Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Distance Time Graph
Distance Time Graph
Uploaded by
mayana agarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 11-Kinematics Practice Test PDFDocument2 pages11-Kinematics Practice Test PDFD'ferti Anggraeni0% (2)
- PHYSICS Assignment Class 9 CBSEDocument1 pagePHYSICS Assignment Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora873860% (5)
- Sprint Start KinematicsDocument18 pagesSprint Start KinematicsJAson KEan0% (1)
- Kin Unit Test 2014Document4 pagesKin Unit Test 2014Nicholas ChevalierNo ratings yet
- Ws On AccelarationDocument4 pagesWs On Accelarationmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Equations of Motion WsDocument5 pagesEquations of Motion Wsmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Average Speed and VelocityDocument6 pagesAverage Speed and Velocitymayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- The Speed of Toy CarsDocument5 pagesThe Speed of Toy CarsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Time and Distance Prepared by M (1) - Giri, Assoc. Prof in Cse, Sitams, ChittoorDocument30 pagesTime and Distance Prepared by M (1) - Giri, Assoc. Prof in Cse, Sitams, ChittoorChemanthi RojaNo ratings yet
- Reasoning and Quantitative Aptitude Time & DistanceDocument29 pagesReasoning and Quantitative Aptitude Time & DistanceRahul Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Speed, Velocity and AccelerationDocument3 pagesSpeed, Velocity and Accelerationharshtulsyan2703No ratings yet
- Speed Worksheet 2 - Distance - Time GraphsDocument2 pagesSpeed Worksheet 2 - Distance - Time GraphsmanthanNo ratings yet
- PrePHYSICS REVISION Quiz S1 MT For 2023-24Document3 pagesPrePHYSICS REVISION Quiz S1 MT For 2023-24Ngọc Thùy Vân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics Lab 4Document5 pagesBiomechanics Lab 4api-542328686No ratings yet
- SCORM Time, Speed and DistanceDocument23 pagesSCORM Time, Speed and Distancesaurav shekharNo ratings yet
- Time and DistanceDocument6 pagesTime and DistanceAshish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Time and Distance ProblamsDocument29 pagesTime and Distance Problamsrenuka mulaNo ratings yet
- Stopping Distance WsDocument3 pagesStopping Distance Wsmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Science Ix Max Marks: 10Document2 pagesScience Ix Max Marks: 10Sathiesh S SelvarajuNo ratings yet
- Revision WorksheetDocument3 pagesRevision WorksheetShyam PatelNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On KinematicsDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank On KinematicsMrigankNo ratings yet
- Di (Topic Wise New Patern) by Mathwizard S.K SharmaDocument33 pagesDi (Topic Wise New Patern) by Mathwizard S.K SharmaRajesh Govekar100% (1)
- Math DemonstrationDocument6 pagesMath DemonstrationMa. Oliva Diana CastroNo ratings yet
- Class 11Document28 pagesClass 11Kotul TantooNo ratings yet
- Speed, Distance and TimeDocument13 pagesSpeed, Distance and TimeMartín Nicolás Gatti100% (1)
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 1Document27 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 1Rekha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Distance and DisplacementDocument1 pageDistance and Displacementmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Time and Distance-PvDocument28 pagesTime and Distance-PvPrepVelvetNo ratings yet
- Motion NumericalsDocument2 pagesMotion Numericalsk2842023No ratings yet
- TSD6Document14 pagesTSD6Aaditya BaidNo ratings yet
- Mypearth Ch1answersDocument5 pagesMypearth Ch1answersVARGAS GUTIERREZ OMAR DANILO DOCENTE DE FISICANo ratings yet
- Practice Questions On Time Speed DistanceDocument3 pagesPractice Questions On Time Speed DistanceSreeharshaveena ElagamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 in MathDocument18 pagesLesson 6 in MathAvito BernaldezNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 3 Notes, Revision Questions and Answers - Educationnewshub - Co.kDocument66 pagesPhysics Form 3 Notes, Revision Questions and Answers - Educationnewshub - Co.kkingsleymakuvaza167No ratings yet
- Ix Physics Question BankDocument4 pagesIx Physics Question BankHanirutha.M 7BNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test Physics (Questions and Answers) : Calculated by Adding or Subtracting Two Measured ValuesDocument10 pagesPre-Test Physics (Questions and Answers) : Calculated by Adding or Subtracting Two Measured ValuesDaisy GamerNo ratings yet
