Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Reviewer (Week 4 Ata)
Science Reviewer (Week 4 Ata)
Uploaded by
Louise Marithe Flor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesDNA stores genetic instructions for making proteins, while RNA helps carry out these instructions. DNA replication copies DNA for cell division. Transcription copies DNA to RNA, and translation uses RNA to build proteins. Mutations in DNA can be genetic or chromosomal, causing disorders like Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and more. Genetic engineering modifies DNA. Karyotyping examines chromosomes to identify genetic issues.
Original Description:
Original Title
Science reviewer (week 4 ata)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDNA stores genetic instructions for making proteins, while RNA helps carry out these instructions. DNA replication copies DNA for cell division. Transcription copies DNA to RNA, and translation uses RNA to build proteins. Mutations in DNA can be genetic or chromosomal, causing disorders like Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and more. Genetic engineering modifies DNA. Karyotyping examines chromosomes to identify genetic issues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesScience Reviewer (Week 4 Ata)
Science Reviewer (Week 4 Ata)
Uploaded by
Louise Marithe FlorDNA stores genetic instructions for making proteins, while RNA helps carry out these instructions. DNA replication copies DNA for cell division. Transcription copies DNA to RNA, and translation uses RNA to build proteins. Mutations in DNA can be genetic or chromosomal, causing disorders like Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and more. Genetic engineering modifies DNA. Karyotyping examines chromosomes to identify genetic issues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Science reviewer [DNA vs RNA, DNA replication, Protein synthesis
(Transcription & Translation) Mutations (Genetic & Chromosomal
mutations), genetic codes, disorder, and engineering]
DNA vs RNA Parts of rNA:
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the information
molecule. it stores instructions for making
other large molecules, called proteins. These
instructions are stored inside each of your
cells, distributed among 46 long structures
called chromosomes. These chromosomes are
made up of thousands of shorter segments of
DNA, called genes.
DNA is double-stranded.
RNA (ribonucleic acid) is present in all living components of DNA and rna
cells. Its principal role is to act as a messenger DNA:
carrying instructions from DNA for adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine
controlling the synthesis of proteins. However, RNA:
in some viruses RNA rather than DNA has the adenine, uracil, thymine, cytosine, guanine
genetic information.
RNA has one strand.
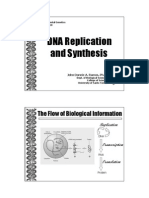
DNA replication
types of RNA: DNA replication is the process through which cells
mRNA (messenger RNA) make copies of the genome's DNA. A cell must first
tRNA (transfer RNA) copy (or duplicate) its entire genome before it can
rRNA (ribosomal RNA) divide, ensuring that each daughter cell has a
complete genome upon division.
Parts of DNA:
Protein synthesis (Transcription
& Translation)
The process by which DNA is copied to RNA is called
transcription, and that by which RNA is used to
produce proteins is called translation.
types of Chromosomal
Genetic codes mutation:
1. deletion - is a type of mutation that involves
the loss of one or more nucleotides from a
segment of DNA.
2. inversion - occurs when a chromosome
breaks in two places; the resulting piece of
DNA is reversed and re-inserted into the
chromosome.
3. translocation - genetic change in which a
piece of one chromosome breaks off and
attaches to another chromosome.
4. duplication - a type of mutation in which one
or more copies of a DNA segment (which can
be as small as a few bases or as large as a
Mutations major chromosomal region) is produced.
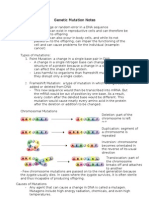
changes in the nucleotide sequence of a DNA 5. nondisjunction - failure of homologous
may occur in somatic cells chromosomes to separate correctly during
may occur in gametes and be passed to meiosis.
offspring
almost all mutations are neutral gene mutation
chemicals and UV radiations can cause A gene mutation is a change to a gene's DNA
mutation sequence to produce something different.
repaired by enzymes
types of gene mutation:
has two types: chromosomal and genetic 1. point mutation - occurs in a genome when a
mutations single base pair is added, deleted or
Chromosomal mutation changed. (deletion, substitution, and
a mutation involving a long segment of DNA. These insertion)
mutations can involve deletions, insertions, 2. frameshift mutation - An insertion or
inversions, or translocations of sections or deletion involving a number of base pairs
segments of DNA. In some cases, deleted portions that are not a multiple of three, which
may attach to other chromosomes, disrupting both consequently disrupts the triplet reading
the chromosomes losing the DNA and the one frame of a DNA sequence.
gaining it.
