Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BME 1 Strategy REV
BME 1 Strategy REV
Uploaded by
Iam IvysupanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BME 1 Strategy REV
BME 1 Strategy REV
Uploaded by
Iam IvysupanCopyright:
Available Formats
BME 1 – HOSPITALITY STRATEGIC Other fields influenced early S.
M:
MANAGEMENT
Marketing
Finance
Psychology
CHAPTER 1 – INTRODUCTION TO
STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT Management
Hospitality Business - is The strategic Management process:
fiercely competitive
McDonald’s - began its rapid expansion in
the middle of 20th century & shaped that
fast-food market
Strategic planning processes -
counterparts
Strategic management tools - high levels
of satisfaction
81% - percentage of companies worldwide
that does strategic planning
89% - percentage of companies in north
America that does SP.
Hospitality Firms - also benefit from Principle of Enactment - can create their
strategic planning own environments
Strategic alliance with stakeholders
Investments in leading technologies
Origin of Strategic Planning
Advertising
Several trends: Political Lobbying
Increasing competition in most Smaller organizations - limited in ability to
industries influence
Modern and cheaper transportation
Key to enactment - adopt completely but
& communication
Technological development
Deliberate strategy - managers
Three Perspectives on Strategic
Management Emergent strategy - trial & error
1. The traditional perspective
2. The resource-based view
3. Stakeholder view Effective Strategic Planning - deliberate
and emergent
1. Traditional Perspective
Both adoption and enactment are
Field of Strategic Management - important to organizations
emerged in the latter part of 20th century Should adopt to environmental
forces one cost of enacting exceeds
the benefit
Proactive in creating opportunities
Organization should engage in
Topics associated with the competitiveness
deliberate strategy but must be
of industries:
willing to make mistakes and learn
Industry concentration - degree of from it.
domination
2. The Resource-based view - has roots
Diversification - new products.
Product differentiation Effective Leadership- important to
-product/service standout. organizational performance, but difficult to
Market power - ability of a company specify
to manipulate or influence prices.
The organization as a bundle of
Economic Researches - focused on resources:
industries
1. Financial resources - monetary 1. Situation Analysis - external &
resources internal environment
o Internal & external sources of 2. Strategic Direction - mission &
financing goals
o Financial strength 3. Strategy Formulation - strengths &
2. Physical resources opportunities or overcome
o Land & buildings weaknesses & threats
o Equipment 4. Strategy Implementation-
o Organizational locations development and execution of plans
o Access to raw materials
3. Human resources
o Skills, background, and SWOT Analysis - a tool strategist use to
training of managers and evaluate strengths, weaknesses,
employees opportunities, & threats.
o Organizational structure Strengths - company resources &
4. Organizational knowledge & capabilities
learning – encompasses all Weaknesses - resources &
resources capabilities that company
5. General organizational resources Opportunity - conditions in the
o firm’s reputation broad environment that allow firm to
o brand names & patents take
o contracts & licenses Threats- conditions in the broad
o Stakeholder relationships environment that may impede
Strategic Direction- the longer-term goals
and objectives of the organization
- defines the purpose for why a company
3. The Organization as a Network of
exists & operates
Stakeholders (Stakeholder Approach)
- often coined in mission & vision
Stakeholder view - alliance and contracts
statements
Negotiating & Contracting - have always
Mission statement - current purpose &
been important to business.
scope of operation
Trend in business is toward more on:
Vision statement - wants to be in the future
strategic alliances
well-established strategic direction-
joint ventures
provide guidance to stakeholders inside the
subcontracting arrangements with organization who carry outs decisions.
stakeholders
well-defined direction - greater
Stakeholder map: understanding
Strategy Formulation- process of planning
strategies
- results in a plan of action for the company
and its various levels
3 levels:
1. Corporate-level strategy-
company’s domain of activity
2. Business-level strategy - pertain to
domain direction & navigation
3. Functional-level strategy-
functional resource areas, business-
level
4. Strategy formulation in a Multi-
business organization:
1. Corporate-level decisions- made
Strategic Management Process: at the highest levels of the
organization (CEO & BOD)
2. Business-level decisions- have CH 2 – THE ENVIRONMENT AND
diversified into multiple areas, EXTERNAL STAKEHOLDERS
3. Functional-level decisions-
represent organizational areas The Broad Environm ent
Sociocultural Influences Technological Influences
The Operating Environm ent
Com petitors
Activist Local
Strategy Implementation - groups comm unities
The Organization
pattern of decisions and actions S uppliers Ow ners/Board of Directors Custom ers
Managers
Organizational control - Unions Employees
The m edia
processes that lead to adjustments Financial
Government agencies
intermediaries
and administrators
Strategic-control system - may tell Economic Influences Political Influences
managers that the mission and strategies
Two Divisions of External Environment:
