Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 viewsSDL Abruptio Placenta Vs Placenta Previa
SDL Abruptio Placenta Vs Placenta Previa
Uploaded by
Vannesa TarifaThis document discusses care of mothers and children at risk. It focuses on the differences between abruptio placenta and placenta previa. While both can cause vaginal bleeding during pregnancy and labor, abruptio placenta involves premature separation of the placenta from the uterus, while placenta previa is an abnormal implantation of the placenta over the cervix. The document outlines key distinctions between the two conditions in terms of description, presence of pain, type of bleeding, confirmatory tests, and complications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Bleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanDocument17 pagesBleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanLizcelle Bihasa86% (7)
- Wifi Jammer: Winter Semester 2020-21 Analog Circuits Ece 2028Document10 pagesWifi Jammer: Winter Semester 2020-21 Analog Circuits Ece 2028Sathwik YadalamNo ratings yet
- Aetiology, Pathology and Management of Enterocutaneous FistulaDocument34 pagesAetiology, Pathology and Management of Enterocutaneous Fistularoselinekhadija100% (2)
- Antepartum Hemorrhage (APH) : It Is A MedicalDocument10 pagesAntepartum Hemorrhage (APH) : It Is A Medicalmed.progressNo ratings yet
- MCN NotesDocument20 pagesMCN NotesLiamLexus JavierNo ratings yet
- 2C Orev Compilation TopicDocument56 pages2C Orev Compilation TopicPaolo AntonioNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument35 pagesAntepartum HemorrhagesubashikNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Hemorrhage: HR BP Oxygen SaturationDocument4 pagesPost Partum Hemorrhage: HR BP Oxygen SaturationErjen Alexandria SiaNo ratings yet
- Maternal Midterm TransesDocument24 pagesMaternal Midterm TransesTaegyu IS SAILING Periodt.No ratings yet
- Antepartum Hemorrhage: Placental CausesDocument9 pagesAntepartum Hemorrhage: Placental CausesadiNo ratings yet
- Jose, Leana Louisse D. Cornell Notes On Ncm109 Module 1 & 2 (Complications of Pregnancy) 02/18/21 Assessment For Risk FactorsDocument19 pagesJose, Leana Louisse D. Cornell Notes On Ncm109 Module 1 & 2 (Complications of Pregnancy) 02/18/21 Assessment For Risk FactorsLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Ante Partum HemorrhageDocument21 pagesAnte Partum HemorrhagejyothinanduriNo ratings yet
- MCN 2Document7 pagesMCN 2GabNo ratings yet
- Complications of Pregnancy: Jose, Leana Louisse D. BSN 2BDocument14 pagesComplications of Pregnancy: Jose, Leana Louisse D. BSN 2BLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Feb 19. CA 2 - 1681737641118Document9 pagesFeb 19. CA 2 - 1681737641118HANNAH BANGKILINGNo ratings yet
- Transes MidtermDocument16 pagesTranses MidtermDexter NicolasNo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument5 pagesPlacenta PreviaMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics - Antepartum HemorrhageDocument4 pagesObstetrics - Antepartum HemorrhageJonathanNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors:: Placenta Previa Lower Uterine SegmentDocument11 pagesPredisposing Factors:: Placenta Previa Lower Uterine Segmentjhachers100% (1)
- Management of Placenta Previa During PregnancyDocument5 pagesManagement of Placenta Previa During PregnancyUlayya Ghina NabillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Woman and Family Experiencing A Postpartal ComplicationDocument43 pagesNursing Care of A Woman and Family Experiencing A Postpartal ComplicationVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Haemorrhage - FinalDocument44 pagesAntepartum Haemorrhage - FinalMLV AbayNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics - Obstretical HemorrhageDocument9 pagesObstetrics - Obstretical HemorrhageJonathanNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placentae by Marzo, Cecille Joyce D.Document22 pagesAbruptio Placentae by Marzo, Cecille Joyce D.Marzo, Cecille JoyceNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument53 pagesAbruptio PlacentaEphremNo ratings yet
