Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Microsoft Word Document
New Microsoft Word Document
Uploaded by
İsmayıl HəsənovOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
New Microsoft Word Document
New Microsoft Word Document
Uploaded by
İsmayıl HəsənovCopyright:
Available Formats
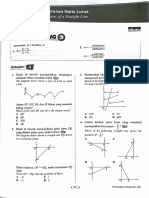
Answer - 1
Material resistance refers to the strength, stiffness and durability of the device elements. In
resistance of materials, bodies are treated as deformable bodies. The resistance of materials
is also called the mechanics of deformable solids. Includes resistance of materials, theory of
elasticity, theory of plasticity, theory of creep. Materials resistance solves many issues and
savings issues. In the resistance of materials, it is necessary to choose a calculation scheme
to calculate the strength of the real object. A simplified real object is called a computational
scheme. When choosing a calculation scheme, simplifications are made in the geometric
dimensions and shape of the real object, the properties of materials and the forces applied to
the device elements. Materials resistance solves many issues and savings issues.
Answer - 2
The material from which the device is made is considered homogeneous. A material with the
same properties is called a homogeneous material. Objects are viewed as whole
environments. According to this hypothesis, a body that is incompressible before
deformation remains incompressible after deformation. Bodies are assumed to be isotropic.
Objects that have the same physical and mechanical properties in all directions are called
isotropic objects. Metals are considered isotropic. Many building materials with a fibrous
structure have different properties in different directions. For example: wood and some
plastic materials. Such materials are called anisotropic materials.
In an uncharged body, the interaction forces of molecules are not taken into account.
According to the nature of the deformation, the following are accepted:
a) displacement of points of the object is very small compared to its dimensions.
b) relative stretches, as well as relative slips (slip angle) are very small per unit.
c) the displacements obtained as a result of the deformation of the body are directly
proportional to the forces that create these displacements
The principle of initial dimensions - According to this hypothesis, the dimensions of the
body do not change when drawing up the balance equations of statics in bodies undergoing
small deformations.
The principle of independence of the effect of forces - According to this principle, when
several forces are applied to the body, the internal forces and deformations caused by the
effect of each of these forces are determined separately and are summed up as a result.
Saint-Venant's principle - According to this principle, the distribution of internal forces at
sufficiently far distances from the point of application of the force does not depend on the
nature of the application of the force.
Answer - 3
You might also like
- Lesson 1Document3 pagesLesson 1المهندس مصطفىNo ratings yet
- Session 01 C1T1 IntroductionDocument7 pagesSession 01 C1T1 Introductionpragatikhanal7No ratings yet
- Elasticity, Sterss and StrainDocument19 pagesElasticity, Sterss and StrainKhairunnisa PutryNo ratings yet
- Relationship To Continuum Mechanics: Solid Mechanics Is The Branch ofDocument2 pagesRelationship To Continuum Mechanics: Solid Mechanics Is The Branch ofaditya2053No ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument114 pagesStrength of MaterialsVivek SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Continuum MechanicsDocument4 pagesContinuum MechanicsRahul MoreNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanical MetallurgyDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Mechanical Metallurgyhsy5478No ratings yet
- MANMIB1 Lecture Notes-Chapter 1b MaterialsDocument39 pagesMANMIB1 Lecture Notes-Chapter 1b Materialsfarayi.gadahNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material Unit 1 - IntroductionDocument10 pagesStrength of Material Unit 1 - IntroductionJulius EtukeNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument6 pagesMechanical Properties of MetalsvinothenergyNo ratings yet
- Course IntroductionDocument4 pagesCourse IntroductionRishan Joshua DsilvaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-8 Power PointDocument28 pagesUNIT-8 Power PointDesta LelagoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of SolidDocument22 pagesMechanical Properties of SolidTrillionare HackNo ratings yet
