Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1108 en 2
1108 en 2
Uploaded by
Docare HROriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1108 en 2
1108 en 2
Uploaded by
Docare HRCopyright:
Available Formats
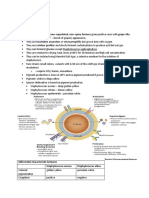
Blood Agar Base Cat.
1108
For the isolation, cultivation and detection of hemolytic activity.
Practical information
Aplications Categories
Selective isolation Fastidious microorganisms
Detection Hemolytic reactions
Industry: Clinical / Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
Principles and uses
Blood Agar Base is used for the isolation, cultivation and detection of hemolytic reaction of fastidious microorganisms.
It is suitable for isolating and cultivating a wide range of microorganisms with difficult growth characteristics. Upon adding blood, it can be utilized for
determining hemolytic reactions.
The heart infusion and meat peptone are rich sources of nitrogen, vitamins, minerals and amino acids essential for growth. Sodium chloride supplies
essential electrolytes for transport and osmotic balance. Bacteriological agar is the solidifying agent.
The addition of blood provides extra growth factors for fastidious microorganisms and is the basis for determining hemolytic reactions. Hemolytic patterns
may vary with the type of blood or base medium used. For example, defibrinated sheep blood gives best results for Group A streptococci.
Formula in g/L
Bacteriological agar 15 Meat peptone 10
Sodium chloride 5 Heart infusion 10
Typical formula g/L * Adjusted and/or supplemented as required to meet performance criteria.
Preparation
Suspend 40 grams of the medium in one liter of distilled water. Mix well and dissolve by heating with frequent agitation. Boil for one minute until complete
dissolution. Sterilize in autoclave at 121 ºC for 15 minutes. Cool to 45-50 ºC and aseptically add 5-10% of sterile defibrinated blood, homogenize and
pour intro Petri dishes. Be careful to avoid bubble formation when adding the blood to the cooled medium and rotate the flask or bottle slowly to create a
homogeneous solution. If desired, Polyenrichment Supplement (Cat. 6011) may be added to increase growth.
Instructions for use
For clinical diagnosis, the type of sample is secretions of the respiratory tract.
- Use standard procedures to obtain isolated colonies from specimens.
- Incubate at 35±2 ºC for 24-48 hours.
- Since many pathogens require carbon dioxide on primary isolation, plates may be incubated in an atmosphere containing approximately 5-10% CO2.
Results:
1. Alpha-hemolysis: greenish discoloration of medium.
2. Beta-hemolysis: clear zone surrounding colony.
3. Gamma-hemolysis: no change.
Inspired by knowledge Page 1 of 2 - Revision number 2 - Date 22/04/2022 www.condalab.com
Quality control
Solubility Appareance Color of the dehydrated medium Color of the prepared medium Final pH (25ºC)
w/o rests Fine powder Toasted Opaque cherry red 7,3±0,2
Microbiological test
Incubation conditions: (35±2 ºC, CO2 atmosphere /24-48 h).
Microorganisms Specification Characteristic reaction
Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228 Good growth
Neisseria meningitidis ATCC 13090 Good growth
Streptococcus pyogenes ATCC 19615 Good growth Beta hemolysis
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 Good growth Beta hemolysis
Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 6305 Good growth Alpha hemolysis
Storage
Temp. Min.:2 ºC
Temp. Max.:25 ºC
Bibliography
Snavely and BrahierA. J. Clin. Path. 33:511. 1 960.Hosty, Freeman and Irwin, Public, Health. Lab., 1953.
Schubert, Edwards and Ramsey J. Bact. 77:648, 1959. APHA Diagnostic Procedures and Reagents 3.a edition, 1951. Tharshis and Frish AM. J. Clin.
Path. 21:101. 1951.