- Bleeding DisordersDocument20 pagesBleeding DisordersSheene Ainasthazia Diego AngNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 APH, PP, VP, AbruptioDocument55 pagesTutorial 3 APH, PP, VP, AbruptioBahirahNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Hemorrhage: Tutorial 6 Case 1Document25 pagesAntepartum Hemorrhage: Tutorial 6 Case 1deangamaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanDocument19 pagesBleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanJack BangcoyoNo ratings yet
- Uterine Inversion Uterine Rupture Amniotic Fluid Embolism MaglangitDocument6 pagesUterine Inversion Uterine Rupture Amniotic Fluid Embolism Maglangitmaglangitjoannamarie1920No ratings yet
- APHDocument40 pagesAPHJayarani AshokNo ratings yet
- Cmca2 (Prelim) 2Document16 pagesCmca2 (Prelim) 2NOEL YRIGONNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta and AbortionDocument10 pagesAbruptio Placenta and Abortiondanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- A Low-Lying Placenta: Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Waste Products Top, Side, Front or Back of The UterusDocument3 pagesA Low-Lying Placenta: Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Waste Products Top, Side, Front or Back of The UterusFREVILYN ABASTANo ratings yet
- Midwifery 102 Module 2aDocument18 pagesMidwifery 102 Module 2aWynjoy NebresNo ratings yet
- Third Trimester: Place The Woman Immediately On Side-Lying PositionDocument7 pagesThird Trimester: Place The Woman Immediately On Side-Lying PositionZoila Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- OBDocument10 pagesOBIan Michael Romero OcampoNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 ReviewerDocument8 pagesNCM 109 ReviewerAlma Janella TOSINO100% (2)
- A 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFDocument47 pagesA 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Abruption PlacentaDocument40 pagesAbruption Placentamruts aregawiNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Complications During Labor and Management - MoralDocument45 pagesHemorrhagic Complications During Labor and Management - MoralAngel Mae BaborNo ratings yet
- Urdaneta City University College of Health Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing ProgramDocument4 pagesUrdaneta City University College of Health Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing ProgramMary Ruth CruzNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument3 pagesAbruptio PlacentaNano KaNo ratings yet
- Lapkas Ruptur UteriDocument10 pagesLapkas Ruptur UterirandyardinalNo ratings yet
- Uterine AtonyDocument14 pagesUterine AtonyLady Jane CaguladaNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument81 pagesAntepartum HemorrhageOmar mohamedNo ratings yet
- Aph Family MedicineDocument79 pagesAph Family MedicineMohammad Nahel SorourNo ratings yet
- Chapter21trans 1Document8 pagesChapter21trans 1syroise margauxNo ratings yet
- MAHAAAAADocument17 pagesMAHAAAAAmameekasim75No ratings yet
- Placenta AccretaDocument12 pagesPlacenta AccretaNavine NavNo ratings yet
- Abnormal LabourDocument21 pagesAbnormal LabourbetablockersNo ratings yet
- Ante Partum HemorrhageDocument30 pagesAnte Partum Hemorrhagetanmai nooluNo ratings yet
- 2 Topics at RiskDocument5 pages2 Topics at RiskGeraldine PatayanNo ratings yet
- Post-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2Document6 pagesPost-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2saeed hasan saeedNo ratings yet
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument53 pagesBleeding in Early PregnancyTemahlungwaneNo ratings yet
- 3rd Trimester BleedingDocument6 pages3rd Trimester BleedingPatrick BayuNo ratings yet
- Readings in Abruptio PlacentaDocument10 pagesReadings in Abruptio PlacentaLizabell TumlosNo ratings yet
- Article 262063-PrintDocument15 pagesArticle 262063-PrintAhsan AuliyaNo ratings yet
