRAL TEST
1. f ( x) 1 is positive, continuous, and decreasing for x 1; 1 dx lim
b 1
dx lim 1 b
x2 1 x2 b 1 x2 b x 1
lim 1 1 1 1 dx converges 1 converges
b b 1 x2 n2
n 1
b 1 b
2. f ( x) 1 is positive, continuous, and decreasing for x 1; 1 dx lim dx lim 5 x 0.8
0.2 1 x 0.2 1 x 0.2 4
x b b 1
lim 54 b0.8 5 1 dx diverges 1 diverges
b 4 1 x 0.2 n0.2
n 1
1 1 dx b 1
3. f ( x) is positive, continuous, and decreasing for x 1; lim dx
x2 4 1 x2 4 b 1 x2 4
1 tan 1x b 1b 11 11
lim lim 12 tan 1 tan 1 tan 1 dx converges
b 2 2 1 b 2 2 2 4 2 2 1 x2 4
1 converges
n2 4
n 1
1 1 dx b 1 b
4. f ( x) x 4
is positive, continuous, and decreasing for x 1; lim dx lim ln x 4
1 x 4 b 1 x 4 b 1
lim ln | b 4| ln 5 1 dx diverges 1 diverges
b 1 x 4 n 4
n 1
b
5. f ( x) e 2 x is positive, continuous, and decreasing for x 1; e 2 x dx lim e 2 x dx
1 b 1
2x b
lim 1e lim 1 1 1 e 2 x dx converges e 2 n converges
b 2 1 b 2e 2 b 2e2 2 e2 1
n 1
Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Section 10.3 The Integral Test 721
1 1 b 1
6. f ( x) is positive, continuous, and decreasing for x 2; dx lim dx
x (ln x )2 2 x (ln x )2 b 2 x (ln x )2
lim 1 b lim 1 1 1 1 dx converges 1 converges
b ln x 2 b ln b ln 2 ln 2 2 x (ln x )2 n (ln n )2
n 2
7. f ( x) x is positive and continuous for x 1, f ( x) 4 x2 0 for x 2, thus f is decreasing for
x2 4 x2 4
2
b b
x 3; x
2
dx lim 2
x dx lim 1 ln x2 4 lim 12 ln b 2 4 1 ln(13) x dx
3 x 4 b 3 x 4 b 2 3 b 2 3 x2 4
diverges n diverges n 1 2 n diverges
n2 4 n2 4 5 8 n2 4
n 3 n 1 n 3
8. f ( x) ln x 2 is positive and continuous for x 2, f ( x) 2 ln x 2 0 for x e, thus f is decreasing for x 3;
x x2
ln x 2 b ln x 2 b ln x 2
x
dx lim x
dx lim 2 ln x lim 2(ln b) 2(ln 3) x
dx diverges
3 b 3 b 3 b 3
ln n 2 diverges ln n 2 ln 4 ln n 2 diverges
n n 2 n
n 3 n 2 n 3
9. f ( x) x2 is positive and continuous for x 1, f ( x)
x ( x 6)
0 for x 6, thus f is decreasing for x 7;
ex 3 3e x 3
b x2 b
x2 dx lim dx lim 3x2 18 x 54 lim 3b 2 18b 54 327 lim
3( 6b 18) 327
7 ex 3 b 7 ex 3 b ex 3 ex 3 e x3
7 b eb 3 e7 3 b eb 3 e7 3
lim 54 327 327 x2 dx converges n2 converges
b3
b e e7 3 e7 3 7 ex 3 en 3
n 7
n2 1 4 9 16 25 36 n2 converges
en 3 e 13
e 23
e1 e4 3 e5 3 e2 en 3
n 1 n 7
10. f ( x) x 4 x 4 is continuous for x 2, f is positive for x 4, and f ( x) 7 x 0 for x 7,
x2 2 x 1 ( x 1)2 ( x 1)3
x 4 b x 1 b 3 b 1 b 3
thus f is decreasing for x 8; dx lim dx dx lim dx dx
8 ( x 1)2 b 8 ( x 1)2 8 ( x 1) 2 b 8 x 1 8 ( x 1)2
lim ln x 1 3 b lim ln b 1 3 ln 7 3 x 4 dx diverges n 4 diverges
b x 1 8 b b 1 7 8 ( x 1) 2 n2 2n 1
n 8
n 4 2 1 0 1 2 3 n 4 diverges
n2 2n 1 4 16 25 36 n2 2 n 1
n 2 n 8
11. converges; a geometric series with r 1 1 12. converges; a geometric series with r 1 1
10 e
13. diverges; by the nth-Term Test for Divergence, lim n 1 0
n n 1
n 5 5 dx
14. diverges by the Integral Test; dx 5ln(n 1) 5ln 2
