Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Science HEART
General Science HEART
Uploaded by
3acsgrp 3acsgrpCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Function Human HeartDocument13 pagesFunction Human Heartshyam_inkNo ratings yet
- The Human HeartDocument3 pagesThe Human HeartEmely SolonNo ratings yet
- Human Heart ScienceDocument7 pagesHuman Heart ScienceJewel Kathryn MorenoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o oDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o okayaldrNo ratings yet
- Second Term Pharmacy 2019-2020 Lecture One Heart and Blood VesselsDocument16 pagesSecond Term Pharmacy 2019-2020 Lecture One Heart and Blood VesselsommNo ratings yet
- Exploration Rough Draft1Document8 pagesExploration Rough Draft1api-540422259No ratings yet
- Unit Seven: Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesUnit Seven: Cardiovascular SystemKath RubioNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 pagesCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Our Heart BeatsDocument7 pagesOur Heart BeatsferyNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy of The Heart: Featured Snippet From The WebDocument4 pagesBasic Anatomy of The Heart: Featured Snippet From The WebMay Larkspur TadeoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartjeffcaselNo ratings yet
- Overview of The HeartDocument3 pagesOverview of The HeartSamanthaKhallanNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardio Vascular SystemguptaasitNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCardiovascular SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 GcsDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 3 GcsNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- CirculatoryDocument8 pagesCirculatoryKristel Faye DioNo ratings yet
- The Human HeartDocument19 pagesThe Human HeartbeshlyNo ratings yet
- With Each HeartbeatDocument6 pagesWith Each HeartbeatnahlajovialNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument1 pageHeartaderonke123No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory System Systemleah rualesNo ratings yet
- Heart and BrainDocument29 pagesHeart and BrainDIPANJAN MAJUMDAR100% (6)
- Cardiovascular System or Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System or Circulatory SystemAleeza gondalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyClint-Marie LaxaNo ratings yet
- Heart Circulation - ModuleDocument1 pageHeart Circulation - ModuleMicth Laica BetoyaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument1 pageCirculatory Systemandrzej36No ratings yet
- Topic 7 Circulatory SystemDocument17 pagesTopic 7 Circulatory Systemkiftia melNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Human HeartDocument17 pagesBiology Project Human HeartdeepmanisharmaNo ratings yet
- Heart: Layers of The Heart WallDocument3 pagesHeart: Layers of The Heart WallAdaNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemABDUL HANANNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument11 pagesThe HeartElisa TapalesNo ratings yet
- Circulation Notes 2B - The HeartDocument4 pagesCirculation Notes 2B - The HeartRihanna E.No ratings yet
- Human Heart: Anatomy, Function & FactsDocument2 pagesHuman Heart: Anatomy, Function & FactsFlorie Fe Rosario OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Blood CirculationDocument8 pagesBlood CirculationnorafidaishakNo ratings yet
- Reading-The Human HeartDocument4 pagesReading-The Human HeartMichelle ViafaraNo ratings yet
- Human Heart Human Heart: Biology Holiday's WorkDocument13 pagesHuman Heart Human Heart: Biology Holiday's WorkHimanshu GargNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System in HumansDocument4 pagesCirculatory System in Humanspetra.t.ayalNo ratings yet
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Document13 pagesBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756No ratings yet
- The Human Heart: OCS Applied Science Mrs. BonifayDocument18 pagesThe Human Heart: OCS Applied Science Mrs. BonifaysudhirNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology The HeartDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology The Heartkheng100% (4)
- Circulatory System: Miss Javi ZúñigaDocument9 pagesCirculatory System: Miss Javi ZúñigaadisNo ratings yet
- Human HeartDocument6 pagesHuman HeartVui SengNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2a CirculationDocument8 pagesWEEK 2a Circulationdoodle dangerNo ratings yet
- The Human Heart: Location, Size and ShapeDocument9 pagesThe Human Heart: Location, Size and ShapeL I G-Arijit HisabiaNo ratings yet
- Tugasan B.IDocument2 pagesTugasan B.IMas IzatulNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Cardiovascular SystemElvira Wisakhadewi100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology ASCVDDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ASCVDAlvheen JoaquinNo ratings yet
- CV SystemDocument11 pagesCV System4everiamarmyNo ratings yet
