Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Poster PDF
Case Poster PDF
Uploaded by
AnuragOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Poster PDF
Case Poster PDF
Uploaded by
AnuragCopyright:
Available Formats
TRANSPLANT TO NORMALCY: A CASE OF LIVER TRANSPLANT IN
ACUTE ON CHRONIC PORTOMESENTRIC THROMBOSIS IN A
PATIENT WITH UNDERLYING CIRRHOSIS OF LIVER
Jayanth Reddy, Anurag Agarwal
INTRODUCTION Portal Vein Thrombosis Grading System DISCUSSION
Chronic liver disease (CLD) is a continuous process of hepatic fibrosis, liver architecture changes, and PVTs are commonly seen in liver cirrhotic patient and are associated with a wide spectrum of
formation of regeneration nodule in response to chronic liver injury that leads to portal hypertension and etiologies like myeloproliferative disease, Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria,
end stage liver disease.1 Portal Vein Thrombosis (PVT) is commonly seen in cirrhotic patient. PVT is Antiphospholipid syndrome, Factor V Leiden, Factor II gene mutation, Inherited antithrombin
develops due to low velocity in portal vein flow and hypercoaguable state induced due to cirrhosis or deficiency, Inherited protein C deficiency, Inherited protein S deficiency, Hyperhomocysteinemia.2,3
prothrombotic predisposition. PVT can be either acute or chronic. Acute PVT usually presents with Patients with PVT are classified based on a system first put forward by Yerdel et al (Table 1). In
abdominal pain and intestinal ischemia, whereas, chronic PVT is associated with signs of decompensation this case she had grade 3 PVT.4
(ascites, varices formation, jaundice) and formation of venous collaterals as a result of neoangiogensis to Systemic anticoagulation is the mainstay for PVT treatment. LMWH is widely used due to easy
2,3
bypass the occlusion of the portal vein.
Table 1: Classification of portal vein thrombosis (PVT) proposed by Yerdel et al.4 administration of the drug subcutaneously twice a day. The recommended dose of enoxaparin is
1mg/kg every 12 hours. A retrospective study done by Hui Chen et al, on anticoagulation in PVT
CASE DESCRIPTION
A B C patient with cirrhosis showed that anticoagulation group had better recanalization than untreated
group with improvement in 68% of patient who were treated with anticoagulation whereas only
25% of patient improved without treatment.5
A prospective study done by Lv et al which focused on Anticoagulation and Transjugular
Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt for the Management of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Cirrhosis
HOPI: 61 year old female with a history of chronic liver disease with portal hypertension and Type II showed that TIPSS and anticoagulation were associated with a higher probability of
Diabetes mellitus presented with complaints of abdominal distension and swelling of both limbs. recanalization.6
Liver transplant (LT) has morphed PVT from an absolute contraindication to a relative
Past medical history: Decompensated cirrhosis of liver with portal hypertension, Type II Diabetes contraindication, depending on the grade of the thrombus. Patients with Yerdel class 1–3 PVT can
mellitus. undergo LT at centers with experience in complex portal vein (PV) dissection, thrombectomy, and
reconstruction. Class 4 PVT, how- ever, is even more complex and may require heroic techniques
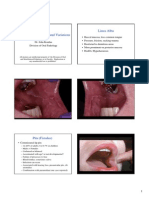
Social History: Lives in Sri Lanka, Worked in a Garment Factory. Fig A, B, C: CT abdomen with contrast showing chronic liver disease, splenomegaly, acute on chronic such as cavoportal hemitransposition, PV arterialization or multivisceral transplant (MVT).7
portal vein thrombosis extending into superior mesenteric vein with multiple collaterals and ascites.
Course of event:
After thorough evaluation, need for liver transplantation was explained to her and work up was initiated
as per protocol. On evaluation, Computed Tomography (CT) Abdomen and pelvis showed an acute on
chronic portal vein thrombosis extending into the superior mesenteric vein. Liver Transplant work up was
D E E
REFERENCES
withheld. She was started on low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) and Transhepatic intrajugualr
1. Schuppan, D., & Afdhal, N. H. (2008). Liver cirrhosis. Lancet (London, England), 371(9615),
portosystemic shunt (TIPSS) after portal vein thrombolysis was done on 16/02/2021.