- Velocity Park Pre Test QuestionsDocument6 pagesVelocity Park Pre Test QuestionsMaestro de GrapicoNo ratings yet
- WWW Quantfunda in 2010 11 Time Speed Distance HTMLDocument5 pagesWWW Quantfunda in 2010 11 Time Speed Distance HTMLVikas PatelNo ratings yet
- Time and Motion PPT 1 - January 2023 (Autosaved)Document23 pagesTime and Motion PPT 1 - January 2023 (Autosaved)Tripti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Average SpeedDocument18 pagesAverage SpeedAvigael CruzNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit Test Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesPhysics Unit Test Questions and Answerscarol janeNo ratings yet
- Activity 4Document6 pagesActivity 4Blesvill BaroroNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsRahul ChandraNo ratings yet
- CH 10. Time and DistanceDocument5 pagesCH 10. Time and Distancerijintom100% (2)
- Speed and Velocity Homework SheetDocument3 pagesSpeed and Velocity Homework Sheetalhemyariaseel55No ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 6 q3 w7Document12 pagesDLL Mathematics 6 q3 w7Marvin Villaquidan100% (1)
- Velocity and SpeedDocument9 pagesVelocity and SpeedJenny Teves DayritNo ratings yet
- Topic Wise Bundle PDF Course 2022 - Quantitative Aptitude Time Speed & Distance Set-1 (Eng)Document5 pagesTopic Wise Bundle PDF Course 2022 - Quantitative Aptitude Time Speed & Distance Set-1 (Eng)anandkumar bojjaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ev Partial 3 Eso Ing 23-24Document1 page1 Ev Partial 3 Eso Ing 23-24Mairela miranda ausínNo ratings yet
- 1079 - B.A. (Geography) Semester-I, IIDocument14 pages1079 - B.A. (Geography) Semester-I, IIrajkumaryogi6172No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Worksheet - Motion - 1Document3 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Worksheet - Motion - 1Menaka SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Physics HWDocument2 pagesPhysics HWapi-3803287No ratings yet
- HHW9 23Document1 pageHHW9 23Arman DehuriNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Learning Activity SheetDocument15 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Learning Activity SheetFluffy Bang Gaming MLNo ratings yet
- Workbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 1 Use The Periodic Table On Page 2 To Help You Answer This QuestionDocument10 pages1 Use The Periodic Table On Page 2 To Help You Answer This Questionmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Revision Sheet 2-Crit ADocument6 pagesPeriodic Table Revision Sheet 2-Crit Amayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Orientation in Space and TimeDocument5 pagesOrientation in Space and Timemayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Periodic - Table - Revision - Sheet - 1 - Crit - ADocument5 pagesPeriodic - Table - Revision - Sheet - 1 - Crit - Amayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Task Sheet - Periodic Table 2023Document10 pagesTask Sheet - Periodic Table 2023mayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Extra Ques ElectromagnetismDocument20 pagesExtra Ques Electromagnetismmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Psg/Myp/Year-4 /Chemistry/Unit2/Fa/Gs/Vc 1Document6 pagesPsg/Myp/Year-4 /Chemistry/Unit2/Fa/Gs/Vc 1mayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Task 1Document3 pagesBibliography Task 1mayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- MYP 4 Ext. Parabolic Tiling BCD - SADocument8 pagesMYP 4 Ext. Parabolic Tiling BCD - SAmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Stopping Distance WsDocument3 pagesStopping Distance Wsmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Turning ForcesDocument3 pagesTurning Forcesmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Average Speed and VelocityDocument6 pagesAverage Speed and Velocitymayana agarwalNo ratings yet
Distance Time Graph
Distance Time Graph
Uploaded by
mayana agarwalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Distance Time Graph
Distance Time Graph
Uploaded by
mayana agarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
MYP-YEAR: 4
UNIT 1: MECHANICS OF PHYSICS
GLOBAL CONTEXT:ORIENTATION IN SPACE AND TIME
Name: Date:
SOI- Understanding the relationships between movement of objects with respect to space and time
has improved human’s way of living.