- Function of The Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesFunction of The Circulatory SystemChristine SegundoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 4 - Circulatory Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Function and Structure of Heart and LungsDocument2 pagesFunction and Structure of Heart and LungsClaChristinaNo ratings yet
- Heart Structure, Function and Arrhythmias: Elizabeth M. Cherry and Flavio H. FentonDocument15 pagesHeart Structure, Function and Arrhythmias: Elizabeth M. Cherry and Flavio H. Fentonmaurice bertrandNo ratings yet
- A Case Study About Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument10 pagesA Case Study About Cardiovascular DiseaseBarben Balaquit100% (1)
- Lesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandLesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- PART-B Question No 7Document3 pagesPART-B Question No 73acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- SPCO AdvDocument2 pagesSPCO Adv3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Based On Constitutions of PakistanDocument16 pagesMcqs Based On Constitutions of Pakistan3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- We Design For Your ExpectationDocument1 pageWe Design For Your Expectation3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Organiztional ChartDocument2 pagesOrganiztional Chart3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- LLB, SM Law College, HR 2Document61 pagesLLB, SM Law College, HR 23acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- AdvonaeDocument1 pageAdvonae3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Rights and Its CasesDocument2 pagesFundamental Rights and Its Cases3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- TESTINGDocument1 pageTESTING3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 6565232Document2 pagesProfile 65652323acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 6212151Document1 pageProfile 62121513acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Our TeamDocument1 pageOur Team3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Work of AdvocateDocument1 pageWork of Advocate3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 55416516Document2 pagesProfile 554165163acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 6326521521Document1 pageProfile 63265215213acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 6221515Document2 pagesProfile 62215153acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- G 456 DFDocument1 pageG 456 DF3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 5454Document2 pagesProfile 54543acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 51561Document2 pagesProfile 515613acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 5Document2 pagesProfile 53acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Provisional Constitution Order 1981Document1 pageProvisional Constitution Order 19813acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- COnstitution of Pakistan by AAmra TariqDocument6 pagesCOnstitution of Pakistan by AAmra Tariq3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Assignemt of Pakistan ConstitutionDocument1 pageAssignemt of Pakistan Constitution3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Principles of PoliciesDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Policies3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- PM Pakistan PowerDocument3 pagesPM Pakistan Power3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court JurisdictionDocument3 pagesSupreme Court Jurisdiction3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of Constitution of Pakistan 1973Document2 pagesSalient Features of Constitution of Pakistan 19733acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Constitution of Pakistan 1973 0N EASSYDocument14 pagesConstitution of Pakistan 1973 0N EASSY3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Eighteenth Amendment 2010Document1 pageEighteenth Amendment 20103acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of Supreme Court AND HIGH COURTDocument3 pagesJurisdiction of Supreme Court AND HIGH COURT3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
General Science HEART
General Science HEART
Uploaded by
3acsgrp 3acsgrpOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Science HEART
General Science HEART
Uploaded by
3acsgrp 3acsgrpCopyright:
Available Formats
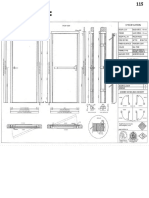
General Science
Human Psychology:
Human psychology is the scientific study of various function of human body in its
normal states.
Cell:
The basic unit of living organism is cell.
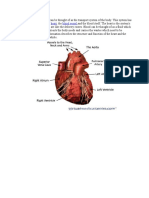
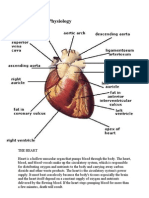
Human Heart:
Human heart is a muscular organ that pumps bloods throughout the body.
If [the heart] is not able to supply blood to the organs and tissues, they'll die.
A human heart is roughly the size of a large fist.
The heart weighs between about 10 to 12 ounces (280 to 340 grams) in men
and 8 to 10 ounces (230 to 280 grams) in women.
