Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DNA Handout Replication Model Folding Activity
DNA Handout Replication Model Folding Activity
Uploaded by
Haeriah Del ValleCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- FGIKReplicationTeacherKey6!18!15 CompressedDocument16 pagesFGIKReplicationTeacherKey6!18!15 CompressedSantiago Teixeira100% (1)
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication Worksheetfabyunaaa100% (1)
- Central Dogma Worksheet 2Document2 pagesCentral Dogma Worksheet 2josh VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- FGIKReplication Student HandoutDocument16 pagesFGIKReplication Student Handoutnj saim100% (1)
- DNA Pairing WSDocument1 pageDNA Pairing WSCheska100% (1)
- Kami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesKami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - DNA Replication WorksheetLuuk Van MeursNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Worksheet 2-16-2023 2Document2 pagesDNA Replication Worksheet 2-16-2023 2dfvccfNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Building DNADocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Building DNAGGNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetHANNA ANGELA LEJANONo ratings yet
- Dna Replication Final WorksheetDocument21 pagesDna Replication Final WorksheetjimmyNo ratings yet
- Q3 WK4 SLem ADM Module Protein SynthesisDocument13 pagesQ3 WK4 SLem ADM Module Protein SynthesisJazther Keishan RectoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetStrawberry RoNo ratings yet
- DelaCena ScienceDocument6 pagesDelaCena ScienceBossNateNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetMaktoumNo ratings yet
- Elijah James - 35-DNA Replication Worksheet - CompleteDocument4 pagesElijah James - 35-DNA Replication Worksheet - CompleteElijah JamesNo ratings yet
- DNA DR In-Class ActivitiesDocument15 pagesDNA DR In-Class ActivitiesCéline Engels100% (1)
- DNA WorksheetDocument4 pagesDNA WorksheetH DNo ratings yet
- MA 7.2 DNA Replication Lab Answer KeyDocument5 pagesMA 7.2 DNA Replication Lab Answer KeyddNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Building DNA: Nucleosides and PhosphatesDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Building DNA: Nucleosides and PhosphatesLESLEY AGUIRRENo ratings yet
- Cut and PasteDocument2 pagesCut and PasteKelsey PerreaultNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Bio Notes Student VersionDocument29 pagesScience 10 Bio Notes Student VersionEvan HuangNo ratings yet
- Cot 3 DNA Replication 2Document56 pagesCot 3 DNA Replication 2jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- GGL DNA ReplicationDocument5 pagesGGL DNA ReplicationYe Zhen HowNo ratings yet
- 2 DNA Replication IPDocument3 pages2 DNA Replication IPCaitlin EmilioNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentDocument4 pagesModule 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentFelix BrockmanNo ratings yet
- DNA ANALYSIS Simulating RecombinationDocument2 pagesDNA ANALYSIS Simulating RecombinationWilliams de la CruzNo ratings yet
- L2 - DNA KNex LabDocument16 pagesL2 - DNA KNex LabChristian MartinezNo ratings yet
- Paperclip Activity-Dna ReplicationDocument4 pagesPaperclip Activity-Dna Replicationapi-201291946No ratings yet
- Essay On Dna in Which You Compare Dna Replication With Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesEssay On Dna in Which You Compare Dna Replication With Protein Synthesisdwf6nx2z100% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesROCHELLE MAGBUONo ratings yet
- DNA & DNA ReplicationDocument26 pagesDNA & DNA Replicationvictoria.hugginsNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Name: Section: ScoreDocument2 pagesDNA Replication: Name: Section: ScoreashNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Practice PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Replication Practice PDFKim100% (1)
- DNA Databases - Evaluative Activity - José Ricardo Ramírez y Juan Diego RojasDocument9 pagesDNA Databases - Evaluative Activity - José Ricardo Ramírez y Juan Diego Rojasjuan diegoNo ratings yet
- BuildingDNA Student Exploration AnswersheetDocument4 pagesBuildingDNA Student Exploration AnswersheetF5 GuntherNo ratings yet
