Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hemodialysis FXN
Hemodialysis FXN
Uploaded by
Sophia Dimayuga0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageHemodialysis filters waste and water from the blood to treat end-stage renal failure caused by conditions like hypertension, diabetes, infections, cysts, or gout. Complications during hemodialysis include hypotension, hypertension, chest pains, hypoglycemia, and cramps. These complications are managed by stopping ultrafiltration, administering fluids or medications like saline, Catapres, isordil, D50, or massage depending on the specific complication. The area above the anastomosis should be checked regularly and patients should limit fluids and avoid high potassium and calcium foods between treatments.
Original Description:
Original Title
Hemodialysis fxn
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHemodialysis filters waste and water from the blood to treat end-stage renal failure caused by conditions like hypertension, diabetes, infections, cysts, or gout. Complications during hemodialysis include hypotension, hypertension, chest pains, hypoglycemia, and cramps. These complications are managed by stopping ultrafiltration, administering fluids or medications like saline, Catapres, isordil, D50, or massage depending on the specific complication. The area above the anastomosis should be checked regularly and patients should limit fluids and avoid high potassium and calcium foods between treatments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageHemodialysis FXN
Hemodialysis FXN
Uploaded by
Sophia DimayugaHemodialysis filters waste and water from the blood to treat end-stage renal failure caused by conditions like hypertension, diabetes, infections, cysts, or gout. Complications during hemodialysis include hypotension, hypertension, chest pains, hypoglycemia, and cramps. These complications are managed by stopping ultrafiltration, administering fluids or medications like saline, Catapres, isordil, D50, or massage depending on the specific complication. The area above the anastomosis should be checked regularly and patients should limit fluids and avoid high potassium and calcium foods between treatments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
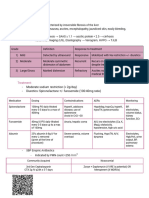
Hemodialysis fxn: Usual Complications:
- Filters waste and water from the blood. 1. Hypotension
Causes of Renal Failure: Mgt:
- Hypertensive arteriolar nephrosclerosis - Stop UF immediately.
(progressive kidney damage caused by - Trendelenburg position
poorly controlled HPN) - 100-200cc Normal Saline Bolus
- Diabetic nephropathy (Common 2. Hypertension
complication of both type 1 & 2 - Catapres 75mg (MAX DOSAGE: 150mg)
diabetes. Def: Poorly controlled a) 1st dose: 75mg
diabetes) b) 2nd dose: 75mg (if BP is
- Chronic glomerulonephritis (Caused by still high)
frequent infx such as UTI, HIV, HepB) c) Nicardipine drip (if BP
- Polycystic kidney disease. (Cysts that remains high)
enlarges kidney and loses its function. 3. Chest pains
Becomes damaged over time.) - Give isordil.
- Gouty Nephropathy (also called "Uric WARNING: Don’t adm if pt’s bp is low.
Acid Nephropathy" due to an increase 4. Hypoglycemia
in uric acid - Give D5050
5. Hyperglycemia
Types of Permanent Access:
- Insulin
1. AV fistula (connected blood vessels) WARNING: Don’t adm before tx. This
2. AV graph (foreign body) will lead to hypoglycemia.
6. Cramps
Best area to check (???) - Massage or Bolus
- 2-3 inches above the anastomosis Health teaching:
(surgical connection between two
structures (blood vessels)). 1. Limit fluids <750ml – 1L/day
2. Avoid fruits (↑ed K), Dairy (↑ed Ca)
Indication for end stage renal failure
1. GFR (Glomerular filtration rate) <15ml/min
Standard Dialysis treatment time: 4hrs
Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome
- Happens during a dialysis in patients
who missed frequent sessions. It is due
to rapid clearance of substances.