- Emergencies ObsDocument7 pagesEmergencies ObsAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- It's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookFrom EverandIt's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Drug Study FormatDocument5 pagesDrug Study FormatVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Template PediaDocument20 pagesTemplate PediaVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Caisip NCM109Document3 pagesCaisip NCM109Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Endocrine Disorder AssignmentDocument7 pagesModule 10 Endocrine Disorder AssignmentVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nursing Portfolio OB WardDocument2 pages1 Nursing Portfolio OB WardVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Midterms Modx LecDocument11 pagesMidterms Modx LecVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- DUTYDUTYDocument2 pagesDUTYDUTYVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- NCP TarifaDocument12 pagesNCP TarifaVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Ob Ward EportDocument7 pagesOb Ward EportVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OR RLEDocument13 pagesDrug Study OR RLEVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- NCP Template W InferenceDocument5 pagesNCP Template W InferenceVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 High Risk Newborn 2023Document25 pagesModule 7 High Risk Newborn 2023Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Lidocaine Drug StudyDocument1 pageLidocaine Drug StudyVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Name: Allyana Bumanlag Section: NU - 202: - Global Communication, Which Is The Practice of Communication That OccursDocument2 pagesName: Allyana Bumanlag Section: NU - 202: - Global Communication, Which Is The Practice of Communication That OccursVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Tarifa, Vannesa Joy B. (NU-202) Module 5 Assignment (NCM-109)Document3 pagesTarifa, Vannesa Joy B. (NU-202) Module 5 Assignment (NCM-109)Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Nursing DXDocument1 pageNursing DXVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Tarifa, Vannesa Joy B. (NU-202) Module 6 Assignment (NCM-109)Document3 pagesTarifa, Vannesa Joy B. (NU-202) Module 6 Assignment (NCM-109)Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Micro para Laboratory Activity 4 - Case Study 2Document5 pagesMicro para Laboratory Activity 4 - Case Study 2Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- NCM109RLE TemplateDocument4 pagesNCM109RLE TemplateVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 5b Report GroupB5 NU 102Document3 pagesLaboratory Activity 5b Report GroupB5 NU 102Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- NCM109RLE TemplateDocument4 pagesNCM109RLE TemplateVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- VACCINESDocument3 pagesVACCINESVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Pro 3 Mplusdevipplus 07Document6 pagesPro 3 Mplusdevipplus 07daylavianNo ratings yet
- Dan Sof TG 0122Document30 pagesDan Sof TG 0122Erick Trujillo100% (1)
- URL #Flushyourmeds Scott BarryDocument8 pagesURL #Flushyourmeds Scott Barryurl-flushyourmedsNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument79 pagesPreviewpdfcrisuanNo ratings yet
- Busbar Protect1Document9 pagesBusbar Protect1syahira87No ratings yet
- PSP Assignment1Document25 pagesPSP Assignment1B BasitNo ratings yet
- 04 - Protection GeneralDocument52 pages04 - Protection GeneralRK KNo ratings yet
- Mother's Personality and Its Interaction With Child Temperament As Predictors of Parenting BehaviorDocument12 pagesMother's Personality and Its Interaction With Child Temperament As Predictors of Parenting BehaviorMichelle PajueloNo ratings yet
- Jedec Standard: Els ServiçosDocument18 pagesJedec Standard: Els ServiçosEverton LuizNo ratings yet
- CHINT Installation Operation Manual For Inverter of 50-60KTLDocument98 pagesCHINT Installation Operation Manual For Inverter of 50-60KTLr.pimentel.souzaNo ratings yet
- G10 1st PERIODICAL TEST MAPEH10 TQDocument5 pagesG10 1st PERIODICAL TEST MAPEH10 TQMaricel LajeraNo ratings yet
- Manual Spray GunDocument6 pagesManual Spray GunSyazwan KhairulNo ratings yet
- ME Lab 2 LectureDocument5 pagesME Lab 2 LectureIan Paul TongolNo ratings yet
- Lyric - Grey HuffingtonDocument371 pagesLyric - Grey HuffingtonCaptain AtomNo ratings yet
- Analise de Agua e EfluentesDocument28 pagesAnalise de Agua e EfluentesFabiano Luiz NavesNo ratings yet
- Weekly Report ExampleDocument3 pagesWeekly Report Examplewawan setiawanNo ratings yet
- Maintain Training Facilities: Submitted By: Aeron M. LumbaDocument10 pagesMaintain Training Facilities: Submitted By: Aeron M. LumbaAeron LumbaNo ratings yet
- Richard ResumeDocument5 pagesRichard ResumePiei CornerNo ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument1 pageOlanzapineKallie ChartrandNo ratings yet