- Guess What I'ma Do It My WayDocument59 pagesGuess What I'ma Do It My Wayn.guledNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication WorksheetDocument3 pagesDna Replication WorksheetSakina İmanovaNo ratings yet
- Dna Structure Function and Replication ActivityDocument6 pagesDna Structure Function and Replication Activityapi-299996815100% (1)
- Activity For Grade 9 RubbyDocument5 pagesActivity For Grade 9 RubbyJocelyn Petallar BalasuelaNo ratings yet
- MIT7 016f18rec5Document5 pagesMIT7 016f18rec5Manish SarkarNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Dna Rna No VirusDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Dna Rna No VirusLara AlbeeshyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan, Student Handouts, Answer Keys/Samples, Supplemental MaterialsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan, Student Handouts, Answer Keys/Samples, Supplemental MaterialsPhranxies Jean Loay BlayaNo ratings yet
- Building DNA GizmoDocument2 pagesBuilding DNA GizmoMatt OrcuttNo ratings yet
- 12.3 Dna Replication HomeworkDocument5 pages12.3 Dna Replication Homeworklfkyunvlf100% (2)
- Building DNASEDocument6 pagesBuilding DNASEAlexis ButlerNo ratings yet
- Scamper Lesson Plan 1 - ColeDocument7 pagesScamper Lesson Plan 1 - Coleapi-750454979No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesROCHELLE MAGBUONo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 Week 2Document4 pagesScience 10 Q3 Week 2LYNO REY TEJADANo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesDNA ReplicationcaveNo ratings yet
- CertificateDocument15 pagesCertificateAbhishek AryaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument12 pagesLab ReportJISAS CLIMAXNo ratings yet
- Grade-10-LAS-Week-4A-3rd - QuarterDocument5 pagesGrade-10-LAS-Week-4A-3rd - QuarterYaRNo ratings yet
- Lab Report DNA PDFDocument8 pagesLab Report DNA PDFpadhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- G12 Biology: Class 10 Homework: Nucleotide ProportionDocument6 pagesG12 Biology: Class 10 Homework: Nucleotide ProportionkioontaghalNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 What Is DNADocument2 pagesActivity 2 What Is DNAAnna Van GoudoeverNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.2 DNA Replication 1Document3 pagesLesson 4.2 DNA Replication 1Marc Laurence LadoresNo ratings yet
- Transcription Translation ProtocolDocument10 pagesTranscription Translation ProtocoladindaNo ratings yet
- IB BladDocument8 pagesIB BladVara Prasad Raju PNo ratings yet
DNA Handout Replication Model Folding Activity
DNA Handout Replication Model Folding Activity
Uploaded by
Haeriah Del ValleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DNA Handout Replication Model Folding Activity
DNA Handout Replication Model Folding Activity
Uploaded by
Haeriah Del ValleCopyright:
Available Formats
DNA Replication Model Activity
BACKGROUND INFORMATION:
A cell’s genetic material (DNA) must be replicated or copied in anticipation of cell division. The new
cells that form after cell divide must be completely alike and have exactly the same amount of DNA to
function normally.
The process of DNA replication has three steps: 1) the DNA molecule unzips; 2) new nucleotides
are added to each side of the original DNA molecule; and 3) enzymes zip up and complete the two DNA
molecules.
PRE-ACTIVITY QUESTIONS:
1. What organic compound grouping does DNA belong to?
2. What is the monomer (basic unit) of the DNA molecule called?
3. What are the three parts of the DNA monomer?
4. What are the four nitrogen bases in DNA and how do they pair with each other?
5. What type of chemical bond holds the two strands of DNA together?
6. Why is DNA important for living organisms?
7. What does it mean when it is said that all living organisms have a universal genetic code?
8. Explain what is meant by if there are only 4 nucleotide types in DNA, why are all living things so
different?
9. Where in the cell does DNA replication take place?
10. What happens during DNA replication?
11. Why is it important that an exact copy of the original DNA is made before cell division (EX: if your
body makes new skin cells or new blood cells)?
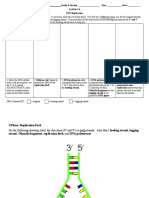
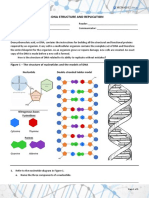
DNA REPLICATION MODELING ACTIVITY
1. List the order of the nitrogenous bases on the left side of the original DNA molecule (see page 3 of this
handout). Then list the order of the bases found on the right side.
