Professional Documents
Culture Documents
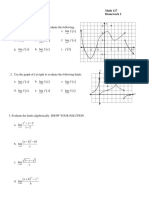
Free Fallling Problems 1
Free Fallling Problems 1
Uploaded by
JmOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Free Fallling Problems 1
Free Fallling Problems 1
Uploaded by
JmCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercises 63
2.33 .. Mars Landing. In January 2004, NASA landed explo- the lander is in free fall. What is the speed of the lander just
ration vehicles on Mars. Part of the descent consisted of the fol- before it touches the surface? The acceleration due to gravity on
lowing stages: the moon is 1.6 m>s2.
2.41 .. A Simple Reaction-Time Test. A meter stick is held ver-
Stage A: Friction with the atmosphere reduced the speed from tically above your hand, with the lower end between your thumb
19,300 km>h to 1600 km>h in 4.0 min. and first finger. On seeing the meter stick released, you grab it with
Stage B: A parachute then opened to slow it down to 321 km>h in these two fingers. You can calculate your reaction time from the
94 s. distance the meter stick falls, read directly from the point where
Stage C: Retro rockets then fired to reduce its speed to zero over a your fingers grabbed it. (a) Derive a relationship for your reaction
distance of 75 m. time in terms of this measured distance, d. (b) If the measured dis-
Assume that each stage followed immediately after the preceding tance is 17.6 cm, what is the reaction time?
one and that the acceleration during each stage was constant. 2.42 .. A brick is dropped (zero initial speed) from the roof of a
(a) Find the rocket’s acceleration (in m>s2) during each stage. building. The brick strikes the ground in 2.50 s. You may ignore air
(b) What total distance (in km) did the rocket travel during stages resistance, so the brick is in free fall. (a) How tall, in meters, is the
A, B, and C? building? (b) What is the magnitude of the brick’s velocity just
2.34 . At the instant the traffic light turns green, a car that has been before it reaches the ground? (c) Sketch ay-t, vy-t, and y-t graphs
waiting at an intersection starts ahead with a constant acceleration for the motion of the brick.
of 3.20 m>s2. At the same instant a truck, traveling with a constant 2.43 .. Launch Failure. A 7500-kg rocket blasts off vertically
speed of 20.0 m>s, overtakes and passes the car. (a) How far from the launch pad with a constant upward acceleration of
beyond its starting point does the car overtake the truck? (b) How 2.25 m>s2 and feels no appreciable air resistance. When it has
fast is the car traveling when it overtakes the truck? (c) Sketch an reached a height of 525 m, its engines suddenly fail so that the
x-t graph of the motion of both vehicles. Take x = 0 at the inter- only force acting on it is now gravity. (a) What is the maximum
section. (d) Sketch a vx-t graph of the motion of both vehicles. height this rocket will reach above the launch pad? (b) How much
time after engine failure will elapse before the rocket comes crash-
Section 2.5 Freely Falling Bodies ing down to the launch pad, and how fast will it be moving just
2.35 .. (a) If a flea can jump straight up to a height of 0.440 m, before it crashes? (c) Sketch ay-t, vy-t, and y-t graphs of the
what is its initial speed as it leaves the ground? (b) How long is it rocket’s motion from the instant of blast-off to the instant just
in the air? before it strikes the launch pad.
2.36 .. A small rock is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 2.44 .. A hot-air balloonist, ris- Figure E2.44
18.0 m>s from the edge of the roof of a 30.0-m-tall building. The ing vertically with a constant
v 5 5.00 m/s
rock doesn’t hit the building on its way back down and lands in the velocity of magnitude 5.00 m>s,
street below. Air resistance can be neglected. (a) What is the speed releases a sandbag at an instant
of the rock just before it hits the street? (b) How much time elapses when the balloon is 40.0 m above
from when the rock is thrown until it hits the street? the ground (Fig. E2.44). After it is
2.37 . A juggler throws a bowling pin straight up with an initial released, the sandbag is in free fall.
