Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsVelocity, Distance - Acceleration 3 QP
Velocity, Distance - Acceleration 3 QP
Uploaded by
shehryar iftikharCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- 1SC0 1PH Exam-Paper 20180524Document24 pages1SC0 1PH Exam-Paper 20180524shehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Edexcel GCSE Combined Science Physics Higher Paper 2 QPDocument20 pagesEdexcel GCSE Combined Science Physics Higher Paper 2 QPshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- Velocity, Distance - Acceleration 2 QPDocument10 pagesVelocity, Distance - Acceleration 2 QPshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Combined Science November 2020 6HDocument24 pagesEdexcel GCSE Combined Science November 2020 6Hshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- 5 Probability TreesDocument11 pages5 Probability Treesshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Mock ExamDocument1 pageLab 6 - Mock Examshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- Angles in Parallel Lines Notes FINALDocument1 pageAngles in Parallel Lines Notes FINALshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
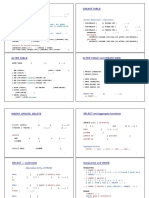
- SQL SyntaxDocument2 pagesSQL Syntaxshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- For Sale PDFDocument1 pageFor Sale PDFshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- ITMB Society Application Form 2023Document6 pagesITMB Society Application Form 2023shehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- (A) G.P.E. Mass × Gravitational Field Strength × HeightDocument5 pages(A) G.P.E. Mass × Gravitational Field Strength × Heightshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
Velocity, Distance - Acceleration 3 QP
Velocity, Distance - Acceleration 3 QP
Uploaded by
shehryar iftikhar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Velocity, Distance _ Acceleration 3 QP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesVelocity, Distance - Acceleration 3 QP
Velocity, Distance - Acceleration 3 QP
Uploaded by
shehryar iftikharCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 4
Forces and motion
1 (a) Here is the velocity time graph for a car for the first 20s of a
journey.
4
12)
10
velocity/
m/s
6
4
2
0
oO 5 10 15 20
time/s
{Calculate the change in velocity of the car during the first 5 s.
change in velocity = m/s
(ii) Calculate the acceleration of the car during the first 5 s.
acceleration = mis?
(iil) State the size of the resultant force between 10 s and 15s
resultant force = N
(b) The mass of a car is 1200 kg.
Calculate the resultant force on the car required to produce an acceleration of
0.8 m/s.
*(©) Acar, travelling at 20 m/s, with just the driver inside takes 70 m to stop in an
emergency.
The same car is then fully loaded with luggage and passengers as well as the
driver.
Explain why it will take a different distance to stop in an emergency from the
same speed.
resultant force
(2)
(6)
(Total for Question = 12 marks)
2. (a) Acaraccelerates at a constant rate of 1.83m/s? along a skit straight road.
The force acting on the car is 1.870 KN.
Calculate the mass of the car.
Give your answer to three significant figures.
mass = kg
(b) The car accelerates from rest for 16 s.
Calculate the speed of the car after 16 s.
speed = on m/s
(c) The car starts on another journey.
Figure 6 shows the graph of the car’s movement.
velocity /
m/s
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
time /s
Figure 6
Show that the distance travelled when the car is moving at a constant speed is
greater than the distance travelled when the car is slowing down.
n= 10 marks)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- 1SC0 1PH Exam-Paper 20180524Document24 pages1SC0 1PH Exam-Paper 20180524shehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Edexcel GCSE Combined Science Physics Higher Paper 2 QPDocument20 pagesEdexcel GCSE Combined Science Physics Higher Paper 2 QPshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- Velocity, Distance - Acceleration 2 QPDocument10 pagesVelocity, Distance - Acceleration 2 QPshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Combined Science November 2020 6HDocument24 pagesEdexcel GCSE Combined Science November 2020 6Hshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- 5 Probability TreesDocument11 pages5 Probability Treesshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Mock ExamDocument1 pageLab 6 - Mock Examshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- Angles in Parallel Lines Notes FINALDocument1 pageAngles in Parallel Lines Notes FINALshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- SQL SyntaxDocument2 pagesSQL Syntaxshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- For Sale PDFDocument1 pageFor Sale PDFshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- ITMB Society Application Form 2023Document6 pagesITMB Society Application Form 2023shehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet
- (A) G.P.E. Mass × Gravitational Field Strength × HeightDocument5 pages(A) G.P.E. Mass × Gravitational Field Strength × Heightshehryar iftikharNo ratings yet