genetic disorders
cri du chat - caused by deletion of part of
the short arm of chromosome 5. babies with
cri du chat have high-pitched cries that
sound like a cat. (deletion)
down syndrome - is caused by an extra copy
of chromosome 21(trisomy) (nondisjunction)
edward's syndrome - is caused by an extra
copy of chromosome 18 (nondisjunction)
Jacobsen syndrome - caused by deletion of
the long arm of chromosome 11. most have a
bleeding disorder called paris-trousseau
syndrome (deletion)
Klinefelter syndrome - caused by additional
x chromosome (nondisjunction)
turner syndrome - one of the X
chromosomes (sex chromosomes) is missing
or partially missing. (deletion)
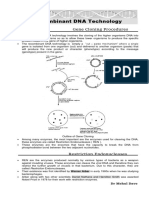
genetic engineering
a process that uses laboratory-based
technologies to alter the DNA makeup of an
organism.
human karyotyping
a test to examine chromosomes in a sample
cells
can help identifying genetic problems as the
cause of disorder or disease.
You might also like
- Lorenz Adlung - Cell and Molecular Biology For Non-Biologists - A Short Introduction Into Key Biological Concepts-Springer (2023)Document132 pagesLorenz Adlung - Cell and Molecular Biology For Non-Biologists - A Short Introduction Into Key Biological Concepts-Springer (2023)I'mLeo Mc100% (2)
- Genome OrganizationDocument19 pagesGenome OrganizationChristin Natalia KalembangNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Biology Test Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Biology Test Multiple Choice QuestionsTravis0% (2)
- Slice 3 Graphic OrganizerDocument1 pageSlice 3 Graphic Organizerapi-463991923No ratings yet
- Microbial GeneticsDocument17 pagesMicrobial Geneticsزين العابدين محمد عويش مشريNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience Reviewerkarljosefdelacruz1017No ratings yet
- III. Molecular Genetics B Landars GroupDocument37 pagesIII. Molecular Genetics B Landars GroupMa.charlina LozadaNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Repair Recombination-1Document32 pagesDNA Replication Repair Recombination-1Mugo JamesNo ratings yet
- Bacterial GeneticsDocument19 pagesBacterial GeneticsNUBWA MEDUGUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ExamKrackers Biomolecules GeneticsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 ExamKrackers Biomolecules GeneticsPatricia CosNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics: The HOW of HeredityDocument49 pagesMolecular Genetics: The HOW of Hereditycorygunther6451No ratings yet
- ٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Document15 pages٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of BiologyDocument6 pagesCentral Dogma of BiologyJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Summary Chart: Genetics Is Defined As The Study of Inheritance orDocument2 pagesSummary Chart: Genetics Is Defined As The Study of Inheritance orChrystelle Mariano TibayNo ratings yet
- Special Topics NotesDocument4 pagesSpecial Topics NotesKristine KayeNo ratings yet
- Micro para 4Document4 pagesMicro para 4Reselle EspirituNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument19 pagesDNA ReplicationLouis HilarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - DnaDocument5 pagesChapter 9 - Dnaapi-272677238No ratings yet
- Microbial GeneticsDocument11 pagesMicrobial GeneticskimeehhNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3. Module 2. Heredity: Inheritance and VariationDocument3 pagesQuarter 3. Module 2. Heredity: Inheritance and VariationEric LucenteNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Review Molecular GeneticsDocument7 pagesAP Bio Review Molecular GeneticsktxoxxoxNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Unit III - Living Things and Its Environment - Heredity: Inheritance & VariationDocument4 pagesGenetics: Unit III - Living Things and Its Environment - Heredity: Inheritance & VariationKirito TobioNo ratings yet
- Dna Replicatin and RepairDocument80 pagesDna Replicatin and RepairAndualemNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Genetics: Genetic Elements Such As Plasmids or Bacteriophages (BacterialDocument14 pagesBacterial Genetics: Genetic Elements Such As Plasmids or Bacteriophages (Bacterialعلي الكوافيNo ratings yet
- PDF 20230417 225731 0000Document27 pagesPDF 20230417 225731 0000Maye JorcaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 BIO1007 NotesDocument10 pagesMODULE 1 BIO1007 NotesMuskaan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology-Lecture 1 5 QuestionsDocument20 pagesMolecular Biology-Lecture 1 5 QuestionsLara ShayaNo ratings yet
