Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Che - 91911 - Identification of Chloride
Che - 91911 - Identification of Chloride
Uploaded by
Jo Standley0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageChloride ions can be identified through a series of tests. When tested with litmus paper and barium nitrate, common anions are eliminated. Adding silver nitrate forms a white precipitate of silver chloride, indicating the presence of a halide ion. To confirm chloride and rule out iodide, ammonia is added to form a colorless, soluble complex of silver and ammonia, uniquely identifying chloride ions.
Original Description:
Original Title
che_91911_Identification of chloride.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChloride ions can be identified through a series of tests. When tested with litmus paper and barium nitrate, common anions are eliminated. Adding silver nitrate forms a white precipitate of silver chloride, indicating the presence of a halide ion. To confirm chloride and rule out iodide, ammonia is added to form a colorless, soluble complex of silver and ammonia, uniquely identifying chloride ions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageChe - 91911 - Identification of Chloride
Che - 91911 - Identification of Chloride
Uploaded by
Jo StandleyChloride ions can be identified through a series of tests. When tested with litmus paper and barium nitrate, common anions are eliminated. Adding silver nitrate forms a white precipitate of silver chloride, indicating the presence of a halide ion. To confirm chloride and rule out iodide, ammonia is added to form a colorless, soluble complex of silver and ammonia, uniquely identifying chloride ions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY AS91911
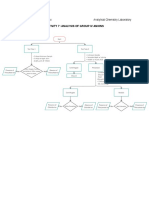
Identification of chloride, Cl-
Chloride ions (Cl-) can be identified in solution through the use of solubility rules and the
ability of the chloride anion to form a complex ion with ammonia.
When a sample is tested with red litmus paper, the paper remains red. This allows for the
elimination of the both the basic hydroxide and carbonate anions.
When 2 drops of barium nitrate is added there is no precipitate, excluding the sulfate anion.
This is because most sulfates are soluble except for calcium, lead and barium sulfate. If the
anion had been a sulfate a precipitate of insoluble barium sulfate would form (solubility rule
#3).
One way to identify chloride ions in solution is to add a solution of silver nitrate (AgNO3) to
a new sample of the unknown solution. This will cause a white precipitate of silver chloride
(AgCl) to form according to the following equation:
Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) → AgCl(s)
Most halides (chlorides and iodides) are soluble except for those with silver and lead
(solubility rule #3) so a precipitate with silver nitrate solution here identifies either silver
chloride or silver iodide.
The nitrate anion (NO3-) does not form a precipitate with silver nitrate as all nitrates are
soluble (solubility rule #3), which is why nitrate ions can be eliminated.
The formation of a white precipitate of AgCl confirms the presence of chloride ions in
solution. However, this test alone is not specific enough to conclusively identify chloride
ions, as other halide ions such iodide (I-) can also form a pale yellow precipitate with silver
nitrate.
To confirm the presence of chloride ions and exclude iodide ions, an additional test can be
performed using ammonia as a complexing agent. Silver ions from AgCl can form a complex
ion with ammonia, [Ag(NH3)2]+, which is soluble in water.
The overall reaction is: Ag+(aq) + 2NH3(aq) → [Ag(NH3)2]+(aq)
Or
AgCl(s) + 2NH3(aq) → [Ag(NH3)2]+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
This complex ion is stable and soluble in water, and the formation of a colourless solution
confirms the presence of chloride ions in the solution. A similar stable complex ion does not
form if the precipitate had been that of silver iodide.
