Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q3 S10 Week 1 Lecture or Notes
Q3 S10 Week 1 Lecture or Notes
Uploaded by
Juben OdalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Q3 S10 Week 1 Lecture or Notes
Q3 S10 Week 1 Lecture or Notes
Uploaded by
Juben OdalCopyright:
Available Formats
LECTURE/NOTES
Topic : The Role of Hormones Involved in the Female and Male Reproductive Systems
Q3-S10-Week 1
MELC: Explain the role of hormones involved in the female and male reproductive systems.
S10LT-IIIb-34
Specific Objectives: Identify the different hormones involved in the male reproductive system.
Identify the different hormones involved in the female reproductive system.
Differentiate the role/function of hormones involved in the male and female
reproductive system.
Explain the effect of hormone secretion in the development of an organism.
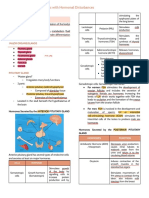
Endocrine System
-The endocrine system is composed of different glands which secrete hormones that
regulate metabolism, growth and development, mood, and reproduction.
-Hormones are organic substances released by the glands of the endocrine system
directly into the bloodstream.
-There are many types of hormones that act on different aspects of bodily
functions and processes. Some of these include:
Development and growth
Metabolism of food items
Sexual function and reproductive growth and health
Cognitive function and mood
Maintenance of body temperature and thirst
-Hormones are secreted from the endocrine glands in the body. The glands are https://www.endocrine.org/patient-engagement
ductless, so hormones are secreted directly into the blood stream rather than by way
of ducts.
GLAND LOCATION HORMONES FUNCTION
RELEASED
PITUITARY GLAND At the base Oxytocin Produces hormones that
of the brain Growth stimulate growth, and
https:// Hormones (GH) controls the functions of
Prolactin (PRL) other glands
Luteinizing Hormone
(LH)
www.ohsu.edu/sites/default/files/2020-01/pituitary-gland-anatomy.jpg
Follicle Stimulating
Hormone (FSH)
Adrenocorticotrophic
hormone (ACTH)
Antidiuretic
hormone (AH)
Thyroid Stimulating
Hormone (TSH)
THYROID In front of Thyroxin, Calcitonin Produces hormones that
https://
the neck and regulate body metabolism,
below the and storage of calcium in
voice box bones
kidshealth.org/en/kids/thyroid.html
PARATHYROID In the neck Parathyromone Produces hormones that
https://
control the calcium levels
in your body, and
normalizes bone growth.
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroid_gland#/media/File:Illu_thyroid_parathyroid.jpg
OP/STC
(02) 8292-7380 / (02) 8293-9850 fax
gtdlnhs2007@gmail.com
w www.gtdlnhs.wordpress.com
THYMUS In front of Thymosin Produces hormones that
the heart enable the body to produce
antibodies-
T cells
https://microbenotes.com/thymus-gland/
ADRENAL On top of Adrenaline Produces hormones that
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
Adrenal_gland#/media/
File:Illu_adrenal_gland.jpg the kidneys affects metabolism,
immune system and blood
pressure, stress reaction
PANCREAS Behind the Insulin, Glucagon Produce hormones that
stomach regulate blood sugar levels.
https://api.kramesstaywell.com/Content/ebd5aa86-5c85-
4a95-a92a-a524015ce556/ucr-images-v1/Images/
illustration-of--the-anatomy-of-the-pancreas-125548
REPRODUCTIVE:
TESTES(MALE) Lower Abdomen Testosterone, Produces hormones that
https:// Androgen control maturation of
sperm and development of
the secondary male sexual
characteristics.
www.endocrine.org/patient-engagement
OVARIES(FEMALE)
https://
Produces hormones that
Lower Abdomen Progesterone influence development of
Estrogen the secondary female
sexual characteristics, and
www.endocrine.org/patient-engagement maturation of the egg cells
and ovulation.
Reproductive System
-The Reproductive System is a collection of organs in an organism that
function together for sexual reproduction.
-The Sex hormones are responsible for driving sexual development
(puberty). The main reproductive hormones are estrogen and testosterone.