- S/S: headache, confusion, blurred vision
You might also like
- Packrat 15 - 2010Document86 pagesPackrat 15 - 2010EmersonMoreno80% (5)
- Usmle Step1 Q&A MukhtarDocument147 pagesUsmle Step1 Q&A MukhtarMuhtar MattursunNo ratings yet
- Approach To Shock, Airway and FluidsDocument63 pagesApproach To Shock, Airway and FluidsJerry GohNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine BookDocument34 pagesFamily Medicine Bookﻣﻠﻚ عيسىNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument5 pagesAcute Renal FailureSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Condition NCM 112Document10 pagesCardiac Condition NCM 112Irish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- (Study Group) Diabetic Nephropathy, Hypertensive NephropathyDocument7 pages(Study Group) Diabetic Nephropathy, Hypertensive NephropathyZarif IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- NURS 140 Exam 3 - Final Med SurgDocument11 pagesNURS 140 Exam 3 - Final Med Surgchristine.avaloNo ratings yet
- 001hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy PDFDocument23 pages001hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy PDFRosechelle Bas SamsonNo ratings yet
- OB - Hypertensive DisordersDocument4 pagesOB - Hypertensive DisordersJasmine Nicole RemetreNo ratings yet
- 1) DM, Cellulits, ACSDocument22 pages1) DM, Cellulits, ACSNu JoeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Investigations and ValuesDocument2 pagesLaboratory Investigations and Valuesniamh traceyNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes: Dr. Nupur SarkarDocument24 pagesFluid and Electrolytes: Dr. Nupur SarkarNupurshinjiniNo ratings yet
- 5 6181227438169653255Document61 pages5 6181227438169653255nurul nabillaNo ratings yet
- RenalDocument11 pagesRenalHero StoreNo ratings yet
- DR Stuart McPherson - Management of Decompensated CirrhosisDocument33 pagesDR Stuart McPherson - Management of Decompensated Cirrhosisana_miulescuNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiology Review: Stages in CKDDocument17 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiology Review: Stages in CKDAjie ZamNo ratings yet
- Long Case PUDDocument6 pagesLong Case PUDNadia SalwaniNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: 1. Reduction in FunctionDocument6 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: 1. Reduction in FunctionKelebogile NkomoNo ratings yet
- Hypertension in PregnancyDocument5 pagesHypertension in PregnancyKat MedNo ratings yet
- Renal Faliure 1Document50 pagesRenal Faliure 1180045No ratings yet
- Potassium DisturbancesDocument23 pagesPotassium DisturbancesThien Nhan MaiNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure - Dr. Wael Omar (AQH) : Functions of The KidneyDocument3 pagesAcute Renal Failure - Dr. Wael Omar (AQH) : Functions of The KidneyasdddNo ratings yet
- DKA Guidelines PDFDocument111 pagesDKA Guidelines PDFzahra zymNo ratings yet
- t2 Kidney DiseaseDocument52 pagest2 Kidney Diseasewany.fyza54No ratings yet
- Mojahid Sheet Complete PDFDocument176 pagesMojahid Sheet Complete PDFOsman SomiNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia EclampsiaDocument10 pagesPreeclampsia EclampsiajasphergliponeoNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury: Dana BabaDocument31 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: Dana Babanaheel98shNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Lecture 1 Critical Care NursingDocument52 pagesAcute Renal Failure Lecture 1 Critical Care NursingDina Rasmita100% (2)
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument18 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryHala AhmadNo ratings yet
- Approach To AKIDocument51 pagesApproach To AKImaruf47774No ratings yet
- Upper GIDocument14 pagesUpper GImuhamadamin90No ratings yet
- Cirrhosis SBPDocument9 pagesCirrhosis SBPapi-690342013No ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument6 pagesRenal SystemBalwayan, January DwayneNo ratings yet
- Self-Study - 24 - EndocrineDocument102 pagesSelf-Study - 24 - EndocrineQurat ul ainNo ratings yet
- 1 Emergency Medicine Medical Emergencies 2019Document35 pages1 Emergency Medicine Medical Emergencies 2019Chol Koryom CholNo ratings yet
- Medsurg ReviewerDocument9 pagesMedsurg ReviewerAmirrah LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders (Study Notes)Document11 pagesEndocrine Disorders (Study Notes)Danelle Harrison, RN90% (10)
- Chronic Kidney Injury OsamaDocument22 pagesChronic Kidney Injury Osamaosamafoud7710No ratings yet
- Endocrinology: Version 2 (2020)Document89 pagesEndocrinology: Version 2 (2020)RaoulSusanto SusantoNo ratings yet
- Noel A. Villanueva, MD, FPCP, FPSNDocument62 pagesNoel A. Villanueva, MD, FPCP, FPSNagilNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests: Myocardial Infarction Cardiac PanelDocument18 pagesDiagnostic Tests: Myocardial Infarction Cardiac PanelLuvleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Emergencies: Anaphylaxis Endocrine Emergencies HaemorrhageDocument38 pagesEmergencies: Anaphylaxis Endocrine Emergencies HaemorrhageRoshana MallawaarachchiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM)Document59 pagesDiabetes Mellitus (DM)Crome operatorNo ratings yet
- Body FluidDocument37 pagesBody FluidBir Mohammad SonetNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes Imbalances. DR Lujan AguilarDocument4 pagesElectrolytes Imbalances. DR Lujan AguilarDavid YousefNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia and EclampsiaaDocument24 pagesPreeclampsia and EclampsiaaCatalina GherbovetchiNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia and EclampsiaDocument24 pagesPreeclampsia and Eclampsialeeseol20yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument74 pagesCongestive Heart FailureNiharikaNo ratings yet