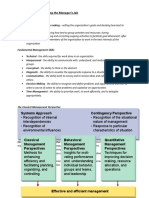
Characteristics/Elements of Strategic 1. Operating Environment-
Thinking: similarities may exists
2. Broad Environment - not
1. Intent Focused - managerial vision firm/industry specific
2. Comprehensive - “systems” perspective.
Envisions the firm as a part of a larger The Broad Environment:
system of value Sociocultural Influences
Economic influences
3. Opportunistic- seizes unanticipated Political influences
opportunities Technological influences
4. Long-Term Oriented- Goes beyond the
here & now
5. Built on Past and Presen- Does not
ignore the past or present The Operating Environments:
6. Hypothesis Driven- sequential process Competitors
Customers
- willing to take risk
Supplies
Strategic Management in the Hospitality The media
Industry: Unions
Hotels & Restaurants- most competitive Local Communities
businesses in the world Activist groups
Financial intermediaries
Hospitality industry- consist of businesses Government agencies &
that provide accommodation and/or F&B administrators
Hospitality Businesses- provide services, The Organization:
which differ from tangible products
Owners/BODs
Segmentation- strategy that distinguishes Managers
properties.
Employees
Smith Travel Research and Bear Stearns-
widely used
Assessment of the Broad Envt.-
Five segments of lodging:
describes many of the most important
1. luxury (upper upscale) forces in the broad environment and how
2. upscale organizations respond to them.
3. midscale with food and beverage
- scanning, forecasting, and adapting to
services
broad envt. Influences
4. midscale without food and beverage
services Broad Environment - forms the context
5. economy
Key elements of Broad Environment:
Ownership Structures- A hotel may be
owned by one company, franchised by 1. Sociocultural influences
2. Global Economic Influences
another, and operated by a third,
3. Political Influences
4. Technological Influences
Legislative Activity- public outcry against
the actions of firms.
A. The Sociocultural context- geographic
regions Socially Responsible firm - refrains from
acting unethically, voluntarily seeks to
Society- composed of individuals
improve society.
Analysis of Societal Trends- value of
B. The Economic Context - profound
watching social trends
influence on organizational
Green hotels & Restaurant menus with
Economic Forces- have a profound
Organic Food- example how broader social
influence on organizational behavin
trends can shape the industry
Economic forces to monitor & predict:
1. Economic Growth - consumer
demand, cost of factors of
production, production
2. Interest Rates- cost of capital for
Hospitality firms that pay attention to new projects, cost of refinancing
social trends can: existing debt
3. Inflation- interest rates, optimism or
Recognize Opportunities
pessimism of stakeholders
Enhance corporate reputation
4. Exchange Rates- ability to
Avoid unwanted legislation
profitability remove profits from
Opportunity Creation- Broader societal foreign ventures.
influences 5. Trade deficits - Government
policies, incentives, trade barriers
Broader societal influences - can create
opportunities for organizations.
C. The Political Context- Political forces,
both at home and abroad,
Demographics/Population
Characteristics – often used in marketing Government - provide and enforce the
research rules by which organizations operate
Demographic trends - can help in the Rules includes:
development of strategy
Laws
Average age of a populations Regulations
Income levels Policies
Ethnic mix
Alliances among governments -
provide additional level of complexity for
Generational and Cultural Awareness businesses with
Culture- set of shared beliefs, values, and D. Technological Context -
attitudes Technological change creates new
products, processes, and
Generation- may shape its identity or
distinctive beliefs and views
Technological Change -
Corporate Reputation- positive creates new products, processes, and
organizational reputation services,
Awareness & Compliance -“bad Computers & telecommunications
corporate citizen” technologies-global marketplace.