- Frenkel's ExerciseDocument40 pagesFrenkel's ExerciseManiu EmeseNo ratings yet
- Cavitation Models in PIPENETDocument3 pagesCavitation Models in PIPENETSamarth PawarNo ratings yet
- Materials Chemistry A: Journal ofDocument7 pagesMaterials Chemistry A: Journal ofFamiloni LayoNo ratings yet
- CM07 Sphere ConstructionDocument146 pagesCM07 Sphere ConstructionHuy Thieu Bui100% (1)
- 2nd Quarter PHILO ReviewerDocument1 page2nd Quarter PHILO ReviewerTrisha Joy Dela Cruz80% (5)
- Stilboestrol Tablets MSDSDocument6 pagesStilboestrol Tablets MSDSIsaac lauricNo ratings yet
- Physical Education IV: (Recreation)Document28 pagesPhysical Education IV: (Recreation)Faye Corazon GaurinoNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 LM Physical Science 1 Module4Document21 pagesGrade 12 LM Physical Science 1 Module4ladyheart ۦۦNo ratings yet
- PintoDocument18 pagesPintosinagadianNo ratings yet
SDL Abruptio Placenta Vs Placenta Previa
SDL Abruptio Placenta Vs Placenta Previa
Uploaded by
Vannesa Tarifa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views3 pagesThis document discusses care of mothers and children at risk. It focuses on the differences between abruptio placenta and placenta previa. While both can cause vaginal bleeding during pregnancy and labor, abruptio placenta involves premature separation of the placenta from the uterus, while placenta previa is an abnormal implantation of the placenta over the cervix. The document outlines key distinctions between the two conditions in terms of description, presence of pain, type of bleeding, confirmatory tests, and complications.
Original Description:
Original Title
SDL abruptio placenta vs placenta previa
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses care of mothers and children at risk. It focuses on the differences between abruptio placenta and placenta previa. While both can cause vaginal bleeding during pregnancy and labor, abruptio placenta involves premature separation of the placenta from the uterus, while placenta previa is an abnormal implantation of the placenta over the cervix. The document outlines key distinctions between the two conditions in terms of description, presence of pain, type of bleeding, confirmatory tests, and complications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views3 pagesSDL Abruptio Placenta Vs Placenta Previa
SDL Abruptio Placenta Vs Placenta Previa
Uploaded by
Vannesa TarifaThis document discusses care of mothers and children at risk. It focuses on the differences between abruptio placenta and placenta previa. While both can cause vaginal bleeding during pregnancy and labor, abruptio placenta involves premature separation of the placenta from the uterus, while placenta previa is an abnormal implantation of the placenta over the cervix. The document outlines key distinctions between the two conditions in terms of description, presence of pain, type of bleeding, confirmatory tests, and complications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
NCM 109 [Publish Date]
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY
DEPARTMENT OF NURSING
MATERNAL AND CHILD CARE NURSING – NCM-109
TOPIC: CARE OF MOTHER, CHILD AT RISK OR WITH PROBLEMS
Name: Kennedy G. Muñoz
Score: (___/19) *60 +40 = ___%
Focus: ABRUPTIO PLACENTA vs PLACENTA PREVIA
SDL Guide Questions:
1. What is common between abruptio placenta and placenta previa? (5 points)
Placental abruption (abruptio placentae) and placenta previa are two
closely related disorders that are easy to mix up even though they have very
distinct pathways, treatments, and interventions. The key point about placental
abruption is that it occurs in a placenta that was implanted normally. Abruptions
are classified from 0 to 3 based on the extent of the abruption. While placenta
previa is a condition in which the placenta has been implanted abnormally, either
near or completely covering the cervix. It is classified based on location. The
difference between placenta previa and placental abruption is that in placenta
previa, the placenta is covering all or part of your cervix. Even though the
placenta is in a complicated position, it’s still attached to your uterus. A placental
abruption is when the placenta detaches from your uterus. Therefore, both
conditions can cause vaginal bleeding during pregnancy and labor .