838–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60383-9
On follow up, rethrombosis of portal vein was noticed and a repeat portal vein thrombolysis was done on 2. Wu, M., Schuster, M., & Tadros, M. (2019). Update on Management of Portal Vein Thrombosis
17/02/2021. Liver Transplant work up resumed following this. and the Role of Novel Anticoagulants. Journal of clinical and translational hepatology, 7(2), 154–
164. https://doi.org/10.14218/JCTH.2018.0005
Durirg Cardiological evaluation, Coronary Artery Angiogram (CAG), she was found to have 3. Young, K., & Wong, R. (2018). Evaluation and management of acute and chronic portal vein
double vessel coronary artery disease of left anterior descending (LAD) artery and right coronary thrombosis in patients with cirrhosis. Clinical liver disease, 10(6), 152–156.
artery (RCA), for which percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) was done along Fig D,E: CT abdomen with contrast showing chronic liver disease, cholelithiasis, patent TIPSS, https://doi.org/10.1002/cld.67
4. Yerdel MA, Gunson B, Mirza D, Karayalçin K, Olliff S, Buckels J, Mayer D, McMaster P,
with stenting to LAD on 07/03/2021. She was on therapeutic dose of anticoagulation. After patent main portal vein, patent splenoportal confluence
Pirenne J. Portal vein thrombosis in adults undergoing liver transplantation: risk factors,
obtaining clearance from the multiple disciplinary team consisting of cardiologist, pulmonologist,
screening, management, and outcome. Transplantation. 2000 May 15;69(9):1873-81. doi:
psychiatrist, hepatologist, gynaecologist, surgeons, physiotherapist, dietician, dentist,
10.1097/00007890-200005150-00023. PMID: 10830225.
endocrinologist and anaesthesiologist, she was placed on Deceased Donor Liver Transplant waiting
5. Chen, H., Liu, L., Qi, X., He, C., Wu, F., Fan, D., & Han, G. (2016). Efficacy and safety of
list.
anticoagulation in more advanced portal vein thrombosis in patients with liver cirrhosis. European
Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 28(1), 82–89. doi:10.1097/meg.0000000000000482
Following availability of suitable Deceased Donor organ, she was counselled and consented for Liver
6. Lv, Yong & Bai, Wei & Li, Kai & Wang, Zhengyu & Guo, Wengang & Luo, Bohan & Wang,
transplant on 21/06/2021. The procedure was uneventful with good graft function and was shifted to
Jianhong & Wang, Qiuhe & Wang, Enxin & Xia, Di & Li, Xiaomei & Yuan, Jie & Han, Na &
Transplant Intensive Care Unit. Daily ultrasound liver Doppler was done between post-operation day
Niu, Jing & Yin, Zhanxin & Fan, Daiming & Han, Guohong. (2021). Anticoagulation and
(POD) 0 to POD 5. Her graft function was good throughout her hospital stay. On POD 2, she got
breathless with drop in saturation level requiring non-invasive ventilation support. Chest- X-ray showed Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt for the Management of Portal Vein Thrombosis in
evidence of pulmonary oedema and pleural effusion for which she was diuresed and pleural effusion was Cirrhosis: A Prospective Observational Study. The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
tapped. By POD 4, her saturation levels improved. She also developed loose stools which was controlled Publish Ahead of Print. 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001194.