speed of 8.20 m> s. How much time elapses until the bowling pin (a) Compute the position and
returns to the juggler’s hand? velocity of the sandbag at 0.250 s
2.38 .. You throw a glob of putty straight up toward the ceiling, and 1.00 s after its release. (b) How
which is 3.60 m above the point where the putty leaves your hand. many seconds after its release will
The initial speed of the putty as it leaves your hand is 9.50 m>s. the bag strike the ground? (c) With
(a) What is the speed of the putty just before it strikes the ceiling? what magnitude of velocity does it
(b) How much time from when it leaves your hand does it take the strike the ground? (d) What is the
putty to reach the ceiling? greatest height above the ground
2.39 .. A tennis ball on Mars, where the acceleration due to grav- that the sandbag reaches? (e) 40.0 m to ground
ity is 0.379g and air resistance is negligible, is hit directly upward Sketch ay-t, vy-t, and y-t graphs for
and returns to the same level 8.5 s later. (a) How high above its the motion.
original point did the ball go? (b) How fast was it moving just after 2.45 . BIO The rocket-driven sled Sonic Wind No. 2, used for
being hit? (c) Sketch graphs of the ball’s vertical position, vertical investigating the physiological effects of large accelerations, runs
velocity, and vertical accelera- on a straight, level track 1070 m (3500 ft) long. Starting from rest,
tion as functions of time while Figure E2.40 it can reach a speed of 224 m>s 1500 mi>h2 in 0.900 s. (a) Com-
it’s in the Martian air. pute the acceleration in m>s2, assuming that it is constant. (b)
2.40 .. Touchdown on the What is the ratio of this acceleration to that of a freely falling body
Moon. A lunar lander is (g)? (c) What distance is covered in 0.900 s? (d) A magazine article
making its descent to Moon states that at the end of a certain run, the speed of the sled
Base I (Fig. E2.40). The lander decreased from 283 m>s 1632 mi>h2 to zero in 1.40 s and that
descends slowly under the retro- during this time the magnitude of the acceleration was greater than
thrust of its descent engine. The 40g. Are these figures consistent?
engine is cut off when the lan- 2.46 . An egg is thrown nearly vertically upward from a point
5.0 m
der is 5.0 m above the surface near the cornice of a tall building. It just misses the cornice on the
and has a downward speed of way down and passes a point 30.0 m below its starting point 5.00 s
0.8 m>s. With the engine off, after it leaves the thrower’s hand. Air resistance may be ignored.
You might also like
- Worksheet VelocityDocument1 pageWorksheet Velocityanon_78301203367% (3)
- Hewitt Chapter 3 Free Fall Note OutlineDocument5 pagesHewitt Chapter 3 Free Fall Note OutlineAsmaa AkraicheNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Plates 1Document32 pagesPlates 1drhrteNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Select and Answer 10 Problems Correctly To Obtain Perfect Score (10 Points Per Problem) - You May Answer More Than 10 Problems. However, Maximum Score Is Limited To 100 PointsDocument9 pagesSelect and Answer 10 Problems Correctly To Obtain Perfect Score (10 Points Per Problem) - You May Answer More Than 10 Problems. However, Maximum Score Is Limited To 100 PointsKRISTINE MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Alternate Problem Set 2 QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesAlternate Problem Set 2 QUESTIONSKRISTINE MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument1 pageProblem SetAicelle AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsBOSS BOSS100% (1)
- Physics Homework Chapter 2: Review Example 2.5Document2 pagesPhysics Homework Chapter 2: Review Example 2.5甯敬芸No ratings yet
- FHSC1014 Mechanics Tutorial 3 SDocument3 pagesFHSC1014 Mechanics Tutorial 3 SSteve ThawNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3Cheryl LowNo ratings yet
- D) 83 M D) Acceleration Remains The Same and Speed IncreasesDocument8 pagesD) 83 M D) Acceleration Remains The Same and Speed IncreasesojuNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Parabolic MotionDocument18 pagesParabolic Motionadrian.hodorNo ratings yet
- Speed Velocity Distance Time 1Document1 pageSpeed Velocity Distance Time 1JmNo ratings yet