1 x 1 1 x 1
Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
722 Chapter 10 Infinite Sequences and Series
15. diverges; 3 3 1 , which is a divergent p-series with p 1
n n 2
n 1 n 1
16. converges; 2 2 1 , which is a convergent p-series with p 3
n n n3 2 2
n 1 n 1
17. converges; a geometric series with r 1 1
8
18. diverges; 8 8 1 and since 1 diverges, 8 1 diverges
n n n n
n 1 n 1 n 1 n 1
n ln x
19. diverges by the Integral Test: dx 1 ln 2 n ln 2 ln x dx
2 x 2 2 x
20. diverges by the Integral Test: ln x dx; t ln x, dt dx
, dx
t
e dt
2 x x
2 b
tet 2 dt lim 2tet 2
4et lim 2eb 2 (b 2) 2e(ln 2) 2 (ln 2 2)
ln 2 b ln 2 b
21. converges; a geometric series with r 2 1
3
22. diverges; lim 5n lim 5n ln 5 lim ln 5 5 n 0
n
n 4 3 n 4n ln 4 n ln 4 4
23. diverges; 2 2 1 , which diverges by the Integral Test
n 1 n 1
n 0 n 0
n dx 1 ln(2n
24. diverges by the Integral Test: 1) as n
1 2x 1 2
25. diverges; lim an lim 2n lim 2n ln 2 0
n n n 1 n 1
n u x 1 n 1 du
26. diverges by the Integral Test: dx ; ln n 1 ln 2 as n
1 x x 1 du dx 2 u
x
1
n 2 n n
27. diverges; lim ln n
lim 1
lim 2
0
n n n n
n
28. diverges; lim an lim 1 1 e 0
n n n
29. diverges; a geometric series with r 1 1.44 1
ln 2
Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Section 10.3 The Integral Test 723
30. converges; a geometric series with r 1 0.91 1
ln 3
1
x 1
31. converges by the Integral Test:
3 (ln x ) (ln x )2 1
dx; u ln x, du x dx
1 b 1
1 du lim sec u lim sec b sec 1 (ln 3) lim cos 1 1
b
sec 1 (ln 3)
ln 3 u u 2
1 b ln 3 b b
cos (0) sec 1 (ln 3)
1
2
sec 1 (ln 3) 1.1439
1
32. converges by the Integral Test: 1 dx x
dx; u ln x, du 1 dx
1 x 1 ln 2 x 1 1 (ln x )2 x
1 b 1
1 du lim tan u lim tan b tan 1 0 0
0 1 u2 b
0
b 2 2
sin 1
33. diverges by the nth-Term Test for divergence; lim n sin 1 lim n
lim sin x 1 0
n n n 1
x 0 x
n
tan 1 1
sec 2 1
1 n n2 n
34. diverges by the nth-Term Test for divergence; lim n tan n
lim 1
lim
n n n n 1
n2
lim sec 2 1
n
sec2 0 1 0
n
35. converges by the Integral Test: ex dx; u e x , du e x dx
1 1 e2 x
1 b 1
1 du lim tan u lim tan b tan 1 e tan 1
e 0.35
e 1 u2 n e b 2
36. converges by the Integral Test: 2 dx; u e x , du e x dx, dx 1 du 2 du
1 1 ex u e u (1 u )
2 2 du lim 2 ln u u b lim 2 ln b 2 ln e 2 ln1 2 ln e 2ln e 0.63
e u u 1 b 1 e b b 1 e 1 e 1 e 1
1
u tan x 2 2
37. converges by the Integral Test: 8 tan 1 x dx; 8u du 4u 2 4
2 2
3 2
1 1 x2 du dx 4 4 4 16 4
1 x2
x u x2 1 1 du 1 ln u b 1 (ln b
38. diverges by the Integral Test: 2
dx; 2 2 u
lim 2
lim 2
ln 2)
1 x 1 du 2 x dx b 2 b
b ex 1 x b
39. converges by the Integral Test: sech x dx 2 lim dx 2 lim tan e
1 b 1 1 e x 2 b 1
1 b 1 1
2 lim tan e tan e 2 tan e 0.71
b
Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
724 Chapter 10 Infinite Sequences and Series
b b
40. converges by the Integral Test: sech 2 x dx lim sech 2 x dx lim tanh x 1 lim (tanh b tanh 1)