LEARNING GOAL – Understand and interpret distance-time graphs
What you need to know
Distance-time graphs are a way of visually expressing a journey. With distance on the y-axis and
time on the x-axis, a distance-time graph tells us how far someone/something has travelled and how
long it took them/it to do so.
Make sure you are happy with the following topics before continuing:
– Gradients of Straight Line Graphs
– Drawing Straight Line Graphs
– Speed distance time
Distance time graphs – Key thinks to remember:
1) The gradient of the line = speed
2) The steeper the graph the greater the speed
3) Flat section means no speed (stopped)
4) Negative gradient = returning to start point (coming back)
PSG/MYP /YEAR- 4/PHYSICS/UNIT 1/WS 6 /NP/VK/AD/KS/2022
1
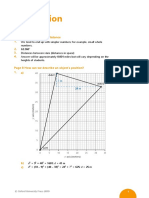
The graph below describes a journey that has several parts to it, each represented by a different
straight line.
Part A: 09:00−11:00, the person travelled 30 km away from their home and that took
them 22 hours.
Part B: 11:00−12:00, we can see that the line is flat, so their distance from home did not change –
they were stationary.
Part C: 12:00−12:30, they moved a further 30 km away from their home.
Part D: 12:30−14:00, they travelled the full 60 km back to where they began.
PSG/MYP /YEAR- 4/PHYSICS/UNIT 1/WS 6 /NP/VK/AD/KS/2022
2
]
PSG/MYP /YEAR- 4/PHYSICS/UNIT 1/WS 6 /NP/VK/AD/KS/2022
3
Example
Valentina is going for a bike ride. Below is a distance-time graph that describes her full journey.
a) How long was she stationary for?
She was stationary for 7.5 minutes
b) What was the total distance travelled during her journey?
5 + 20 + 25 = 50km
c) What was her average speed in kilometres per hour between 17:15 and 17:45?
30 minutes hours
30/60 = 0.5hours
20
0.5
= 40 km/hr
PSG/MYP /YEAR- 4/PHYSICS/UNIT 1/WS 6 /NP/VK/AD/KS/2022
4
Question 2: Below is a distance-time graph describing a 1500 m race run by Chris. Work out the
maximum speed he reached during this run to 3 significant figures.
Mph = miles per hour
1st lap = 0 – 72s (600 miles) 2nd lap = 72 – 180s (280 miles) 3rd lap = 180 – 282s (640 miles)
Average speed = 600/1.2 Average speed = 280/1.8 Average speed = 640/1.7
= 500 mph = 156 mph = 376 mph
Maximum speed reached by her was on her first lap
Question 3: A cyclist on a training ride records the distance she travels away from home. The data
only shows the first 150 minutes of the ride before her cycling computer ran out of battery.
PSG/MYP /YEAR- 4/PHYSICS/UNIT 1/WS 6 /NP/VK/AD/KS/2022
5
(a) How far did she ride in the first 150 minutes.
- She rode 38 km in the first 150 minutes
(b) For how long was she stationary
- She was stationary for 30 minutes
Question 4: A car journey on a day trip to the coast is recorded. (a) Work out the maximum speed
over the course of the trip.
