Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circle Theorems Lesson Plan
Circle Theorems Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
Nia Ram0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views15 pagesThe document discusses circle theorems and how to solve geometric problems involving properties of circles. It defines key circle terms like radius, diameter, chord, and lists 8 circle theorems for determining and justifying angles, such as theorems relating the angle at the center of a circle to the angle at the circumference, angles in the same segment being equal, and a tangent being perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. It concludes with notes on past paper questions and a quiz on circle theorems.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses circle theorems and how to solve geometric problems involving properties of circles. It defines key circle terms like radius, diameter, chord, and lists 8 circle theorems for determining and justifying angles, such as theorems relating the angle at the center of a circle to the angle at the circumference, angles in the same segment being equal, and a tangent being perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. It concludes with notes on past paper questions and a quiz on circle theorems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views15 pagesCircle Theorems Lesson Plan
Circle Theorems Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
Nia RamThe document discusses circle theorems and how to solve geometric problems involving properties of circles. It defines key circle terms like radius, diameter, chord, and lists 8 circle theorems for determining and justifying angles, such as theorems relating the angle at the center of a circle to the angle at the circumference, angles in the same segment being equal, and a tangent being perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact. It concludes with notes on past paper questions and a quiz on circle theorems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 15
MATHS
CIRCLE THEOREMS
Solve geometric problems using properties of circles and circle theorems; Radius, diameter,
chord, circumference, arc, tangent, segment, sector, semicircle, pi.
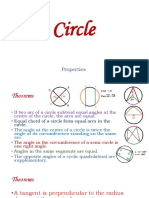
Determining and justifying angles using the circle theorems:
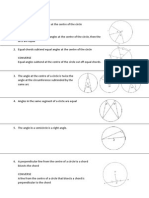
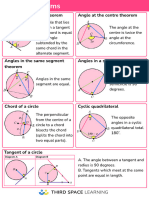
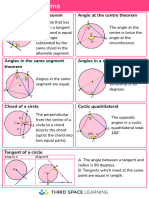
1. The angle at which an arc of a circle subtends at the centre of a circle is twice the angle
it subtends at any point on the remaining part of the circumference.
2. Angles at the circumference in the same segment of a circle and subtended by the same
arc/chord are equal.
3. The angle at the circumference subtended by the diameter is a right angle. The opposite
angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary.
4. The exterior angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is equal to the interior opposite angle.
5. The angle between a tangent to a circle and a chord through the point of contact is equal
to the angle in the alternate segment.
6. A tangent of a circle is perpendicular to the radius/diameter of that circle at the point of
contact.
7. The lengths of two tangents from an external point to the points of contact on the circle
are equal.
8. The line joining the centre of a circle to the midpoint of a chord is perpendicular to the
chord
NOTES
PAST PAPER QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
QUIZ
You might also like
- Maths Project For Class 10Document18 pagesMaths Project For Class 10John Nguyen57% (42)
- Properties of CircleDocument2 pagesProperties of CircleHarshNo ratings yet
- 295 Topper 21 101 1 3 80 Circles Up201807061123 1530856414 049Document6 pages295 Topper 21 101 1 3 80 Circles Up201807061123 1530856414 049Vaibhav PundhirNo ratings yet
- Circle Geometry NotesDocument2 pagesCircle Geometry NotesGeoffrey WongNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremsDocument4 pagesCircle TheoremsHazel Clemente Carreon100% (1)
- Glossary Terms: R Is The Radius of The Circle and L Is The Arc LengthDocument4 pagesGlossary Terms: R Is The Radius of The Circle and L Is The Arc LengthBonbert LascoNo ratings yet
- Circile TheoremsDocument1 pageCircile Theoremssuryanshkothari14No ratings yet
- Circles Arc and Cyclic PropertiesDocument3 pagesCircles Arc and Cyclic PropertiesBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Maths Circle RulesDocument3 pagesMaths Circle RulesmuzzafuzzamuzzafuzzaNo ratings yet
- Theorems and Postulates On Math Q2 Q3Document3 pagesTheorems and Postulates On Math Q2 Q3glaiveashNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorems For CIE IGCSE MathematicsDocument2 pagesCircle Theorems For CIE IGCSE Mathematicshasan akhtarNo ratings yet
- Circles Review For Test 1 1Document4 pagesCircles Review For Test 1 1api-256105506No ratings yet
- Circle Theorem 1-9CDocument35 pagesCircle Theorem 1-9CNatasia JonesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DraftDocument6 pagesChapter 3 DraftPaopao MacalaladNo ratings yet
- ADVGEOM Lecture5 Nov20Document26 pagesADVGEOM Lecture5 Nov20Ellaine LimpangogNo ratings yet
- Circles PPT 1Document14 pagesCircles PPT 1johnzky aquinoNo ratings yet
