Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Objective 2
Objective 2
Uploaded by
JUDITH APOSTOLOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Objective 2
Objective 2
Uploaded by
JUDITH APOSTOLCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Caraga Administrative Region
Schools Division of Bislig City
SIKAHOY NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Objective 2: Used researched-based knowledge and principles of teaching and
learning to enhance professional practice
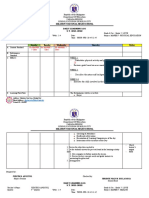
Part I. Objectives:
It is imperative to understand that there are different types of learners who
have varying needs. Studies by Benjamin Bloom (on cognitive domain), David
Krathwohl (affective domain) and Anita Harrow (Psychomotor domain) have been
encompassed into the three domains of learning (Sousa, 2016). Thus, the teacher
developed and delivered the lesson using the three domains of learning: cognitive,
psychomotor and affective to ensure that the needs among learners are being
addressed.
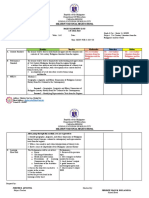
Part 2. Instructional Activities:
Ensuring that the learners capture the essential ideas, the teacher employed
the 7Es framework (Eisenkraft 2003) in delivering the instructional activities which
stands for Elicit, Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, Evaluate and Extend.
In the “Elicit” stage, a picture is posted while guiding students through
questions. Here, learners’ prior knowledge are found. In the “Engage” part, learners
are asked to arrange the situation in the context of a students’ experience. In this
stage the teacher wants to engage interest and curiosity among learners and raise
“The BIG questions” and introduce new learning through teacher explanation
modelling. For the learners to understand the concept of food chain, the learners
“Explore” through a task by classifying the organisms according to their feeding
process alongside the guide questions. Learners are given opportunities to work
together following the initial teacher input to solve/explore problems, building
concepts through first-hand experience. Key concepts are then discussed in the
“Explain” part. Using deep questioning and also explanation/modelling the teacher
builds the scientific explanation. To correct the misconceptions, learners complete a
diagram through labels alongside the guide questions in the “Elaborate” part. This is
the stage that will be KEY in assessing learners’ progress, knowledge and
understanding. In this stage, students may work independently to demonstrate
learning. To check the learners’ understanding, they will answer the short quiz in the
“Evaluate” part. And lastly, learners are opted to answer the additional “Extend” stage.
In this stage learners are encouraged to apply or extend the concepts and skills
through asking about organisms that makes a food chain.
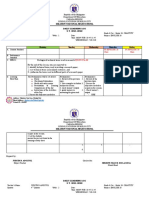
Part 3. Assessments
To ensure thorough understanding and transfer of learning, level of difficulty is
gradually introduced all throughout. Various formative assessments are used in the
lesson plan. One type of assessment is through sequencing of events. Sequencing is
one of many skills that contributes to students' ability to comprehend what they read.
Sequencing refers to the identification of the components of a story — the beginning,
middle, and end — and also to the ability to retell the events within a given text in the
order in which they occurred. The ability to sequence events in a text is a key
comprehension strategy, especially for narrative texts. Sequencing is also an
important component of problem-solving across subjects (Reading Rockets, 2015).
Address: Sikahoy, San Jose, Bislig City
Email Address: sikahoyhs@deped.gov.ph
Facebook Page: Sikahoy National High School
School ID: 304869
Results-based Performance Management System 2021-2022
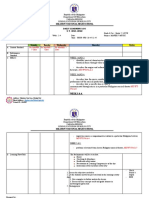
The teacher also employed assessment using diagrams. A study suggests that
giving students pertinent visual information, such as a diagram or outline, at the start
of a lesson will lead to better understanding of that lesson. The study, by Mark A.
McDaniel, a professor of psychology at Washington University in St. Louis, and
graduate student Dung C. Bui, found that students who had visual aids given to them
during science lecture were better able to understand and remember the lecture, but
illustrative diagrams helped more than outlines.
The use of differentiated instruction is also used in the lesson. Tomlinson
(2005), a leading expert in this field, defines differentiated instruction as a philosophy
of teaching that is based on the premise that students learn best when their teachers
accommodate the differences in their readiness levels, interests and learning profiles.