You might also like
- DIscussion of Reactions of Halides in SolutionDocument6 pagesDIscussion of Reactions of Halides in SolutionTingYuan Hoi76% (17)
- Colloidalt Gold and Silver - Production of Colloidal Gold With Electrolysis and Green SynthesisDocument14 pagesColloidalt Gold and Silver - Production of Colloidal Gold With Electrolysis and Green SynthesisDevon Narok100% (1)
- MV & RV: Elements Periodic TableDocument4 pagesMV & RV: Elements Periodic TableCaerin LawNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT NO. 2 Guide (The Silver Group)Document6 pagesEXPERIMENT NO. 2 Guide (The Silver Group)Kaye OmoNo ratings yet
- Aluminium and Its CompoundsDocument7 pagesAluminium and Its CompoundsNandaSekarGalihN100% (1)
- Experiment 5 7 Qualitative AnalysisDocument14 pagesExperiment 5 7 Qualitative AnalysisRAZAFIMAHARO SERGE MICHELNo ratings yet
- Lab Act 7Document3 pagesLab Act 7Alleyah May GiducosNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Potassium TrisDocument3 pagesPreparation of Potassium TrisAndile ManyoniNo ratings yet
- Che - 91911 Identification of Al3+Document1 pageChe - 91911 Identification of Al3+Jo StandleyNo ratings yet
- Chem 31.1 Experiment 8A-E HandoutDocument2 pagesChem 31.1 Experiment 8A-E HandoutshershireNo ratings yet
- 5 3 2 Revision Guide Qualitative AnalysisDocument2 pages5 3 2 Revision Guide Qualitative AnalysisGarret GordonNo ratings yet
- The Copper Cycle For Mzila IfpDocument7 pagesThe Copper Cycle For Mzila IfpLwandiswa MncubeNo ratings yet
- 1225 Experiment 07Document8 pages1225 Experiment 07Mahmoud AbdAllah0% (1)
- Csec Identification of Cations and AnionsDocument6 pagesCsec Identification of Cations and AnionsDarrion BruceNo ratings yet
- Cocl 6 NH Orange-Yellow Cocl 5 NH H O Red Cocl 5 NH Purple Cocl 4 NH GreenDocument3 pagesCocl 6 NH Orange-Yellow Cocl 5 NH H O Red Cocl 5 NH Purple Cocl 4 NH GreenNur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Skill Building ExercisesDocument4 pagesSkill Building ExercisesLex QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Precipitation TitrationDocument19 pagesPrecipitation TitrationRoj Waleed BarwaryiNo ratings yet
- Group 1 and 4 Cation AnalysisDocument26 pagesGroup 1 and 4 Cation Analysistwinkledreampoppies100% (1)
- 2.3. Group 7 The HalogensDocument6 pages2.3. Group 7 The HalogensDalton chirchirNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Group 4 and 5 AnionsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Group 4 and 5 AnionsFaijah MarohomsalicNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 SolutionsDocument27 pagesAssignment 4 SolutionsMahimaNo ratings yet
- Cation SeparationDocument22 pagesCation SeparationDiane Angeles50% (2)
- s4 Chlorine and Its Compound TR MugumyaDocument15 pagess4 Chlorine and Its Compound TR MugumyaLwin MoeNo ratings yet
- Identifying A Simple Salt: Ion ColorDocument15 pagesIdentifying A Simple Salt: Ion ColorNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8: Separation of Cations: An ExampleDocument4 pagesExperiment 8: Separation of Cations: An ExampleRodrigoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Carbon To Carbon Double BondDocument2 pagesChemistry Carbon To Carbon Double BondJAYLEN TRACEYNo ratings yet
- Chem PaperDocument3 pagesChem PaperPendo KaranjaNo ratings yet
- Complexation of Metallic IonsDocument10 pagesComplexation of Metallic IonsAdnan RaufNo ratings yet
- Pitogo, Chanie Experiment 2Document7 pagesPitogo, Chanie Experiment 2Chanie Baguio PitogoNo ratings yet
- A Level Notes On Period 3Document13 pagesA Level Notes On Period 3kmoiz427No ratings yet
- Argentometric TitrationsDocument4 pagesArgentometric TitrationsMuhammad Ali AsgharNo ratings yet
- Gases and Ions 4a1Document7 pagesGases and Ions 4a1TAKUNDA MARIMENo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument16 pagesSalt AnalysisAnshik BansalNo ratings yet