The human heart has four chambers: two upper chambers (the atria)
and two lower ones (the ventricles).
The heart circulates blood through two pathways: the pulmonary circuit
and the systemic circuit.
In the pulmonary circuit, deoxygenated blood leaves the right ventricle
of the heart via the pulmonary artery and travels to the lungs, then
returns as oxygenated blood to the left atrium of the heart via the
pulmonary vein.
In the systemic circuit, oxygenated blood leaves the body via the left
ventricle to the aorta, and from there enters the arteries and capillaries
where it supplies the body's tissues with oxygen. Deoxygenated blood
returns via veins to the venae cavae, re-entering the heart's right
atrium.
Blockage of any of these arteries can cause a heart attack, or damage
to the muscle of the heart.
The heart beats about 100,000 times per day (about 3 billion beats in a
lifetime).
An adult heart beats about 60 to 80 times per minute.
Newborns' hearts beat faster than adult hearts, about 70 to 190 beats per
minute.
The heart pumps about 6 quarts (5.7 liters) of blood throughout the body.
The heart is located in the center of the chest, usually pointing slightly left.
You might also like
- Function Human HeartDocument13 pagesFunction Human Heartshyam_inkNo ratings yet
- The Human HeartDocument3 pagesThe Human HeartEmely SolonNo ratings yet
- Human Heart ScienceDocument7 pagesHuman Heart ScienceJewel Kathryn MorenoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o oDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o okayaldrNo ratings yet
- Second Term Pharmacy 2019-2020 Lecture One Heart and Blood VesselsDocument16 pagesSecond Term Pharmacy 2019-2020 Lecture One Heart and Blood VesselsommNo ratings yet
- Exploration Rough Draft1Document8 pagesExploration Rough Draft1api-540422259No ratings yet
- Unit Seven: Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesUnit Seven: Cardiovascular SystemKath RubioNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 pagesCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Our Heart BeatsDocument7 pagesOur Heart BeatsferyNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy of The Heart: Featured Snippet From The WebDocument4 pagesBasic Anatomy of The Heart: Featured Snippet From The WebMay Larkspur TadeoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartjeffcaselNo ratings yet
- Overview of The HeartDocument3 pagesOverview of The HeartSamanthaKhallanNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardio Vascular SystemguptaasitNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCardiovascular SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 GcsDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 3 GcsNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- CirculatoryDocument8 pagesCirculatoryKristel Faye DioNo ratings yet
- The Human HeartDocument19 pagesThe Human HeartbeshlyNo ratings yet
- With Each HeartbeatDocument6 pagesWith Each HeartbeatnahlajovialNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument1 pageHeartaderonke123No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory System Systemleah rualesNo ratings yet
- Heart and BrainDocument29 pagesHeart and BrainDIPANJAN MAJUMDAR100% (6)
- Cardiovascular System or Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System or Circulatory SystemAleeza gondalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyClint-Marie LaxaNo ratings yet
- Heart Circulation - ModuleDocument1 pageHeart Circulation - ModuleMicth Laica BetoyaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument1 pageCirculatory Systemandrzej36No ratings yet
- Topic 7 Circulatory SystemDocument17 pagesTopic 7 Circulatory Systemkiftia melNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Human HeartDocument17 pagesBiology Project Human HeartdeepmanisharmaNo ratings yet
- Heart: Layers of The Heart WallDocument3 pagesHeart: Layers of The Heart WallAdaNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemABDUL HANANNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument11 pagesThe HeartElisa TapalesNo ratings yet
- Circulation Notes 2B - The HeartDocument4 pagesCirculation Notes 2B - The HeartRihanna E.No ratings yet
- Human Heart: Anatomy, Function & FactsDocument2 pagesHuman Heart: Anatomy, Function & FactsFlorie Fe Rosario OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Blood CirculationDocument8 pagesBlood CirculationnorafidaishakNo ratings yet
- Reading-The Human HeartDocument4 pagesReading-The Human HeartMichelle ViafaraNo ratings yet
- Human Heart Human Heart: Biology Holiday's WorkDocument13 pagesHuman Heart Human Heart: Biology Holiday's WorkHimanshu GargNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System in HumansDocument4 pagesCirculatory System in Humanspetra.t.ayalNo ratings yet
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Document13 pagesBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756No ratings yet
- The Human Heart: OCS Applied Science Mrs. BonifayDocument18 pagesThe Human Heart: OCS Applied Science Mrs. BonifaysudhirNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology The HeartDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology The Heartkheng100% (4)
