Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views13 D Enamel Structure
13 D Enamel Structure
Uploaded by
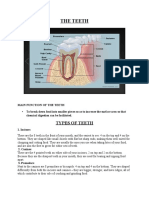
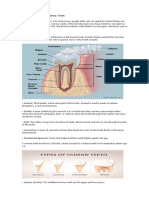
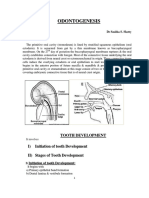
VEnamel is the hardest tissue in the body, consisting of microscopic hydroxyapatite crystals arranged in layers and surrounded by water. Carbonated apatite, a mineral in enamel, makes the tooth structure easier to dissolve by allowing acids to enter and minerals to leave the tooth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Adhesive Restoration of Endodontically Treated TeethFrom EverandAdhesive Restoration of Endodontically Treated TeethRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Componentes de OdDocument1 pageComponentes de Odbenancia lopezaNo ratings yet
- Tooth Structure: Vertical Section Through IncisorDocument1 pageTooth Structure: Vertical Section Through IncisorKymbat MukhtarovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. DentistryDocument11 pagesChapter 2. DentistryNo IdeaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Position of Tooth and Teeth (Powerpoint)Document11 pagesStructure and Position of Tooth and Teeth (Powerpoint)Jannin HwangNo ratings yet
- Tooth Structure 9075Document2 pagesTooth Structure 9075Andreea CojocariNo ratings yet
- Parts of The ToothDocument22 pagesParts of The Toothd389No ratings yet
- Teeth NotesDocument3 pagesTeeth NotesTamisha JacobsNo ratings yet
- Oral Histology Lecture 8Document20 pagesOral Histology Lecture 8Mohamed Harun B. SanohNo ratings yet
- Dentition NotesDocument3 pagesDentition Notescarlishadean23No ratings yet
- TeethDocument15 pagesTeethTallia LewisNo ratings yet
- Composition of Crown Layers: Dental AnatomyDocument8 pagesComposition of Crown Layers: Dental AnatomymahmoodNo ratings yet
- TeethDocument3 pagesTeethSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Tooth Origin and FormationDocument22 pagesTooth Origin and FormationRebeca GârboanNo ratings yet
- Presentación Diapositivas Negocio Catering Comida Ilustrativo Verde y BeigeDocument12 pagesPresentación Diapositivas Negocio Catering Comida Ilustrativo Verde y BeigeIsabela HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Lec3 EnamelDocument4 pagesLec3 EnamelGaelle AtNo ratings yet
- ToothpasteDocument15 pagesToothpastesuraj hanvateNo ratings yet
- Oral Care: Image Collection: Human AnatomyDocument2 pagesOral Care: Image Collection: Human Anatomyacer04266No ratings yet
- Morphology II - Lecture 1, Dental StructuresDocument22 pagesMorphology II - Lecture 1, Dental StructuresJoschiNo ratings yet
- Dental Crowns: Everything You Need To Know AboutDocument16 pagesDental Crowns: Everything You Need To Know AboutPomarida SimboNaNo ratings yet
- Orban Chapter 1Document2 pagesOrban Chapter 1Shreya VyasNo ratings yet
- ToothDocument2 pagesToothGeorgiana ValeanuNo ratings yet
- 4-Demineralization and RemineralizationDocument3 pages4-Demineralization and Remineralizationjpa100% (1)
- 7.3 Mechanical DigestionDocument5 pages7.3 Mechanical DigestionelizabethNo ratings yet
- IFDEA Dental Anatomy Educational Teaching ResourceDocument38 pagesIFDEA Dental Anatomy Educational Teaching ResourceaerowongNo ratings yet
- The Teeth: © PDST Home EconomicsDocument12 pagesThe Teeth: © PDST Home EconomicsfouadNo ratings yet