-Puberty is a term used to described developmental changes a child
undergoes to become sexually mature and physiologically ready for
reproduction. It normally begins between the ages of 8 – 14 in females and
between the ages of 10-16 in males.
When does puberty starts? And what are the different endocrine glands
that are involve in this changes? https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/assets/images/reproductive_health2.jpg
-Hypothalamus is a small region of the brain. It is located at the base of the
brain near the pituitary gland.
-Puberty begins when the hypothalamus starts to release GONADOTROPIN-
RELEASING HORMONE (GnRH) and travels to the Pituitary gland.
-Pituitary gland is a small gland under the brain that produces hormones that
control other glands in the body.
OP/STC
(02) 8292-7380 / (02) 8293-9850 fax
gtdlnhs2007@gmail.com
w www.gtdlnhs.wordpress.com
-GnRH (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone) is a responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and
luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary.
-Luteinizing Hormone and Follicle Stimulating Hormone acts on the primary reproductive organs OVARIES in female
and TESTES in male.
Male Reproductive System
https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/male-repro.html
The Role of Hormones in Male Reproductive Systems
• GnRH (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone) is a trophic peptide hormone responsible for the release of follicle-
stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary.
• LH (Luteinizing hormone) is produced by the anterior pituitary gland and in males causes the synthesis and
secretion of testosterone and androgen.
• FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) stimulates testicular growth and enhances the production of Androgen.
• ANDROGENS are the group of sex hormones that give men their 'male' characteristics. It regulates the
development and maintenance of male characteristics.
• TESTOSTERONE affects a man’s appearance and sexual development. It stimulates sperm production as well as
a man’s sex drive.
The Hormonal Regulation in Male Reproductive Systems
At the onset of puberty, the
hypothalamus begins secreting high
pulses of GnRH, or gonadotropin-
releasing hormone.
In response pituitary gland releases
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and
luteinizing hormone (LH).
As the FSH enters the testes, it
stimulates the Sertoli cells that are
responsible for nourishing the sperm
cells that the testes produce to facilitate
the process of sperm production.
OP/STC
(02) 8292-7380 / (02) 8293-9850 fax
gtdlnhs2007@gmail.com
w www.gtdlnhs.wordpress.com
Also, LH enters the testes to stimulate the interstitial cells called the Leydig cells to make and release
testosterone into the testes and the blood.
The hormone testosterone is responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics and
stimulates the process of sperm production in the testes.
Female Reproductive System
FUNCTIONS OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM:
1. Produces female sex cells.
2. Receives sperm cells from the male.
3. Nurtures the development of and provides
nourishment for the new individual.
Prepared by :
DONNA MARIE P. SABALZA
Science 10 Teacher/MT I
https://www.everydayhealth.com/sexual-health/
female-reproductive-organs.aspx
The Role of Hormones in Female
Reproductive Systems
• GnRH (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone) is a trophic peptide hormone responsible for the release of follicle-
stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary.
• LH (Luteinizing hormone) stimulates Estrogen and Progesterone production from the ovary.
• FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) stimulates the development/maturation of egg cells, called ova.
• ESTROGEN is responsible for female reproduction and the secondary sexual characteristics.
• PROGESTERONE helps prepare the female body for conception and pregnancy. It triggers the lining of the
uterus to thicken to accept a fertilized egg and regulate the monthly menstrual cycle.
The Hormonal Regulation in Female Reproductive Systems
The hypothalamus begins secreting high pulses
of GnRH, or gonadotropin-releasing hormone.
FSH stimulates the development of egg cells,
called ova, which develop in structures called
follicles.
Follicle cells produce the hormone inhibin,
which inhibits FSH production.
LH also plays a role in the development of ova,
as well as in the induction of ovulation and
stimulation of estrogen and progesterone
production by the ovaries.
Estrogen and progesterone are steroid
hormones that prepare the body for pregnancy.