- Biology Genetic Mutation NotesDocument1 pageBiology Genetic Mutation NotesTiffany Gallina100% (2)
- Bacterial Genetics: By: Dr. Guma AbdeldaimDocument67 pagesBacterial Genetics: By: Dr. Guma AbdeldaimMarwan Alferjani0% (1)
- Part 3Document18 pagesPart 3Ultima PhaseNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: An Introduction: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarDocument29 pagesCell Biology: An Introduction: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarmskikiNo ratings yet
- Coursenotesdomain 4 InformationDocument29 pagesCoursenotesdomain 4 Informationapi-300668314No ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular GeneticsDocument19 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular GeneticsVerlyn Mae L. MatituNo ratings yet
- R DNA TechnologyDocument17 pagesR DNA TechnologyDRMEHUL DAVENo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Comp Unit in One Shot Mindmaps by Rakshita SinghDocument7 pagesBiotechnology Comp Unit in One Shot Mindmaps by Rakshita Singhkchahar886No ratings yet
- 2nd Bio AssgnmntDocument6 pages2nd Bio AssgnmntNitinmanubanshNo ratings yet
- Medical Biology and Genetics: For Pharmacy 2020-2021Document63 pagesMedical Biology and Genetics: For Pharmacy 2020-2021Cordelia BrownNo ratings yet
- Transposons & Mechanisms of Transposition: Krystine Garcia, Tao Jing, Alexander MeyersDocument25 pagesTransposons & Mechanisms of Transposition: Krystine Garcia, Tao Jing, Alexander MeyersIndiani SaniNo ratings yet
- Primer: DNA Double-Strand Break RepairDocument3 pagesPrimer: DNA Double-Strand Break RepairSony SaefullohNo ratings yet
- Lect 3 - 4 DOGMA CENTRAL-1Document76 pagesLect 3 - 4 DOGMA CENTRAL-1Asfi AniNo ratings yet
- Organisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomeDocument8 pagesOrganisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomeNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- C9 Topology Functional Deformations of DNADocument34 pagesC9 Topology Functional Deformations of DNAIsSisNo ratings yet
- Coding &non Coding DNADocument31 pagesCoding &non Coding DNAGiD MOhNo ratings yet
- The Replication of DNA in ProkaryotesDocument6 pagesThe Replication of DNA in ProkaryotesAditya KukretiNo ratings yet
- DNA: Structure, Function and DiscoveryDocument15 pagesDNA: Structure, Function and DiscoveryDoctor Muhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids DNA and RNADocument17 pagesNucleic Acids DNA and RNAAgnes GarciaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4Th Edition Bauman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesMicrobiology With Diseases by Body System 4Th Edition Bauman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFlloydkieran71epfi100% (14)
- Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Solutions ManualDocument9 pagesMicrobiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Solutions Manualzacharymeliora0h86100% (34)
- Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Solutions ManualDocument39 pagesMicrobiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Solutions Manualcharles90br100% (17)
- Transposons Mediated MutagenesisDocument41 pagesTransposons Mediated Mutagenesissaurabh784No ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument28 pagesCentral DogmaBryant Villarin BaldivicioNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Genetics: DR - Tetty Aman Nasution M Med SCDocument59 pagesBacterial Genetics: DR - Tetty Aman Nasution M Med SCAndry SipahutarNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Synthesis: The Flow of Biological InformationDocument12 pagesDNA Replication and Synthesis: The Flow of Biological InformationRenz L. SalumbreNo ratings yet
- Science Finals Reviewer: Nucleic Acid and Their Connection With Inheritance (E-Book Pages 261-262)Document5 pagesScience Finals Reviewer: Nucleic Acid and Their Connection With Inheritance (E-Book Pages 261-262)Mareck VerdanNo ratings yet
- 1 5041923187504316858Document67 pages1 5041923187504316858John Estrada100% (1)
- Mekanisme Replikasi, Repair DNA Dan Rekombinan DNADocument50 pagesMekanisme Replikasi, Repair DNA Dan Rekombinan DNAnolaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology - Principle ProcessDocument9 pagesBiotechnology - Principle Processtamalbio7No ratings yet
- Principles of Microbiology 1 (Summary)Document8 pagesPrinciples of Microbiology 1 (Summary)Mabelle DucusinNo ratings yet
- RizalDocument25 pagesRizalPhia LorenNo ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- RESEARCH Chapter 1 PDFDocument15 pagesRESEARCH Chapter 1 PDFLouise Marithe FlorNo ratings yet