- Development of TeethDocument20 pagesDevelopment of TeethSubhashini RajshekarNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Mechanical DigestionDocument5 pages7.3 Mechanical Digestionges100% (1)
- Development of TeethDocument20 pagesDevelopment of TeethMehri Aisha ShanavasNo ratings yet
- TEETHDocument4 pagesTEETHSaad NaseerNo ratings yet
- Structure of Tooth m121Document13 pagesStructure of Tooth m121amirhossein vaeziNo ratings yet
- Naim Oral CareDocument34 pagesNaim Oral Carenaim157No ratings yet
- Terminology Used To Describe The Tissues of A Tooth: DR - Yad Raouf BDS, Efb, MrcsedDocument20 pagesTerminology Used To Describe The Tissues of A Tooth: DR - Yad Raouf BDS, Efb, MrcsedRabarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument8 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionShilpi BdsNo ratings yet
- Oral Hist1Document21 pagesOral Hist1saleemshaikh23No ratings yet
- Dentin: V.Nivedha First Year MDS 14.07.2017Document118 pagesDentin: V.Nivedha First Year MDS 14.07.2017Khalid Lafi100% (1)
- Week 5 - Basic of Dentistry: TeethDocument2 pagesWeek 5 - Basic of Dentistry: Teethnoelah salcedoNo ratings yet
- Oral AnatomyDocument25 pagesOral AnatomyFlip CartNo ratings yet
- 2 - Biologic Consideration of Enamel and Its Clinical Significance in Operative DentistryDocument7 pages2 - Biologic Consideration of Enamel and Its Clinical Significance in Operative DentistryMohammedNo ratings yet
- Oral Biochemistry: DR/ Mohammed EL-sebaieDocument8 pagesOral Biochemistry: DR/ Mohammed EL-sebaieDr-AHmad Fasfous AL-QaisiNo ratings yet
- Zähne BioDocument2 pagesZähne BioNoemi SuveicaNo ratings yet
- Digestion (Teeth)Document4 pagesDigestion (Teeth)OJ ICONICNo ratings yet
- Yellowish-Brown DiscolourationDocument8 pagesYellowish-Brown Discolourationأحمد تركي كحيوشNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy Teeth Types and Diff Basic TerminologyDocument73 pagesDental Anatomy Teeth Types and Diff Basic Terminologymakondotakunda11No ratings yet
- Introduction To Oral HistologyDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Oral HistologyShalini NairNo ratings yet
- Enamel, Dentin, Pulp Biological ConsiderationDocument41 pagesEnamel, Dentin, Pulp Biological ConsiderationMohammad ANo ratings yet
- Embryologie DentaireDocument23 pagesEmbryologie DentaireElmassal SergeoNo ratings yet
- Tooth DevelopmentDocument15 pagesTooth DevelopmentSascha WuNo ratings yet
- AdamDocument6 pagesAdammaantom3No ratings yet
- Plaque and Tartar ControlDocument2 pagesPlaque and Tartar ControldentdeepNo ratings yet
- Tmpyjlins - Chuong 1 Over ViewDocument54 pagesTmpyjlins - Chuong 1 Over ViewMinh Thu VũNo ratings yet
- Tooth AnatomyDocument31 pagesTooth Anatomydhea wirantiNo ratings yet
- Biologic Considerations of Enamel Structure and Its Clinical Significance in Practice of Operative DentistryDocument25 pagesBiologic Considerations of Enamel Structure and Its Clinical Significance in Practice of Operative DentistryAmee PatelNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy and Dental HistologyDocument206 pagesDental Anatomy and Dental HistologySwati Pathak GiriNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument14 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentPriybrat SharmaNo ratings yet