- Extra Exercises Chapter 2: (4 Ms - 4 Ms 0 2 MS)Document4 pagesExtra Exercises Chapter 2: (4 Ms - 4 Ms 0 2 MS)hadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- Test Generator - Create Question Papers OnlineDocument7 pagesTest Generator - Create Question Papers OnlineDETECTIVE UNKNOWNNo ratings yet
- Session 1: Kinematics QuestionsDocument2 pagesSession 1: Kinematics Questionsapi-3804363100% (1)
- Midterm Practice1 Sc3Document11 pagesMidterm Practice1 Sc3Toni TonesNo ratings yet
- Projectile - Revision SheetDocument3 pagesProjectile - Revision SheetNazek KhayatNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document9 pagesSheet 1Tony AtefNo ratings yet
- Mechanics - Quarter 2 - Quiz N0.1Document3 pagesMechanics - Quarter 2 - Quiz N0.1Charles Miguel F. RalaNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Revision??Document3 pagesRevision??2023406014No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (2) DqwdqwdasdadxasxzaxaxaDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 (2) DqwdqwdasdadxasxzaxaxaAmeer AmefNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 1Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 1Nguyễn Quốc ThúcNo ratings yet
- 10-1-12 Projectile Motion Practice Problems APBDocument14 pages10-1-12 Projectile Motion Practice Problems APBAngel MereteNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document4 pagesTutorial 3伟铭No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - KinematicsDocument4 pagesTutorial 3 - KinematicsDanny MutamboNo ratings yet
- DPP 12octDocument2 pagesDPP 12octSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- PP 150 ProblemsDocument17 pagesPP 150 ProblemsRanda CarterNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part2 SolutionDocument9 pagesUSTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part2 SolutionNguyen Duy NgocNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledDenisse Torizo OlanNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion at An Angle QuestionDocument1 pageProjectile Motion at An Angle QuestiontuvvacNo ratings yet
- Tuto Student CHP 2 - Stage 3Document4 pagesTuto Student CHP 2 - Stage 3VENTLOVENo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IDocument4 pagesAssignment - Ituhina27No ratings yet
- Physics Quarter 1 Study GuideDocument14 pagesPhysics Quarter 1 Study GuideGeorge RangnahahbilmangoyumdidahmgehNo ratings yet
- MOTION UNDERGRAVITY+NON UNIFORM 'A'-GraphsDocument12 pagesMOTION UNDERGRAVITY+NON UNIFORM 'A'-Graphsarjun shindeNo ratings yet
- PPP0101 Principles of Physics Tutorial 2: 2 o R o SDocument5 pagesPPP0101 Principles of Physics Tutorial 2: 2 o R o STAN XIN YINo ratings yet
- Projectile ProblemsDocument2 pagesProjectile ProblemsJmNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 1Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 1Nguyễn KhôiNo ratings yet
- Exercise02a Kinematic OnlyDocument2 pagesExercise02a Kinematic Only22000496No ratings yet
- Kinematics Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC I-Jun 13Document11 pagesKinematics Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC I-Jun 13Mohit GargNo ratings yet
- B) Ball A Hits The Tabletop at The Same Time As Ball BDocument9 pagesB) Ball A Hits The Tabletop at The Same Time As Ball BErica DocotNo ratings yet
- AIEEE Module Q.P. Kinematics)Document6 pagesAIEEE Module Q.P. Kinematics)MOHAMMED ASIF100% (1)
- Physic 1-Homework Chapter 1Document2 pagesPhysic 1-Homework Chapter 1Dương Ngọc ThếNo ratings yet
- University Physics Chapter2Document9 pagesUniversity Physics Chapter2Karlo OrnietaNo ratings yet
- 1D Worksheet PDFDocument2 pages1D Worksheet PDFGenesis ValerioNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Projectile Motion WarmUpDocument1 page2.2 Projectile Motion WarmUpNoah SegalNo ratings yet
- Session 3: Work Energy Power QuestionsDocument4 pagesSession 3: Work Energy Power Questionsapi-3804363100% (1)
- Worksheet - Projectile Motion 2Document5 pagesWorksheet - Projectile Motion 2mjdaihmohammedNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Review 1D - Without AnswersDocument3 pagesKinematics Review 1D - Without AnswersShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Business Report VillarDocument17 pagesBusiness Report VillarJmNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document2 pagesHomework 2JmNo ratings yet