Estrogen is the reproductive hormone in
females that assists in endometrial regrowth,
ovulation, and calcium absorption; it is also
responsible for the secondary sexual
characteristics of females. These include breast
development, flaring of the hips, and a shorter
period necessary for bone maturation.
Progesterone assists in endometrial re-growth
and inhibition of FSH and LH release.
References: https://slideplayer.com/slide/5215015/
OP/STC
(02) 8292-7380 / (02) 8293-9850 fax
gtdlnhs2007@gmail.com
w www.gtdlnhs.wordpress.com
• Science 10 Learner’s Material Unit 3 Living Things and Their Environment pp.241
• https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/endocrine.html#:~:text=Endocrine%20glands%20release%20hormones
%20into,of%20each%20hormone%20is%20released.
• https://slideplayer.com/slide/5215015/
• http https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-are-Hormones.aspx
• https://med.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Anatomy_and_Physiology/Book
%3A_Anatomy_and_Physiology_(Boundless)/26%3A_The_Reproductive_System/
26.4%3A_Physiology_of_the_Male_Reproductive_System/26.4E
%3A_Hormonal_Regulation_of_the_Male_Reproductive_System
• https://youtu.be/mLPPC-ujI2U
• https://slideplayer.com/slide/3858308
OP/STC
(02) 8292-7380 / (02) 8293-9850 fax
gtdlnhs2007@gmail.com
w www.gtdlnhs.wordpress.com
You might also like
- Medical Terminology in A FLASH!Document66 pagesMedical Terminology in A FLASH!Martha Herr88% (16)
- 3rd Quarter Science Module 1Document13 pages3rd Quarter Science Module 1Vincq100% (2)
- Ch.1 Quiz ADocument1,055 pagesCh.1 Quiz ASultan AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- 3 +endocrine+systemDocument41 pages3 +endocrine+systemDew JirawatNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Q3 Mod1 The Endocrine System Glands and Their HormonesDocument3 pagesSci10 Q3 Mod1 The Endocrine System Glands and Their Hormonestomman warmanNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY HahaDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY Hahagbs040479No ratings yet
- ENDOCRIONOLOGYDocument15 pagesENDOCRIONOLOGYmoepiNo ratings yet
- 5M: Care of Clients With Hormonal Disturbances: Endocrine SystemDocument19 pages5M: Care of Clients With Hormonal Disturbances: Endocrine SystemEmmanuelle Soroño AmoresNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument2 pagesControl and Coordinationcoolsk2580No ratings yet
- 19 Hormones and Homeostasis NotesDocument7 pages19 Hormones and Homeostasis NotesHabeeb AL-AbsiNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesWeek 5 Endocrine SystemJiro MarianoNo ratings yet
- To Print Cut and Paste Add Photos To TabbbleleleDocument5 pagesTo Print Cut and Paste Add Photos To TabbbleleleRimaHimeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument26 pagesEndocrine SystemMichel Jay Arguelles EspulgarNo ratings yet
- Q3 Activity 2 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesQ3 Activity 2 Endocrine Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- Local Media2182658933713495317Document129 pagesLocal Media2182658933713495317JAYMAYMA ELGARIONo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKAUSTUBH SAWANTNo ratings yet
- 15a Test Yourself EndocrineDocument7 pages15a Test Yourself Endocrinestar lightNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesGr10 Endocrine SystemDomuNo ratings yet
- Topic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesDocument18 pagesTopic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesHaris AliNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine Systemadrianacasanov199No ratings yet
- Ing - Sistem EndokrinDocument9 pagesIng - Sistem EndokrinWarman PurbaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jan 13, 2024Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Jan 13, 2024Abhijeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemIvy Jana BelenNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3Document4 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument12 pagesEndocrine GlandMikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- CA 2 MOD 10 - Endocrine Disorders 2022-2023 PDFDocument16 pagesCA 2 MOD 10 - Endocrine Disorders 2022-2023 PDFAyen PaloNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Assistant Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesLab Report Assistant Endocrine SystemJohn Louis AguilaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System and Endocrine GlandsDocument7 pagesEndocrine System and Endocrine GlandsMr.VivStarNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument29 pagesHormonesCandy Chieng67% (3)