A chief objective of differentiated instruction is to take full advantage of every student’s
ability to learn (Tomlinson, 2001a, 2001c, 2004c, 2005). Knowing students well allows
teachers to figure out their strengths, thereby helping them to move forward
(MacGillivray and Rueda, 2001). Engaging students actively in the learning process
and in the content allows them to see patterns developing, to see the overlap between
disciplines, to see learning as a cumulative whole (Coleman, 2001).
The teacher used the individual assessment through a short quiz. Quizzes have
several advantages compared to other types of assessments: quizzes are quicker to
execute, quicker to grade, quicker to return with feedback and less stressful than
major examinations (Kennedy 2015). It enhancea the students' learning experience.
Short, low-stakes tests also help teachers gauge how well students understand the
material and what they need to reteach (Berwick 2019).
Address: Sikahoy, San Jose, Bislig City
Email Address: sikahoynhs@deped.gov.ph
Facebook Page: Sikahoy National High `School
School ID: 304869
You might also like
- Gamification Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesGamification Lesson Planapi-282154717100% (1)
- MAPEH 7 - PE and Health 4TH Q-DLLDocument4 pagesMAPEH 7 - PE and Health 4TH Q-DLLJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- 21ST Century - 4TH Q-DLLDocument9 pages21ST Century - 4TH Q-DLLJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- C P E A 1: Urriculum LAN Valuation SsignmentDocument4 pagesC P E A 1: Urriculum LAN Valuation SsignmentMartella ThomasNo ratings yet
- Edn568 Assignment 2 Instructional Strategy PlanDocument18 pagesEdn568 Assignment 2 Instructional Strategy Planapi-337568373No ratings yet
- Outsmart Yourself Brain-Based Strategies To A Better YouDocument210 pagesOutsmart Yourself Brain-Based Strategies To A Better YouRodrigo Castro100% (10)
- PDYP SampleDocument18 pagesPDYP SampleBillW2010100% (1)
- Action Research ProposalDocument8 pagesAction Research ProposalJade JuanilloNo ratings yet
- 8601 SolutionDocument14 pages8601 SolutionAsad AliNo ratings yet
- Assignment Spring 2021: Name: ABCDocument16 pagesAssignment Spring 2021: Name: ABCFarhat AbbasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Asar Na Q Sau 2Document16 pagesChapter 1 Asar Na Q Sau 2Josel CecilioNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Differentiating Instruction 1Document15 pagesRunning Head: Differentiating Instruction 1eugenia_4No ratings yet
- 8601, Assignment 1Document14 pages8601, Assignment 1Abdul WajidNo ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching Ii: Edlyn Mae C. Sarmiento, MaedDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Teaching Ii: Edlyn Mae C. Sarmiento, MaedAiza C. Abungan-GalzoteNo ratings yet
- 5-EsDocument21 pages5-EsApril ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Group3 Chapter 1 3 BSED MATH 3 1Document25 pagesGroup3 Chapter 1 3 BSED MATH 3 1Toreno JamesNo ratings yet
- Students' Difficulties Understanding A Specific Topic or SubjectDocument7 pagesStudents' Difficulties Understanding A Specific Topic or SubjectJoana Marie De TorresNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 (Jojo)Document12 pagesPractical Research 2 (Jojo)capoquianj642No ratings yet
- Module 1 Week 2Document12 pagesModule 1 Week 2Josh MallariNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science - Semi Finals and Finals 3Document9 pagesTeaching Science - Semi Finals and Finals 3Florven Buscas DesabilleNo ratings yet
- Teacher Artifacts-Intasc PortfolioDocument15 pagesTeacher Artifacts-Intasc Portfolioapi-742075237No ratings yet
- Spencer WalkerDocument8 pagesSpencer WalkerNor Rasidah Binti AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Bridging The Gap of The Implemented Modular Learing Modality in The New NormalDocument22 pagesBridging The Gap of The Implemented Modular Learing Modality in The New NormalDENMARKNo ratings yet
- Assessing KPUP ArticleDocument5 pagesAssessing KPUP ArticleCarlo MagnoNo ratings yet
