Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acid Dissociation Constants Answer Key
Acid Dissociation Constants Answer Key
Uploaded by
Samia KabirOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid Dissociation Constants Answer Key
Acid Dissociation Constants Answer Key
Uploaded by
Samia KabirCopyright:
Available Formats
SCH 4U/G Name: ________
Acid Dissociation Constants answer key
1. An acid is a substance HA that can form H3O+ (aq) in the equilibrium:
HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
a) Does equilibrium favour reactants or products for strong acid?
Large Ka =
H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
HA (aq) + H2O (l)
b) Does equilibrium favour reactants or products for a very weak acid?
Small Ka =
H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
HA (aq) + H2O (l)
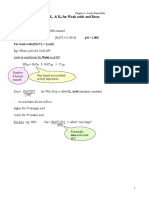
c) If acid HA1 is a stronger acid than acid HA2 is K1 a larger or smaller number than K2?
K1 = [H3O+][A1-] / [HA1] K2 = [H3O+][A2-] / [HA2]
2. Use your table of Acid Dissociation Constants (KA, C9 page 803) to find:
a) Which of the following acids are the strongest and which are the weakest?
Ammonium ion, NH4+ (in an NH4Cl solution) 5.8 X 10-10 weakest
Hydrogen sulfate ion, HSO4 (in a KHSO4 solution)
-
1.0 X 10-2 strongest
Hydrogen sulfide, H2S 1.1 X 10-7
b) If 0.1 M solutions are made of NH4Cl, KHSO4, and H2S, in which will [H3O+] be highest and in
which will it be lowest?
0.1 M NH4Cl lowest
0.1 M KHSO4 highest
0.1 M H2S
3. Write the equation for the reaction in each of the following examples. For each reaction,
predict whether reactants or products are favored (using values of K A given in C9 page 803).
a) HNO2 (aq) + NH3 (aq) ⇄ NO21- (aq) + NH4+ (aq)
acid base base acid
7.2 X 10-4 5.8 X 10-10
product favoured (conjugate acid is weaker)
b) NH4+ (aq) + F- (aq) ⇄ NH3 (aq) + HF (aq)
acid base base acid
5.8 X 10-10 6.6 X 10-4
reactant favoured (conjugate acid is stronger)
4. A 0.25 M solution of benzoic acid (symbolize it HA) is found to have [H 3O+] = 4 x 10-3 M.
Assuming the simple reaction:
HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
I 0.25 M 0 0
C -x +x +x
E 0.25 – x X = 4 x 10-3 M X = 4 x 10-3 M
= 0.25 - 4 x 10-3 M
= 0.246 M
Calculate KA for benzoic acid.
SCH 4U/G Name: ________
KA = (4 x 10-3 M)2 / 0.246
= 6.5 x 10-5
5. If 23 grams of formic acid, HCOOH, are dissolved in 10.0 liters of water at 20 oC, the [H3O+] is
found to be 3.0 x 10-3 M. Calculate KA.
HCOOH (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ H3O+ (aq) + HCOO- (aq)
I (23/46) mol/10.0 L = 0 0
0.050 M
C -x +x +x
E 0.050 – x x = 3.0 x 10-3 x = 3.0 x 10-3
0.050 - 3.0 x 10-3
= 0.047
KA = (3.0 x 10-3)2 / 0.047
= 1.9 x 10-4
What is the pKa of formic acid?
KA = 1.9 x 10-4
pKa = -log (1.9 x 10-4)
= 3.7
Used for comparing the relative strengths of acids (the smaller the pKa the stronger the acid)
You might also like
- 1N 08 BuffersDocument12 pages1N 08 Bufferssammyjnort0% (2)
- Acids BasesDocument8 pagesAcids Basesthephantom096No ratings yet
- Acid Dissociation ConstantsDocument2 pagesAcid Dissociation ConstantsSamia KabirNo ratings yet
- 2022 H2 CAS Tutorial 8.1 Section A AnsDocument8 pages2022 H2 CAS Tutorial 8.1 Section A AnsGareth WongNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Equilibrium Slides - StudentDocument74 pagesAcid-Base Equilibrium Slides - StudenteiwkNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Worksheet III Answers 2011Document6 pagesAcid Base Worksheet III Answers 2011Adolfo OlmosNo ratings yet
- Stuff: Please Read Ahead and Don't Fall Behind, One Big Push at The End Will Help ManyDocument12 pagesStuff: Please Read Ahead and Don't Fall Behind, One Big Push at The End Will Help ManyCybrille Fleur Siobhan QúeensNo ratings yet
- Answer Key To Acid/Base Problem Set 1. This Is A Strong Base ProblemDocument21 pagesAnswer Key To Acid/Base Problem Set 1. This Is A Strong Base ProblemSwisskelly1No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Answers 2019-2020Document11 pagesChapter 3 Answers 2019-2020Nuraina NabihahNo ratings yet
- Ques192 212abe2frDocument3 pagesQues192 212abe2frKerimberdiNo ratings yet
- 21.3 Weak Acids & BasesDocument27 pages21.3 Weak Acids & BasesJackie HardakerNo ratings yet
- 4.14 - Long Notes - Ka and KBDocument11 pages4.14 - Long Notes - Ka and KBMSMNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Equilibria Tutorial - With AnswersDocument10 pagesAcid Base Equilibria Tutorial - With AnswersNguYen QuE AnhNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Problems SolutionsDocument20 pagesAcid Base Problems SolutionsldfwykbhnuklerNo ratings yet
- There Are A Couple of Ways To Define Acids and Bases Brønsted-Lowry Acids and BasesDocument38 pagesThere Are A Couple of Ways To Define Acids and Bases Brønsted-Lowry Acids and BasesellieNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Unit Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesAcid Base Unit Review QuestionsSamia KabirNo ratings yet
