Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nuclear Power Plant: Definition: The Power Plant That Is Used To Warm The Water To
Nuclear Power Plant: Definition: The Power Plant That Is Used To Warm The Water To
Uploaded by
Yash SoniCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Renewable Energy Sources - Wind, Solar and Hydro Energy Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandRenewable Energy Sources - Wind, Solar and Hydro Energy Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksNo ratings yet
- Powerplant EngineeringDocument12 pagesPowerplant EngineeringBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- Types of Power PlantDocument12 pagesTypes of Power PlantJonaz CruzNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 BcmeDocument21 pagesUnit-3 BcmeBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 3 BCME FinalDocument26 pagesUNIT - 3 BCME FinalAnith Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Power Plants in India and Abroad.: Siddhant Yadav RA1911026010043 Waste To Wealth To Wheels AssignmentDocument5 pagesDifferent Types of Power Plants in India and Abroad.: Siddhant Yadav RA1911026010043 Waste To Wealth To Wheels AssignmentSiddhant YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Ch6602 Energy Engineering Hydro Electric Power PlantDocument10 pagesUnit Ii Ch6602 Energy Engineering Hydro Electric Power PlantSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- What Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Document3 pagesWhat Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Rahul GhoshNo ratings yet
- Operation of A Nuclear Power PlantDocument8 pagesOperation of A Nuclear Power PlantMuhamad FaizNo ratings yet
- Ch-4-Nuclear EnergyDocument5 pagesCh-4-Nuclear Energysayyohabba2021No ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument22 pagesNuclear Power PlantMuhammad Ahkam KhanNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50Document3 pagesEnergy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50pagal noobNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument6 pagesPower PlantsyogusmiluNo ratings yet
- NuclearDocument49 pagesNuclearA ABHISHEK MARSHALLNo ratings yet
- BVRIT HYDERABAD College of Engineering For WomenDocument10 pagesBVRIT HYDERABAD College of Engineering For WomenChetan GuliaNo ratings yet
- Types of Power PlantsDocument8 pagesTypes of Power PlantsAdhanom G.No ratings yet
- Energy Tech UNIT 2Document53 pagesEnergy Tech UNIT 2Dhaksha AnieshNo ratings yet
- Various Plants Used For Generation of Electric Power Hydroelectric, Nuclear and Thermal Energy Plants Parts & WorkingDocument6 pagesVarious Plants Used For Generation of Electric Power Hydroelectric, Nuclear and Thermal Energy Plants Parts & WorkingWilson Fuentes100% (1)
- Nuclear Power Plant ReportDocument9 pagesNuclear Power Plant ReportJIL IbaanNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument20 pagesPower Plantsjvharsha.sNo ratings yet
- Battery DC Generator Electric Power Voltage: NextDocument13 pagesBattery DC Generator Electric Power Voltage: NextHussam GujjarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantsDocument24 pagesThermal Power Plantslakshmigsr6610100% (1)
- REPORT On Power Plants and Electric Transmission196035Document11 pagesREPORT On Power Plants and Electric Transmission196035Rohit SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PowerplantDocument5 pagesNuclear PowerplantAri HariNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument7 pagesNuclear Power PlantzzaanNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report at Atomic Power Station, RawatbhataDocument40 pagesSummer Training Report at Atomic Power Station, RawatbhataKrishan Pal Sila100% (2)
- Power System by PawanDocument20 pagesPower System by PawanPäwän Kümär MäüryäNo ratings yet
- Notes Power Plant EngineeringDocument8 pagesNotes Power Plant EngineeringDeepo Varinder MaandleyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurDocument27 pagesNuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurNikhil ChopraNo ratings yet
- Power Plants Part-1Document9 pagesPower Plants Part-1Mukesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument30 pagesSteam Power PlantIAN MIGOTNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument25 pagesPower Plant EngineeringlitonNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mechanical Engineering: "The Journey of A Thousand Miles Begins With A Single Step."Document56 pagesBasics of Mechanical Engineering: "The Journey of A Thousand Miles Begins With A Single Step."Pushparaj ManickamNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant: Department of Mechanical Engineering, GCE, RamanagaraDocument143 pagesSteam Power Plant: Department of Mechanical Engineering, GCE, RamanagaraSrikanth Kabbal MNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power StationDocument4 pagesNuclear Power StationAnjo PepitoNo ratings yet