Distrust of Corporations- goes hand in Internet- new communications and
hand marketing tool
Social media web sites & blogs- important Technology - human knowledge about
tool for prospective hotel guests products and services
Online Buzz- bad & good info Dealing with Technological Change
Technological forecasting efforts:
Social Responsibility -
Correct assessment 1. Monitor Trends- by surfing the web,
studying journals,
2. Solicit the opinion of experts outside - bargaining power of customers
the organization- more formal method of
Bargaining power- a form of economic
tech forecasting
power. Ability to influence a firm’s behaviour
3. Develop scenarios of alternative
technological futures- capture different
Vertical Integration - firm moves forward
rates of innovation and conduct “what-if”
to become its own customer or moves
analysis.
backward to become
Gathering Information on International its own supplier
Environments- these kinds of broad
Bargaining power of customers -
environmental insights necessary for good
degree of customers exercise active
strategic decision making
influence over pricing
World Trade Organization - provides
Powerful customers - must be given high
statistics and market reports for a wide
priority in strategic management activities.
variety of countries and regions
Smith Travel Research & The Bench-
provide comprehensive database of hotel B. Economic Power of Suppliers-
performance Powerful suppliers
Hospitality Valuation Services- wide C. Competition, Concentration, &
array of articles about all aspects of Monopoly Power
hospitality
Competitive Moves - incite retaliation or
countermoves
Analysis of External Stakeholders and
the Operating Environment
Examples of Competitive moves:
Operating Environment- consists of
stakeholders with whom organizations Advertising programs
interact Sales force expansions
Capacity expansion
Stakeholders - who the organization
New-service introductions
interact with.
Long-term contracts with customers
3 Stakeholder groups with economic
Major forces that lead to high levels of
power:
competition:
1. Customers
1. There are many competitors in the
2. Suppliers
industry, and none of them possess a
3. Competitors
dominant position
Porter’s 5 force model of industry
Pure competition- organizations
competition:
must work hard to maintain their
positions, because customers have
many options
2. The industry is growing slowly
3. Products in the industry are not easily
differentiated
Lack of Product differentiation-
price-cutting strategies
4. High fixed costs exist- associated with
large hotel properties, airlines, or cruise
lines
High fixed cost- firms are under
pressure to increase sales to cover
their costs
A. Economic power of customers- 5. High Exist barriers exist - firms may
Customers provide demand for products lose all or most of their investments
and services Entry Barriers & Substitutes
Entry Barriers - Forces that keep new tool for
competitors out assessing the best practices of
direct competitors and firms
New Entrants - increase competition which
may drive down prices and profits, Political strategies - all
organizational activities that have as one of
their objectives the
Examples of Entry Barriers:
creation of a friendlier political
Economies of Scale a service at climate for the organization
higher volume
Lobbyist - organizations
Capital requirements start- hire them to represent views to
up costs, political leader
Product differentiation - enjoy a
loyal customer base.
High switching costs- can also
Partnering with External Stakeholders:
serve as an entry barrier
Inimitable resources- Resources Types of Organizational cooperation:
possessed by industry participants
1. Joint ventures 2 or more
Government policy - Sometimes
firms pool
governments
2. Networks- hub-and-wheel
External Stakeholders, Formal Power, 3. Consortia- specialized joint
and Political Influence ventures encompassing many
different arrangements
Formal power- means legal or contractual 4. Trade associations -
right to make decisions Organizations (non-profit)
Economic power- ability to withhold 5. Alliances - arrangement
between 2 or more firms that
Political power- lawmakers, establishes an exchange
relationship but no joint ownership
involved
Typical Roles of Various Stakeholder 6. Interlocking directorate- second firm.
STRATEGIC DIRECTION – CH 3
Strategic Direction - established and
communicated through tools such as
visions, missions, and values
Strategic Direction - provides a
framework d
Organizational Identity- high-performing
companies
Top managers- responsible for providing
Managing the Operating Environment long-term
Economic Actions - Firms may
take a variety of ____ to offset forces in the
Three perspectives of “What is our
operating
Business”:
environment
1. Who is being satisfied
Competitive Tactics - Industry
2. What is being satisfied
rivals apply a variety of ___ in order to win
3. How are customer needs satisfied
market share,
increase revenues, and increase profits at Scope of an organization - breadth s
the expense of rivals. markets.
Advertising Key Influences on Direction
New-product launches
Internal & External stakeholders- both
New service methods
influences strategic direction.