- Projectile ProblemsDocument2 pagesProjectile ProblemsJmNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 0Document1 pageWorksheet 0JmNo ratings yet
- 1 - Functions and ContinuityDocument59 pages1 - Functions and ContinuityJmNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM10Document1 pagePROBLEM10JmNo ratings yet
- Projectile Problems Odd Number AnswersDocument1 pageProjectile Problems Odd Number AnswersJmNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM8Document1 pagePROBLEM8JmNo ratings yet
- Speed Velocity Distance Time 1Document1 pageSpeed Velocity Distance Time 1JmNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM3Document1 pagePROBLEM3JmNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM2Document1 pagePROBLEM2JmNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM5Document1 pagePROBLEM5JmNo ratings yet
- Expansion Joints ResearchDocument8 pagesExpansion Joints ResearchKovan AzizNo ratings yet
- 3D Elasticity TheoryDocument6 pages3D Elasticity TheorySaurabh PednekarNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Flexible Multibody Dynamics ConDocument16 pages1 Introduction To Flexible Multibody Dynamics ConMoezNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6ADocument2 pagesWorksheet 6AZhang JiangNo ratings yet
- Simulation Research On An Electric Vehicle Chassis System Based On A Collaborative Control SystemDocument18 pagesSimulation Research On An Electric Vehicle Chassis System Based On A Collaborative Control SystemJulius RojoNo ratings yet
- Optimum Redesign of Axial Fan Blade AttachmentDocument15 pagesOptimum Redesign of Axial Fan Blade AttachmentNarayanaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Sem1 PhysicsDocument2 pagesImportant Questions Sem1 Physicsprashanth kumar100% (1)
- Lec 2 Mechanical Properties of Dental MateriaslDocument59 pagesLec 2 Mechanical Properties of Dental MateriaslAbrar AxNo ratings yet
- Brass AnnealingDocument11 pagesBrass AnnealingChristos KalavrytinosNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech ProblemsDocument2 pagesFluid Mech ProblemsMarky SantosNo ratings yet
- CE6303-Mech FL Unit 1-5Document60 pagesCE6303-Mech FL Unit 1-5Mohan SivaNo ratings yet
- Domino WavesDocument11 pagesDomino WavesSahil ChadhaNo ratings yet
- SD 2013 IYPT Reference Kit PDFDocument81 pagesSD 2013 IYPT Reference Kit PDFMateus Corato ZanarellaNo ratings yet
- Wear Introduction of WearDocument22 pagesWear Introduction of WearVinit ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- SPH3U FormulasDocument1 pageSPH3U FormulasmarcNo ratings yet
- 2008 - Filkovic - Graduate Work - 3D Panel MethodDocument70 pages2008 - Filkovic - Graduate Work - 3D Panel MethodMatej AndrejašičNo ratings yet
- Computer-Aided Analysis of Mechanical Systems PDFDocument388 pagesComputer-Aided Analysis of Mechanical Systems PDFnbritomarNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical Properties of WoodDocument257 pagesThe Mechanical Properties of WoodEngineering VideosNo ratings yet
- Water HammerDocument57 pagesWater HammervikrammotiNo ratings yet
- Bearings Starting Running Torque NSK PDFDocument5 pagesBearings Starting Running Torque NSK PDFcarlfelipeNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesFaculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringpranithNo ratings yet
- Aficio MP 301Document74 pagesAficio MP 301Oficina ProduçãoNo ratings yet
- Anchored Sheet Pile Wall DesignDocument7 pagesAnchored Sheet Pile Wall Designmahmoud meslehNo ratings yet
- Applied ScienceDocument7 pagesApplied ScienceSharon AmondiNo ratings yet
- Gamma-Ray Anisotropy ThermometersDocument4 pagesGamma-Ray Anisotropy ThermometersSameh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Kippap Diagnostic Exam May 2022Document9 pagesKippap Diagnostic Exam May 2022Maryrose Aguirre SerranoNo ratings yet
- Leg Support Stress For VesselDocument7 pagesLeg Support Stress For VesselTan Chee MingNo ratings yet
- UIC 510-5 - Wyd. 2, V 2007 - AngDocument72 pagesUIC 510-5 - Wyd. 2, V 2007 - Angwekew78320No ratings yet