- AKI in OBSTETRICSDocument41 pagesAKI in OBSTETRICSDebajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCardiovascular SystemLeigh Maxenne IcoNo ratings yet
- Acute Liver FailureDocument4 pagesAcute Liver FailurejosephNo ratings yet
- Stagii - Nefrologie Stagiu UnuDocument7 pagesStagii - Nefrologie Stagiu UnuIoana DiaconuNo ratings yet
- Mojahid Sheet CompleteDocument176 pagesMojahid Sheet CompleteAdams AdamNo ratings yet
- مجاهد PDFDocument176 pagesمجاهد PDFHalema Al OkshNo ratings yet
- AKI, CKD SummaryDocument4 pagesAKI, CKD SummaryMuathNo ratings yet
- RENALDocument10 pagesRENALTeriese BautistaNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Disturbance-1Document22 pagesElectrolyte Disturbance-1Doaa Abd El-WahabNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: - ClassificationDocument22 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: - ClassificationFernando Junior Parra UchasaraNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury: Erika Phillie T. Chua Internal Medicine ResidentDocument48 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: Erika Phillie T. Chua Internal Medicine ResidenterikaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyyyyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyyyySophia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Case AnalysisDocument20 pagesCase AnalysisSophia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- SACI - Tracheostomy Care - ChecklistDocument2 pagesSACI - Tracheostomy Care - ChecklistSophia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- ABG ProcedureDocument25 pagesABG ProcedureSophia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- SACI - Obtaining An ABG Sample ChecklistDocument2 pagesSACI - Obtaining An ABG Sample ChecklistSophia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Obtaining An ECG ChecklistDocument2 pagesObtaining An ECG ChecklistSophia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- ERDrug Study DimayugaDocument25 pagesERDrug Study DimayugaSophia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- LumnereDocument232 pagesLumnereAlkaNo ratings yet
- Pink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 22Document16 pagesPink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 22jennmoyerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 28 - Pathology of DiabetesDocument34 pagesLecture 28 - Pathology of Diabetesapi-3703352100% (4)
- InterferenceDocument156 pagesInterferencebudi darmantaNo ratings yet
- Renal MCQ DiDocument10 pagesRenal MCQ Diahmed100% (1)
- Nephrology 7E 2016 PDFDocument2,710 pagesNephrology 7E 2016 PDFĐàoTrườngGiangNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Glomerular DiseasesDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Glomerular DiseasesMaryam Fadah100% (1)
- Lupus Nephritis - Treatment of Relapsing Focal or Diffuse Lupus Nephritis - UpToDateDocument16 pagesLupus Nephritis - Treatment of Relapsing Focal or Diffuse Lupus Nephritis - UpToDateOlga BabiiNo ratings yet
- Webinar FlyerDocument1 pageWebinar FlyerJoy DublasNo ratings yet
- AlexpaulosDocument21 pagesAlexpaulossabela afrilaNo ratings yet
- PlabDocument214 pagesPlabKarata SinghNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Urinary Tract Changes Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument5 pagesPregnancy Induced Urinary Tract Changes Urinary Tract InfectionsDilausan B MolukNo ratings yet
- 1 - 6 Managing Feline Renal Disease PDFDocument7 pages1 - 6 Managing Feline Renal Disease PDFIme PrezimeNo ratings yet
- HH August 2020Document80 pagesHH August 2020Fuente DelavidaNo ratings yet
- Travel Insurance - MadhuDocument7 pagesTravel Insurance - MadhudprosenjitNo ratings yet
- Utah KidneyDocument16 pagesUtah KidneyChristineGonzalesNo ratings yet
- KDIGO 2021 GD Guideline Executive SummaryDocument27 pagesKDIGO 2021 GD Guideline Executive SummaryMahmoud Elsheikh100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar Pustakakanarienvogel3No ratings yet
- Pathology Board Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesPathology Board Exam QuestionschristinejoanNo ratings yet
- Nephsap Article Pi IDocument94 pagesNephsap Article Pi Idoc keddyNo ratings yet
- Uric Acid, The Metabolic Syndrome, and Renal DiseaseDocument4 pagesUric Acid, The Metabolic Syndrome, and Renal DiseaseraynanthaNo ratings yet
- Pan Arab ConferenceDocument18 pagesPan Arab Conferencewalid hemidaNo ratings yet
- Report Global Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis Market Size Estimates & Forecasts Through 2027Document235 pagesReport Global Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis Market Size Estimates & Forecasts Through 2027FaisalNo ratings yet
- Guideline On Pediatric Renal - by DR Damte-3Document172 pagesGuideline On Pediatric Renal - by DR Damte-3Lensa H. BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Spanish Thesis IdeasDocument7 pagesSpanish Thesis Ideasreneefrancoalbuquerque100% (1)
- Flaxseed For Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesFlaxseed For Kidney DiseaseSagar Damani100% (1)
- Color Handbook Renal MedDocument231 pagesColor Handbook Renal MedounsNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of PreeclampsiaDocument9 pagesDiagnosis and Management of PreeclampsiaEka YogaNo ratings yet