Competitive Benchmarking - popular
technique for keeping up with competitors. A
Amount of influence stakeholders have is 2. Inspire higher levels of performance
proportional to: and pride in association – mission
1. Economic power 3. Communicate organizational purpose
2. Political power & values- resolve dilemmas
3. Formal power
4. Enhance organizational reputation –
mission statements should be carefully
Strategic Direction- forms the foundation articulated so that they enhance reputation
Feedback- organization’s history Organizational Vision/Vision- ideal and
unique image
History- can potentially assist strategic
planning processes Well-understood vision- can help
managers and employees believe that their
Past successes- strong structural inertia
actions have meaning
Structural Inertia- status quo
Organizational Values- company’s culture
Inertia - is stronger when an organization & ethics.
has been successful in the past, managers
Values Statements - common throughout
believe that past success will translate into
the hospitality industry.
future success
- potential threat to the survival and
prosperity of an organization Social Responsibility - Embedded
within the concept
Four Major components of Social
Forces at work that maintain Status quo:
Responsibility:
1. Systems
1. Economic responsibilities-
2. Structures
productive and profitable
3. Processes
2. Legal responsibilities- confines of
4. Culture
written law.
5. Sunk Costs
3. Moral obligations- unwritten
6. Internal Politics
codes,.
7. Barriers to entry & exit
4. Discretionary responsibilities- are
Predictability - Most humans desire volitional or philanthropic in nature.
Influences on Strategic Direction:
Green Initiatives- Hotel companies are
beginning to recognize that the choices they
make affect the impact their guests have on
the environment.
Environmental responsibility- is emerging
as the hospitality industry
Enterprise Strategy - joining of ethical and
strategic thinking
- a natural extension
“What do we stand for”- critical link
Ethical decision making- a way of doing
business
Ethical Frames of Reference- The pattern
of decisions
Ethical dimensions - types of decisions
Ethical Dilemma- exists when the values of
Mission Statement - brief statement different stakeholders
Multiple Uses of Mission Statements: Five Theoretical models:
1. Direct Decision & Resource Allocation- 1. Economic Theory maximize profits
use terms that are understandable
Profit maximization- greatest benefit
2. Legal Theory - Laws are a reflection 2. Predelivery support
of what society 3. Delivery
3. Religion- Everyone should act in 4. Post-delivery support - involve
accordance with religious teachings. ongoing customer relationship
management by several
4. Utilitarian theory - Focused on the
tourism providers.
outcome of a decision
Delivery of Tourism Product:
5. Universalist Theory- intent of the
decision. 1. Inbound transportation
2. Accommodation
Code of Ethics- further effort
3. Entertainment operations
Ethics System- to ensure employees abide 4. Outbound transportation
by the corporate code of ethics.
Ethics in Global Environments -
Tangible resources - can be seen,
Dealing with the ethics of employees,
touched, and/or quantified.
customers, and other
stakeholders Intangible resources- most important
resources and capabilities Brand
ORGNIZATIONAL RESOURCES &
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE – CH 4 Knowledge
Employee trust
Resources & Capabilities - the bread
and butter Reputation of firm
Internal Analysis & Competitive Causal Ambiguity - difficult to determine
Advantage Firm Resources and Capabilities:
Sustainable Competitive Advantages 1. Financial resources
when a firm has a long-lasting o Excellent cash flow
o Strong balance sheet
o Superior past performance
Value-Adding Activities- To visualize the 2. Human-based resources
activities and processes o Superior CEO characteristics
Value Chain- a useful tool o Experienced managers
o Well trained, motived, loyal
- It divides organizational processes employees
Michael Porter - 3. General Organizational resources
developed the value chain framework o Patents
o Exclusive contracts
o Excellent reputation or brand
Value Chain for the Wine Industry: name
4. Physical resources
o Superior location or raw
materials
Wine o Outstanding products and/or
G rowing Distribution Marketing Retailing
Making services
o State-of-the-are plant or
machinery
Inbound O perations O utbound Marketing Service 5. Knowledge and
Logistics Logistics
Learning/Knowledge-based
resources
o Superior technology
development
o Outstanding learning
processes
Value-Chain Activities- The operations of a
hotel or a restaurant
Tourism Value Chain - Solid Investment Strategy - should focus
Recent on human-resource development and
superior
Value Chain process:
physical assets and processes
1. Winning the order
A. Financial resources-unique or difficult to skills and a unique perspective of
imitate how the
organization should respond
Financial Ratios:
to demands
Profitability ratios - overall Five Important Responsibilities of
financial success Strategic leadership:
Liquidity ratios - help
an organization determine its ability 1. Creating organizational vision
to pay short-term 2. Establishing core values for the
obligations. Financiers are organization
interested in this ratio 3. Developing strategies and a
Leverage - a common management structure
measure of financial risk, which 4. Fostering an environment that is
often takes the form of conducive to organizational learning
a loan or other borrowing and development
(debt) 5. Serving as a steward for the
organization
B. Physical Resources - Developing Strategies & Structure
resources people see when they observe
the organization. Strategic leaders - directly
responsible for overseeing the development
- Superior of strategies the
physical resources such as prime locations organization should follow
and
outstanding facilities are sources of Entrepreneur - serves as the
competitive advantage sole strategist for small organizations.