- Chapter 11 - HormonesDocument8 pagesChapter 11 - Hormonesbussniesm05No ratings yet
- Biochemistry of HormonesDocument26 pagesBiochemistry of HormonesZayan Haider0% (1)
- Anatomy of The Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine SystemMesum Jutt100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemcjhundaleNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument8 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYshaairatogleNo ratings yet
- Describe Hormones and Their CompositionDocument7 pagesDescribe Hormones and Their CompositionShahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 DiplomaDocument6 pagesLec 1 DiplomaEman saadiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezDocument144 pagesEndocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezTrixie Rose Ebona CortezNo ratings yet
- Pathology Tests ExplainedDocument4 pagesPathology Tests ExplainedFabiola Fuentes RomeroNo ratings yet
- TICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 15Document14 pagesTICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 15Abram TicmanNo ratings yet
- Unit IXDocument10 pagesUnit IXPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDocument10 pagesEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Endocrine System: EquilibriumDocument20 pagesFunctions of The Endocrine System: EquilibriumKumah WisdomNo ratings yet
- Bio ReportDocument4 pagesBio ReportKate MabanagNo ratings yet
- Unit2-Hypothalamus and PituitaryDocument80 pagesUnit2-Hypothalamus and Pituitarypranutan739No ratings yet
- Thyrotropin-Releasing HormoneDocument8 pagesThyrotropin-Releasing HormoneBhagyaNo ratings yet
- 10SUMMARYENDOCRINESYSTEMDocument14 pages10SUMMARYENDOCRINESYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- 102 Hormon and Enzym MechanismDocument31 pages102 Hormon and Enzym MechanismTIARA CAHYA RINUKTINo ratings yet
- Notes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemAlven ReyNo ratings yet
- Glands Hormones Description of Hormones Diseases: HypothalamusDocument3 pagesGlands Hormones Description of Hormones Diseases: HypothalamusLouise BernardoNo ratings yet
- Pages 152 Physiological Psychology HormonesDocument7 pagesPages 152 Physiological Psychology HormonesLei CorralesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument19 pagesEndocrine Systemethel roseNo ratings yet
- Term Paper : Isabela State UniversityDocument9 pagesTerm Paper : Isabela State UniversityFlor SagnipNo ratings yet
- Endocrine in Animals (CBSE)Document3 pagesEndocrine in Animals (CBSE)Ashwani GahlotNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument32 pagesEndocrine PhysiologyAziem ShazwanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesEndocrine SystemEdsel Ian S. FuentesNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIDocument9 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFDocument17 pagesThe Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFStephanie Kate PelenioNo ratings yet
- Lesson (2) Endocrine SystemDocument29 pagesLesson (2) Endocrine SystemClapZ karimNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ResonanceDocument51 pagesEndocrine ResonanceEkta ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument56 pagesEndocrine SystemNoreen BengoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesEndocrine Anatomy and PhysiologyJojo JustoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandEndocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Triple IIIDocument1 pageTriple IIIJuben OdalNo ratings yet
- Paper For Seminar in Research Writing Frances E. Odal July 2022Document50 pagesPaper For Seminar in Research Writing Frances E. Odal July 2022Juben OdalNo ratings yet
- LITERATURE REVIEW-Biblical Implication of The Theology of Predestination and It's Impact in Discipleship and EvangelismDocument4 pagesLITERATURE REVIEW-Biblical Implication of The Theology of Predestination and It's Impact in Discipleship and EvangelismJuben OdalNo ratings yet