- Ion Test PDFDocument11 pagesIon Test PDFAnderson XiaoNo ratings yet
- Precipitation ReactionsDocument10 pagesPrecipitation ReactionsSarthakAggarwalNo ratings yet
- 2-Test For Ions (Qualitative Analysis)Document3 pages2-Test For Ions (Qualitative Analysis)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Cations 123 Take Home ActivityDocument3 pagesCations 123 Take Home ActivityEd GildaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument6 pagesQualitative AnalysisAshley SpiceNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab 2BDocument2 pagesPre-Lab 2BRobertHarringtonNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument47 pagesUntitled DocumentJeffrey HoNo ratings yet
- ArsenicDocument10 pagesArsenicsinaNo ratings yet
- Solubility RulesDocument6 pagesSolubility RulesErika Leah ManaloNo ratings yet
- Exer 10Document2 pagesExer 10Mariel TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Chloride MohrDocument2 pagesChloride MohrHasan Abuy100% (1)
- Experiment 5 NewDocument19 pagesExperiment 5 NewsaramanaeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of ChlorineDocument41 pagesChemistry of ChlorineKennedy ChitayiNo ratings yet
- Class-IX Subject-Chemistry Half-Yearly Syllabus Handout-4 Chapter-18 Chemical TestsDocument6 pagesClass-IX Subject-Chemistry Half-Yearly Syllabus Handout-4 Chapter-18 Chemical TestsZunaira AliNo ratings yet
- Note On Identifying Transition Metal IonsDocument10 pagesNote On Identifying Transition Metal Ionsdebelaregasa1No ratings yet
- Precipitations Reactions: Separates Out in Solution. For Example, When An Aqueous Solution of Silver Nitrate (AgnoDocument3 pagesPrecipitations Reactions: Separates Out in Solution. For Example, When An Aqueous Solution of Silver Nitrate (AgnoLissa HannahNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis Wired ChemistDocument18 pagesQualitative Analysis Wired ChemistFrances GanotisiNo ratings yet
- Period 3-Sodium To ArgonDocument56 pagesPeriod 3-Sodium To ArgonKumar FongNo ratings yet
- 1-Precipitation Titration3 PDFDocument27 pages1-Precipitation Titration3 PDFimjd2No ratings yet
- Anions Group IDocument2 pagesAnions Group IAbdulNo ratings yet
- Model Answers For Inorg Quiz 2010Document2 pagesModel Answers For Inorg Quiz 2010Sunil kumar KumawatNo ratings yet
- Leaching ProcessesDocument65 pagesLeaching ProcessesSegundo Colorado VillarNo ratings yet
- Cations IdentificationsDocument39 pagesCations IdentificationsAndari RahmadhaniNo ratings yet
- Argentometry PDFDocument2 pagesArgentometry PDFhaver mutsNo ratings yet
- KNO3Document10 pagesKNO3reinhard guevaraNo ratings yet
- Determination of the Atomic Weight of Cadmium and the Preparation of Certain of Its Sub-CompoundsFrom EverandDetermination of the Atomic Weight of Cadmium and the Preparation of Certain of Its Sub-CompoundsNo ratings yet
- Che2 - Things To Remember - AsbenergyDocument2 pagesChe2 - Things To Remember - AsbenergyJo StandleyNo ratings yet
- Che 91164 Shape Plus AnswersDocument27 pagesChe 91164 Shape Plus AnswersJo StandleyNo ratings yet
- Che - 91164 - Things To Remember - AsbenergyDocument2 pagesChe - 91164 - Things To Remember - AsbenergyJo StandleyNo ratings yet
- Types of Solids Hint SheetDocument1 pageTypes of Solids Hint SheetJo StandleyNo ratings yet
- Che - 91911 Significance of Pb2+ v2Document1 pageChe - 91911 Significance of Pb2+ v2Jo StandleyNo ratings yet
- Che - 91911 Significance of Zn2+Document1 pageChe - 91911 Significance of Zn2+Jo StandleyNo ratings yet
- Che - 91911 Identification of Al3+Document1 pageChe - 91911 Identification of Al3+Jo StandleyNo ratings yet
- Che - 91911 Significance of Cu2+Document1 pageChe - 91911 Significance of Cu2+Jo StandleyNo ratings yet
- Che - 91911 Significance of Al3+Document3 pagesChe - 91911 Significance of Al3+Jo StandleyNo ratings yet