Fig 1: Ultrasound abdomen post-liver transplant showing normal liver echotexture and normal 7. Tekin, A., Beduschi, T., Vianna, R., & Mangus, R. S. (2020). Multivisceral Transplant As An
with altered diet and medication. She was discharged on POD 16 with good graft function and good
haemodynamical status. She is currently of routine follow-up in out-patient department basis with normal hepatic, portal vein and normal hepatic artery with normal inferior vena cava. Option To Transplant Cirrhotic Patients With Severe Portal Vein Thrombosis. International
graft function. Journal of Surgery. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.07.010
You might also like
- How To Read Pediatric ECGsDocument3 pagesHow To Read Pediatric ECGsGuillermo CalderaroNo ratings yet
- Disorders of PancreasDocument17 pagesDisorders of PancreasjonasNo ratings yet
- 4444vyuggewdffv PDFDocument1 page4444vyuggewdffv PDFMi-sun ParkNo ratings yet
- Acute On Chronic Liver FailureDocument4 pagesAcute On Chronic Liver Failurechavezhebert585No ratings yet
- Two Cases of Variceal Haemorrhage During Living DoDocument3 pagesTwo Cases of Variceal Haemorrhage During Living DoRENAULTNo ratings yet
- Decompensated Liver CirrhosisDocument6 pagesDecompensated Liver CirrhosisJulian HuningkorNo ratings yet
- Splanchnic Vein Thrombosis in Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A 2-Year, Single-Institution ExperienceDocument5 pagesSplanchnic Vein Thrombosis in Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A 2-Year, Single-Institution ExperienceFacundo AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Antiagre AnticoagDocument15 pagesAntiagre AnticoagpilarNo ratings yet
- Captopril PDFDocument8 pagesCaptopril PDFLadipo Temitope AyodejiNo ratings yet
- Postendoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography PancreatitisDocument7 pagesPostendoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography PancreatitisErnest Ang GrekNo ratings yet
- Educational Case: Kidney Transplant Rejection: Kevin Kuan, MD and Daniel Schwartz, MDDocument7 pagesEducational Case: Kidney Transplant Rejection: Kevin Kuan, MD and Daniel Schwartz, MDL ANo ratings yet
- JCTH 7 154Document11 pagesJCTH 7 154Andreea AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Renal Replacement Therapy in Acute Kidney Injury 2017Document14 pagesRenal Replacement Therapy in Acute Kidney Injury 2017piero reyes100% (1)
- Jurnal Pendukung Proposal 9Document4 pagesJurnal Pendukung Proposal 9Munawwar AweNo ratings yet
- Gastro Lat 2013 N 100004Document4 pagesGastro Lat 2013 N 100004paula andrea cardenas gomezNo ratings yet
- Yagmur Et Al 2013 Platelet Hyperaggregability Is Highly Prevalent in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease AnDocument7 pagesYagmur Et Al 2013 Platelet Hyperaggregability Is Highly Prevalent in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease AnMister FannaniNo ratings yet
- Weinstein 1963Document14 pagesWeinstein 1963Mumtaz MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument15 pagesManagement of Acute Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingShiva ValeskaNo ratings yet
- 10.1038@s41572 018 0022 7Document17 pages10.1038@s41572 018 0022 7Luis LopezNo ratings yet
- BMJ l536 FullDocument15 pagesBMJ l536 Fulldendy17018No ratings yet
- Jha2 2 118Document3 pagesJha2 2 118Renato DantasNo ratings yet
- British JournalDocument9 pagesBritish JournalAndreea AlexandruNo ratings yet
- J Mpmed 2019 09 010Document5 pagesJ Mpmed 2019 09 010Fiorelly FernándezNo ratings yet
- Creatinine ClearanceDocument6 pagesCreatinine ClearancedianaNo ratings yet
- Renal Artery StenosisDocument3 pagesRenal Artery StenosisauxtalleriocomNo ratings yet