- Triple IDocument1 pageTriple IJuben OdalNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument1 pageDefinitionJuben OdalNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Summative Test ReviewerDocument4 pages3rd Quarter Summative Test ReviewerJuben OdalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Earth As A SystemDocument22 pagesLesson 2 - Earth As A SystemJuben OdalNo ratings yet
- When Did You Start Your BusinessDocument1 pageWhen Did You Start Your BusinessJuben OdalNo ratings yet
- 30 Day Meal PlanDocument1 page30 Day Meal PlanJuben OdalNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury: Mark BevanDocument42 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: Mark BevannasimhsNo ratings yet
- Concentration of Urine: Maj DR Shavana R.L RanaDocument22 pagesConcentration of Urine: Maj DR Shavana R.L RanaChandan Sah100% (1)
- Skenario A Blok 17 L3 FixDocument35 pagesSkenario A Blok 17 L3 FixSelli Novita BelindaNo ratings yet
- Transportation in AnimalsDocument6 pagesTransportation in AnimalskrovrainkNo ratings yet
- Clinical Hematology Atlas (PK 1) (03-04)Document2 pagesClinical Hematology Atlas (PK 1) (03-04)maryano 0015No ratings yet
- Describe The Process of Urine Formation in Our BodyDocument3 pagesDescribe The Process of Urine Formation in Our BodySamia TazinNo ratings yet
- 9 Intravenous TherapyDocument23 pages9 Intravenous TherapyKareem Mae Pines RaborNo ratings yet
- BT ReactionDocument8 pagesBT ReactionMary Elijah Jane PopesNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of The NewbornDocument36 pagesPhysical Examination of The NewbornKaren Joyce TribianaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 SCIENCE: © Boardworks LTD 2004Document20 pagesGrade 10 SCIENCE: © Boardworks LTD 2004Modesto Valdriz100% (1)
- Mixed Lymphocyte Culture / Reaction (MLC / MLR)Document2 pagesMixed Lymphocyte Culture / Reaction (MLC / MLR)Muthi KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Relapse Versus Natural DevelopmentDocument2 pagesOrthodontic Relapse Versus Natural DevelopmentCatherine NocuaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: MSN 4006 Advanced PsychopathophysiologyDocument15 pagesEndocrine System: MSN 4006 Advanced Psychopathophysiologybane1925No ratings yet
- BSC MLT Syllabus 2020 - SeptemberDocument70 pagesBSC MLT Syllabus 2020 - SeptemberDani DanyNo ratings yet
- Biology 11 - Cardiovascular System True/False Intro Activity (With Answers)Document2 pagesBiology 11 - Cardiovascular System True/False Intro Activity (With Answers)ascd_msvuNo ratings yet
- Topic: References:: 2 Quarter: 6 - 7 Week For Science 6 Lesson 7: The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesTopic: References:: 2 Quarter: 6 - 7 Week For Science 6 Lesson 7: The Nervous SystemNovelhyne DomerezNo ratings yet
- Bell 1977Document28 pagesBell 1977Reshma DeepakNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument70 pagesLymphatic SystemNang Maizana Megat Yahya100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal: Metastatic Melanoma of The TractDocument5 pagesGastrointestinal: Metastatic Melanoma of The TractCristi PopescuNo ratings yet
- Sense of TasteDocument1 pageSense of TasteSesang J SalibadNo ratings yet
- 50 MCQ For P&he 2019 Part 1#1t3Document3 pages50 MCQ For P&he 2019 Part 1#1t3Prem VeerNo ratings yet
- Water Regulation - Indd - OsmosisDocument7 pagesWater Regulation - Indd - OsmosisRishi Raj NRNo ratings yet
- MICU Case Study PresentationDocument55 pagesMICU Case Study Presentationjmarc_21100% (4)
- Hormones:: Signaling MoleculesDocument20 pagesHormones:: Signaling MoleculesSangeeta DwivediNo ratings yet
- Bio 342Document76 pagesBio 342Steph VeeNo ratings yet
- A Pair For The Impaired - Orthodontic and Surgical Combination Treatment of Skeletal Class III Malocclusion: A Two Year Follow UpDocument9 pagesA Pair For The Impaired - Orthodontic and Surgical Combination Treatment of Skeletal Class III Malocclusion: A Two Year Follow UprohitNo ratings yet
- Way To English 4 Unit Seven Part of The BodyDocument2 pagesWay To English 4 Unit Seven Part of The BodyAnonymous LNyFXSMNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument11 pagesUntitled Presentationapi-421863070No ratings yet