- Young's Modulus - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesYoung's Modulus - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNarablues IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsDocument8 pagesMechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsJenniferNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1Young BrotherNo ratings yet
- SM225 Module 1 IntroductionDocument2 pagesSM225 Module 1 IntroductionJustine IanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document28 pagesChapter 1Dina Rivera RabilasNo ratings yet
- Mechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsDocument7 pagesMechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsJenniferNo ratings yet
- 02 Strength of Materials IntroDocument19 pages02 Strength of Materials IntroEricka HuseñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1Misganaw YeshiwasNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahan Kontruksi Teknik Kimia Part 3Document17 pagesTugas Bahan Kontruksi Teknik Kimia Part 3Ervan BowoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics: MechanicsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Statistics: MechanicsJohn Alexis AncianoNo ratings yet
- Material Types PropertiesDocument5 pagesMaterial Types PropertiesemregungorNo ratings yet
- Continuous Media MechanicsDocument31 pagesContinuous Media MechanicsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Review: PreambleDocument1 pageIntroduction and Review: Preambleshiva_ssk17No ratings yet
- Lecture1 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture1 PDFshivam18No ratings yet
- Physics Greek Deform ForcesDocument5 pagesPhysics Greek Deform Forcesaditya2053No ratings yet
- Stress AnalysisDocument13 pagesStress AnalysismaloyNo ratings yet
- CMT Lesson 2Document14 pagesCMT Lesson 2April Jhen BenavidezNo ratings yet
- Physics and Mechanics Booklet SS2020Document19 pagesPhysics and Mechanics Booklet SS2020Alan MeridaNo ratings yet
- BFBM Unit - 3Document38 pagesBFBM Unit - 3Kripa NNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chemistry of Engineering MaterialsDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Chemistry of Engineering Materialsksm rachasNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics in OrthopedicsDocument93 pagesBiomechanics in OrthopedicsnasradinNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document3 pagesQuiz 1Greg LoncaricNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Teaching 12Document6 pagesAdaptive Teaching 12Grophel MesaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document22 pagesLecture 1Warikozi johnNo ratings yet
- Lectura2 ConstitutivasDocument5 pagesLectura2 ConstitutivasFelipe Venegas GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Elastic Solids - Lesson - TeachEngineering PDFDocument7 pagesMechanics of Elastic Solids - Lesson - TeachEngineering PDFIhsan BazirganNo ratings yet
- 11.mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument22 pages11.mechanical Properties of MaterialsHarish LakshminarayananNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Continuum Theory: KnownDocument2 pages1.1 Continuum Theory: KnownJason OliverNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument1 pageStrength of MaterialsSheffy AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Chem 131......... 2Document13 pagesChem 131......... 2Nicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Finite Deformation General Theory 2013 11 25Document67 pagesFinite Deformation General Theory 2013 11 25msyexploreNo ratings yet
- Vincent Ivan Abanales Final PT in PhysicsDocument5 pagesVincent Ivan Abanales Final PT in PhysicsNikki Hanniah Capa CatalanNo ratings yet
- Linear Vs Nonlinera Alysis in FEADocument8 pagesLinear Vs Nonlinera Alysis in FEAMamush GslasieNo ratings yet
- Useful Solutions For Standard ProblemsDocument2 pagesUseful Solutions For Standard ProblemsAmjad Khan BanuzaiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics, Elasticity, Rheology (Paronia) PhysicsDocument33 pagesMechanics, Elasticity, Rheology (Paronia) Physicssharamaeparonia629No ratings yet
- Biomaterials Unit 1Document64 pagesBiomaterials Unit 1R.GowthamNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction To Engineering MaterialsDocument5 pages1.0 Introduction To Engineering MaterialsAliciaNo ratings yet
