Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Upsc 2022 1 PDF
Upsc 2022 1 PDF
Uploaded by
kv chandrasekerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Upsc 2022 1 PDF
Upsc 2022 1 PDF
Uploaded by
kv chandrasekerCopyright:
Available Formats
61
Diode circuits : Clipping, clamping, rectifier. Biasing and bias stability. FET amplifiers. Current mirror;
Amplifiers : single and multi-stage, differential, operational feedback and power. Analysis of
amplifiers; frequency-response of amplifiers. OPAMP circuits. Filters; sinusoidal oscillators : criterion for
oscillation; single-transistor and OPAMP configurations. Function generators and wave-shaping circuits.
Linear and switching power supplies.
5. Digital Electronics :
Boolean algebra; minimisation of Boolean functions; logic gates; digital IC families (DTL, TTL, ECL,
MOS, CMOS). Combinational circuits : arithmetic circuits, code converters, multiplexers and decoders.
Sequential circuits: latches and flip-flops, counters and shift-registers. Comparators, timers,
multivibrators. Sample and hold circuits, ADCs and DACs. Semiconductor memories. Logic
implementation using programmable devices (ROM, PLA, FPGA).
6. Energy Conversion :
Principles of electromechanical energy conversion : Torque and emf in rotating machines. DC
machines : characteristics and performance analysis; starting and speed control of motors. Transformers :
principles of operation and analysis; regulation, efficiency; 3-phase transformers. 3-phase induction
machines and synchronous machines : characteristics and performance analysis; speed control.
7. Power Electronics and Electric Drives :
Semi-conductor power devices : diode, transistor, thyristor, triac, GTO and MOSFET-static
characteristics and principles of operation; triggering circuits; phase control rectifiers; bridge converters :
fully-controlled and half-controlled; principles of thyristor choppers and inverters; DC-DC converters;
Switch mode inverter; basic concepts of speed control of dc and ac motor drives applications of variable-
speed drives.
8. Analog Communication :
Random variables : continuous, discrete; probability, probability functions. Statistical averages;
probability models; Random signals and noise : white noise, noise equivalent bandwidth; signal
transmission with noise; signal to noise ratio. Linear CW modulation : Amplitude modulation : DSB, DSB-
SC and SSB. Modulators and Demodulators; Phase and Frequency modulation : PM & FM signals;
narrows band FM; generation & detection of FM and PM, Deemphasis, Preemphasis. CW modulation
system : Superhetrodyne receivers, AM receivers, communication receivers, FM receivers, phase locked
loop, SSB receiver Signal to noise ratio calculation or AM and FM receivers.
PAPER II
1. Control Systems :
Elements of control systems; block-diagram representations; open-loop & closed-loop systems;
principles and applications of feed-back. Control system components. LTI systems : time-domain and
transform-domain analysis. Stability : Routh Hurwitz criterion, root-loci, Bode-plots and polor plots,
Nyquist’s criterion; Design of lead-lad compensators. Proportional, PI, PID controllers. State-variable
representation and analysis of control systems.
2. Microprocessors and Microcomputers :
PC organisation; CPU, instruction set, register settiming diagram, programming, interrupts,
memory interfacing, I/O interfacing, programmable peripheral devices.
Government strives to have a workforce which reflects gender balance and women candidates are encouraged to apply.