- Development and Acceptability of Modules - ROY ELSISURA TIAPEDocument17 pagesDevelopment and Acceptability of Modules - ROY ELSISURA TIAPEJerbs PacundoNo ratings yet
- Heather Lesson Study Research PaperDocument41 pagesHeather Lesson Study Research Paperapi-442046733No ratings yet
- Haromaya UniversityDocument63 pagesHaromaya UniversityBeni N SoloNo ratings yet
- 22 Effective Teaching Strategies As Perceived by Bambad National High School'Document12 pages22 Effective Teaching Strategies As Perceived by Bambad National High School'Syvil Mae GerotapeNo ratings yet
- Validity of Learning MaterialsDocument14 pagesValidity of Learning MaterialsZARINA ANNE JOY CABUSNo ratings yet
- For PrintingDocument44 pagesFor PrintingApril Rose SoleraNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument14 pagesResearchVanessa BoncalesNo ratings yet
- Oribia - Angelo, R - Reseach Study and SynthesisDocument8 pagesOribia - Angelo, R - Reseach Study and SynthesisAngelo Rebayla OribiaNo ratings yet
- School of Saint Anthony: A Comparative Study On The Effectiveness of Classroom Instruction in Selected Grade 7 SectionsDocument32 pagesSchool of Saint Anthony: A Comparative Study On The Effectiveness of Classroom Instruction in Selected Grade 7 SectionsAloisia Rem RoxasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 To 3 Ovillo RevisedDocument28 pagesChapter 1 To 3 Ovillo RevisedAlera KimNo ratings yet
- Trends and Issues in Curriculum DevelopmentDocument6 pagesTrends and Issues in Curriculum DevelopmentJe CortezNo ratings yet
- Local Media8328540136846962755Document18 pagesLocal Media8328540136846962755Eden RempilloNo ratings yet
- Developing Higher Level ThinkingDocument9 pagesDeveloping Higher Level ThinkingArwina Syazwani Binti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Learning TheoriesDocument10 pagesLearning Theoriesyonaseskezia8No ratings yet
- Finals Theo PaperDocument29 pagesFinals Theo PaperAdrian AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Chap1-3 ProposalDocument21 pagesChap1-3 Proposalvan anthony dagapiosoNo ratings yet
- Flipped Inclusion Classroom Action Research Jeanette VillanuevaDocument16 pagesFlipped Inclusion Classroom Action Research Jeanette VillanuevaMr. BatesNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument26 pagesFinal ProjectLIFE WITH BRIANNANo ratings yet
- Group 6 - Edn 1202-13 - Written ReportDocument75 pagesGroup 6 - Edn 1202-13 - Written ReportRez Joseph CresciniNo ratings yet
- ELE02 Learning Task 1 MidtermDocument4 pagesELE02 Learning Task 1 MidtermMichele VelascoNo ratings yet
- EDU 603: Final Curriculum Project: Completing CVC WordsDocument18 pagesEDU 603: Final Curriculum Project: Completing CVC Wordslucygreene2018No ratings yet
- HMEF5123Document22 pagesHMEF5123Juliana Jaffar100% (1)
- Module 5 - Principles and Strategies (Lesson Planning)Document10 pagesModule 5 - Principles and Strategies (Lesson Planning)Jesryl Remerata OrtegaNo ratings yet
- General Methods of Teaching (EDU301)Document7 pagesGeneral Methods of Teaching (EDU301)Rukhsar TariqNo ratings yet
- PED 105 Module No. 6Document7 pagesPED 105 Module No. 6Jonathan Micah Joy LaureanoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Explicit Teaching As A Major Strategy in Implementing Secondary Science ClassesDocument19 pagesAssessment of Explicit Teaching As A Major Strategy in Implementing Secondary Science ClassesJefferson EspinaNo ratings yet
- NEWLY IMPROVED BUCK (BEEd III-A)Document10 pagesNEWLY IMPROVED BUCK (BEEd III-A)Edzel JosonNo ratings yet
- Bem 1202:fundamentals of Pedagogy Cat1: - B) Appropriate Reaction To MisbehaviourDocument7 pagesBem 1202:fundamentals of Pedagogy Cat1: - B) Appropriate Reaction To MisbehaviourericNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Instructional Quality of Grade EightDocument14 pagesEvaluation of The Instructional Quality of Grade EightRon AntonioNo ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching 2 Ted 3Document47 pagesPrinciples of Teaching 2 Ted 3Nestor Langit GaladoNo ratings yet
- EJ1264262Document12 pagesEJ1264262tsegaye8384No ratings yet