- PRESENTASI - Salt Hydrolysis and ExercisesDocument34 pagesPRESENTASI - Salt Hydrolysis and ExercisesSalim Sanjaya100% (1)
- Ka KB KsppreapDocument14 pagesKa KB KsppreapvishakhshuklaNo ratings yet
- WR1.3 Acid-Base Chemistry (Solns)Document3 pagesWR1.3 Acid-Base Chemistry (Solns)Person GainableNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Problems SolutionsDocument20 pagesAcid Base Problems SolutionsAnusha PatelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - BuffersDocument12 pagesLecture 9 - BuffersKaizer NdoloNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (B)Document58 pagesModule 3 (B)SoniNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Kesetimbangan LarutanDocument136 pages9.1 Kesetimbangan Larutanlyla novitaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Acids and Bases v2Document42 pagesLecture 6 Acids and Bases v2Yahmeela SernaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 (Acids and Bases)Document7 pagesChapter 18 (Acids and Bases)Richard KimNo ratings yet
- HW8 Soln PDFDocument9 pagesHW8 Soln PDFPatricia de Leon100% (1)
- Weak Acid and Base EditedDocument52 pagesWeak Acid and Base EditedoofNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (A)Document47 pagesModule 3 (A)SoniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Acids and Bases HWDocument9 pagesChapter 17 Acids and Bases HWAlejo CardoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5. Aqueous Equilibrium Problems Simple EquilibriaDocument3 pagesWorksheet 5. Aqueous Equilibrium Problems Simple EquilibriaJohnHenryYambaoNo ratings yet
- Acid Base ChemistryDocument23 pagesAcid Base ChemistryJunegreg CualNo ratings yet
- Chem 2206 Unit 2Document69 pagesChem 2206 Unit 2Danica Rose ZapanzaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Solutions: Major Contributor of HDocument8 pagesChemistry of Solutions: Major Contributor of HmusicbrahNo ratings yet
- Kesetimbangan LarutanDocument123 pagesKesetimbangan LarutanFirda SafitriNo ratings yet
- Solving ChemDocument2 pagesSolving ChemAbiegail Asas PelenioNo ratings yet
- Acids BasesDocument6 pagesAcids BasesELAINE FAITH MEJOSNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Solving Equilibrium Problems For Bases (SCH4U)Document3 pages8.3 Solving Equilibrium Problems For Bases (SCH4U)Michelle NgNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Significant Figures and LogarithmsDocument15 pagesExercises: Significant Figures and LogarithmsSarah ChoiNo ratings yet
- Nima Mohammadi Chem Homework Chapter 14Document5 pagesNima Mohammadi Chem Homework Chapter 14Nima MohammadiNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Key 1dhdbrl PDFDocument51 pagesCH 5 Key 1dhdbrl PDFJason ShaoNo ratings yet
- Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria: Chapte R17Document92 pagesAdditional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria: Chapte R17api-683027695No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document29 pagesChapter 7mohamedzyad7717No ratings yet
- Ib - HL Acid and Base Paper 1Document14 pagesIb - HL Acid and Base Paper 1Arda RahmainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Exercises.Document5 pagesChapter 7 Exercises.jimmysroujiNo ratings yet
- Ap ChemDocument4 pagesAp ChemEthan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Activity 2. Water, Acids and Bases, BuffersDocument12 pagesActivity 2. Water, Acids and Bases, BuffersShei PalmesNo ratings yet
- U08 Notes Part3 Weak A BDocument32 pagesU08 Notes Part3 Weak A Bapi-546066323No ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Acid Base Equilibrium and BuffersDocument22 pagesExperiment 7 Acid Base Equilibrium and BuffersUzo Paul NwabuisiNo ratings yet
- New Acids & BasesDocument37 pagesNew Acids & Basesbagz_555No ratings yet
- Acid Base CH 16 ComprehensiveDocument4 pagesAcid Base CH 16 ComprehensiveAidah AmirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 Physical Chemistry Lecture NotesDocument48 pagesChemistry 2 Physical Chemistry Lecture Noteskittycat1chauNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Acids and BasesDocument39 pagesLecture 5 Acids and BasesAllen SiaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Equilibrium: See Aqueousions in Chemistry 1110 Online Notes For Review of Acid-Base Fundamentals!Document31 pagesAcid-Base Equilibrium: See Aqueousions in Chemistry 1110 Online Notes For Review of Acid-Base Fundamentals!Janna EchavezNo ratings yet
- Module 15-20 NotesDocument31 pagesModule 15-20 Notesjared.greenwood93No ratings yet
- AB Titration WSDocument6 pagesAB Titration WSiwinthushaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter5-Kesetimbangan Asam BasaDocument115 pagesChapter5-Kesetimbangan Asam BasaAnnisah MardiyyahNo ratings yet
- Lec Notes 21Document6 pagesLec Notes 21sanath kumarNo ratings yet
- Chem3369 Chapter09 BuffersDocument18 pagesChem3369 Chapter09 BuffersrickNo ratings yet