You might also like
- UPSC Syllabus Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesUPSC Syllabus Electrical EngineeringMOHD ALI SHAMSINo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Syllabus For IESDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineering Syllabus For IESSanjay YadavNo ratings yet
- UPSC CSE Electrical Engineering SyllabusDocument2 pagesUPSC CSE Electrical Engineering Syllabusbpsharmab1p1No ratings yet
- Paper - I 1. Circuit Theory:: Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesPaper - I 1. Circuit Theory:: Electrical EngineeringEr Paramjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrical SyllabusDocument2 pagesElectrical SyllabusSumit SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrical Main Syll IasDocument3 pagesElectrical Main Syll IasRNikaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Syllabus For UPSC Main ExaminationDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineering Syllabus For UPSC Main ExaminationsujaraghupsNo ratings yet
- Eletrical SyllabusDocument3 pagesEletrical SyllabusRadhey LoyaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For IESDocument3 pagesSyllabus For IESSaranya PrabagaranNo ratings yet
- Upsc CSE Ele SyllabusDocument2 pagesUpsc CSE Ele SyllabusgppNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Electrical Engineering PrelimsDocument3 pagesSyllabus of Electrical Engineering Prelimsapi-3710029No ratings yet
- Electrical Engg SyllabusDocument6 pagesElectrical Engg Syllabuschirag_cs7No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Preliminary SyllabusDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineering Preliminary Syllabusசுப.தமிழினியன்100% (2)
- NTPC SyllabusDocument2 pagesNTPC SyllabusSuraj KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 03 Electrical PDFDocument3 pages03 Electrical PDFSultan SheikhNo ratings yet
- Gate 2012 Slybus Ee&EcDocument2 pagesGate 2012 Slybus Ee&EcAkku MumbaiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Mains of Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesSyllabus Mains of Electrical Engineeringapi-3710029No ratings yet
- Upsc Electrical Engineering Syllabus PDF 7ec21c12Document5 pagesUpsc Electrical Engineering Syllabus PDF 7ec21c12mojo xoxoNo ratings yet
- DRDO Syll (Ece)Document3 pagesDRDO Syll (Ece)elisettynarendraNo ratings yet
- Computer Peripherals Internets: Engineering Knowledge Test (EKT) SyllabusDocument2 pagesComputer Peripherals Internets: Engineering Knowledge Test (EKT) SyllabusMKaihnsaNo ratings yet
- APRCET SyllabusDocument2 pagesAPRCET SyllabusHappy SoulNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering - Ies (Paper - I)Document4 pagesElectronics & Telecommunication Engineering - Ies (Paper - I)Archana TripathiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Electrical Engg CseDocument7 pagesSyllabus Electrical Engg CseKrishna Mohan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Networks, Signals and Systems Network Solution MethodsDocument2 pagesNetworks, Signals and Systems Network Solution MethodsmanojNo ratings yet
- Ph.D. Entrance Test Syllabus For Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument2 pagesPh.D. Entrance Test Syllabus For Electronics and Communication EngineeringAnalog LayoutNo ratings yet
- EC-101 Electrical Sciences 3-1-0-8: Texts/ReferenceDocument15 pagesEC-101 Electrical Sciences 3-1-0-8: Texts/Referenceparveenrohilla26No ratings yet
- Instrumentation MTDocument1 pageInstrumentation MTKannanNo ratings yet
- GATE2010 InfoBrochure 1Document2 pagesGATE2010 InfoBrochure 1Prem ChetryNo ratings yet
- Junior Telecom Officer (JTO)Document1 pageJunior Telecom Officer (JTO)Siva Kumar AvisNo ratings yet
- RSMSSB JEN Electrical SyllabusDocument2 pagesRSMSSB JEN Electrical Syllabusashwinivema1980No ratings yet
- M.Tech. (Systems & Signal Processing)Document4 pagesM.Tech. (Systems & Signal Processing)Chinnu ChinuNo ratings yet
- RaoufDocument2 pagesRaoufRaouf ValayappuramNo ratings yet
- Paper-1: IES Electrical Engineering SyllabusDocument3 pagesPaper-1: IES Electrical Engineering SyllabusJampana ShivaramakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics SyllabusDocument2 pagesElectrical and Electronics SyllabusVignesh2610No ratings yet
- Syllabus For IES in Electronics&Communication PaperDocument4 pagesSyllabus For IES in Electronics&Communication PaperRitesh Kumar BhadaniNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument3 pagesElectronics and Communication EngineeringmrameshmeNo ratings yet
- UGC NET Electronic Science SyllabusDocument3 pagesUGC NET Electronic Science Syllabuskumar HarshNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For PHDFDocument2 pagesSyllabus For PHDFchandravinitaNo ratings yet
- Ugc-Net-2019-Electronic Science SyllabusDocument4 pagesUgc-Net-2019-Electronic Science Syllabussasi kiran sNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For VLSI and Embedded SystemDocument1 pageSyllabus For VLSI and Embedded SystemAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Ies Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesIes Syllabus PDFSK PNo ratings yet