ORIGINAL DNA MOLECULE
LEFT SIDE RIGHT SIDE
_________ __________
_________ __________
_________ __________
_________ __________
_________ __________
2. Complete the activity steps for modeling DNA REPLICATION found on page 3 on this handout.
3. In the chart below show the results of what happened to the original DNA model when it underwent
replication. List the nitrogenous bases on the lines. How do the strands compare? _______________
NEW DNA MOLECULE #1 NEW DNA MOLECULE #2
OLD STRAND NEW STRAND OLD STRAND NEW STRAND
____________ ____________ ____________ ____________
____________ ____________ ____________ ____________
____________ ____________ ____________ ____________
____________ ____________ ____________ ____________
____________ ____________ ____________ ____________
Name
Class
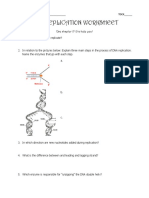
DNA REPLICATION MODELING Date
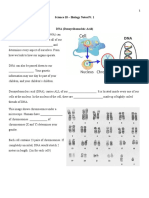
KEY:
T= 1. Fold a flap to the
A= back of the page
along this line.
C=
G=
S= 2. Follow your
teacher’s model
P= and
ORIGINAL DNA fold page in half
STRAND on this line.
Draw in new DNA ORIGINAL DNA
strand here STRAND
3. Fill in the shapes for the original
DNA strands with the letters A, T,
C, G, S, and P.
4. Color in the key and the original
DNA strands according to the key
you set up.
5. To replicate the original DNA, draw
in, label and color complementary
nucleotides for 2 new strands
formed by DNA replication.
6. Compare/contrast the original DNA molecule (old strands) with the 2 new DNA
molecules created by the replication process. How is this unlike making a photocopy of
the original DNA molecule?
You might also like
- FGIKReplicationTeacherKey6!18!15 CompressedDocument16 pagesFGIKReplicationTeacherKey6!18!15 CompressedSantiago Teixeira100% (1)
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication Worksheetfabyunaaa100% (1)
- Central Dogma Worksheet 2Document2 pagesCentral Dogma Worksheet 2josh VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- FGIKReplication Student HandoutDocument16 pagesFGIKReplication Student Handoutnj saim100% (1)
- DNA Pairing WSDocument1 pageDNA Pairing WSCheska100% (1)
- Kami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesKami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - DNA Replication WorksheetLuuk Van MeursNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Worksheet 2-16-2023 2Document2 pagesDNA Replication Worksheet 2-16-2023 2dfvccfNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Building DNADocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Building DNAGGNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetHANNA ANGELA LEJANONo ratings yet
- Dna Replication Final WorksheetDocument21 pagesDna Replication Final WorksheetjimmyNo ratings yet
- Q3 WK4 SLem ADM Module Protein SynthesisDocument13 pagesQ3 WK4 SLem ADM Module Protein SynthesisJazther Keishan RectoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetStrawberry RoNo ratings yet
- DelaCena ScienceDocument6 pagesDelaCena ScienceBossNateNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetMaktoumNo ratings yet
- Elijah James - 35-DNA Replication Worksheet - CompleteDocument4 pagesElijah James - 35-DNA Replication Worksheet - CompleteElijah JamesNo ratings yet
- DNA DR In-Class ActivitiesDocument15 pagesDNA DR In-Class ActivitiesCéline Engels100% (1)
- DNA WorksheetDocument4 pagesDNA WorksheetH DNo ratings yet
- MA 7.2 DNA Replication Lab Answer KeyDocument5 pagesMA 7.2 DNA Replication Lab Answer KeyddNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Building DNA: Nucleosides and PhosphatesDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Building DNA: Nucleosides and PhosphatesLESLEY AGUIRRENo ratings yet
- Cut and PasteDocument2 pagesCut and PasteKelsey PerreaultNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Bio Notes Student VersionDocument29 pagesScience 10 Bio Notes Student VersionEvan HuangNo ratings yet
- Cot 3 DNA Replication 2Document56 pagesCot 3 DNA Replication 2jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- GGL DNA ReplicationDocument5 pagesGGL DNA ReplicationYe Zhen HowNo ratings yet