- "Thermal Power Generation": Seminar Report OnDocument10 pages"Thermal Power Generation": Seminar Report OnAram Nasih MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Colour)Document44 pagesPower Plant Colour)Er Anoop GuptaNo ratings yet
- L 03 - Ece 4109Document26 pagesL 03 - Ece 4109reza prantickNo ratings yet
- Mani Report 1Document53 pagesMani Report 1Mani MukatiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Nuclear Power PlantADocument13 pagesAssignment On Nuclear Power PlantAtheunsung tale100% (1)
- Types of Power Plant and Their Working PrinciplesDocument11 pagesTypes of Power Plant and Their Working PrinciplesRamzi JamalNo ratings yet
- Assignments: Ahmed Ali AlazmoniDocument39 pagesAssignments: Ahmed Ali Alazmonihazem tebineNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument13 pagesNuclear Power PlantlintangellaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 1999926643798667794Document10 pagesInbound 1999926643798667794bvcxd7m4j4No ratings yet
- Energy Management Module IDocument18 pagesEnergy Management Module ISalikNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument9 pagesSteam Power PlantAnne Gabrielle DavidNo ratings yet
- e Content Electrical Power IDocument185 pagese Content Electrical Power Igkulkarni298No ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument20 pagesSteam Power PlantSiddi Sampath Kumar Reddy100% (1)
- Project ReportDocument103 pagesProject ReportSeth CamachoNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 BPPE NotesDocument22 pagesUnit-3 BPPE Notes20WH1A0557 KASHETTY DEEKSHITHANo ratings yet
- 1) Conventional - Non Renewable Power GenerationDocument49 pages1) Conventional - Non Renewable Power GenerationManmit SalunkeNo ratings yet
- Types of Power Plants - 2018 PDFDocument71 pagesTypes of Power Plants - 2018 PDFJeff Justine GeragaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteDocument15 pagesNuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteRonald Andrei DaguioNo ratings yet
- EE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationDocument62 pagesEE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationKarthikeyan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About ItDocument7 pagesThermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About Itngoc hoangNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant (PLTU)Document5 pagesSteam Power Plant (PLTU)Aldi Erzanuari100% (1)
- Thermal Power Generation Full Seminar Report 74537Document23 pagesThermal Power Generation Full Seminar Report 74537Umang Vyas88% (8)
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 02-May-2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 02-May-2023Yash SoniNo ratings yet
- White Simple Student CV ResumeDocument1 pageWhite Simple Student CV ResumeYash SoniNo ratings yet
- Student CVDocument1 pageStudent CVYash SoniNo ratings yet
- DiplomaDocument1 pageDiplomaYash SoniNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Air ConditioningDocument6 pagesRefrigeration & Air ConditioningYash SoniNo ratings yet
Nuclear Power Plant: Definition: The Power Plant That Is Used To Warm The Water To
Nuclear Power Plant: Definition: The Power Plant That Is Used To Warm The Water To
Uploaded by
Yash SoniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nuclear Power Plant: Definition: The Power Plant That Is Used To Warm The Water To
Nuclear Power Plant: Definition: The Power Plant That Is Used To Warm The Water To
Uploaded by
Yash SoniCopyright:
Available Formats
Nuclear Power Plant
Definition: The power plant that is used to warm the water to
generate steam, then this steam can be used for rotating huge turbines
for generating electricity. These plants use the heat to warm the water
which is generated by nuclear fission. So the atoms in the nuclear
fission will split into different smaller atoms for generating energy.
Nuclear Power Plant Working Principle
In the power plant, the fission takes place in the reactor and the middle
of the reactor is known as the core that includes uranium fuel, and this
can be formed into pellets of ceramic. Every pellet generates 150
gallons of oil energy. The total energy generated from the pellets is
stacked in metal fuel rods. A bunch of these rods is known as a fuel
assembly and a reactor core includes several fuel assemblies
During nuclear fission, the heat can be generated within the core of the
reactor. This heat can be used to warm the water into steam so that
turbine blades can be activated. Once the turbine blades activated then
they drive the generators to make electricity. In a power plant, a cooling
tower is available to cool the steam into the water otherwise they use
the water from different resources. Finally, the cooled water can be
reused to generate steam.