PSG/MYP /YEAR- 4/PHYSICS/UNIT 1/WS 6 /NP/VK/AD/KS/2022
6
9 – 10 10 :30 – 12
Average speed = 40/1 Average speed = 26/1.5
= 4 km/ph = 17 km/ph
PSG/MYP /YEAR- 4/PHYSICS/UNIT 1/WS 6 /NP/VK/AD/KS/2022
7
You might also like
- 11-Kinematics Practice Test PDFDocument2 pages11-Kinematics Practice Test PDFD'ferti Anggraeni0% (2)
- PHYSICS Assignment Class 9 CBSEDocument1 pagePHYSICS Assignment Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora873860% (5)
- Sprint Start KinematicsDocument18 pagesSprint Start KinematicsJAson KEan0% (1)
- Kin Unit Test 2014Document4 pagesKin Unit Test 2014Nicholas ChevalierNo ratings yet
- Ws On AccelarationDocument4 pagesWs On Accelarationmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Equations of Motion WsDocument5 pagesEquations of Motion Wsmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Average Speed and VelocityDocument6 pagesAverage Speed and Velocitymayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- The Speed of Toy CarsDocument5 pagesThe Speed of Toy CarsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Time and Distance Prepared by M (1) - Giri, Assoc. Prof in Cse, Sitams, ChittoorDocument30 pagesTime and Distance Prepared by M (1) - Giri, Assoc. Prof in Cse, Sitams, ChittoorChemanthi RojaNo ratings yet
- Reasoning and Quantitative Aptitude Time & DistanceDocument29 pagesReasoning and Quantitative Aptitude Time & DistanceRahul Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Speed, Velocity and AccelerationDocument3 pagesSpeed, Velocity and Accelerationharshtulsyan2703No ratings yet
- Speed Worksheet 2 - Distance - Time GraphsDocument2 pagesSpeed Worksheet 2 - Distance - Time GraphsmanthanNo ratings yet
- PrePHYSICS REVISION Quiz S1 MT For 2023-24Document3 pagesPrePHYSICS REVISION Quiz S1 MT For 2023-24Ngọc Thùy Vân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics Lab 4Document5 pagesBiomechanics Lab 4api-542328686No ratings yet
- SCORM Time, Speed and DistanceDocument23 pagesSCORM Time, Speed and Distancesaurav shekharNo ratings yet
- Time and DistanceDocument6 pagesTime and DistanceAshish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Time and Distance ProblamsDocument29 pagesTime and Distance Problamsrenuka mulaNo ratings yet
- Stopping Distance WsDocument3 pagesStopping Distance Wsmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Science Ix Max Marks: 10Document2 pagesScience Ix Max Marks: 10Sathiesh S SelvarajuNo ratings yet
- Revision WorksheetDocument3 pagesRevision WorksheetShyam PatelNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On KinematicsDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank On KinematicsMrigankNo ratings yet
- Di (Topic Wise New Patern) by Mathwizard S.K SharmaDocument33 pagesDi (Topic Wise New Patern) by Mathwizard S.K SharmaRajesh Govekar100% (1)
- Math DemonstrationDocument6 pagesMath DemonstrationMa. Oliva Diana CastroNo ratings yet
- Class 11Document28 pagesClass 11Kotul TantooNo ratings yet
- Speed, Distance and TimeDocument13 pagesSpeed, Distance and TimeMartín Nicolás Gatti100% (1)
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 1Document27 pagesLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 1Rekha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Distance and DisplacementDocument1 pageDistance and Displacementmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Time and Distance-PvDocument28 pagesTime and Distance-PvPrepVelvetNo ratings yet
- Motion NumericalsDocument2 pagesMotion Numericalsk2842023No ratings yet
- TSD6Document14 pagesTSD6Aaditya BaidNo ratings yet
- Mypearth Ch1answersDocument5 pagesMypearth Ch1answersVARGAS GUTIERREZ OMAR DANILO DOCENTE DE FISICANo ratings yet
- Practice Questions On Time Speed DistanceDocument3 pagesPractice Questions On Time Speed DistanceSreeharshaveena ElagamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 in MathDocument18 pagesLesson 6 in MathAvito BernaldezNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 3 Notes, Revision Questions and Answers - Educationnewshub - Co.kDocument66 pagesPhysics Form 3 Notes, Revision Questions and Answers - Educationnewshub - Co.kkingsleymakuvaza167No ratings yet