Architectural & Sustainable Design- Fostering Organizational Learning-
practice done by boutique hotels. organizational scholars believe that the true
role of a leader is to
Boutique Hotels - differentiate harness the creative energy of the
themselves from larger chain or individual
branded hotels by
their intense focus on the Leaders -
physical space. should create an environment for
Europe & Asia - lead organizational learning by serving
the way in producing architecturally as a coach, teacher,
interesting hotels. & facilitator.
Sustainable design - One Learning environment - is
emerging area for future competitive created by helping organizational
positioning is the members question their
movement toward this design assumptions about
the business and its environment.
Serving as a Steward -
C. Human-Based Resources - The leaders care about the company and the
humans that make up an organization are society in which it
its lifeblood—its operates, both voluntary and
unique and most valuable asset involuntary stakeholders.
Strategic Leadership -
highest-ranking officer in a large
organization can be called by many Leadership Approaches and
titles, but the most common Organizational Fit:
is chief executive officer 1. Commander - CEO
Chief Exec. Officer - has primary formulates strategy and then directs
responsibility for setting the strategic top managers to
direction of the implement it
firm 2. Change - CEO
Top management team - formulates strategy, then plans the
heterogeneous group of three to ten changes in structure,
top executives assembled by personnel, information
CEO. Bring unique set of systems, and administration
3. Collaborative - CEO initiates levels of experience and
a planning session with executive training
and division Turnover - at least
managers. After each partially an indication of how
participant presents ideas, the group employees feel about their
discusses and jobs
agrees to a strategy.
4. Cultural - CEO
and other top-level managers mold Structure & Culture - Leaders,
the organization’s culture managers, directors, and employees can all
so that all organizational be sources of
members make decisions that are competitive advantage.
consistent with
the vision. Organizational Structure- structure
5. Crescive - Lower-level has a lot to do with how successful a
managers are encouraged to firm will be
formulate and implement Organization culture- closely
their own strategic plans. related to structure & reflects the
CEO encourages innovation & filter values and leadership
inappropriate styles of executives and
programs. managers
Four very common organization
orientations:
Ownership and Management
1. Craftspeople - employees
Sole proprietorships - owner and are passionate about quality. Quality
top manager is the same individual is the primary
- no owner– driver of the corporate culture
manager conflicts of interest exist and pride.
2. Builders - Growth is the
Top Managers - primary goal. Managers are
become the agents for the owners of the rewarded for taking risks
firm and is duty to act in that result in growth.
the owners’ best interest. 3. Pioneers - build their
businesses through leadership
positions in new product
Executive Compensation - Agency and service development.
problems often arise because of the way 4. Salespeople - excellent
executives are marketers who create successful
compensated. brand names and
distribution channels, and
Board of Directors - Perhaps the
pursue aggressive advertising
greatest agency problems occur when top
managers serve
on the board of directors.
Several contributing factors can drive a
CEO Duality - the CEO in successful organization to an unsuccessful
the position of chairperson of the extreme:
board.
1. Overconfidence -
Leadership may get overconfident
Employees - Labor is the from its past successes
single greatest cost item in most hospitality 2. Dominant managers & subunits-
businesses, which One manager or unit may become
is why employees and the way they are overly dominant,
managed can be attracting the best
important sources of competitive managerial talent and exercising
advantage. unbalanced
influence
Labor - single 3. Complacency - successful
greatest cost item strategies of the past may have
Labor productivity - a good become embedded in
indication of how well managed the routine policies.
employees are and their
1. Patents -
protect an invention
D. Knowledge-based Resources
2. Copyrights - protect
Knowledge economy - “original works of authorship.”
knowledge is used to produce economic 3. Trademarks - protect
value. words, names, and symbols used to
distinguish a good
- is driven by 4. Servicemarks - protect
the importance of intangible people skills words, names, and symbols used to
and distinguish a service
intellectual asset
Knowledge - an intangible
asset Brands & Organizational Reputation
can be used by several parties Brand - viewed as a
simultaneously. key value-creating resource, because they
knowledge does not wear out, its are firm
value depreciates rapidly as new specific and difficult to imitate
knowledge is created. - identity of a
difficult to measure the amount of good or service
knowledge transferred or its value.