- Circulatory System: Miss Javi ZúñigaDocument9 pagesCirculatory System: Miss Javi ZúñigaadisNo ratings yet
- Human HeartDocument6 pagesHuman HeartVui SengNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2a CirculationDocument8 pagesWEEK 2a Circulationdoodle dangerNo ratings yet
- The Human Heart: Location, Size and ShapeDocument9 pagesThe Human Heart: Location, Size and ShapeL I G-Arijit HisabiaNo ratings yet
- Tugasan B.IDocument2 pagesTugasan B.IMas IzatulNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Cardiovascular SystemElvira Wisakhadewi100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology ASCVDDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ASCVDAlvheen JoaquinNo ratings yet
- CV SystemDocument11 pagesCV System4everiamarmyNo ratings yet
- Function of The Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesFunction of The Circulatory SystemChristine SegundoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 4 - Circulatory Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Function and Structure of Heart and LungsDocument2 pagesFunction and Structure of Heart and LungsClaChristinaNo ratings yet
- Heart Structure, Function and Arrhythmias: Elizabeth M. Cherry and Flavio H. FentonDocument15 pagesHeart Structure, Function and Arrhythmias: Elizabeth M. Cherry and Flavio H. Fentonmaurice bertrandNo ratings yet
- A Case Study About Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument10 pagesA Case Study About Cardiovascular DiseaseBarben Balaquit100% (1)
- Lesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandLesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- PART-B Question No 7Document3 pagesPART-B Question No 73acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- SPCO AdvDocument2 pagesSPCO Adv3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Based On Constitutions of PakistanDocument16 pagesMcqs Based On Constitutions of Pakistan3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- We Design For Your ExpectationDocument1 pageWe Design For Your Expectation3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Organiztional ChartDocument2 pagesOrganiztional Chart3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- LLB, SM Law College, HR 2Document61 pagesLLB, SM Law College, HR 23acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- AdvonaeDocument1 pageAdvonae3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Rights and Its CasesDocument2 pagesFundamental Rights and Its Cases3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- TESTINGDocument1 pageTESTING3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 6565232Document2 pagesProfile 65652323acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 6212151Document1 pageProfile 62121513acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Our TeamDocument1 pageOur Team3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Work of AdvocateDocument1 pageWork of Advocate3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 55416516Document2 pagesProfile 554165163acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 6326521521Document1 pageProfile 63265215213acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 6221515Document2 pagesProfile 62215153acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- G 456 DFDocument1 pageG 456 DF3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 5454Document2 pagesProfile 54543acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 51561Document2 pagesProfile 515613acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Profile 5Document2 pagesProfile 53acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Provisional Constitution Order 1981Document1 pageProvisional Constitution Order 19813acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- COnstitution of Pakistan by AAmra TariqDocument6 pagesCOnstitution of Pakistan by AAmra Tariq3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Assignemt of Pakistan ConstitutionDocument1 pageAssignemt of Pakistan Constitution3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Principles of PoliciesDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Policies3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- PM Pakistan PowerDocument3 pagesPM Pakistan Power3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court JurisdictionDocument3 pagesSupreme Court Jurisdiction3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of Constitution of Pakistan 1973Document2 pagesSalient Features of Constitution of Pakistan 19733acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Constitution of Pakistan 1973 0N EASSYDocument14 pagesConstitution of Pakistan 1973 0N EASSY3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Eighteenth Amendment 2010Document1 pageEighteenth Amendment 20103acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of Supreme Court AND HIGH COURTDocument3 pagesJurisdiction of Supreme Court AND HIGH COURT3acsgrp 3acsgrpNo ratings yet