1 b 1 b b
1 tanh 1 0.76
a 1 b (b 2) a 3a (b 2) a 3a
41. x 2 x 4
dx lim a ln x 2 ln x 4 lim ln b 4
ln 5
lim ln b 4
ln 5
;
1 b 1 b b
(b 2) a , a 1
lim b 4
a lim (b 2)a 1 the series converges to ln 53 if a 1 and diverges to if
b b 1, a 1
a 1. If a 1, the terms of the series eventually become negative and the Integral Test does not apply. From
that point on, however, the series behaves like a negative multiple of the harmonic series, and so it diverges.
b
42. 1 2a dx lim ln x 1 lim ln b 1 ln 2 lim ln b 1 ln 2 ;
3 x 1 x 1 b ( x 1)2 a b (b 1)2 a 42 a b (b 1) 2 a 42 a
3
1, a 1
b 1 1 2 4 1
lim lim the series converges to ln ln 2 if a and diverges to
b (b 1) 2 a b 2 a ( b 1)2 a 1
, a 1 2 2
2
if a 1. If a 1, the terms of the series eventually become negative and the Integral Test does not apply.
2 2
From that point on, however, the series behaves like a negative multiple of the harmonic series, and so it
diverges.
43. (a)
(b) There are (13)(365)(24)(60)(60) 109 seconds in 13 billion years; by part (a) sn 1 ln n where
n (13)(365)(24)(60)(60) 109 sn 1 ln (13)(365)(24)(60)(60) 109
1 ln(13) ln(365) ln(24) 2 ln(60) 9 ln(10) 41.55
44. No, because 1 1 1 and 1 diverges
nx x n n
n 1 n 1 n 1
an an
45. Yes. If an is a divergent series of positive numbers, then 12 an 2
also diverges and 2
an .
n 1 n 1 n 1
There is no smallest divergent series of positive number: for any divergent series an of positive
n 1
an
numbers 2
has smaller terms and still diverges.
n 1
Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Section 10.3 The Integral Test 725
46. No, if an is a convergent series of positive numbers, then 2 an 2an also converges, and
n 1 n 1 n 1
2 an an . There is no largest convergent series of positive numbers.
47. (a) Both integrals can represent the area under the curve f ( x) 1 , and the sum s50 can be considered an
x 1
50
approximation of either integral using rectangles with x 1. The sum s50 1 is an overestimate
n 1
n 1
51 1 dx.
of the integral The sum s50 represents a left-hand sum (that is, the we are choosing the
1 x 1
left-hand endpoint of each subinterval for ci ) and because f is a decreasing function, the value of f is
a maximum at the left-hand endpoint of each subinterval. The area of each rectangle overestimates the true
51 50 50
area, thus 1 dx 1 . In a similar manner, s50 underestimates the integral 1 dx. In
1 x 1 n 1 0 x 1
n 1
this case, the sum s50 represents a right-hand sum and because f is a decreasing function, the value of f is
a minimum at the right-hand endpoint of each subinterval. The area of each rectangle underestimates the
50 50 51 51
true area, thus 1 1 dx. Evaluating the integrals we find 1 dx 2 x 1
n 1 0 x 1 1 x 1 1
n 1
50 50 50
2 52 2 2 11.6 and 1 dx 2 x 1 2 51 2 1 12.3. Thus, 11.6 1 12.3.