- 1122-Article Text-2199-1-10-20210803Document4 pages1122-Article Text-2199-1-10-20210803jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Direct Instruction, Expository Teaching, and Mastery LearningDocument11 pagesDirect Instruction, Expository Teaching, and Mastery Learningalda5santos-2No ratings yet
- A Learning Cycle For All Students: Modifying The 5E Instructional Model To Address The Needs of All LearnersDocument5 pagesA Learning Cycle For All Students: Modifying The 5E Instructional Model To Address The Needs of All LearnersDina DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Pupils' Punctuality and Recognition Scheme of Grade Two Mabini of Busok Elementary School, SCHOOL YEAR 2019-2020 I. Content and RationaleDocument10 pagesPupils' Punctuality and Recognition Scheme of Grade Two Mabini of Busok Elementary School, SCHOOL YEAR 2019-2020 I. Content and RationaleHero MirasolNo ratings yet
- MastersDocument47 pagesMastersJellyn GutibNo ratings yet
- Competency #6 Ay 2022-2023 Social StudiesDocument14 pagesCompetency #6 Ay 2022-2023 Social StudiesCharis RebanalNo ratings yet
- Lababo Wilson B.S.E.D Fil-2 Prof - Ed 205 (20141) Instructor: Mrs Meldring Valles Activity 12 Question No.2Document4 pagesLababo Wilson B.S.E.D Fil-2 Prof - Ed 205 (20141) Instructor: Mrs Meldring Valles Activity 12 Question No.2Sink WilsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I: 1.0. Computer Aided Lesson Planning (Calp) - A New Era in Indian Teaching Learning ProcessDocument55 pagesChapter - I: 1.0. Computer Aided Lesson Planning (Calp) - A New Era in Indian Teaching Learning ProcessDiksha UttamNo ratings yet
- The Structured Method of Pedagogy: Effective Teaching in the Era of the New Mission for Public Education in the United StatesFrom EverandThe Structured Method of Pedagogy: Effective Teaching in the Era of the New Mission for Public Education in the United StatesNo ratings yet
- Using Cutting-Edge Technology: Tools to Consider for Enhancing Learning In Grades Six through TwelveFrom EverandUsing Cutting-Edge Technology: Tools to Consider for Enhancing Learning In Grades Six through TwelveNo ratings yet
- My Reflection Journal in Measure of PositionDocument2 pagesMy Reflection Journal in Measure of PositionJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- Attendance SheetDocument2 pagesAttendance SheetJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- Group 1 (Literature Review)Document3 pagesGroup 1 (Literature Review)JUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- ANNOTATIONSDocument1 pageANNOTATIONSJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- Eapp - Q3-Week5b-DllDocument8 pagesEapp - Q3-Week5b-DllJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- Zemi Detailed Lesson Plan in EAPP EXPLICIT TEACHINGDocument11 pagesZemi Detailed Lesson Plan in EAPP EXPLICIT TEACHINGJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- EAPP Q3 Week 3Document12 pagesEAPP Q3 Week 3JUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- ACTION RESEARCH PROPOSAL Paderes - ApostolDocument8 pagesACTION RESEARCH PROPOSAL Paderes - ApostolJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- 3rd Q MAPEH 9 Weekly-Home-Learning-Plan-for-Modular-Distance-LearningDocument6 pages3rd Q MAPEH 9 Weekly-Home-Learning-Plan-for-Modular-Distance-LearningJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- Borrower Slip Student v1.2 PDFDocument1 pageBorrower Slip Student v1.2 PDFJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- MP Customer Information Update Form - CIU Form 4.22Document3 pagesMP Customer Information Update Form - CIU Form 4.22JUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- Action Plan RREDocument2 pagesAction Plan RREJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- English 10 - 4TH Q-DLLDocument9 pagesEnglish 10 - 4TH Q-DLLJUDITH APOSTOL100% (1)