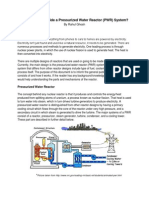
Components of Nuclear Power Plant
In the above nuclear power plant block diagram, there are different
components which include the following.
Nuclear Reactor
In a power plant, a nuclear reactor is an essential component like a heat
source that includes the fuel & its reaction of nuclear chain including the
waste products of nuclear. The nuclear fuel used in the nuclear reactor
is Uranium & its reactions are heat generated in a reactor. Then, this
heat can be transferred to the coolant of the reactor to generate heat to
all the parts in the power plant.
There are different types of nuclear reactors that are used in the
manufacturing of plutonium, ships, satellites & aircraft for research as
well as medical purposes. The power plant includes not only includes
the reactor and also includes turbines, generators, cooling towers, a
variety of safety systems.
Steam Generation
In all the power plants, the production of steam is general; however, the
way of generating will change. Most of the plants use water reactors by
using two loops of rotating water to generate steam. The primary loop
carries very hot water for heating an exchange once water at a low-
pressure is circulated, then it warms the water to generate the steam to
transmit to the turbine section.
Generator & Turbine
Once the steam is generated, then it travels with high pressures to
speed up the turbine. The rotating of the turbines can be used to rotate
an electric generator for generating electricity that is transmitted to the
electrical grid.
components, construction & applications
Working of Nuclear Power Plant
The elements like Uranium or Thorium are sued nuclear fission reaction
of a nuclear reactor. Because of this fission, a huge amount of heat
energy can be generated and it is transmitted to the coolant reactor.
Here, the coolant is nothing but water, liquid metal otherwise gas. The
water is heated to flow in a heat exchanger so that it changes into high-
temperature steam. Then the steam which is produced is permitted to
make a steam turbine run. Again the steam can be changed back into
the coolant & recycled to use for the heat exchanger. So, the turbine
and alternator are connected to produce electricity. By using a
transformer, the electricity which is produced can be increased to use in
long-distance communication.
The Efficiency of the Nuclear Power Plant
The nuclear power plant efficiency can be decided equally to other heat
engines because technically the plant is a large heat engine. The sum of
electric power generated for every unit of thermal power will provide the
plant is thermal efficiency & because of the thermodynamics second
law, there is a higher limit to how efficient these power plants can be.
The normal nuclear power plants attain efficiencies approximately 33 to
37%, equivalent to fossil-fueled plants. High temperature & more current
designs such as the Generation IV reactors could acquire above 45%
efficiency.
Types of Nuclear Power Plant
There are two types of nuclear power plants such as pressurized water
reactor and boiling water reactor.
Pressurized Water Reactor
In this kind of reactor, regular water is used as a coolant. This is kept at
extremely high force so that it does not get a boil. A heat exchanger in
this reactor transfers the heated water where the water from the
secondary coolant circle is changed into vapor. Therefore, this loop is
totally free from the material of radioactive. In this reactor, the coolant
water works as a moderator. Because of these benefits, these reactors
are used most frequently.
Boiling Water Reactor
In this kind of reactor, a single coolant loop is only available. The water
is permissible to heat within the reactor. The steam is produced from the
reactor when it heads out from the reactor & the steam will flow
throughout the steam turbine. The main drawback of this reactor is, the
coolant water approaches the fuel rods & the turbine. So, radioactive
material could be located over the turbine.
Site Selection for Nuclear Power Plant
The selection of the site for nuclear PowerPoint can be done by
considering the technical requirement. The arrangement and working of
a nuclear power plant mainly depend on the characteristics of the site.
While designing the plant, the risks from the site must be considered.
The plant design has to handle with tremendous natural occurrence &
human-induced actions, without damaging the operational security of
the plant
Advantages
The advantages of nuclear power plants include the following.
It uses less space compared with other power plants
It is extremely economical and generates huge electric power.
These plants are located near the load center because there is no
requirement of huge fuel.