Superior Relationships with
Stakeholders
Internal Knowledge Creation and Relationships with stakeholders- can also
Organizational Learning: be described as an organizational resource
Facilitating knowledge - one
of the most important managerial tasks
Four Knowledge facilitation tasks:
1. Knowledge creation - requires
systems that encourage innovative
thinking throughout
the firm
2. Knowledge retention - A lot
of knowledge exists in an
organization. Only part of that
knowledge is
shared, but very little of that sharing
gets recorded
3. Knowledge Sharing - Sharing of
knowledge is as important as
creating it.
4. Knowledge Utilization - an
organization has to clear the way for
knowledge to be translated
into new processes and
programs
Relational Ability - ability to
interact with other companies, can increase
a firm’s
ability to obtain and transfer
knowledge
E. General Organizational Resources- a
varied collection of organizational
possessions that can have
a tremendous impact on financial
success and survival.
You might also like
- DissertationDocument135 pagesDissertationKhushbu ChadhaNo ratings yet
- 15-19 MayDocument27 pages15-19 MayIsmail OmaryNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Cement BrandDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire On Cement Branddigvijay_b201283% (12)
- ECO401 Mega Solved MCQs File For Mid Term Exam PreparationDocument44 pagesECO401 Mega Solved MCQs File For Mid Term Exam PreparationMuhammad Irfan33% (3)
- Job Offer LetterDocument4 pagesJob Offer LetterassignmentsmbaNo ratings yet
- Roopanpreet Kaur SopDocument5 pagesRoopanpreet Kaur SopWaraich Education Consultants OPC Pvt. Ltd100% (1)
- Intermediate Accounting 16e PDFDocument84 pagesIntermediate Accounting 16e PDFMiharu Kim100% (1)
- The Relationships Among Sea-Food Restaurant Service Quality Perceived Value Customer Satisfaction and Behavioral IntentionsDocument5 pagesThe Relationships Among Sea-Food Restaurant Service Quality Perceived Value Customer Satisfaction and Behavioral IntentionsashisbhuniyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1erleen sumileNo ratings yet
- STFM RecitationDocument7 pagesSTFM RecitationAnna Lyssa BatasNo ratings yet
- 1737bconcept of Strategy Strategic Management Session 2 Ver2Document14 pages1737bconcept of Strategy Strategic Management Session 2 Ver2asifanisNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Strategic ManagementDocument4 pagesThe Nature of Strategic Managementscribd uploaderNo ratings yet
- Corporate Strategy Module 1Document28 pagesCorporate Strategy Module 1Omkar MulekarNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesStrategic Financial ManagementMario AmorinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans: The Value ChainDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans: The Value ChainJunaid AhmedNo ratings yet
- TQM Module 4Document2 pagesTQM Module 4Youngmi LeeNo ratings yet
- Summary Strategic ManagementDocument16 pagesSummary Strategic Managementasmara.savira1115No ratings yet
- Strategic Management ReviewerDocument2 pagesStrategic Management ReviewerChatty MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: January 2015Document5 pagesStrategic Management: January 2015Reshid MustefaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: January 2015Document5 pagesStrategic Management: January 2015Zahid Ahmed JokhyoNo ratings yet
- Purpose: To Exploit and Create New and Different: Chapter 1 - The Nature of Strategic ManagementDocument3 pagesPurpose: To Exploit and Create New and Different: Chapter 1 - The Nature of Strategic ManagementJanelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: January 2015Document5 pagesStrategic Management: January 2015Shariqua AfsheenNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Strategic Management-IntroductionDocument32 pagesChapter-1: Strategic Management-IntroductionChirag Kishor SardharaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Strategic Business Analysis / Strategic Planning TerminologiesDocument8 pagesThe Nature of Strategic Business Analysis / Strategic Planning TerminologiesGomamameNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Prelim ReviewerDocument6 pagesStrategic Management Prelim ReviewerNeekah JoyNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: January 2015Document5 pagesStrategic Management: January 2015ABHISHEK SAKHARENo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Chapter Summary and HighlightsDocument7 pagesStrategic Management Chapter Summary and HighlightsNerizza SomeraNo ratings yet