- Mapeh 7 2ND Month - Summative Test PDFDocument8 pagesMapeh 7 2ND Month - Summative Test PDFJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- One PursuitDocument24 pagesOne PursuitJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 7 - Music and Arts 4TH Q-DLLDocument5 pagesMAPEH 7 - Music and Arts 4TH Q-DLLJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Tool NumeracyDocument3 pagesMonitoring Tool NumeracyJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- DLL Co-1Document5 pagesDLL Co-1JUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- Sikahoy National High School Judith D. Apostol Century Literature Monday-Tuesday 8:30-9:30Document18 pagesSikahoy National High School Judith D. Apostol Century Literature Monday-Tuesday 8:30-9:30JUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- English 7 - 4TH Q-DLLDocument15 pagesEnglish 7 - 4TH Q-DLLJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Caraga Region Schools Division of Bislig CityDocument12 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Caraga Region Schools Division of Bislig CityJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets: Ma. Lourdes A. HuelvaDocument27 pagesLearning Activity Sheets: Ma. Lourdes A. HuelvaJUDITH APOSTOLNo ratings yet
- (Write-Up) AQA Biology (9-1) Required Practical 7: Reaction TimeDocument3 pages(Write-Up) AQA Biology (9-1) Required Practical 7: Reaction Timeromania ioqwjhreNo ratings yet
- Learning and Memory: Consumer Behavior, 10EDocument29 pagesLearning and Memory: Consumer Behavior, 10Emustinsar100% (1)
- From Inside Track To Successful Academic WritingDocument1 pageFrom Inside Track To Successful Academic WritingsylviakarNo ratings yet
- L-Theanine and Caffeine Improve Task Switching But Not IntersensoryDocument4 pagesL-Theanine and Caffeine Improve Task Switching But Not IntersensoryFrancisco Ahumada MéndezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Variations in ConsciousnessDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Variations in ConsciousnessChehekNo ratings yet
- Theory of BrainDocument2 pagesTheory of BrainAnissh WaranNo ratings yet
- Facilitation Technique Tai Chi 1 1Document4 pagesFacilitation Technique Tai Chi 1 1api-339418889No ratings yet
- SLH S 20 00050Document34 pagesSLH S 20 00050VsnuNo ratings yet
- Reading Passage 3Document4 pagesReading Passage 3Nguyen Hoang AnhNo ratings yet
- Kelompo K: Employee EngagementDocument2 pagesKelompo K: Employee EngagementBaharudin BahrinNo ratings yet
- Learning TheoriesDocument20 pagesLearning TheoriesDaniel DubeNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Síntomas HomeopáticosDocument191 pagesTabla de Síntomas HomeopáticosC.s. JessicaNo ratings yet
- Neurological History and Physical ExaminationDocument21 pagesNeurological History and Physical Examinationg3murtulu100% (1)
- A Flexible Sequence For Teaching Acceptance Skills - Russ HarrisDocument2 pagesA Flexible Sequence For Teaching Acceptance Skills - Russ Harrispsiho2024No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Artificial Neural NetworkDocument77 pagesLesson 3 Artificial Neural NetworkVIJENDHER REDDY GURRAMNo ratings yet
- A New Neurofeedback Protocol For DepressionDocument12 pagesA New Neurofeedback Protocol For DepressionVezér RóbertNo ratings yet
- DNIC in The SensesDocument12 pagesDNIC in The Sensesfrancisca rojasNo ratings yet
- Learning Unit 2Document9 pagesLearning Unit 2PERTUNIA KORABINo ratings yet
- Trauma and RecoveryDocument34 pagesTrauma and RecoveryAndreea Ghivnici100% (1)
- II - The Stage Od Development and Developmental Task PDFDocument43 pagesII - The Stage Od Development and Developmental Task PDFpaul degz80% (5)
- Autism Symptoms Checklist 01Document1 pageAutism Symptoms Checklist 01karunaNo ratings yet
- Module 3-HUMANITIES Art AppreciationDocument3 pagesModule 3-HUMANITIES Art AppreciationKentoy Galagate GoleNo ratings yet
- Perlita Laxamana Datu, Ph. DDocument50 pagesPerlita Laxamana Datu, Ph. DKaren Mae Altarejos AlocNo ratings yet
- The Psychology of The Child (PDFDrive) PDFDocument221 pagesThe Psychology of The Child (PDFDrive) PDFVincent BIKORIMANA100% (3)
- Oral Communication Grade 11Document9 pagesOral Communication Grade 11Lunita Benlot100% (1)
- Week 2 KnowingDocument43 pagesWeek 2 KnowingMarie Elaine MelencionNo ratings yet
- Student ProtocolDocument14 pagesStudent ProtocolGabriela Sofia Ortiz NarvaezNo ratings yet