It generates a huge amount of power in the process of each nuclear
fission
It uses less fuel to generate huge energy
Its operation is reliable
When compared with steam power plants, it is very clean and neat
The operating cost is small
It doesn’t produce polluting gases
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of nuclear power plants include the following.
The cost of primary installation is extremely high when compared with
other power stations.
The nuclear fuel is expensive so recovering is difficult
High capital cost compare with other power plants
Technical knowledge is required to operate this plat. So maintenance,
as well as salary, will be high.
There is a chance of radioactive pollution
The response is not efficient
The requirement of cooling water is double compare with a steam power
plant.
Nuclear Power Plants in India
There seven nuclear power plants in India which include the following.
Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant, located in Tamil Nadu
Tarapur Nuclear Reactor, located in Maharashtra
Rajasthan Atomic Power Plant, located in Rajasthan
Kaiga Atomic Power Plant, located in Karnataka
Kalapakkam Nuclear Power Plant, located in Tamil Nadu
Narora Nuclear Reactor, located in Uttar Pradesh
Kakarapar Atomic Power Plant, located in Gujarat
You might also like
- Renewable Energy Sources - Wind, Solar and Hydro Energy Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandRenewable Energy Sources - Wind, Solar and Hydro Energy Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksNo ratings yet
- Powerplant EngineeringDocument12 pagesPowerplant EngineeringBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- Types of Power PlantDocument12 pagesTypes of Power PlantJonaz CruzNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 BcmeDocument21 pagesUnit-3 BcmeBalaji GaneshNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 3 BCME FinalDocument26 pagesUNIT - 3 BCME FinalAnith Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Power Plants in India and Abroad.: Siddhant Yadav RA1911026010043 Waste To Wealth To Wheels AssignmentDocument5 pagesDifferent Types of Power Plants in India and Abroad.: Siddhant Yadav RA1911026010043 Waste To Wealth To Wheels AssignmentSiddhant YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Ch6602 Energy Engineering Hydro Electric Power PlantDocument10 pagesUnit Ii Ch6602 Energy Engineering Hydro Electric Power PlantSudarshan GopalNo ratings yet
- What Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Document3 pagesWhat Happens Inside A Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) System?Rahul GhoshNo ratings yet
- Operation of A Nuclear Power PlantDocument8 pagesOperation of A Nuclear Power PlantMuhamad FaizNo ratings yet
- Ch-4-Nuclear EnergyDocument5 pagesCh-4-Nuclear Energysayyohabba2021No ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument22 pagesNuclear Power PlantMuhammad Ahkam KhanNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50Document3 pagesEnergy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50pagal noobNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument6 pagesPower PlantsyogusmiluNo ratings yet
- NuclearDocument49 pagesNuclearA ABHISHEK MARSHALLNo ratings yet
- BVRIT HYDERABAD College of Engineering For WomenDocument10 pagesBVRIT HYDERABAD College of Engineering For WomenChetan GuliaNo ratings yet
- Types of Power PlantsDocument8 pagesTypes of Power PlantsAdhanom G.No ratings yet
- Energy Tech UNIT 2Document53 pagesEnergy Tech UNIT 2Dhaksha AnieshNo ratings yet
- Various Plants Used For Generation of Electric Power Hydroelectric, Nuclear and Thermal Energy Plants Parts & WorkingDocument6 pagesVarious Plants Used For Generation of Electric Power Hydroelectric, Nuclear and Thermal Energy Plants Parts & WorkingWilson Fuentes100% (1)
- Nuclear Power Plant ReportDocument9 pagesNuclear Power Plant ReportJIL IbaanNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument20 pagesPower Plantsjvharsha.sNo ratings yet
- Battery DC Generator Electric Power Voltage: NextDocument13 pagesBattery DC Generator Electric Power Voltage: NextHussam GujjarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantsDocument24 pagesThermal Power Plantslakshmigsr6610100% (1)
- REPORT On Power Plants and Electric Transmission196035Document11 pagesREPORT On Power Plants and Electric Transmission196035Rohit SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PowerplantDocument5 pagesNuclear PowerplantAri HariNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument7 pagesNuclear Power PlantzzaanNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report at Atomic Power Station, RawatbhataDocument40 pagesSummer Training Report at Atomic Power Station, RawatbhataKrishan Pal Sila100% (2)