- STD Iv Sci L-2 PPTDocument22 pagesSTD Iv Sci L-2 PPTManit ShahNo ratings yet
- Identifikasi Gigi BingDocument3 pagesIdentifikasi Gigi BingGhefiraNo ratings yet
- Teeth Development: Bud StageDocument7 pagesTeeth Development: Bud Stageburdall100% (1)
- Lec 6+7 Oral H.Document35 pagesLec 6+7 Oral H.حسين العراقيNo ratings yet
- 3 Assisting in A Crown or BridgeDocument3 pages3 Assisting in A Crown or BridgeVNo ratings yet
- Performing Caries Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesPerforming Caries Risk AssessmentVNo ratings yet
- 13 C Oral Biofilm Questions and AnswersDocument1 page13 C Oral Biofilm Questions and AnswersVNo ratings yet
- 13 e The Caries Process Questions and AnswersDocument1 page13 e The Caries Process Questions and AnswersVNo ratings yet
- 13 A Caries Introduction Questions and AnswersDocument1 page13 A Caries Introduction Questions and AnswersVNo ratings yet
- 13 B Bacterial Infection Questions and Answers From Text BookDocument1 page13 B Bacterial Infection Questions and Answers From Text BookVNo ratings yet
13 D Enamel Structure
13 D Enamel Structure
Uploaded by
V0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageEnamel is the hardest tissue in the body, consisting of microscopic hydroxyapatite crystals arranged in layers and surrounded by water. Carbonated apatite, a mineral in enamel, makes the tooth structure easier to dissolve by allowing acids to enter and minerals to leave the tooth.
Original Description:
Original Title
13 d Enamel Structure.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnamel is the hardest tissue in the body, consisting of microscopic hydroxyapatite crystals arranged in layers and surrounded by water. Carbonated apatite, a mineral in enamel, makes the tooth structure easier to dissolve by allowing acids to enter and minerals to leave the tooth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 page13 D Enamel Structure
13 D Enamel Structure
Uploaded by
VEnamel is the hardest tissue in the body, consisting of microscopic hydroxyapatite crystals arranged in layers and surrounded by water. Carbonated apatite, a mineral in enamel, makes the tooth structure easier to dissolve by allowing acids to enter and minerals to leave the tooth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
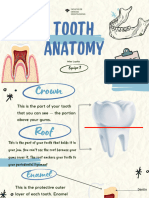
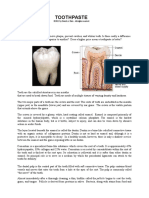
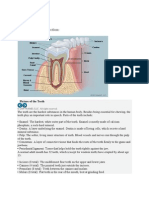
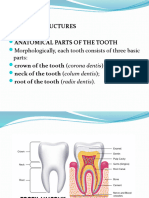
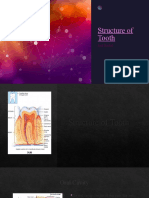
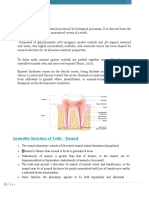
Enamel Structure
Enamel is described as the most: highly mineralized tissue in the body
Enamel is stronger than: bone
Enamel consists of microscopic crystals of: hydroxyapatite
The hydroxyapatite found in enamel is arranged in: structural layers or rods, also known as prisms
These crystals of hydroxyapatite are surrounded by: water
Primary teeth compared to permanent teeth, are made up of slightly more: water
The water in enamel allows _____to flow into the tooth and _______to flow out of the tooth: acids to flow
into the tooth and minerals to flow out of the tooth
A mineral in enamel that makes it easier for the tooth structure to dissolve: Carbonated apatite
Carbonated apatite is: a mineral in enamel, makes it easier for the tooth structure to dissolve.