- Tour 216 - Strama: A Manoeuvre Intended To Outwit An Opponent or Competitor' Minzberg Et Al,. 2002:3Document1 pageTour 216 - Strama: A Manoeuvre Intended To Outwit An Opponent or Competitor' Minzberg Et Al,. 2002:3Nathalia BautistaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Final TermDocument4 pagesMarketing Final TermClarice TorresNo ratings yet
- Marketing Final TermDocument9 pagesMarketing Final TermClarice TorresNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning For Small BusinessDocument1 pageStrategic Planning For Small BusinessGhie Morales100% (1)
- Chapter Outline 1-3 Strategic ManagementDocument13 pagesChapter Outline 1-3 Strategic ManagementVanessa PallarcaNo ratings yet
- V GhiDocument18 pagesV GhiLê Quỳnh ChiNo ratings yet
- BST Notes 2023Document132 pagesBST Notes 2023Blablabla100% (1)
- Strama Reviewer Chapter 1 3Document7 pagesStrama Reviewer Chapter 1 3Mark Ladores Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Program Doktor Ilmu Akuntansi Universitas Airlangga: Corporate Strategy: A Resource Based Approach (Summary Chapter 1-5)Document20 pagesProgram Doktor Ilmu Akuntansi Universitas Airlangga: Corporate Strategy: A Resource Based Approach (Summary Chapter 1-5)David FelkaiNo ratings yet
- Sammut BonnicistrategicmanagementDocument5 pagesSammut BonnicistrategicmanagementZahed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Orgnizational Management: Planning Techniques and ToolsDocument3 pagesOrgnizational Management: Planning Techniques and ToolsOSHIENo ratings yet
- Business StrategyDocument18 pagesBusiness StrategyAxtraa ANo ratings yet
- Excerpt From Sun Tzu's "The Art of War Writings"Document2 pagesExcerpt From Sun Tzu's "The Art of War Writings"XNo ratings yet
- StratmaDocument6 pagesStratmagjst102801No ratings yet
- 3 - Corporate Strategy and Long Range Planning: Strategic Management LessonDocument8 pages3 - Corporate Strategy and Long Range Planning: Strategic Management LessonMich AlbaniaNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument5 pagesReviewerMARKNo ratings yet
- 2024 Strama Chapter1Document21 pages2024 Strama Chapter1jennylyneyoyo14No ratings yet
- Establishing Company Direction - Lecture 2Document6 pagesEstablishing Company Direction - Lecture 2api-3710170100% (1)
- Prelim CbmeDocument3 pagesPrelim CbmeDivina Angeline TudlaNo ratings yet
- Sem-2 MBA Strategic Management All PPTs PDFDocument220 pagesSem-2 MBA Strategic Management All PPTs PDFDixit NellithayNo ratings yet
- StaMan ReviewerDocument8 pagesStaMan ReviewerJohn Dominic CruzNo ratings yet
- Strat Man Chap 4Document7 pagesStrat Man Chap 4Cesar LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Competitiveness Strategy and Productivity Part 2Document12 pagesChapter 2 Competitiveness Strategy and Productivity Part 2Rolly ViernesNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document71 pagesChap 2Jaka SeptiadiNo ratings yet
- Strategy & Strategic PlanningDocument9 pagesStrategy & Strategic PlanningThe Natak CompanyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveNina ManginsayNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Midterm Acct 054Document4 pagesReviewer Midterm Acct 054James LuoNo ratings yet
- Strama P MDocument5 pagesStrama P MMARKNo ratings yet
- Unit I (Strategic Management)Document20 pagesUnit I (Strategic Management)RAMESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- F ReviewerDocument7 pagesF ReviewerGAS - Rafael, Mikhail john P.No ratings yet
- PGJ1-Introduction To Strategic ManagementDocument28 pagesPGJ1-Introduction To Strategic ManagementPrashant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management ReviewerDocument3 pagesOrganization and Management ReviewerRoanaNo ratings yet