2. Differentiate abruptio placenta vs placenta previa. (8 points)
Abruptio Placenta Placenta Previa
Description A rare but serious A condition where the
condition of pregnancy. placenta (a temporary
Abruptio placentae is a organ that develops
premature separation of during pregnancy)
the placenta from the covers the opening of the
uterus and would need cervix. It can cause
immediate medical severe bleeding during
attention. pregnancy.
Presence of Pain It usually occurs in the Most observed
last trimester of symptoms include:
pregnancy. Symptoms - Bright red vaginal
include: bleeding without
ARLEEN E. MONTERDE RN MAN 1
NCM 109 [Publish Date]
- Vaginal bleeding pain during the
- Abdominal pain second trimester
- Symptoms of early - Uterine
labor - stomach contractions
pain, uterine - Abdominal pain
contraction, back Complications may
pain include:
- Fetal distress - Bleeding during
If not attended labor can be life-
immediately, abruptio threatening.
placentae can cause - Preterm birth as
severe complications to severe bleeding
the mother and baby. calls for an urgent
Complications that may C-section
occur to the mother
include:
- Blood loss that
requires blood
transfusion
- Kidney failure or
any other organ
failure due to
blood loss
Complications that may
occur to the baby include:
- Restricted growth-
due to lack of
enough nutrients
- Insufficient oxygen
supply
- Premature birth
- Stillbirth
Type of Bleeding Vaginal bleeding, if it Also, the type of bleeding
occurs, may be bright red is vaginal bleeding. The
or dark. A placental placenta is near or
abruption caused by covers the cervical
arterial bleeding at the opening. The greatest
center of the placenta risk of placenta previa is
leads to sudden bleeding (or
development of severe hemorrhage). Bleeding
symptoms and life- often occurs as the lower
threatening conditions part of the uterus thins
including fetal heart rate during the third trimester
abnormalities, severe of pregnancy in
maternal hemorrhage, preparation for labor.
ARLEEN E. MONTERDE RN MAN 2
NCM 109 [Publish Date]
and disseminated This causes the area of the
intravascular coagulation placenta over the cervix to
(DIC). Placental abruption bleed. The more of the
is dangerous because of placenta that covers the
the risk of uncontrolled cervical os (the opening of
bleeding (hemorrhage). the cervix), the greater the
risk for bleeding.
Confirmatory Test Diagnosis includes physical The following laboratory
examination and tests. tests are indicated in
- Physical women with suspected
examination: To placenta previa: Rh
check uterine compatibility test. levels of
tenderness or fibrin split products (FSP)
rigidity. and fibrinogen.
- Blood test: To Prothrombin time
identify possible (PT)/activated partial
sources of uterine thromboplastin time (aPTT)
bleeding. Blood type and cross; hold
- Urine test: To check for at least 4 units.
creatinine levels. Complete blood cell (CBC)
- Ultrasound: To count.
observe the placenta
and its displacement.
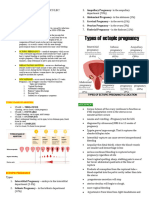
3. Using the picture on the next page, identify whether the illustration shows
abruptio placenta and placenta previa. (6 points)
A. Placenta Previa
B. Placenta Previa
C. Placenta Previa
D. Abruptio Placenta
E. Abruptio Placenta
F. Abruptio Placenta
ARLEEN E. MONTERDE RN MAN 3
You might also like
- Bleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanDocument17 pagesBleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanLizcelle Bihasa86% (7)
- Wifi Jammer: Winter Semester 2020-21 Analog Circuits Ece 2028Document10 pagesWifi Jammer: Winter Semester 2020-21 Analog Circuits Ece 2028Sathwik YadalamNo ratings yet
- Aetiology, Pathology and Management of Enterocutaneous FistulaDocument34 pagesAetiology, Pathology and Management of Enterocutaneous Fistularoselinekhadija100% (2)
- Antepartum Hemorrhage (APH) : It Is A MedicalDocument10 pagesAntepartum Hemorrhage (APH) : It Is A Medicalmed.progressNo ratings yet
- MCN NotesDocument20 pagesMCN NotesLiamLexus JavierNo ratings yet