What is the soft, sticky bacterial mass that adheres to the teeth: pellicle
What is the mineral in the enamel that makes the tooth structure easier to dissolve: Carbonated apatite
You might also like
- Adhesive Restoration of Endodontically Treated TeethFrom EverandAdhesive Restoration of Endodontically Treated TeethRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Componentes de OdDocument1 pageComponentes de Odbenancia lopezaNo ratings yet
- Tooth Structure: Vertical Section Through IncisorDocument1 pageTooth Structure: Vertical Section Through IncisorKymbat MukhtarovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. DentistryDocument11 pagesChapter 2. DentistryNo IdeaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Position of Tooth and Teeth (Powerpoint)Document11 pagesStructure and Position of Tooth and Teeth (Powerpoint)Jannin HwangNo ratings yet
- Tooth Structure 9075Document2 pagesTooth Structure 9075Andreea CojocariNo ratings yet
- Parts of The ToothDocument22 pagesParts of The Toothd389No ratings yet
- Teeth NotesDocument3 pagesTeeth NotesTamisha JacobsNo ratings yet
- Oral Histology Lecture 8Document20 pagesOral Histology Lecture 8Mohamed Harun B. SanohNo ratings yet
- Dentition NotesDocument3 pagesDentition Notescarlishadean23No ratings yet
- TeethDocument15 pagesTeethTallia LewisNo ratings yet
- Composition of Crown Layers: Dental AnatomyDocument8 pagesComposition of Crown Layers: Dental AnatomymahmoodNo ratings yet
- TeethDocument3 pagesTeethSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Tooth Origin and FormationDocument22 pagesTooth Origin and FormationRebeca GârboanNo ratings yet
- Presentación Diapositivas Negocio Catering Comida Ilustrativo Verde y BeigeDocument12 pagesPresentación Diapositivas Negocio Catering Comida Ilustrativo Verde y BeigeIsabela HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Lec3 EnamelDocument4 pagesLec3 EnamelGaelle AtNo ratings yet
- ToothpasteDocument15 pagesToothpastesuraj hanvateNo ratings yet
- Oral Care: Image Collection: Human AnatomyDocument2 pagesOral Care: Image Collection: Human Anatomyacer04266No ratings yet
- Morphology II - Lecture 1, Dental StructuresDocument22 pagesMorphology II - Lecture 1, Dental StructuresJoschiNo ratings yet
- Dental Crowns: Everything You Need To Know AboutDocument16 pagesDental Crowns: Everything You Need To Know AboutPomarida SimboNaNo ratings yet
- Orban Chapter 1Document2 pagesOrban Chapter 1Shreya VyasNo ratings yet
- ToothDocument2 pagesToothGeorgiana ValeanuNo ratings yet
- 4-Demineralization and RemineralizationDocument3 pages4-Demineralization and Remineralizationjpa100% (1)
- 7.3 Mechanical DigestionDocument5 pages7.3 Mechanical DigestionelizabethNo ratings yet
- IFDEA Dental Anatomy Educational Teaching ResourceDocument38 pagesIFDEA Dental Anatomy Educational Teaching ResourceaerowongNo ratings yet
- The Teeth: © PDST Home EconomicsDocument12 pagesThe Teeth: © PDST Home EconomicsfouadNo ratings yet
- Development of TeethDocument20 pagesDevelopment of TeethSubhashini RajshekarNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Mechanical DigestionDocument5 pages7.3 Mechanical Digestionges100% (1)
- Development of TeethDocument20 pagesDevelopment of TeethMehri Aisha ShanavasNo ratings yet
- TEETHDocument4 pagesTEETHSaad NaseerNo ratings yet
- Structure of Tooth m121Document13 pagesStructure of Tooth m121amirhossein vaeziNo ratings yet
- Naim Oral CareDocument34 pagesNaim Oral Carenaim157No ratings yet
- Terminology Used To Describe The Tissues of A Tooth: DR - Yad Raouf BDS, Efb, MrcsedDocument20 pagesTerminology Used To Describe The Tissues of A Tooth: DR - Yad Raouf BDS, Efb, MrcsedRabarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument8 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionShilpi BdsNo ratings yet
