Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BN 72 فوزي عبد الجواد فوزي R4
BN 72 فوزي عبد الجواد فوزي R4
Uploaded by
Fawzy Abd AlgawadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BN 72 فوزي عبد الجواد فوزي R4
BN 72 فوزي عبد الجواد فوزي R4
Uploaded by
Fawzy Abd AlgawadCopyright:
Available Formats
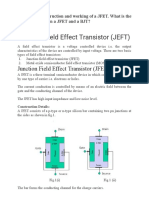
1-Polarity:
BJT: BJT is a bipolar device, which means it operates with both types of charge carriers, i.e., electrons
and holes.
FET: FET is a unipolar device, which means it operates with either electrons or holes, depending on the
type of FET.
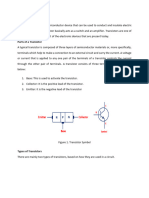
2-How the transistor (current source) is controlled:
BJT: BJT is a current-controlled device, which means its output current is controlled by the input current
applied to the base-emitter junction.
FET: FET is a voltage-controlled device, which means its output current is controlled by the voltage
applied to the gate.
3-Linearity of the device:
BJT: BJT has a high linearity, which means it is suitable for applications where the output signal needs to
be an amplified replica of the input signal.
FET: FET has a lower linearity compared to BJT, which makes it suitable for applications where non-
linearity is acceptable, such as in digital circuits.
4-Input impedance:
BJT: BJT has a low input impedance, which means it requires a significant input current to drive it.
FET: FET has a high input impedance, which means it requires a low input current to drive it.
5-Fabrication simplicity:
BJT: BJT is more complex to fabricate due to its three-layer structure and the requirement of precise
doping of each layer.
FET: FET is simpler to fabricate compared to BJT as it requires only one type of doping and a thin
insulating layer.
You might also like
- FET and BJTDocument7 pagesFET and BJTshaik usmanganiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 0 - Điện tử tương tự I: 1. BJT and FETDocument6 pagesAssignment 0 - Điện tử tương tự I: 1. BJT and FETQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics - Types of Transistors - PHY212DDocument4 pagesBasic Electronics - Types of Transistors - PHY212Dtprince2018No ratings yet
- Impedence Is High Compared Then BJT - Jfet Is Voltage Driven DeviceDocument1 pageImpedence Is High Compared Then BJT - Jfet Is Voltage Driven Devicemshweta_44944984No ratings yet
- Difference Between BJT and FETDocument4 pagesDifference Between BJT and FETabdelrhmanmu4No ratings yet
- TransistorDocument4 pagesTransistorcomputer tricksNo ratings yet
- Know The Major Difference Between BJT and FETDocument11 pagesKnow The Major Difference Between BJT and FETabraham kaseyaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between BJT and FETDocument2 pagesDifference Between BJT and FETkanwaljiaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between BJT and FETDocument4 pagesDifference Between BJT and FETdchouhan72004No ratings yet
- (Done) Compare and Contrast The FET With The BJTDocument8 pages(Done) Compare and Contrast The FET With The BJTexe.dave.qNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document46 pagesChapter 2raju chandanshiveNo ratings yet
- Draw Symbol of FET Name The Terminals.: FET Has Several Advantages Over BJTDocument4 pagesDraw Symbol of FET Name The Terminals.: FET Has Several Advantages Over BJTY RAMANJANEYULUNo ratings yet
- The First TransistorDocument14 pagesThe First TransistorWaqad Hashmi100% (1)
- Field Effect Transistor (FET)Document2 pagesField Effect Transistor (FET)darren mayorNo ratings yet
- Construction and Working of A JFETDocument6 pagesConstruction and Working of A JFETSatish Mali100% (1)
- Differences Between BJT and FETDocument2 pagesDifferences Between BJT and FETJESSYLLNNo ratings yet
- EEE 202 Lecture Note On TransistorDocument7 pagesEEE 202 Lecture Note On Transistoralexapierre08No ratings yet
- Mosfet: Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor Is Abbreviated As MOSFET. It Is Merely A UnipolarDocument6 pagesMosfet: Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor Is Abbreviated As MOSFET. It Is Merely A UnipolarJade JoseNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - L-3-4 - Introduction To BJT and FETDocument13 pagesUnit-1 - L-3-4 - Introduction To BJT and FETwebip33713No ratings yet
- IGBT NoteDocument3 pagesIGBT NoteBheshNo ratings yet
- JFET NotesDocument83 pagesJFET Notessheela lNo ratings yet
- FET SmallDocument1 pageFET Smallajayiitm05No ratings yet
- MOSFET CircuitDocument9 pagesMOSFET CircuitMahmoud SherifNo ratings yet
- Ee 211 Chapter 3Document19 pagesEe 211 Chapter 3RickNo ratings yet
