Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VFD 1
VFD 1
Uploaded by
Kiruba Eathiraj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThe VFD controller consists of three sub-systems: a rectifier bridge converter, a DC link with capacitor, and an inverter. It converts AC power to AC output for driving motors, though some configurations convert DC to AC. The rectifier is a three-phase, six-pulse diode bridge that produces DC from AC. The inverter then converts the smoothed DC back to quasi-sinusoidal AC for motor control.
Original Description:
Original Title
vfd 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe VFD controller consists of three sub-systems: a rectifier bridge converter, a DC link with capacitor, and an inverter. It converts AC power to AC output for driving motors, though some configurations convert DC to AC. The rectifier is a three-phase, six-pulse diode bridge that produces DC from AC. The inverter then converts the smoothed DC back to quasi-sinusoidal AC for motor control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageVFD 1
VFD 1
Uploaded by
Kiruba EathirajThe VFD controller consists of three sub-systems: a rectifier bridge converter, a DC link with capacitor, and an inverter. It converts AC power to AC output for driving motors, though some configurations convert DC to AC. The rectifier is a three-phase, six-pulse diode bridge that produces DC from AC. The inverter then converts the smoothed DC back to quasi-sinusoidal AC for motor control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
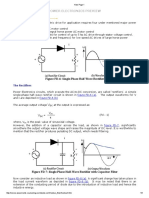
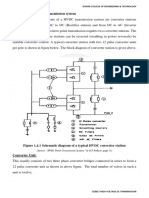
The VFD controller is a solid-state power electronics conversion system consisting
of three distinct sub-systems: a rectifier bridge converter, a direct current (DC)
link, and an inverter. Voltage-source inverter (VSI) drives (see 'Generic
topologies' sub-section below) are by far the most common type of drives. Most
drives are AC-AC drives in that they convert AC line input to AC inverter output.
However, in some applications such as common DC bus or solar applications, drives
are configured as DC-AC drives. The most basic rectifier converter for the VSI
drive is configured as a three-phase, six-pulse, full-wave diode bridge. In a VSI
drive, the DC link consists of a capacitor which smooths out the converter's DC
output ripple and provides a stiff input to the inverter. This filtered DC voltage
is converted to quasi-sinusoidal AC voltage output using the inverter's active
switching elements. VSI drives provide higher power factor and lower harmonic
distortion than phase-controlled current-source inverter (CSI) and load-commutated
inverter (LCI) drives (see 'Generic topologies' sub-section below). The drive
controller can also be configured as a phase converter having single-phase
converter input and three-phase inverter output.[9]
You might also like
- VFD 12Document1 pageVFD 12Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- VFD 14Document1 pageVFD 14Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency DriveDocument9 pagesVariable Frequency DriveOsama SalemNo ratings yet
- Simha 214Document76 pagesSimha 214Vamsi SakhamuriNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency Drive: Seminar ReportDocument7 pagesVariable Frequency Drive: Seminar ReportPavan KamatNo ratings yet
- Researchpaper Simulation of Active Front End Converter Based VFD For Induction MotorsDocument6 pagesResearchpaper Simulation of Active Front End Converter Based VFD For Induction MotorsAnonymous zmV3UaG0TNo ratings yet
- HVDC Lecture 2Document18 pagesHVDC Lecture 2MuHammad AbuNaga0% (1)
- AR Notes - 2w - 1 To 3 - 1Document17 pagesAR Notes - 2w - 1 To 3 - 1Vijayalakshmi PatilNo ratings yet
- Converters and Rectifiers (NEW)Document29 pagesConverters and Rectifiers (NEW)I AM NOT CHINESENo ratings yet
- Major Components of The HVDC Converter Station (Single Line Diagram Explained)Document12 pagesMajor Components of The HVDC Converter Station (Single Line Diagram Explained)Iyung RuslanNo ratings yet
- Vsi Csi With Various LoadsDocument56 pagesVsi Csi With Various LoadsDeependra RastogiNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency DrivesDocument17 pagesVariable Frequency DrivesAshok SutharNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifiers With Resistive and Inductive LoadDocument5 pagesHalf Wave Rectifiers With Resistive and Inductive Loadluqman059No ratings yet
- Current Source & Voltage Source InvertersDocument2 pagesCurrent Source & Voltage Source InvertersAhmed El SebaiiNo ratings yet
- Power InverterDocument11 pagesPower Inverterriz2010No ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifiersDocument8 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifiersRavindra SinghNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)Document9 pagesHVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)oeric2kNo ratings yet
- VFDDocument4 pagesVFDchandrakanth100% (2)
- RectifierDocument5 pagesRectifierpreethiNo ratings yet
- Ece Vii Power Electronics (06ec73) SolutionDocument77 pagesEce Vii Power Electronics (06ec73) SolutionVijay SaiNo ratings yet
- REPORT HVDC (Basic Transmission)Document5 pagesREPORT HVDC (Basic Transmission)joNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC) : Presented byDocument9 pagesHVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC) : Presented byKantipudi RajasekharNo ratings yet
- Early Radio Receivers, Called Crystal Radios, Used A "Cat's Whisker" of Fine Wire Pressing On A Crystal ofDocument4 pagesEarly Radio Receivers, Called Crystal Radios, Used A "Cat's Whisker" of Fine Wire Pressing On A Crystal ofPoonam bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv: Fundamentals of Harmonics: Fig.1: Current Distortion Caused by Nonlinear ResistanceDocument12 pagesUnit Iv: Fundamentals of Harmonics: Fig.1: Current Distortion Caused by Nonlinear Resistancelvb123No ratings yet