Inspired by knowledge Page 2 of 2 - Revision number 2 - Date 22/04/2022 www.condalab.com
You might also like
- Ubiquity of BacteriaDocument4 pagesUbiquity of BacteriaThe seri100% (1)
- Aoac 972.44 PDFDocument2 pagesAoac 972.44 PDFPablo Emilio Martinez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) : IndustryDocument2 pagesEosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) : Industrysigit the pembalapNo ratings yet
- CLED AgarDocument4 pagesCLED Agarsameera ruffaiNo ratings yet
- Campylobacter Agar Base Blood Free (CCDA) ISO: Industry RegulationsDocument2 pagesCampylobacter Agar Base Blood Free (CCDA) ISO: Industry RegulationsDOKTER HEWAN TVNo ratings yet
- 1345 en 7Document2 pages1345 en 7Eka Putri Juniarti IgirisaNo ratings yet
- Sheep Blood Agar Base, Modified Plate For MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesSheep Blood Agar Base, Modified Plate For MicrobiologyKunal VermaNo ratings yet
- Columbia Cna Agar (7126) : Pseudomonas SPP., and Allowing Yeast, Staphylococci, Streptococci, and Enterococci To GrowDocument3 pagesColumbia Cna Agar (7126) : Pseudomonas SPP., and Allowing Yeast, Staphylococci, Streptococci, and Enterococci To GrowDip MajumderNo ratings yet
- 1177_en_4Document2 pages1177_en_4JHOAN ALFREDO PLUA MONTIELNo ratings yet
- Principle General Information PreparationDocument2 pagesPrinciple General Information PreparationHaidar HanifNo ratings yet
- BBL™ Mannitol Salt Agar - BDDocument2 pagesBBL™ Mannitol Salt Agar - BDyyewelsNo ratings yet
- 1074 en 2Document2 pages1074 en 2krroblesNo ratings yet
- Hoyle Tellurite AgarDocument3 pagesHoyle Tellurite AgarSani Asmi RamdaniNo ratings yet
- Chocolate AgarDocument5 pagesChocolate AgarBramita Beta ArnandaNo ratings yet
- Culture Bacterial Media Methods by Conventional Automated NotesDocument12 pagesCulture Bacterial Media Methods by Conventional Automated NoteskontamuruNo ratings yet
- 201020120500-CLED Agar With Andrade IndicatorDocument3 pages201020120500-CLED Agar With Andrade Indicatorsofimar sanzNo ratings yet
- Bi-State Blood Culture Bottle IFU September 26,2011Document3 pagesBi-State Blood Culture Bottle IFU September 26,2011Hadi AlbitarNo ratings yet
- KAQ0621 Rev1Document16 pagesKAQ0621 Rev124redred4578No ratings yet
- Buffered Charcoal Yeast Extract Agar Technicaldetails 27020230327.100923Document2 pagesBuffered Charcoal Yeast Extract Agar Technicaldetails 27020230327.100923ikinNo ratings yet
- Agar EdwardsDocument2 pagesAgar EdwardsGeraldine CacaceNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology OSPEDocument20 pagesBacteriology OSPEKrithik B Rajesh100% (1)
- Sim Medium ProtocolDocument2 pagesSim Medium ProtocolabrahamNo ratings yet
- BD - Bulk Erythrocyte Lysing With Ammonium Chloride For Flow Cytometry ImmunophenotypingDocument3 pagesBD - Bulk Erythrocyte Lysing With Ammonium Chloride For Flow Cytometry ImmunophenotypingBcells AutoimmunityNo ratings yet
- 7178 PiDocument3 pages7178 PiChristine DestyaraNo ratings yet
- BETA-SSA Agar (Group A Streptococci Selective Agar)Document3 pagesBETA-SSA Agar (Group A Streptococci Selective Agar)uttam.micro404No ratings yet
- Brain Heart Infusion (Bhi) Agar: Intended UseDocument1 pageBrain Heart Infusion (Bhi) Agar: Intended Usemss67No ratings yet
- Haemophilus Isolation AgarDocument1 pageHaemophilus Isolation AgarHữư ThiệnNo ratings yet
- Arginineglucose Yeast Extract Agar - Technicaldetails - 9720210526.050253Document3 pagesArginineglucose Yeast Extract Agar - Technicaldetails - 9720210526.050253MSc Penélope MeloNo ratings yet
- BBL CLED Agar: ™ L007367 - Rev. 04 - May 2006Document3 pagesBBL CLED Agar: ™ L007367 - Rev. 04 - May 2006Muhammad Hadi ArwaniNo ratings yet
- Littman Oxgall Agar W/ Streptomycin: Intended UseDocument1 pageLittman Oxgall Agar W/ Streptomycin: Intended UseJUAN PABLO VERGARA REYESNo ratings yet