0 x 1 0 n 1
n 1
n 1 n 1 2
(b) sn 1000 1 dx 2 x 1 2 n 1 2 2 1000 n 500 2 1 251414.2
1 x 1 1
n 251415.
30
48. (a) Since we are using s30 1 to estimate 1, the error is given by 1. We can consider this
n4 n4 n4
n 1 n 1 n 31
sum as an estimate of the area under the curve f ( x) 1 when x 30 using rectangles with x 1 and
x4
ci is the right-hand endpoint of each subinterval. Since f is a decreasing function, the value of f is a
1 1 b 1
minimum at the right-hand endpoint of each subinterval, thus dx lim dx
n4 30 x 4 b 30 x 4
n 31
b
lim 1
3
lim 1 1 1.23 10 5. Thus the error 1.23 10 5.
b 3 x 30 b 3b3 3(30)3
b 1 b
(b) We want S sn 0.000001 1 dx 0.000001 1 dx lim dx lim 1
n x4 n x4 b n x4 b
3
3x n
lim 1 1 1 0.000001 n 3 1000000 69.336 n 70.
b 3b3 3n3 3 n3 3
b 1 b
49. We want S sn 0.01 1 dx 0.01 1 dx lim dx lim 1 lim 1 1
n x3 n x3 b n x3 b
2
2x n b 2b 2 2 n2
8
1 0.01 n 50 7.071 n 8 S s8 1 1.195
2 n2 n3
n 1
Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
726 Chapter 10 Infinite Sequences and Series
b 1 b
50. We want S sn 0.1 1 dx 0.1 lim dx lim 1 tan 1 x
n x2 4 b n x2 4 b 2 2 n
lim 1 tan 1 b 1 tan 1 n 1 tan 1 n 0.1 n 2 tan 0.2 9.867 n 10
b 2 2 2 2 4 2 2 2
10
S s10 1 0.57
n2 4
n 1
b 1 b
51. S sn 0.00001 1 dx 0.00001 1 dx lim dx lim 10 lim 10 10
n x1.1 n x 1.1
b n x1.1 b x 0.1
n b b0.1 n0.1
10 0.00001 n 100000010 n 1060
n0.1
b
1 1 b 1 1
52. S sn 0.01 dx 0.01 dx lim dx lim
n x (ln x )3 n x (ln x )3 b n x (ln x )3 b 2(ln x ) 2 n
lim 1 1 1 0.01 n e 50 1177.405 n 1178
b 2(ln b) 2 2(ln n )2 2(ln n )2
n n
53. Let An ak and Bn 2k a , where {ak } is a nonincreasing sequence of positive terms converging
2k
k 1 k 1
to 0. Note that { An } and {Bn } are nondecreasing sequences of positive terms. Now,
Bn 2a2 4a4 8a8 2n a
2n
2a2 2a4 2a4 2a8 2a8 2a8 2a8 2a 2a 2a
2n 2n 2n
2n 1 terms
2a1 2a2 2a3 2a4 2a5 2a6 2a7 2a8 2a 2a 2a 2A
2n 1
2n 1
1 2n 2n
2 ak . Therefore if ak converges, then {Bn } is bounded above 2k a converges. Conversely,
2k
k 1
An a1 a2 a3 a4 a5 a6 a7 an a1 2a2 4a4 2n a a1 Bn a1 2k a .
2n 2k
k 1
Therefore, if 2k a converges, then { An } is bounded above and hence converges.
2k
k 1
54. (a) a 1 1 2n a 2n 1 1 1, which diverges
2n 2n ln 2n 2n n (ln 2) 2n 2n n (ln 2) ln 2 n
n 2 n 2 n 2
1 diverges.
n ln n
n 2
n
(b) a n
1 2n a n 2n 1 1 1 , a geometries series that converges if
2 2np 2 2np n
p 1
2 p 1
n 1 n 1 n 1 2 n 1
1 1 or p 1, but diverges if p 1.