- Final 1Document78 pagesFinal 1Steve JantzenNo ratings yet
- The ABCs (And 1-2-3s) of Variable Frequency Drives - Machine DesignDocument9 pagesThe ABCs (And 1-2-3s) of Variable Frequency Drives - Machine DesignanuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HVDC TransmissionDocument25 pagesChapter 5 HVDC TransmissionTalha Khanzada100% (1)
- The ABC of Variable Freq - Drives-YaskawaDocument7 pagesThe ABC of Variable Freq - Drives-YaskawaAirton Flores100% (1)
- Learning ObjectivesDocument36 pagesLearning ObjectivesredyirawanNo ratings yet
- HVDC ReportDocument43 pagesHVDC ReportD Sreenivas KarthikNo ratings yet
- STATCOMDocument17 pagesSTATCOMAbdel-Rahman Saifedin ArandasNo ratings yet
- RemovePagesResult 2023 11 10 01 50 17Document20 pagesRemovePagesResult 2023 11 10 01 50 17Spandana priyaNo ratings yet
- Small Variable-Frequency DriveDocument11 pagesSmall Variable-Frequency DriveYasir ButtNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - InverterDocument9 pagesTopic 4 - InverterAvinesh ChandNo ratings yet
- VFD-types, Working, Soft-Starter, Market Scope.: Dharnish Kumar V G Abhyas InternshipDocument11 pagesVFD-types, Working, Soft-Starter, Market Scope.: Dharnish Kumar V G Abhyas InternshipdharnishNo ratings yet
- VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) : Report OnDocument5 pagesVFD (Variable Frequency Drive) : Report OnZohaib MehmoodNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters: AbstractDocument8 pagesHVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters: AbstractVelu SamyNo ratings yet
- RECTIFIERDocument4 pagesRECTIFIERVishavjeet Singh GarchaNo ratings yet
- 125 130 PDFDocument6 pages125 130 PDFJubin JainNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument11 pagesRectifierasislakhaNo ratings yet
- Rectifier: Let Your Voice Be Heard! Give Your Input On The Draft of Our New Privacy PolicyDocument33 pagesRectifier: Let Your Voice Be Heard! Give Your Input On The Draft of Our New Privacy PolicySri MathiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home AppliancesDocument21 pagesElectronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home AppliancesTushar GoelNo ratings yet
- Important Questions - APS - IDocument3 pagesImportant Questions - APS - IAakash MehtaNo ratings yet
- Shiwani Ref4 PDFDocument7 pagesShiwani Ref4 PDFPRACHI KATARENo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)Document10 pagesHVDC Transmission Using Voltage Source Converters (VSC)kanthbcNo ratings yet
- IDC Unit-4Document9 pagesIDC Unit-4Gaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency Drives in A Power Plant: SynopsisDocument22 pagesVariable Frequency Drives in A Power Plant: SynopsisReuben VargheseNo ratings yet
- HVDC Transmission Basic CircuitDocument3 pagesHVDC Transmission Basic CircuitDEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of A 6-Pulse Converter and A 12-Pulse Converter For HVDC Station.Document6 pagesA Comparative Study of A 6-Pulse Converter and A 12-Pulse Converter For HVDC Station.Naveen JainNo ratings yet
- Inverters For Ac Motor DriveDocument17 pagesInverters For Ac Motor DriveAslam SdNo ratings yet
- Using A Synchronous Converter For Harmonic Mitigation With AC DrivesDocument10 pagesUsing A Synchronous Converter For Harmonic Mitigation With AC Drivesmit85No ratings yet
- Improvement of Power Factor and Harmonic Reduction With VSC For HVDC SystemDocument7 pagesImprovement of Power Factor and Harmonic Reduction With VSC For HVDC SystemGiwrgos GewrgiadisNo ratings yet
- Main Circuit Power Electronic Topologies Applied To The Con-Trol of Rotating-Field MotorsDocument44 pagesMain Circuit Power Electronic Topologies Applied To The Con-Trol of Rotating-Field MotorsnysretNo ratings yet
- 'What Is A Rectifier:-: Types of RectifiersDocument10 pages'What Is A Rectifier:-: Types of RectifiersRutvikNo ratings yet
- Challenges Faced in HVDC SystemsDocument12 pagesChallenges Faced in HVDC SystemsPKNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power High-Voltage Electricity Transmission (1) (2) Flexible AC Transmission SystemDocument11 pagesReactive Power High-Voltage Electricity Transmission (1) (2) Flexible AC Transmission SystemsirishaNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument13 pagesReflectionCharlie KingNo ratings yet
- Component and Types of VFDDocument11 pagesComponent and Types of VFDArsalan Danish100% (1)
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsFrom EverandHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- VFD e Manual13Document4 pagesVFD e Manual13Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- Delta VFD 5Document7 pagesDelta VFD 5Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- Sensore 5Document2 pagesSensore 5Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- Delta VFD 3Document2 pagesDelta VFD 3Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- Limit Switch 3Document1 pageLimit Switch 3Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- Limit Switch 1Document1 pageLimit Switch 1Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- Sensore 2Document1 pageSensore 2Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- Sensore 1Document1 pageSensore 1Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- SensoreDocument1 pageSensoreKiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- Service 5Document2 pagesService 5Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- Service 4Document2 pagesService 4Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- Service 2Document1 pageService 2Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- VFD 14Document1 pageVFD 14Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet
- VFD 12Document1 pageVFD 12Kiruba EathirajNo ratings yet