- 1210 en 2 PDFDocument2 pages1210 en 2 PDFDocare HRNo ratings yet
- Signal Blood Culture BC0100MDocument2 pagesSignal Blood Culture BC0100MAthar Dhiaurrahman PutraNo ratings yet
- XLD AGAR MSDSDocument6 pagesXLD AGAR MSDSFreddy Cañar TinitanaNo ratings yet
- Hektoen Enteric Agar (Oxoid) - CM0419Document2 pagesHektoen Enteric Agar (Oxoid) - CM0419luuthanhthu91No ratings yet
- Campylobacter Medium: Microbiology Dr. Heba AlsalamyDocument10 pagesCampylobacter Medium: Microbiology Dr. Heba AlsalamyHaider MountherNo ratings yet
- Assignment NO 2 BTI619Document19 pagesAssignment NO 2 BTI619Mashal WakeelaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Clinical LabDocument9 pagesGroup 2 Clinical LabaidazerraNo ratings yet
- TBX Chromogenic Agar (Tryptone Bile X-Glucuronide) ISO: Industry RegulationsDocument2 pagesTBX Chromogenic Agar (Tryptone Bile X-Glucuronide) ISO: Industry RegulationsMinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- 1016Document2 pages1016syaemaNo ratings yet
- ResourceDocument5 pagesResourcechindobr8No ratings yet
- CM0995 Burkholderia Cepacia Agar Base - TDSDocument2 pagesCM0995 Burkholderia Cepacia Agar Base - TDSAna ParaveNo ratings yet
- Technical Data: Plate Count Agar (Standard Methods Agar)Document2 pagesTechnical Data: Plate Count Agar (Standard Methods Agar)பொ.தெய்வராஜன்No ratings yet
- 1190 en 1Document2 pages1190 en 1Kevin Montero100% (1)
- 1522 en 2Document2 pages1522 en 2Anel RedzicNo ratings yet
- 064-Ba1005 enDocument2 pages064-Ba1005 enLaveria LaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 1.2 Techniques Oriented Examination of Specimens-Blood, CSF, Body Fluids, Pus and Aspirates, Throat Swab, StoolDocument47 pagesUnit 1 - 1.2 Techniques Oriented Examination of Specimens-Blood, CSF, Body Fluids, Pus and Aspirates, Throat Swab, StoolProvince Public Health Laboratory JanakpurNo ratings yet
- XLD Agar (Xylose-Lysine-Desoxycholate Agar) : Instructions For Use - Ready-To-Use Plated MediaDocument4 pagesXLD Agar (Xylose-Lysine-Desoxycholate Agar) : Instructions For Use - Ready-To-Use Plated MediaJulissa Magaly Silva HuamanNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci The Staphylococci CharacteristicsDocument15 pagesGram Positive Cocci The Staphylococci CharacteristicsKyle PicocNo ratings yet
- Plate Count Agar (Standard Methods Agar) : CompositionDocument2 pagesPlate Count Agar (Standard Methods Agar) : CompositionAgitha KhariesmaNo ratings yet
- M080. LSTDocument3 pagesM080. LSToktaNo ratings yet
- 1301 en 2Document2 pages1301 en 2lgoNo ratings yet
- Plate Count Agar (Standard Methods Agar) : Intended UseDocument3 pagesPlate Count Agar (Standard Methods Agar) : Intended UsenuraenirianNo ratings yet
- 127-Article Text-210-1-10-20200902Document12 pages127-Article Text-210-1-10-20200902Miku BinondoNo ratings yet
- Agar Brucella Campy PDFDocument2 pagesAgar Brucella Campy PDFMICHELLE GENESIS SOTO BURGOSNo ratings yet
- 5148 en 1Document2 pages5148 en 1Penny HuynhNo ratings yet
- Biolife: Nutrient AgarDocument2 pagesBiolife: Nutrient AgarZoza SalamaNo ratings yet
- 1062Document2 pages1062Nisadiyah Faridatus ShahihNo ratings yet
- P.ging MediaDocument2 pagesP.ging MediaAhmed Tawfig GamalNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping ReagentsDocument7 pagesBlood Grouping ReagentsDominic EmerencianaNo ratings yet
- Core Practical Garlic and MintDocument4 pagesCore Practical Garlic and MintMohamed Al SharkawyNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Granucult™ Plate Count Skimmed Milk Agar Acc. Iso 4833 and Iso 17410Document4 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: Granucult™ Plate Count Skimmed Milk Agar Acc. Iso 4833 and Iso 17410Sofia BedoyaNo ratings yet