- Analouge JFETDocument1 pageAnalouge JFETAfiq AbidinNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorXhaNo ratings yet
- ECE 027 - Module 3 - Introduction of Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Document58 pagesECE 027 - Module 3 - Introduction of Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Miyuki NakiriNo ratings yet
- Jamaica Naz Online Worksheet - Laboratory 6 Part 2Document3 pagesJamaica Naz Online Worksheet - Laboratory 6 Part 2Koji OdoNo ratings yet
- Electronics IIDocument11 pagesElectronics IIABATAN OLATUNDENo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between BJT and FET TransistorsDocument16 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between BJT and FET TransistorsgezahegnNo ratings yet
- Basic Study of Jfet. (Paper)Document3 pagesBasic Study of Jfet. (Paper)Manish DebnathNo ratings yet
- Change Sonam BawaDocument6 pagesChange Sonam BawaSunny BediNo ratings yet
- Field Effect Transistors: Field Effect Transistor Is A Semiconductor Device Which Depends On Electric Field For ItsDocument34 pagesField Effect Transistors: Field Effect Transistor Is A Semiconductor Device Which Depends On Electric Field For ItsSivagami AmmuNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Circuits: UNIT-4Document22 pagesElectronic Devices & Circuits: UNIT-40fficial SidharthaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document28 pagesLecture 102019n00984No ratings yet
- The Igbt Is A Power Switching Transistor Which Combines The Advantages of Mosfets and Bjts For Use in Power Supply and Motor Control CircuitsDocument6 pagesThe Igbt Is A Power Switching Transistor Which Combines The Advantages of Mosfets and Bjts For Use in Power Supply and Motor Control CircuitsAsha DurafeNo ratings yet
- Phy210 Notes-2Document8 pagesPhy210 Notes-2Praise AribisalaNo ratings yet
- Junction Field Effect Transistors Field Effect TransistorsDocument22 pagesJunction Field Effect Transistors Field Effect TransistorsderejeNo ratings yet
- Project FileDocument74 pagesProject Filevinaysnair89100% (1)
- ECEN 60 - Lesson 1Document10 pagesECEN 60 - Lesson 1Jaime-Nemilyn Ati-id FadcharNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices: 2 Marks 1. Define The Term Hybrid ParametersDocument4 pagesElectronic Devices: 2 Marks 1. Define The Term Hybrid ParametersMahendra BabuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Semiconductor Devices and Circuits: JFET and MOSFETDocument25 pagesLecture Notes For Semiconductor Devices and Circuits: JFET and MOSFETdevashri gaurkedeNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsnaidooriNo ratings yet
- Bab 3-bjtDocument80 pagesBab 3-bjtNoor Hanisah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Notes Module2 (FET Part) Basic Electronics 22BBEE203Document12 pagesNotes Module2 (FET Part) Basic Electronics 22BBEE203Hani MNo ratings yet
- GRP 6Document10 pagesGRP 6JOYPRAKASH GHOSHNo ratings yet
- BJT IntroductionDocument4 pagesBJT IntroductionMr KNo ratings yet
- NPN Transistor TemplateDocument4 pagesNPN Transistor Templateuser.rony302No ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument19 pagesTransistorsEunice NuñezNo ratings yet
- AE Unit - 2Document13 pagesAE Unit - 2aamirnasirNo ratings yet
- sd_jfet_1Document125 pagessd_jfet_1sanjeevkumarsudhanshu345No ratings yet
- Suitable Power Semi Conductor Device What Is SemiconductorDocument4 pagesSuitable Power Semi Conductor Device What Is SemiconductorSubhajit RoyNo ratings yet
- Insulated Gate Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesInsulated Gate Bipolar TransistorTuhin ShahNo ratings yet
- 5.introduction To JFETDocument22 pages5.introduction To JFETGowshalya PerinbanayakamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FET-Field Effect TransistorDocument2 pagesIntroduction To FET-Field Effect TransistorRushikesh TrimbakeNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument2 pagesTransistorSOR SOTYNo ratings yet
- BEE (R-20) : Parameters Half-Wave Rectifiers Full-Wave RectifiersDocument4 pagesBEE (R-20) : Parameters Half-Wave Rectifiers Full-Wave Rectifierssurya pratapNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsJoão CorreiaNo ratings yet
- Insulated Gate Bipolar TransistorDocument4 pagesInsulated Gate Bipolar TransistorVignesh GuruNo ratings yet
- Dialux SortcutDocument2 pagesDialux SortcutFawzy Abd AlgawadNo ratings yet
- Bn 72 فوزي عبدالجواد فوزي R 2 PDFDocument3 pagesBn 72 فوزي عبدالجواد فوزي R 2 PDFFawzy Abd AlgawadNo ratings yet
- Bn 72 فوزي عبدالجواد فوزي R1Document2 pagesBn 72 فوزي عبدالجواد فوزي R1Fawzy Abd AlgawadNo ratings yet
- Skin EffectDocument5 pagesSkin EffectFawzy Abd AlgawadNo ratings yet