- 2C Orev Compilation TopicDocument56 pages2C Orev Compilation TopicPaolo AntonioNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument35 pagesAntepartum HemorrhagesubashikNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Hemorrhage: HR BP Oxygen SaturationDocument4 pagesPost Partum Hemorrhage: HR BP Oxygen SaturationErjen Alexandria SiaNo ratings yet
- Maternal Midterm TransesDocument24 pagesMaternal Midterm TransesTaegyu IS SAILING Periodt.No ratings yet
- Antepartum Hemorrhage: Placental CausesDocument9 pagesAntepartum Hemorrhage: Placental CausesadiNo ratings yet
- Jose, Leana Louisse D. Cornell Notes On Ncm109 Module 1 & 2 (Complications of Pregnancy) 02/18/21 Assessment For Risk FactorsDocument19 pagesJose, Leana Louisse D. Cornell Notes On Ncm109 Module 1 & 2 (Complications of Pregnancy) 02/18/21 Assessment For Risk FactorsLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Ante Partum HemorrhageDocument21 pagesAnte Partum HemorrhagejyothinanduriNo ratings yet
- MCN 2Document7 pagesMCN 2GabNo ratings yet
- Complications of Pregnancy: Jose, Leana Louisse D. BSN 2BDocument14 pagesComplications of Pregnancy: Jose, Leana Louisse D. BSN 2BLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- Feb 19. CA 2 - 1681737641118Document9 pagesFeb 19. CA 2 - 1681737641118HANNAH BANGKILINGNo ratings yet
- Transes MidtermDocument16 pagesTranses MidtermDexter NicolasNo ratings yet
- Placenta PreviaDocument5 pagesPlacenta PreviaMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics - Antepartum HemorrhageDocument4 pagesObstetrics - Antepartum HemorrhageJonathanNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors:: Placenta Previa Lower Uterine SegmentDocument11 pagesPredisposing Factors:: Placenta Previa Lower Uterine Segmentjhachers100% (1)
- Management of Placenta Previa During PregnancyDocument5 pagesManagement of Placenta Previa During PregnancyUlayya Ghina NabillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Woman and Family Experiencing A Postpartal ComplicationDocument43 pagesNursing Care of A Woman and Family Experiencing A Postpartal ComplicationVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Haemorrhage - FinalDocument44 pagesAntepartum Haemorrhage - FinalMLV AbayNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics - Obstretical HemorrhageDocument9 pagesObstetrics - Obstretical HemorrhageJonathanNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placentae by Marzo, Cecille Joyce D.Document22 pagesAbruptio Placentae by Marzo, Cecille Joyce D.Marzo, Cecille JoyceNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument53 pagesAbruptio PlacentaEphremNo ratings yet
- Bleeding DisordersDocument20 pagesBleeding DisordersSheene Ainasthazia Diego AngNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 APH, PP, VP, AbruptioDocument55 pagesTutorial 3 APH, PP, VP, AbruptioBahirahNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Hemorrhage: Tutorial 6 Case 1Document25 pagesAntepartum Hemorrhage: Tutorial 6 Case 1deangamaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanDocument19 pagesBleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanJack BangcoyoNo ratings yet
- Uterine Inversion Uterine Rupture Amniotic Fluid Embolism MaglangitDocument6 pagesUterine Inversion Uterine Rupture Amniotic Fluid Embolism Maglangitmaglangitjoannamarie1920No ratings yet
- APHDocument40 pagesAPHJayarani AshokNo ratings yet
- Cmca2 (Prelim) 2Document16 pagesCmca2 (Prelim) 2NOEL YRIGONNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta and AbortionDocument10 pagesAbruptio Placenta and Abortiondanica grace gubaNo ratings yet
- A Low-Lying Placenta: Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Waste Products Top, Side, Front or Back of The UterusDocument3 pagesA Low-Lying Placenta: Oxygen and Nutrients Removes Waste Products Top, Side, Front or Back of The UterusFREVILYN ABASTANo ratings yet
- Midwifery 102 Module 2aDocument18 pagesMidwifery 102 Module 2aWynjoy NebresNo ratings yet
- Third Trimester: Place The Woman Immediately On Side-Lying PositionDocument7 pagesThird Trimester: Place The Woman Immediately On Side-Lying PositionZoila Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- OBDocument10 pagesOBIan Michael Romero OcampoNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 ReviewerDocument8 pagesNCM 109 ReviewerAlma Janella TOSINO100% (2)