- SOP For Media Preparation For Microbial AnalysisDocument3 pagesSOP For Media Preparation For Microbial AnalysiskcbijuNo ratings yet
- Astm G22-23Document3 pagesAstm G22-23mahdi gazeriNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Propagation of Malaysian Cassava (Manihot Esculenta Crantz) Variety Through Low Cost Tissue Culture MediaDocument4 pagesIn Vitro Propagation of Malaysian Cassava (Manihot Esculenta Crantz) Variety Through Low Cost Tissue Culture MediaIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Environmental Monitoring Solutions Brochure enDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Monitoring Solutions Brochure enNgoc Chau Nguyen PhanNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Media: Microbiology BIOL 275Document9 pagesPreparation of Media: Microbiology BIOL 275Nur AishaNo ratings yet
- EMB Agar (Eosin Methylene-Blue Lactose Sucrose Agar) : See Also General Instruction of UseDocument2 pagesEMB Agar (Eosin Methylene-Blue Lactose Sucrose Agar) : See Also General Instruction of UseDidik PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Spirit Blue AgarDocument2 pagesSpirit Blue AgarEugenia RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cetrimide Agar Base (European Pharmacopoeia) : CAT Nº: 1102Document2 pagesCetrimide Agar Base (European Pharmacopoeia) : CAT Nº: 1102Tatjana MarkovicNo ratings yet
- Seaweed Study (RRL For Soil Burial)Document16 pagesSeaweed Study (RRL For Soil Burial)Princess Jesselen EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Ia Biology 3.2Document7 pagesIa Biology 3.2alejandro fcNo ratings yet
- GPT Protocol - Trypcase Soy AgarDocument8 pagesGPT Protocol - Trypcase Soy AgarmailboxofmurliNo ratings yet
- Final ProjetcDocument38 pagesFinal ProjetcMahes100% (2)
- Agar Plate Children'S: Activity PackDocument7 pagesAgar Plate Children'S: Activity PackNatalija Atanasova-PancevskaNo ratings yet
- Growth of Chromobacterium Violaceum On R2A and Tryptic Soy AgarDocument3 pagesGrowth of Chromobacterium Violaceum On R2A and Tryptic Soy AgarvitorNo ratings yet
- Sip Research PaperDocument6 pagesSip Research PaperanjelynNo ratings yet
- 01 Bacteria Yeast and Mold Count Qcg0001Document4 pages01 Bacteria Yeast and Mold Count Qcg0001ASHOK KUMAR LENKANo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Analysis and Antimicrobial Activity of Ocimum Tenuiflorum (Tulsi), A Known Indian Folk Medicinal PlantDocument5 pagesPhytochemical Analysis and Antimicrobial Activity of Ocimum Tenuiflorum (Tulsi), A Known Indian Folk Medicinal PlantCDB 1st Semester 2077No ratings yet
- Usp 81 PDFDocument15 pagesUsp 81 PDFSreedurgalakshmi KNo ratings yet
- Development of Larval Artificial Diet of Chrysoperla: Carnea (Stephens) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae)Document5 pagesDevelopment of Larval Artificial Diet of Chrysoperla: Carnea (Stephens) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae)Mijahel Arturo Lara HerenciaNo ratings yet
- CLF Microbiology Method Collection Web VersionDocument248 pagesCLF Microbiology Method Collection Web VersionNenad BalsicNo ratings yet
- Is 1622 1981Document39 pagesIs 1622 1981hpradeep100% (2)
- Sabouraud Dextrose BrothDocument2 pagesSabouraud Dextrose Brothf.baxyNo ratings yet
- Murashige and Skoog Basal Salt MediumDocument3 pagesMurashige and Skoog Basal Salt MediumvishcrimeNo ratings yet
- AquacultureDocument400 pagesAquacultureNallely Vazquez100% (1)
- Growth and Metabolic Characterization of Macrorhabdus OrnithogasterDocument10 pagesGrowth and Metabolic Characterization of Macrorhabdus OrnithogasterFiroz RezaNo ratings yet
- Buffered Charcoal Yeast Extract Agar Technicaldetails 27020230327.100923Document2 pagesBuffered Charcoal Yeast Extract Agar Technicaldetails 27020230327.100923ikinNo ratings yet