2p 1
Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Section 10.3 The Integral Test 727
p 1 b
55. (a) dx ; u ln x, du dx u p du lim u p 1 lim 1 1p b p 1 (ln 2) p 1
2 x (ln x ) p x ln 2 b ln 2 b
1 p 1
(ln 2) p 1
p 1 the improper integral converges if p 1 and diverges if p 1. For p 1 :
, p 1
dx b
lim ln(ln x) 2 lim ln(ln b) ln(ln 2) , so the improper integral diverges if p 1.
2 x ln x b b
(b) Since the series and the integral converge or diverge together, 1 converges if and only if p 1.
n (ln n) p
n 2
56. (a) p 1 the series diverges
(b) p 1.01 the series converges
(c) 1 1 1 ; p 1 the series diverges
n ln n3 3 n (ln n )
n 2 n 2
(d) p 3 the series converges
1 1, n 11
57. (a) From Fig. 10.11 (a) in the text with f ( x) x
and ak k
we have x
dx 1 12 1
3
1
n
1
n
1 f ( x) dx ln( n 1) 1 12 1
3
1
n
1 ln n 0 ln ( n 1) ln n 1 12 1
3
1
n
ln n 1.
1
Therefore the sequence 1 12 1
3
1
n
ln n is bounded above by 1 and below by 0.
1, 1 n 11
(b) From the graph in Fig. 10.11 (b) with f ( x) x n 1 x
dx ln (n 1) ln n
n
0 1 ln ( n 1) ln n 1 12 1 1 ln ( n 1) 1 12 1 1 ln n .
n 1 3 n 1 3 n
If we define an 1 12 13 n1 ln n, then 0 an 1 an an 1 an {an } is a decreasing
sequence of nonnegative terms.
2 b 2
58. e x e x for x 1, and e x dx lim e x lim e b e 1 e 1 e x dx converges by the
1 b 1 b 1
2 2
Comparison Test for improper integrals e n 1 e n converges by the Integral Test.
n 0 n 1
b b
59. (a) s10 1 1.97531986; 1 dx lim x 3dx lim x 2 lim 1 1 1
n3 11 x3 b 11 b 2 11 b 2b 2 242 242
n 1
b b
and 1 dx lim x 3 dx lim x 2 lim 1 1 1
10 x3 b 10 b 2 10 b 2b 2 200 200
1
1.97531986 242 s 1.97531986 1 1.20166 s 1.20253
200
(b) s 1 1.20166 1.20253 1.202095; error 1.2025321.20166 0.000435
n3 2
n 1
Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
728 Chapter 10 Infinite Sequences and Series
10 b b
60. (a) s10 1 1.082036583; 1 dx lim x 4 dx lim x 3 lim 1 1 1
n4 11 x 4 b 11 b 3 11 b 3b3 3993 3993
n 1
b b
and 1 dx lim x 4 dx lim x 3 lim 1 1 1
10 x 4 b 10 b 3 10 b 3b3 3000 3000
1
1.082036583 3993 s 1
1.082036583 3000 1.08229 s 1.08237
(b) s 1 1.08229 1.08237 1.08233; error 1.08237 1.08229 0.00004
n4 2 2
n 1
2
1 1 1 1 1 1
61. The total area will be 2
. The p-series 2
converges to and
n 1
n n n 1 n 1 n n( n 1) n 1n
6
1
converges to 1 (see Example 5). Thus we can write the area as the difference of these two values,
n 1
n( n 1)
2
or 1 0.64493.
6
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
62. The area of the nth trapezoid is . The total area will be
2 n n 1 n n 1 2 n2 ( n 1) 2
1 1 1 1
2 2
, since the series telescopes and has a value of 1.