- Acute-On-Chronic Liver Failure - Concept, Natural History, and PrognosisDocument5 pagesAcute-On-Chronic Liver Failure - Concept, Natural History, and PrognosisEyal RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Piis0085253815527324 PDFDocument5 pagesPiis0085253815527324 PDFdodong skyroseNo ratings yet
- Sabiston Ed. 19 Hemoragii DigestiveDocument22 pagesSabiston Ed. 19 Hemoragii DigestiveCristian CozmaNo ratings yet
- Using Ace Inhibitors and ARBDocument4 pagesUsing Ace Inhibitors and ARBJose ShelldonNo ratings yet
- Trousseau's Syndrome in CholangiocarcinomaDocument7 pagesTrousseau's Syndrome in CholangiocarcinomaAnna MariaNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument36 pagesBlood TransfusionpedsoncoaiimsNo ratings yet
- Kidney News Article p20 7Document2 pagesKidney News Article p20 7ilgarciaNo ratings yet
- Hepatorrenal PrimerDocument17 pagesHepatorrenal PrimerDianaScandaOlveraCabreraNo ratings yet
- A Prospective Study To CorrelateDocument6 pagesA Prospective Study To Correlateelaaannabi1No ratings yet
- Cirro SisDocument13 pagesCirro Sisbruno baileyNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Advances in Hepatology Terlipressin: An Asset For Hepatologists!Document5 pagesDiagnostic and Therapeutic Advances in Hepatology Terlipressin: An Asset For Hepatologists!Laras Bani WasesoNo ratings yet
- Hep 24519 PDFDocument5 pagesHep 24519 PDFLaras Bani WasesoNo ratings yet
- Efficacy and Safety of Early Systemic.14Document5 pagesEfficacy and Safety of Early Systemic.14Dr WittyNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Tatalaksana 2Document7 pagesJurnal Tatalaksana 2winny kartikaNo ratings yet
- 28-Year-Old Man With Crohn Disease and Hematuria: Residents ' ClinicDocument5 pages28-Year-Old Man With Crohn Disease and Hematuria: Residents ' ClinicDesi HutapeaNo ratings yet
- Terlipressin and The Treatment of Hepatorenal Syndrome How The CONFIRMDocument9 pagesTerlipressin and The Treatment of Hepatorenal Syndrome How The CONFIRMMarice QCNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Problems in Renal DysfunctionDocument5 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Problems in Renal Dysfunctionfachrudin arNo ratings yet
- Anestesia Transplat FigadoDocument7 pagesAnestesia Transplat FigadocaioaccorsiNo ratings yet
- Current Pharmacologic Therapies For Hepatorenal Syndrome Acute KidneyDocument8 pagesCurrent Pharmacologic Therapies For Hepatorenal Syndrome Acute KidneyEdgar QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Management of Acquired Coagulation Disorders in Emergency and Intensive-Care MedicineDocument12 pagesManagement of Acquired Coagulation Disorders in Emergency and Intensive-Care Medicineshinichi kudoNo ratings yet
- 7 Article2Document9 pages7 Article2Emily CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Liver InjuryDocument2 pagesIschemic Liver InjuryDanuNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base and Electrolyte Teaching Case Diuretic Resistance: Ewout J. Hoorn, MD, PHD, and David H. Ellison, MDDocument7 pagesAcid-Base and Electrolyte Teaching Case Diuretic Resistance: Ewout J. Hoorn, MD, PHD, and David H. Ellison, MDDiana GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Pylephlebitis Incidentally Found On A Patient With Gastric CancerDocument3 pagesPylephlebitis Incidentally Found On A Patient With Gastric CancerTony NouhNo ratings yet
- Tromboci 2Document11 pagesTromboci 2Pablo AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Renal CaseDocument3 pagesRenal CaseAndy BiersackNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Anaemia in Decompensated Chronic Liver DiseaseDocument5 pagesPrevalence of Anaemia in Decompensated Chronic Liver DiseaseElang SudewaNo ratings yet
- Art Hipertension SecundariaDocument15 pagesArt Hipertension SecundariaLisset FernandezNo ratings yet
- Early Ercp and Papillotomy Compared With Conservative Treatment For Acute Biliary PancreatitisDocument6 pagesEarly Ercp and Papillotomy Compared With Conservative Treatment For Acute Biliary PancreatitisRT_BokNo ratings yet