- Oral Hist1Document21 pagesOral Hist1saleemshaikh23No ratings yet
- Dentin: V.Nivedha First Year MDS 14.07.2017Document118 pagesDentin: V.Nivedha First Year MDS 14.07.2017Khalid Lafi100% (1)
- Week 5 - Basic of Dentistry: TeethDocument2 pagesWeek 5 - Basic of Dentistry: Teethnoelah salcedoNo ratings yet
- Oral AnatomyDocument25 pagesOral AnatomyFlip CartNo ratings yet
- 2 - Biologic Consideration of Enamel and Its Clinical Significance in Operative DentistryDocument7 pages2 - Biologic Consideration of Enamel and Its Clinical Significance in Operative DentistryMohammedNo ratings yet
- Oral Biochemistry: DR/ Mohammed EL-sebaieDocument8 pagesOral Biochemistry: DR/ Mohammed EL-sebaieDr-AHmad Fasfous AL-QaisiNo ratings yet
- Zähne BioDocument2 pagesZähne BioNoemi SuveicaNo ratings yet
- Digestion (Teeth)Document4 pagesDigestion (Teeth)OJ ICONICNo ratings yet
- Yellowish-Brown DiscolourationDocument8 pagesYellowish-Brown Discolourationأحمد تركي كحيوشNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy Teeth Types and Diff Basic TerminologyDocument73 pagesDental Anatomy Teeth Types and Diff Basic Terminologymakondotakunda11No ratings yet
- Introduction To Oral HistologyDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Oral HistologyShalini NairNo ratings yet
- Enamel, Dentin, Pulp Biological ConsiderationDocument41 pagesEnamel, Dentin, Pulp Biological ConsiderationMohammad ANo ratings yet
- Embryologie DentaireDocument23 pagesEmbryologie DentaireElmassal SergeoNo ratings yet
- Tooth DevelopmentDocument15 pagesTooth DevelopmentSascha WuNo ratings yet
- AdamDocument6 pagesAdammaantom3No ratings yet
- Plaque and Tartar ControlDocument2 pagesPlaque and Tartar ControldentdeepNo ratings yet
- Tmpyjlins - Chuong 1 Over ViewDocument54 pagesTmpyjlins - Chuong 1 Over ViewMinh Thu VũNo ratings yet
- Tooth AnatomyDocument31 pagesTooth Anatomydhea wirantiNo ratings yet
- Biologic Considerations of Enamel Structure and Its Clinical Significance in Practice of Operative DentistryDocument25 pagesBiologic Considerations of Enamel Structure and Its Clinical Significance in Practice of Operative DentistryAmee PatelNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy and Dental HistologyDocument206 pagesDental Anatomy and Dental HistologySwati Pathak GiriNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument14 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentPriybrat SharmaNo ratings yet
- STD Iv Sci L-2 PPTDocument22 pagesSTD Iv Sci L-2 PPTManit ShahNo ratings yet
- Identifikasi Gigi BingDocument3 pagesIdentifikasi Gigi BingGhefiraNo ratings yet
- Teeth Development: Bud StageDocument7 pagesTeeth Development: Bud Stageburdall100% (1)
- Lec 6+7 Oral H.Document35 pagesLec 6+7 Oral H.حسين العراقيNo ratings yet
- 3 Assisting in A Crown or BridgeDocument3 pages3 Assisting in A Crown or BridgeVNo ratings yet
- Performing Caries Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesPerforming Caries Risk AssessmentVNo ratings yet
- 13 C Oral Biofilm Questions and AnswersDocument1 page13 C Oral Biofilm Questions and AnswersVNo ratings yet
- 13 e The Caries Process Questions and AnswersDocument1 page13 e The Caries Process Questions and AnswersVNo ratings yet
- 13 A Caries Introduction Questions and AnswersDocument1 page13 A Caries Introduction Questions and AnswersVNo ratings yet
- 13 B Bacterial Infection Questions and Answers From Text BookDocument1 page13 B Bacterial Infection Questions and Answers From Text BookVNo ratings yet