- A 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFDocument47 pagesA 3.1 Sudden Pregnancy Complications PDFCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Abruption PlacentaDocument40 pagesAbruption Placentamruts aregawiNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Complications During Labor and Management - MoralDocument45 pagesHemorrhagic Complications During Labor and Management - MoralAngel Mae BaborNo ratings yet
- Urdaneta City University College of Health Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing ProgramDocument4 pagesUrdaneta City University College of Health Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing ProgramMary Ruth CruzNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument3 pagesAbruptio PlacentaNano KaNo ratings yet
- Lapkas Ruptur UteriDocument10 pagesLapkas Ruptur UterirandyardinalNo ratings yet
- Uterine AtonyDocument14 pagesUterine AtonyLady Jane CaguladaNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument81 pagesAntepartum HemorrhageOmar mohamedNo ratings yet
- Aph Family MedicineDocument79 pagesAph Family MedicineMohammad Nahel SorourNo ratings yet
- Chapter21trans 1Document8 pagesChapter21trans 1syroise margauxNo ratings yet
- MAHAAAAADocument17 pagesMAHAAAAAmameekasim75No ratings yet
- Placenta AccretaDocument12 pagesPlacenta AccretaNavine NavNo ratings yet
- Abnormal LabourDocument21 pagesAbnormal LabourbetablockersNo ratings yet
- Ante Partum HemorrhageDocument30 pagesAnte Partum Hemorrhagetanmai nooluNo ratings yet
- 2 Topics at RiskDocument5 pages2 Topics at RiskGeraldine PatayanNo ratings yet
- Post-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2Document6 pagesPost-Partum Hge - @medicine - Way2saeed hasan saeedNo ratings yet
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument53 pagesBleeding in Early PregnancyTemahlungwaneNo ratings yet
- 3rd Trimester BleedingDocument6 pages3rd Trimester BleedingPatrick BayuNo ratings yet
- Readings in Abruptio PlacentaDocument10 pagesReadings in Abruptio PlacentaLizabell TumlosNo ratings yet
- Article 262063-PrintDocument15 pagesArticle 262063-PrintAhsan AuliyaNo ratings yet
- Emergencies ObsDocument7 pagesEmergencies ObsAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvarian Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- It's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookFrom EverandIt's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Drug Study FormatDocument5 pagesDrug Study FormatVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Template PediaDocument20 pagesTemplate PediaVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Caisip NCM109Document3 pagesCaisip NCM109Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Endocrine Disorder AssignmentDocument7 pagesModule 10 Endocrine Disorder AssignmentVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nursing Portfolio OB WardDocument2 pages1 Nursing Portfolio OB WardVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Midterms Modx LecDocument11 pagesMidterms Modx LecVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- DUTYDUTYDocument2 pagesDUTYDUTYVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- NCP TarifaDocument12 pagesNCP TarifaVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Ob Ward EportDocument7 pagesOb Ward EportVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OR RLEDocument13 pagesDrug Study OR RLEVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- NCP Template W InferenceDocument5 pagesNCP Template W InferenceVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 High Risk Newborn 2023Document25 pagesModule 7 High Risk Newborn 2023Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Lidocaine Drug StudyDocument1 pageLidocaine Drug StudyVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Name: Allyana Bumanlag Section: NU - 202: - Global Communication, Which Is The Practice of Communication That OccursDocument2 