- Imunosupresie in HCVDocument8 pagesImunosupresie in HCVdeliaNo ratings yet
- Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis: Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesDecompensated Liver Cirrhosis: Learning ObjectivesAuliaNo ratings yet
- Compli Cirrhosis RXDocument10 pagesCompli Cirrhosis RXdrgmavmhNo ratings yet
- Autoinmune y TrasplanteDocument10 pagesAutoinmune y TrasplantejosedavidgonzalezeNo ratings yet
- Clinical StudyDocument8 pagesClinical StudypratiwifatmasariNo ratings yet
- Instrument - Automated External DefibrillatorDocument2 pagesInstrument - Automated External DefibrillatorJulio ArgañarazNo ratings yet
- Level 1 Measure Child Age 11 To 17Document3 pagesLevel 1 Measure Child Age 11 To 17waleskacrzNo ratings yet
- NCP For EclampsiaDocument3 pagesNCP For EclampsiaFatma Nor Aljanna Macog100% (1)
- Physical, Leisure, and Daily Living Activities In.3Document11 pagesPhysical, Leisure, and Daily Living Activities In.3yogithajeganathan5197No ratings yet
- Julie Daniels ResumeDocument2 pagesJulie Daniels Resumeapi-252299559No ratings yet
- Patent Foramen Ovale PFODocument3 pagesPatent Foramen Ovale PFOvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Topic: Components of Consumer Health: Learning Activity Sheet # 1 in Health 10Document4 pagesTopic: Components of Consumer Health: Learning Activity Sheet # 1 in Health 10Jy ArtsyNo ratings yet
- OSCE OB - PDF Version 1Document15 pagesOSCE OB - PDF Version 1FNaF is love FNaF is lifeNo ratings yet
- Afast TfastDocument7 pagesAfast TfastEduardo LeónNo ratings yet
- Clinical Oral Implants Res - 2020 - Neckel - Influence of Implant Specific Radiation Doses On Peri Implant Hard and SoftDocument13 pagesClinical Oral Implants Res - 2020 - Neckel - Influence of Implant Specific Radiation Doses On Peri Implant Hard and SoftFelix SchweppeNo ratings yet
- Developmental DefectsDocument16 pagesDevelopmental DefectsdeenmNo ratings yet
- Drug CelexaDocument1 pageDrug CelexaSrkocher100% (1)
- McAndrew, Leske 2019Document17 pagesMcAndrew, Leske 2019Adriana SerratoNo ratings yet
- Discovery of PenicillinDocument2 pagesDiscovery of PenicillinPatNo ratings yet
- Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in The Obese .1Document8 pagesMicrosurgical Breast Reconstruction in The Obese .1oezeamuzieNo ratings yet
- FDA Executive Summary Dermal FillersDocument41 pagesFDA Executive Summary Dermal FillersAhmed Sad100% (1)
- Cerebrovascular Autoregulation in Pediatric Moyamoya DiseaseDocument11 pagesCerebrovascular Autoregulation in Pediatric Moyamoya DiseasewithoutlifeNo ratings yet
- NTCC Daily Log SheetDocument27 pagesNTCC Daily Log SheetMuskan SukhejaNo ratings yet
- Global Prevalence of Childhood Cataract: A Systematic ReviewDocument10 pagesGlobal Prevalence of Childhood Cataract: A Systematic ReviewnurhariNo ratings yet
- Thyroid StormDocument33 pagesThyroid StormVaibhav Krishna50% (2)
- SyncopeDocument3 pagesSyncopeanishdNo ratings yet
- Myoril Capsules PIDocument6 pagesMyoril Capsules PIHaris MusakhelNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support Training Manualnew PDFDocument88 pagesBasic Life Support Training Manualnew PDFkekoho4589100% (1)
- Juan Dela Cruz, RRT: Personal InformationDocument3 pagesJuan Dela Cruz, RRT: Personal InformationShiela Leomo-VillaramaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor and Postpartum CareDocument7 pagesStages of Labor and Postpartum CareAkash SamuelNo ratings yet
- Uetquwiuj 912083949Document4 pagesUetquwiuj 912083949TzvineZNo ratings yet
- The Anti-Inflammatory Handbook - 1st Edition 2023Document116 pagesThe Anti-Inflammatory Handbook - 1st Edition 2023king_zeusxNo ratings yet
- Madya Visha & MadatyayaDocument33 pagesMadya Visha & Madatyayaraghabendrasahu1998No ratings yet