- Apgenco Ae Electronics SyllabusDocument3 pagesApgenco Ae Electronics SyllabusDhanu NetintiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For ElectronicsDocument2 pagesSyllabus For Electronicssarav dNo ratings yet
- 5.5.10 Electronics and Communication Engineering (EC) : Linear Algebra: CalculusDocument2 pages5.5.10 Electronics and Communication Engineering (EC) : Linear Algebra: CalculusMohan Kumar NNo ratings yet
- Section 1: Networks, Signals and SystemsDocument3 pagesSection 1: Networks, Signals and SystemsSagar PatilNo ratings yet
- TRB Syllabus For Ece FinalDocument2 pagesTRB Syllabus For Ece FinalbhavyaNo ratings yet
- Ies SyllabusBooks For IesDocument2 pagesIes SyllabusBooks For IesAlind DubeyNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCCDocument3 pagesCCCCCCCCCKumar AbhinavNo ratings yet
- GATE Syllabus Instrumentation EngineeringDocument5 pagesGATE Syllabus Instrumentation Engineeringabcd3511No ratings yet
- AP Genco SyllabusDocument2 pagesAP Genco Syllabusbalu56kvNo ratings yet
- (For Both Objective and Conventional Type Papers) : Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Paper-IDocument5 pages(For Both Objective and Conventional Type Papers) : Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Paper-IgeombajobsNo ratings yet
- Drdo Syllabus InstrumentationDocument2 pagesDrdo Syllabus InstrumentationArvind SinghNo ratings yet
- 5.5.10 Electronics and Communication Engineering (EC) : Linear Algebra: CalculusDocument4 pages5.5.10 Electronics and Communication Engineering (EC) : Linear Algebra: CalculusAnurag PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Syll Lec Elecroeng 29 09 2014Document2 pagesSyll Lec Elecroeng 29 09 2014Dharmendra MehtaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering DR B R Ambedkar National Institute of Technology Jalandhar-144011 Syllabus For Admission To PHD Program 2012-2013Document2 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering DR B R Ambedkar National Institute of Technology Jalandhar-144011 Syllabus For Admission To PHD Program 2012-2013Karan RathoreNo ratings yet
- Gate SyllDocument2 pagesGate SyllavrunniNo ratings yet
- 6 Asst Prof Electronics & Communication - 1 - 230328 - 183218 PDFDocument6 pages6 Asst Prof Electronics & Communication - 1 - 230328 - 183218 PDFSujith kumarNo ratings yet
- Name of The Post: Assistant Foreman (E&T) T&S GR - C: Networks TheoryDocument2 pagesName of The Post: Assistant Foreman (E&T) T&S GR - C: Networks TheorySushant JadhavNo ratings yet
- BSNL Jto SyllabusDocument3 pagesBSNL Jto Syllabuslakshmi2348No ratings yet
- The New India Assurance Co. Ltd. (Government of India Undertaking)Document3 pagesThe New India Assurance Co. Ltd. (Government of India Undertaking)kv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- PolicyBazaar Two Wheeler InsuranceDocument1 pagePolicyBazaar Two Wheeler Insurancekv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- Degree Programmes: Table 1Document3 pagesDegree Programmes: Table 1kv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- 2012a Buyback NoticeDocument4 pages2012a Buyback Noticekv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- Veterinaryand: Are To The TheDocument1 pageVeterinaryand: Are To The Thekv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- UG Practical Test Notification 2020-21Document1 pageUG Practical Test Notification 2020-21kv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- Karnataka Veterinary, Animal and Fisheries Sciences University, BidarDocument3 pagesKarnataka Veterinary, Animal and Fisheries Sciences University, Bidarkv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- Recipes To Cure Lifestyle Diseases - Posts 4Document1 pageRecipes To Cure Lifestyle Diseases - Posts 4kv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- Whats New-26.06.2020 PDFDocument1 pageWhats New-26.06.2020 PDFkv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- Recipes To Cure Lifestyle Diseases - Posts 1aDocument1 pageRecipes To Cure Lifestyle Diseases - Posts 1akv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- Unfilled Stray VacanciesDocument1 pageUnfilled Stray Vacancieskv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- 1 Day Detox PDFDocument9 pages1 Day Detox PDFkv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- Orientation Programme: Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Veterinary Education and ResearchDocument2 pagesOrientation Programme: Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Veterinary Education and Researchkv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- Satish Serial Publishing House: Year 2011 Subscription InformationDocument1 pageSatish Serial Publishing House: Year 2011 Subscription Informationkv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
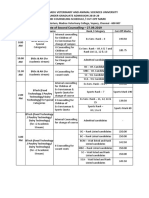
- Date of Second Counselling - 27.09.2019Document1 pageDate of Second Counselling - 27.09.2019kv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- Gmail - RedBus Ticket - TNB660721326Document1 pageGmail - RedBus Ticket - TNB660721326kv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- Book PDFDocument6 pagesBook PDFkv chandrasekerNo ratings yet
- PaperbackDocument32 pagesPaperbackkv chandrasekerNo ratings yet