2n 1 n ( n 1) 2
You might also like
- 2015b Mat271b Exa MemoDocument9 pages2015b Mat271b Exa MemoMduduzi Magiva Mahlangu100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4Izzati AtirahNo ratings yet
- Improper Integrals: DX X FDocument12 pagesImproper Integrals: DX X FEric GokNo ratings yet
- 3.8 Derivatives of Inverse Trig Functions: Lewis and Clark Caverns, MontanaDocument9 pages3.8 Derivatives of Inverse Trig Functions: Lewis and Clark Caverns, MontanaSelina LeeNo ratings yet
- 2019 YIJC Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsDocument14 pages2019 YIJC Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsGeorge ChooNo ratings yet
- Math Suggestion2Document22 pagesMath Suggestion211polash68emonNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus - Definite IntegralsDocument3 pagesIntegral Calculus - Definite IntegralsPaul BrownNo ratings yet
- Differentiation - Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument6 pagesDifferentiation - Hyperbolic FunctionsTbos ThabisoNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 End of Chapter TestDocument6 pagesCh. 5 End of Chapter TestOld NewbornNo ratings yet
- FSC Derivative Integration FormulasDocument2 pagesFSC Derivative Integration Formulasمحمد اليافعيNo ratings yet
- H2 MYE Revision Package Techniques of Differentiation SolutionsDocument5 pagesH2 MYE Revision Package Techniques of Differentiation SolutionsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Improper Integrals and The Integral Test - GDLCDocument11 pagesImproper Integrals and The Integral Test - GDLCWarda JoryNo ratings yet
- 2016b Mat271b Exb Memo v1 Main ExamDocument10 pages2016b Mat271b Exb Memo v1 Main ExamMduduzi Magiva MahlanguNo ratings yet
- 39 Ext 12Document1 page39 Ext 12api-3706821No ratings yet
- Alg2 Formula SheetDocument4 pagesAlg2 Formula SheetbrdshnNo ratings yet
- Integration 2Document30 pagesIntegration 2Peter WambuorNo ratings yet
- DX X F DX X F: 2.2 Integrals Whose Integrands Become InfiniteDocument12 pagesDX X F DX X F: 2.2 Integrals Whose Integrands Become InfiniteEric GokNo ratings yet
- Calculus II - MTHN003 - Solutions of Previous Mid Term ExamsDocument37 pagesCalculus II - MTHN003 - Solutions of Previous Mid Term ExamsMahmoud shendyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Self Review SolutionsDocument2 pagesLecture 4 Self Review SolutionsGareth WongNo ratings yet
- The Uniform Distribution From A To B: Continuous DistributionsDocument71 pagesThe Uniform Distribution From A To B: Continuous Distributionsمروان الحاسيNo ratings yet
- Lesson 07 Differentiation of Inverse Hyperbolic FunctionsDocument2 pagesLesson 07 Differentiation of Inverse Hyperbolic FunctionsMUSIIWA LIGAVHANo ratings yet
- tp2 SolnDocument11 pagestp2 SolnMrinmay Dev SarmaNo ratings yet
- Math AA HL 2Document6 pagesMath AA HL 2Aryan Waghdhare100% (1)
- Num Int 1 DDocument32 pagesNum Int 1 DAhmad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Integration by SubstitutionDocument4 pagesIntegration by SubstitutionMacrine GraceNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review: 1 A 1 B Intersection Point ADocument16 pagesChapter Review: 1 A 1 B Intersection Point AnasehaNo ratings yet
- 2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test (Solutions)Document14 pages2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test (Solutions)Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- 0775 Further Maths 2021 MG p2Document6 pages0775 Further Maths 2021 MG p2Théophile MbameNo ratings yet
- AEM-Chapter01 (PD Orde 1)Document57 pagesAEM-Chapter01 (PD Orde 1)Achmad FauziNo ratings yet
- MYE Timed Trial 2 - SolutionsDocument13 pagesMYE Timed Trial 2 - SolutionsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Integration of Rational Functions by Partial FractionDocument22 pagesIntegration of Rational Functions by Partial FractionRitzz ThakurNo ratings yet
- Exercises: 1.1 - Volumes Using Cross-SectionsDocument9 pagesExercises: 1.1 - Volumes Using Cross-SectionsRodrigo TorresNo ratings yet
- Integration Notes PDFDocument7 pagesIntegration Notes PDFLim Lester Yu JunNo ratings yet