- Recipe Album-SaladsDocument11 pagesRecipe Album-SaladsLouise Marithe FlorNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Week 5 Ata)Document6 pagesScience Reviewer (Week 5 Ata)Louise Marithe FlorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document6 pagesChapter 2Louise Marithe FlorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5Louise Marithe FlorNo ratings yet
- Research Chapter 4 2Document4 pagesResearch Chapter 4 2Louise Marithe FlorNo ratings yet
- Determining The Relevance and Truthfulness of The Ideas Presented in The Material Viewed (Part 1)Document13 pagesDetermining The Relevance and Truthfulness of The Ideas Presented in The Material Viewed (Part 1)Louise Marithe Flor100% (1)
- Mitosis - WikipediaDocument39 pagesMitosis - WikipediaMuhammad Azhar MagsiNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Reproduction in Organisms (NCERT)Document10 pages12.1 Reproduction in Organisms (NCERT)One Tegar PambudiNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Report FinalDocument40 pagesMini Project Report Final【BEING MYSTIC】 (teen rider)No ratings yet
- Molecular Diagnostic Services Diagnostic Test Request Form (Neuromuscular)Document6 pagesMolecular Diagnostic Services Diagnostic Test Request Form (Neuromuscular)myalvinNo ratings yet
- A Two-Dimensional Modified Le Vy-Walk Model For The DNA SequencesDocument11 pagesA Two-Dimensional Modified Le Vy-Walk Model For The DNA SequencesanrrisNo ratings yet
- Gene Cloning Research Paper PDFDocument6 pagesGene Cloning Research Paper PDFjmforlwgf100% (1)
- Grade: 8 Subject: Science Quarter: IV Week No: 2 Day No. 2 I. ObectivesDocument6 pagesGrade: 8 Subject: Science Quarter: IV Week No: 2 Day No. 2 I. ObectivesCathy MoronioNo ratings yet
- Ib Psych NotesDocument114 pagesIb Psych NotesLucy Han100% (2)
- Introduction To Bioinformatics: Tolga CanDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Bioinformatics: Tolga CanvinothlcNo ratings yet
- SHERLOCK: Nucleic Acid Detection With CRISPR Nucleases: ProtocolDocument29 pagesSHERLOCK: Nucleic Acid Detection With CRISPR Nucleases: ProtocolShreya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Evolution Quiz2-StudentDocument4 pagesEvolution Quiz2-Studentapi-236443418No ratings yet
- Variability and Genetic Divergence in Paprika (Capsicum Annuum L.) 1Document6 pagesVariability and Genetic Divergence in Paprika (Capsicum Annuum L.) 1Sabina OproiuNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument2 pagesCurriculum VitaechinthooseNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics For MSC Medical MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesThesis Topics For MSC Medical Microbiologychristinasantospaterson100% (2)
- Regulation of Sex Expression and Flowering in Papaya (Carica Papaya)Document3 pagesRegulation of Sex Expression and Flowering in Papaya (Carica Papaya)Gustavo SantosNo ratings yet
- Bulk Segregant AnalysisDocument5 pagesBulk Segregant AnalysisAditya Mohan GuptaNo ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON PLAN-Non Mendelian HeredityDocument8 pagesDAILY LESSON PLAN-Non Mendelian HeredityBryan PasionNo ratings yet
- Early Development in Sea UrchinDocument10 pagesEarly Development in Sea UrchinSyeda Fizza Batool100% (1)
- Running Head: Assignment 2 1Document7 pagesRunning Head: Assignment 2 1sabihuddinNo ratings yet
- COURSE Syllabus: The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance CenterDocument10 pagesCOURSE Syllabus: The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance CenterlanaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY XI CHAP 1 Question-556227Document4 pagesBIOLOGY XI CHAP 1 Question-556227Arti ThokchomNo ratings yet
- Advice Sheet Social Structure of Horse - IAABCDocument2 pagesAdvice Sheet Social Structure of Horse - IAABCHenrique GarciaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1934590920302009 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S1934590920302009 MainMOVEMENT SCHOOLNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: For General Biology 1 / Grade 11 Quarter 1/week 3Document22 pagesThe Cell Cycle: For General Biology 1 / Grade 11 Quarter 1/week 3zeth.111No ratings yet
- Tuck Seng Wong - Kang Lan T - A Practical Guide To Protein Engineering, 1st EditionDocument213 pagesTuck Seng Wong - Kang Lan T - A Practical Guide To Protein Engineering, 1st EditionparavelloNo ratings yet
- Yeast Surface Display 2022Document643 pagesYeast Surface Display 2022xz2020wustlNo ratings yet
- 07 100 HW F18 MendelDocument7 pages07 100 HW F18 MendelAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pages09 Science Notes Ch05 Fundamental Unit of Lifemunnithakur5285No ratings yet