- AST 212 M2 2021 Strength of MaterialsDocument15 pagesAST 212 M2 2021 Strength of MaterialsJessa BadilloNo ratings yet
- Basic Explanation of Creep ProcessesDocument7 pagesBasic Explanation of Creep ProcessesRiza KhanNo ratings yet
- Stress..strain in Thick PlatesDocument63 pagesStress..strain in Thick PlatesHitesh MudgilNo ratings yet
- Lecs 1 To 5 - SushilDocument110 pagesLecs 1 To 5 - SushilBhavesh ThakkarNo ratings yet
- MT 6201 Strength of MaterialsDocument57 pagesMT 6201 Strength of MaterialsMichael NammanjeNo ratings yet
- MECS Unit1 Notes1Document14 pagesMECS Unit1 Notes1michaelrithishNo ratings yet
- Physics VivaDocument19 pagesPhysics VivaAkhila ANo ratings yet
- Phys 111 - Lecture NotesDocument96 pagesPhys 111 - Lecture Notesosmankamara557No ratings yet
- Boardworks 1 .PPT - LightDocument9 pagesBoardworks 1 .PPT - LightsrenNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Paraboloid ShellsDocument2 pagesHyperbolic Paraboloid ShellsWilson Andres Echeverri GutierrrezNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18 Oct 2022Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 18 Oct 2022alt 2No ratings yet
- PHY112 Lecture1Document131 pagesPHY112 Lecture18wc9sncvpwNo ratings yet
- GOC Short NotesDocument7 pagesGOC Short Notesredop9opNo ratings yet
- Astm e 92 - 82 R97Document9 pagesAstm e 92 - 82 R97Luis Fernando RuedaNo ratings yet
- Digimat For Engineering Plastics1 4Document12 pagesDigimat For Engineering Plastics1 4Lu HkarrNo ratings yet
- CH - 4 The Adventure Answer KeyDocument3 pagesCH - 4 The Adventure Answer Keyhawrahaider52No ratings yet
- Cladding of Low-Carbon Steel To Austenitic Stainless Steel by Hot-Roll Bonding: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties..Document13 pagesCladding of Low-Carbon Steel To Austenitic Stainless Steel by Hot-Roll Bonding: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties..Rami GhorbelNo ratings yet
- GATE Electrical Engineering Paper 2018 PDFDocument17 pagesGATE Electrical Engineering Paper 2018 PDFAnand KalNo ratings yet
- AdmixtureDocument5 pagesAdmixtureMishra dtuNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operating Instruction: Gas Burner WG10 /1-D ZM-LNDocument112 pagesInstallation and Operating Instruction: Gas Burner WG10 /1-D ZM-LNdarrel gimoteaNo ratings yet
- SGP 2Document8 pagesSGP 2Soumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World: Assignment #2Document32 pagesMathematics in The Modern World: Assignment #2Carl Anthony P. PilapilNo ratings yet
- Eotechnical Easurements: Ab and IeldDocument107 pagesEotechnical Easurements: Ab and Ieldjuan carlosNo ratings yet
- Latihan 1: (Konsep Belajar TOEFL Dari NOL)Document8 pagesLatihan 1: (Konsep Belajar TOEFL Dari NOL)Widya TriwulanNo ratings yet
- Simulation Models For Wind Parks With Variable Speed Wind Turbines in EmtpDocument58 pagesSimulation Models For Wind Parks With Variable Speed Wind Turbines in EmtpDes LawlessNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Shapes: Standard Specification ForDocument3 pagesStructural Steel Shapes: Standard Specification ForNgoc BuiNo ratings yet
- Digital Multimeter: Instruction ManualDocument16 pagesDigital Multimeter: Instruction ManualHenryAndersonAroapazaCasillaNo ratings yet
- Theory and Simulation of Crystal GrowthDocument47 pagesTheory and Simulation of Crystal GrowthDerya KaradenizNo ratings yet
- Astm b381 - Titanium ForgingDocument8 pagesAstm b381 - Titanium ForgingJUSUF SIANTURINo ratings yet
- Vari Level Lb3 - BrochureDocument12 pagesVari Level Lb3 - BrochureAlexNo ratings yet
- Pib04 PDFDocument3 pagesPib04 PDFANGIE PAOLA RODELO PANZANo ratings yet
- Motion in A Circle Updated 11Document3 pagesMotion in A Circle Updated 11Yahya Salman GamingNo ratings yet
- Soil and Its PropertiesDocument20 pagesSoil and Its PropertiesHarsha HarapanahalliNo ratings yet
- Tabulated Values of Shockley-Queisser Limit For Single Junction Solar CellsDocument9 pagesTabulated Values of Shockley-Queisser Limit For Single Junction Solar CellsSachin DesaradaNo ratings yet
- Maxima by Example: Ch. 12, Dirac Algebra and Quantum ElectrodynamicsDocument83 pagesMaxima by Example: Ch. 12, Dirac Algebra and Quantum Electrodynamicsprakush_prakushNo ratings yet
- AASHTO Supplement, Rigid Pavement DesignDocument91 pagesAASHTO Supplement, Rigid Pavement DesignAlvaro HerbasNo ratings yet
- Mt105a 2023 Pass Paper No TipsDocument5 pagesMt105a 2023 Pass Paper No Tipslosika.mosupiNo ratings yet
- STEREOISOMERISMDocument11 pagesSTEREOISOMERISMSuresh KumarNo ratings yet