- 2 DNA Replication IPDocument3 pages2 DNA Replication IPCaitlin EmilioNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentDocument4 pagesModule 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentFelix BrockmanNo ratings yet
- DNA ANALYSIS Simulating RecombinationDocument2 pagesDNA ANALYSIS Simulating RecombinationWilliams de la CruzNo ratings yet
- L2 - DNA KNex LabDocument16 pagesL2 - DNA KNex LabChristian MartinezNo ratings yet
- Paperclip Activity-Dna ReplicationDocument4 pagesPaperclip Activity-Dna Replicationapi-201291946No ratings yet
- Essay On Dna in Which You Compare Dna Replication With Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesEssay On Dna in Which You Compare Dna Replication With Protein Synthesisdwf6nx2z100% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesROCHELLE MAGBUONo ratings yet
- DNA & DNA ReplicationDocument26 pagesDNA & DNA Replicationvictoria.hugginsNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Name: Section: ScoreDocument2 pagesDNA Replication: Name: Section: ScoreashNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Practice PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Replication Practice PDFKim100% (1)
- DNA Databases - Evaluative Activity - José Ricardo Ramírez y Juan Diego RojasDocument9 pagesDNA Databases - Evaluative Activity - José Ricardo Ramírez y Juan Diego Rojasjuan diegoNo ratings yet
- BuildingDNA Student Exploration AnswersheetDocument4 pagesBuildingDNA Student Exploration AnswersheetF5 GuntherNo ratings yet
- Guess What I'ma Do It My WayDocument59 pagesGuess What I'ma Do It My Wayn.guledNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication WorksheetDocument3 pagesDna Replication WorksheetSakina İmanovaNo ratings yet
- Dna Structure Function and Replication ActivityDocument6 pagesDna Structure Function and Replication Activityapi-299996815100% (1)
- Activity For Grade 9 RubbyDocument5 pagesActivity For Grade 9 RubbyJocelyn Petallar BalasuelaNo ratings yet
- MIT7 016f18rec5Document5 pagesMIT7 016f18rec5Manish SarkarNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Dna Rna No VirusDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Dna Rna No VirusLara AlbeeshyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan, Student Handouts, Answer Keys/Samples, Supplemental MaterialsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan, Student Handouts, Answer Keys/Samples, Supplemental MaterialsPhranxies Jean Loay BlayaNo ratings yet
- Building DNA GizmoDocument2 pagesBuilding DNA GizmoMatt OrcuttNo ratings yet
- 12.3 Dna Replication HomeworkDocument5 pages12.3 Dna Replication Homeworklfkyunvlf100% (2)
- Building DNASEDocument6 pagesBuilding DNASEAlexis ButlerNo ratings yet
- Scamper Lesson Plan 1 - ColeDocument7 pagesScamper Lesson Plan 1 - Coleapi-750454979No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesROCHELLE MAGBUONo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3 Week 2Document4 pagesScience 10 Q3 Week 2LYNO REY TEJADANo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesDNA ReplicationcaveNo ratings yet
- CertificateDocument15 pagesCertificateAbhishek AryaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument12 pagesLab ReportJISAS CLIMAXNo ratings yet
- Grade-10-LAS-Week-4A-3rd - QuarterDocument5 pagesGrade-10-LAS-Week-4A-3rd - QuarterYaRNo ratings yet
- Lab Report DNA PDFDocument8 pagesLab Report DNA PDFpadhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- G12 Biology: Class 10 Homework: Nucleotide ProportionDocument6 pagesG12 Biology: Class 10 Homework: Nucleotide ProportionkioontaghalNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 What Is DNADocument2 pagesActivity 2 What Is DNAAnna Van GoudoeverNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.2 DNA Replication 1Document3 pagesLesson 4.2 DNA Replication 1Marc Laurence LadoresNo ratings yet
- Transcription Translation ProtocolDocument10 pagesTranscription Translation ProtocoladindaNo ratings yet
- IB BladDocument8 pagesIB BladVara Prasad Raju PNo ratings yet