- Theorems and Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument2 pagesTheorems and Trigonometric IdentitiesSrinithi MeenakshiNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept in GeometryDocument17 pagesBasic Concept in GeometryKevin Almoete VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.1 - 6.4 Chapter 6.1 Chord Properties: Homework P. 310-311 (1-10, 16)Document2 pagesChapter 6.1 - 6.4 Chapter 6.1 Chord Properties: Homework P. 310-311 (1-10, 16)Xin Yuan ZhuNo ratings yet
- Circles and Other Related TermsDocument36 pagesCircles and Other Related TermsPatricia CadacioNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument23 pagesCirclekesterweirdNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument19 pagesCirclealexandradeleon080508No ratings yet
- Mathsclinic Smartprep Gr12 Eng 3 230126 102713Document75 pagesMathsclinic Smartprep Gr12 Eng 3 230126 102713Mac Mawasha100% (1)
- Chapter - 10 CirclesDocument36 pagesChapter - 10 CirclesYash GoyalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CircleDocument5 pagesIntroduction To CircleMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Summary of Circle TheoremsDocument1 pageSummary of Circle TheoremsPat KhanNo ratings yet
- Maths Class 9 Notes For CirclesDocument3 pagesMaths Class 9 Notes For CirclesAdnan BashirNo ratings yet
- Tangent and CircleDocument1 pageTangent and Circleaimgod100No ratings yet
- IX Math 10 CirclesDocument1 pageIX Math 10 Circlesksiya0707No ratings yet
- Special Segments of TrianglesDocument13 pagesSpecial Segments of TrianglesRohank_123No ratings yet
- GeometryDocument51 pagesGeometryneerja92No ratings yet
- 2022 Gr12 Maths WKBKDocument23 pages2022 Gr12 Maths WKBKssdavieNo ratings yet
- Circle and TheoremsDocument32 pagesCircle and Theoremsalexandradeleon080508No ratings yet
- 2017-JIT Grade 11 Term 2Document34 pages2017-JIT Grade 11 Term 2tongmasegowNo ratings yet
- Worksheet06dated16072021 PDFDocument1 pageWorksheet06dated16072021 PDFPushpendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Report On The CircleDocument8 pagesReport On The CircleZanderNo ratings yet
- Geometry Unit 4a Circles 2019Document23 pagesGeometry Unit 4a Circles 2019api-287816312No ratings yet
- Common Competency 1 - Perform Mensuration and CalculationDocument45 pagesCommon Competency 1 - Perform Mensuration and CalculationAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4: CirclesDocument20 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4: CirclesJennyNo ratings yet
- MELVINDocument16 pagesMELVINRosito BaragoNo ratings yet
- Circles TheoremsDocument3 pagesCircles Theoremslorrain hussainNo ratings yet
- Geometry Postulates TheoremsDocument4 pagesGeometry Postulates TheoremsCresencio Genobiagon JrNo ratings yet
- Circle and TheoremsDocument1 pageCircle and TheoremsDare JamesNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorems PosterDocument1 pageCircle Theorems PosterPatrick Chukwunonso A.No ratings yet
- Circle Theorems PosterDocument1 pageCircle Theorems PosterDare JamesNo ratings yet
- PRE CALCULUS Q2 Angle Measures in A Unit Circle Standard Position of Angles and Its Coterminal AnglesDocument16 pagesPRE CALCULUS Q2 Angle Measures in A Unit Circle Standard Position of Angles and Its Coterminal AnglesekloymontecalvoNo ratings yet
- Circles TheoryDocument4 pagesCircles TheoryJamal AliyevNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 Quiz BDocument3 pagesMathematics 10 Quiz BChristelJaneAbaoBadalNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Plane FiguresDocument47 pagesModule 1 Plane FiguresRennel MallariNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument7 pagesIntroductionDhanush AnimationNo ratings yet
- Circle CLass 10 Nepal RevisionDocument10 pagesCircle CLass 10 Nepal RevisionBINAYA POKHARELNo ratings yet
- Circle Geometry SimplifiedDocument60 pagesCircle Geometry Simplifiedcrass5469No ratings yet
- In Euclidean GeometryDocument32 pagesIn Euclidean GeometryGilar JatisundaNo ratings yet
- Objective: - Identify and Describe Terms Related To CircleDocument16 pagesObjective: - Identify and Describe Terms Related To CircleDarlyn LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Math 3rd Year - Arcs and Angles 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesReviewer Math 3rd Year - Arcs and Angles 3rd QuarterNanay GiNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremsDocument21 pagesCircle Theoremsvicent johnNo ratings yet
- Properties of Triangles (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandProperties of Triangles (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- MS For All Labs - 2020Document13 pagesMS For All Labs - 2020Nia RamNo ratings yet
- Milk - PDDocument2 pagesMilk - PDNia RamNo ratings yet
- Spanish Orals Chapter 5Document33 pagesSpanish Orals Chapter 5Nia RamNo ratings yet
- Lab Write Up Guidelines For Plan and DesignDocument2 pagesLab Write Up Guidelines For Plan and DesignNia RamNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Circles Lesson Two (Circle Theorem)Document7 pagesMathematics - Circles Lesson Two (Circle Theorem)Nia RamNo ratings yet
- Csec Physics p1 June 2020 PDF FreeDocument18 pagesCsec Physics p1 June 2020 PDF FreeNia RamNo ratings yet
- June 2018 p1Document16 pagesJune 2018 p1Nia RamNo ratings yet
- Transitional DevicesDocument8 pagesTransitional DevicesNia RamNo ratings yet
- Spanish VocabularyDocument30 pagesSpanish VocabularyNia RamNo ratings yet
- June 2003 Paper 1 SpanishDocument12 pagesJune 2003 Paper 1 SpanishNia RamNo ratings yet