- STRATEGY AND ENTERPRISE PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT (AutoRecovered)Document39 pagesSTRATEGY AND ENTERPRISE PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT (AutoRecovered)Rishika RamtekkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Strat ManDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - Strat ManHannah LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Strategy Strategic MGT Ch.1Document37 pagesStrategy Strategic MGT Ch.1manisha2ndjanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management NotesDocument29 pagesStrategic Management NotesAditya GuptaNo ratings yet
- North Central Mindanao College: BM7: Organizational ManagementDocument6 pagesNorth Central Mindanao College: BM7: Organizational ManagementAndriea MathitNo ratings yet
- 1 - Strategic Management Inputs and CompetitivenessDocument17 pages1 - Strategic Management Inputs and CompetitivenessAnn BalmesNo ratings yet
- Strama Chapter 6 To 11Document9 pagesStrama Chapter 6 To 11GAS - Rafael, Mikhail john P.No ratings yet
- THC 7 ReviewerDocument6 pagesTHC 7 ReviewerIam IvysupanNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionnairesDocument2 pagesSample QuestionnairesIam IvysupanNo ratings yet
- Occupation, Problems, and BenefitsDocument2 pagesOccupation, Problems, and BenefitsIam IvysupanNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document1 pageCase Study 1Iam IvysupanNo ratings yet
- Bme 1 FinalsDocument13 pagesBme 1 FinalsIam IvysupanNo ratings yet
- THC 7 FinalsDocument3 pagesTHC 7 FinalsIam IvysupanNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Supan, Ivy C.Document2 pagesActivity 2 - Supan, Ivy C.Iam IvysupanNo ratings yet
- STS - Activity 1 - Supan, Ivy C.Document2 pagesSTS - Activity 1 - Supan, Ivy C.Iam IvysupanNo ratings yet
- En Re Preneur ShipDocument21 pagesEn Re Preneur ShipisabelaNo ratings yet
- APLL Franchise ProposalDocument13 pagesAPLL Franchise ProposalncitindiaNo ratings yet
- VFC Meeting 8.31 Discussion Materials PDFDocument31 pagesVFC Meeting 8.31 Discussion Materials PDFhadhdhagshNo ratings yet
- MANP005 Individual Report - EditedDocument21 pagesMANP005 Individual Report - EditedMeshy EnlightmentNo ratings yet
- Dereje MekonnenDocument104 pagesDereje Mekonnenjoseph andrewNo ratings yet
- PDP Project ReportDocument35 pagesPDP Project Reportbharatpurasharma100% (5)
- The Power of PricingDocument12 pagesThe Power of PricingvitrahulNo ratings yet
- Microsoft: Competing On Talent (A)Document24 pagesMicrosoft: Competing On Talent (A)lamyanurzahidahNo ratings yet
- ECMDocument14 pagesECMSuryanarayana TataNo ratings yet
- IPL Midterms ReviewerDocument24 pagesIPL Midterms ReviewerShammah Rey MahinayNo ratings yet
- Deed of Absolute Sale of Motor Vehicle SampleDocument1 pageDeed of Absolute Sale of Motor Vehicle Sample4geniecivilNo ratings yet
- Sem-VI Intellectual Property RightsDocument2 pagesSem-VI Intellectual Property RightsJAGANNATH PRASADNo ratings yet
- New Standing Order Instruction Nwi50000eDocument1 pageNew Standing Order Instruction Nwi50000ejamalazoz05No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To ManagementDocument30 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To ManagementHanafeah Ab RahmanNo ratings yet
- Little Oil CompanyDocument10 pagesLittle Oil CompanyJosann Welch100% (1)
- A Project On "Financial Statement Analysis of .'': IMBA Program: Semester-I Batch: 2019-24Document30 pagesA Project On "Financial Statement Analysis of .'': IMBA Program: Semester-I Batch: 2019-24mahawish kadriNo ratings yet
- Shadan Institute of Management Studies For BoysDocument18 pagesShadan Institute of Management Studies For BoysDivakar kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Retailing Wholesaling: Chapter PreviewDocument34 pagesRetailing Wholesaling: Chapter PreviewMikaelaNo ratings yet
- Ib Export ImportDocument32 pagesIb Export ImportUtkarsh PanditNo ratings yet
- Marketing History: Bridgestone - High Performance With Value For MoneyDocument10 pagesMarketing History: Bridgestone - High Performance With Value For MoneyAashish SemwaalNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Tobacco Company LimitedDocument10 pagesPakistan Tobacco Company LimitedMinhas KhanNo ratings yet
- Globalización? Análisis de Su Marketing-Mix Internacional: Mango: ¿Un Caso de Estrategia y Política deDocument15 pagesGlobalización? Análisis de Su Marketing-Mix Internacional: Mango: ¿Un Caso de Estrategia y Política demichxel psNo ratings yet