- TRIAL MATHEMATICS T 2021 Kluang Q P2Document2 pagesTRIAL MATHEMATICS T 2021 Kluang Q P2ZurainiNo ratings yet
- A2 Level Trigonometry Revision: Three Further Trig RatiosDocument7 pagesA2 Level Trigonometry Revision: Three Further Trig RatiosLauren ChikwehwaNo ratings yet
- Gen Math - LESSON-4-RATIONAL-FUNCTIONDocument39 pagesGen Math - LESSON-4-RATIONAL-FUNCTIONJhade Layug ManatigaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 02 Limits and DerivativeDocument67 pagesLecture - 02 Limits and Derivativezjn1816333625No ratings yet
- Differential Equations 2Document16 pagesDifferential Equations 2LNo ratings yet
- TP 2Document7 pagesTP 2Mrinmay Dev SarmaNo ratings yet
- S5 Further Calculus 4 Integration 1-2Document6 pagesS5 Further Calculus 4 Integration 1-2isaiahseruyangeNo ratings yet
- Higher Maths: Revision NotesDocument26 pagesHigher Maths: Revision NotesAsep sunaryaNo ratings yet
- 7.8 Improper IntegralsDocument17 pages7.8 Improper Integralsمصطفى احمدNo ratings yet
- 01 Indefinate IntegrationDocument8 pages01 Indefinate IntegrationKalp JethaniNo ratings yet
- Integation (Without Ans) 13.05 PDFDocument49 pagesIntegation (Without Ans) 13.05 PDFDhruv ModiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document35 pagesLecture 6eustachebimenyimanaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Random VariableDocument24 pagesContinuous Random VariableEriick He'No ratings yet
- Sma 201 - 2007Document154 pagesSma 201 - 2007Paul LoyapanNo ratings yet
- 3 Continuous DistributionsDocument9 pages3 Continuous DistributionszzaanNo ratings yet
- Test 22B IntegrationDocument2 pagesTest 22B IntegrationHa MinhNo ratings yet
- 7 Bernoullis Equation NotesDocument6 pages7 Bernoullis Equation NotesOjit QuizonNo ratings yet
- Improper IntegralsDocument46 pagesImproper IntegralsLiliana Amp0% (1)
- BP (A)Document11 pagesBP (A)zoe yinzNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 IntegrationDocument88 pagesChapter7 Integrationhyacinth4eveNo ratings yet
- Integration #2Document57 pagesIntegration #2Chinaidine Petit-FrereNo ratings yet
- Differential CalculasDocument15 pagesDifferential CalculasShamim RahmatNo ratings yet
- Integrace 3Document1 pageIntegrace 3simcasromovaNo ratings yet
- Materi Minggu Ke-6Document26 pagesMateri Minggu Ke-6Qod RiyaNo ratings yet
- INPS-DEFINITE INTEGRAL-Study-MaterialDocument16 pagesINPS-DEFINITE INTEGRAL-Study-MaterialSps BloggerNo ratings yet
- Elementary Exercise Motion SolutionDocument4 pagesElementary Exercise Motion Solutionnainaradhey24No ratings yet
- 2 - Sequences Solutions PDFDocument11 pages2 - Sequences Solutions PDFI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- 1 - SequencesDocument4 pages1 - SequencesI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- 3 - Infinite SeriesDocument3 pages3 - Infinite SeriesI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Book-CH 3 PDFDocument48 pagesChemistry Book-CH 3 PDFI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- 5 - The Integral TestDocument2 pages5 - The Integral TestI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Updated PDFDocument91 pagesChapter 4 Updated PDFI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Transient Response RL & RCDocument23 pagesChapter 7 - Transient Response RL & RCI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Ch12 Ch13 ALL ProblemsDocument18 pagesCh12 Ch13 ALL ProblemsI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Ch9 Ch10 ALL ProblemsDocument32 pagesCh9 Ch10 ALL ProblemsI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Ch8 ALL ProblemsDocument92 pagesCh5 Ch8 ALL ProblemsI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Simple Resistive CircuitsDocument2 pagesChapter 3 - Simple Resistive CircuitsI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Inductance and CapacitanceDocument7 pagesChapter 6 - Inductance and CapacitanceI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Circuit ElementsDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - Circuit ElementsI am SmoothieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Techniques of Circuit AnalysisDocument31 pagesChapter 4 - Techniques of Circuit AnalysisI am SmoothieNo ratings yet