- Power System by PawanDocument20 pagesPower System by PawanPäwän Kümär MäüryäNo ratings yet
- Notes Power Plant EngineeringDocument8 pagesNotes Power Plant EngineeringDeepo Varinder MaandleyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurDocument27 pagesNuclear Power Plant: Swami Keshvanand Institute of Technology Management & Gramothan, JaipurNikhil ChopraNo ratings yet
- Power Plants Part-1Document9 pagesPower Plants Part-1Mukesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument30 pagesSteam Power PlantIAN MIGOTNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument25 pagesPower Plant EngineeringlitonNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mechanical Engineering: "The Journey of A Thousand Miles Begins With A Single Step."Document56 pagesBasics of Mechanical Engineering: "The Journey of A Thousand Miles Begins With A Single Step."Pushparaj ManickamNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant: Department of Mechanical Engineering, GCE, RamanagaraDocument143 pagesSteam Power Plant: Department of Mechanical Engineering, GCE, RamanagaraSrikanth Kabbal MNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power StationDocument4 pagesNuclear Power StationAnjo PepitoNo ratings yet
- "Thermal Power Generation": Seminar Report OnDocument10 pages"Thermal Power Generation": Seminar Report OnAram Nasih MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Colour)Document44 pagesPower Plant Colour)Er Anoop GuptaNo ratings yet
- L 03 - Ece 4109Document26 pagesL 03 - Ece 4109reza prantickNo ratings yet
- Mani Report 1Document53 pagesMani Report 1Mani MukatiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Nuclear Power PlantADocument13 pagesAssignment On Nuclear Power PlantAtheunsung tale100% (1)
- Types of Power Plant and Their Working PrinciplesDocument11 pagesTypes of Power Plant and Their Working PrinciplesRamzi JamalNo ratings yet
- Assignments: Ahmed Ali AlazmoniDocument39 pagesAssignments: Ahmed Ali Alazmonihazem tebineNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument13 pagesNuclear Power PlantlintangellaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 1999926643798667794Document10 pagesInbound 1999926643798667794bvcxd7m4j4No ratings yet
- Energy Management Module IDocument18 pagesEnergy Management Module ISalikNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument9 pagesSteam Power PlantAnne Gabrielle DavidNo ratings yet
- e Content Electrical Power IDocument185 pagese Content Electrical Power Igkulkarni298No ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument20 pagesSteam Power PlantSiddi Sampath Kumar Reddy100% (1)
- Project ReportDocument103 pagesProject ReportSeth CamachoNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 BPPE NotesDocument22 pagesUnit-3 BPPE Notes20WH1A0557 KASHETTY DEEKSHITHANo ratings yet
- 1) Conventional - Non Renewable Power GenerationDocument49 pages1) Conventional - Non Renewable Power GenerationManmit SalunkeNo ratings yet
- Types of Power Plants - 2018 PDFDocument71 pagesTypes of Power Plants - 2018 PDFJeff Justine GeragaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteDocument15 pagesNuclear Powerplant: Dan Emil A. Bernardino Sherwin Q. Bihasa Harry Lhon B. PobleteRonald Andrei DaguioNo ratings yet
- EE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationDocument62 pagesEE1452 - Electric Energy Generation, Conservation and UtilizationKarthikeyan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About ItDocument7 pagesThermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About Itngoc hoangNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant (PLTU)Document5 pagesSteam Power Plant (PLTU)Aldi Erzanuari100% (1)
- Thermal Power Generation Full Seminar Report 74537Document23 pagesThermal Power Generation Full Seminar Report 74537Umang Vyas88% (8)
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 02-May-2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 02-May-2023Yash SoniNo ratings yet
- White Simple Student CV ResumeDocument1 pageWhite Simple Student CV ResumeYash SoniNo ratings yet
- Student CVDocument1 pageStudent CVYash SoniNo ratings yet
- DiplomaDocument1 pageDiplomaYash SoniNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Air ConditioningDocument6 pagesRefrigeration & Air ConditioningYash SoniNo ratings yet