pagesName: Allyana Bumanlag Section: NU - 202: - Global Communication, Which Is The Practice of Communication That OccursVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Tarifa, Vannesa Joy B. (NU-202) Module 5 Assignment (NCM-109)Document3 pagesTarifa, Vannesa Joy B. (NU-202) Module 5 Assignment (NCM-109)Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Nursing DXDocument1 pageNursing DXVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Tarifa, Vannesa Joy B. (NU-202) Module 6 Assignment (NCM-109)Document3 pagesTarifa, Vannesa Joy B. (NU-202) Module 6 Assignment (NCM-109)Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Micro para Laboratory Activity 4 - Case Study 2Document5 pagesMicro para Laboratory Activity 4 - Case Study 2Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- NCM109RLE TemplateDocument4 pagesNCM109RLE TemplateVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 5b Report GroupB5 NU 102Document3 pagesLaboratory Activity 5b Report GroupB5 NU 102Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- NCM109RLE TemplateDocument4 pagesNCM109RLE TemplateVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- VACCINESDocument3 pagesVACCINESVannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- Pro 3 Mplusdevipplus 07Document6 pagesPro 3 Mplusdevipplus 07daylavianNo ratings yet
- Dan Sof TG 0122Document30 pagesDan Sof TG 0122Erick Trujillo100% (1)
- URL #Flushyourmeds Scott BarryDocument8 pagesURL #Flushyourmeds Scott Barryurl-flushyourmedsNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument79 pagesPreviewpdfcrisuanNo ratings yet
- Busbar Protect1Document9 pagesBusbar Protect1syahira87No ratings yet
- PSP Assignment1Document25 pagesPSP Assignment1B BasitNo ratings yet
- 04 - Protection GeneralDocument52 pages04 - Protection GeneralRK KNo ratings yet
- Mother's Personality and Its Interaction With Child Temperament As Predictors of Parenting BehaviorDocument12 pagesMother's Personality and Its Interaction With Child Temperament As Predictors of Parenting BehaviorMichelle PajueloNo ratings yet
- Jedec Standard: Els ServiçosDocument18 pagesJedec Standard: Els ServiçosEverton LuizNo ratings yet
- CHINT Installation Operation Manual For Inverter of 50-60KTLDocument98 pagesCHINT Installation Operation Manual For Inverter of 50-60KTLr.pimentel.souzaNo ratings yet
- G10 1st PERIODICAL TEST MAPEH10 TQDocument5 pagesG10 1st PERIODICAL TEST MAPEH10 TQMaricel LajeraNo ratings yet
- Manual Spray GunDocument6 pagesManual Spray GunSyazwan KhairulNo ratings yet
- ME Lab 2 LectureDocument5 pagesME Lab 2 LectureIan Paul TongolNo ratings yet
- Lyric - Grey HuffingtonDocument371 pagesLyric - Grey HuffingtonCaptain AtomNo ratings yet
- Analise de Agua e EfluentesDocument28 pagesAnalise de Agua e EfluentesFabiano Luiz NavesNo ratings yet
- Weekly Report ExampleDocument3 pagesWeekly Report Examplewawan setiawanNo ratings yet
- Maintain Training Facilities: Submitted By: Aeron M. LumbaDocument10 pagesMaintain Training Facilities: Submitted By: Aeron M. LumbaAeron LumbaNo ratings yet
- Richard ResumeDocument5 pagesRichard ResumePiei CornerNo ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument1 pageOlanzapineKallie ChartrandNo ratings yet
- Frenkel's ExerciseDocument40 pagesFrenkel's ExerciseManiu EmeseNo ratings yet
- Cavitation Models in PIPENETDocument3 pagesCavitation Models in PIPENETSamarth PawarNo ratings yet
- Materials Chemistry A: Journal ofDocument7 pagesMaterials Chemistry A: Journal ofFamiloni LayoNo ratings yet
- CM07 Sphere ConstructionDocument146 pagesCM07 Sphere ConstructionHuy Thieu Bui100% (1)
- 2nd Quarter PHILO ReviewerDocument1 page2nd Quarter PHILO ReviewerTrisha Joy Dela Cruz80% (5)
- Stilboestrol Tablets MSDSDocument6 pagesStilboestrol Tablets MSDSIsaac lauricNo ratings yet
- Physical Education IV: (Recreation)Document28 pagesPhysical Education IV: (Recreation)Faye Corazon GaurinoNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 LM Physical Science 1 Module4Document21 pagesGrade 12 LM Physical Science 1 Module4ladyheart ۦۦNo ratings yet
- PintoDocument18 pagesPintosinagadianNo ratings yet