- Ix Physics Question BankDocument4 pagesIx Physics Question BankHanirutha.M 7BNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test Physics (Questions and Answers) : Calculated by Adding or Subtracting Two Measured ValuesDocument10 pagesPre-Test Physics (Questions and Answers) : Calculated by Adding or Subtracting Two Measured ValuesDaisy GamerNo ratings yet
- Velocity Park Pre Test QuestionsDocument6 pagesVelocity Park Pre Test QuestionsMaestro de GrapicoNo ratings yet
- WWW Quantfunda in 2010 11 Time Speed Distance HTMLDocument5 pagesWWW Quantfunda in 2010 11 Time Speed Distance HTMLVikas PatelNo ratings yet
- Time and Motion PPT 1 - January 2023 (Autosaved)Document23 pagesTime and Motion PPT 1 - January 2023 (Autosaved)Tripti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Average SpeedDocument18 pagesAverage SpeedAvigael CruzNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit Test Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesPhysics Unit Test Questions and Answerscarol janeNo ratings yet
- Activity 4Document6 pagesActivity 4Blesvill BaroroNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsRahul ChandraNo ratings yet
- CH 10. Time and DistanceDocument5 pagesCH 10. Time and Distancerijintom100% (2)
- Speed and Velocity Homework SheetDocument3 pagesSpeed and Velocity Homework Sheetalhemyariaseel55No ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 6 q3 w7Document12 pagesDLL Mathematics 6 q3 w7Marvin Villaquidan100% (1)
- Velocity and SpeedDocument9 pagesVelocity and SpeedJenny Teves DayritNo ratings yet
- Topic Wise Bundle PDF Course 2022 - Quantitative Aptitude Time Speed & Distance Set-1 (Eng)Document5 pagesTopic Wise Bundle PDF Course 2022 - Quantitative Aptitude Time Speed & Distance Set-1 (Eng)anandkumar bojjaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ev Partial 3 Eso Ing 23-24Document1 page1 Ev Partial 3 Eso Ing 23-24Mairela miranda ausínNo ratings yet
- 1079 - B.A. (Geography) Semester-I, IIDocument14 pages1079 - B.A. (Geography) Semester-I, IIrajkumaryogi6172No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Worksheet - Motion - 1Document3 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Worksheet - Motion - 1Menaka SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Physics HWDocument2 pagesPhysics HWapi-3803287No ratings yet
- HHW9 23Document1 pageHHW9 23Arman DehuriNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Learning Activity SheetDocument15 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Learning Activity SheetFluffy Bang Gaming MLNo ratings yet
- Workbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 1 Use The Periodic Table On Page 2 To Help You Answer This QuestionDocument10 pages1 Use The Periodic Table On Page 2 To Help You Answer This Questionmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Revision Sheet 2-Crit ADocument6 pagesPeriodic Table Revision Sheet 2-Crit Amayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Orientation in Space and TimeDocument5 pagesOrientation in Space and Timemayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Periodic - Table - Revision - Sheet - 1 - Crit - ADocument5 pagesPeriodic - Table - Revision - Sheet - 1 - Crit - Amayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Task Sheet - Periodic Table 2023Document10 pagesTask Sheet - Periodic Table 2023mayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Extra Ques ElectromagnetismDocument20 pagesExtra Ques Electromagnetismmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Psg/Myp/Year-4 /Chemistry/Unit2/Fa/Gs/Vc 1Document6 pagesPsg/Myp/Year-4 /Chemistry/Unit2/Fa/Gs/Vc 1mayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Task 1Document3 pagesBibliography Task 1mayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- MYP 4 Ext. Parabolic Tiling BCD - SADocument8 pagesMYP 4 Ext. Parabolic Tiling BCD - SAmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Stopping Distance WsDocument3 pagesStopping Distance Wsmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Turning ForcesDocument3 pagesTurning Forcesmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Average Speed and VelocityDocument6 pagesAverage Speed and Velocitymayana agarwalNo ratings yet