Professional Documents
Culture Documents
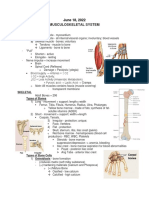
Muskuloskeletal Disorders
Muskuloskeletal Disorders
Uploaded by
Maren Lyle Co0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesThis document summarizes several musculoskeletal disorders including osteoporosis, gouty arthritis, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis. It covers the causes, risk factors, pathophysiology, symptoms, diagnostics, and management of each condition. Key points include that osteoporosis is caused by decreased bone mass leading to fragile bones, gouty arthritis results from uric acid crystal deposition in joints causing inflammation, osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease common in weight-bearing joints, and rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder causing symmetrical inflammation of small joints. Diagnostics include x-rays, lab tests, and physical exams while management focuses on lifestyle changes, medications, exercise and joint protection.
Original Description:
Original Title
MUSKULOSKELETAL-DISORDERS.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes several musculoskeletal disorders including osteoporosis, gouty arthritis, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis. It covers the causes, risk factors, pathophysiology, symptoms, diagnostics, and management of each condition. Key points include that osteoporosis is caused by decreased bone mass leading to fragile bones, gouty arthritis results from uric acid crystal deposition in joints causing inflammation, osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease common in weight-bearing joints, and rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder causing symmetrical inflammation of small joints. Diagnostics include x-rays, lab tests, and physical exams while management focuses on lifestyle changes, medications, exercise and joint protection.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesMuskuloskeletal Disorders
Muskuloskeletal Disorders
Uploaded by
Maren Lyle CoThis document summarizes several musculoskeletal disorders including osteoporosis, gouty arthritis, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis. It covers the causes, risk factors, pathophysiology, symptoms, diagnostics, and management of each condition. Key points include that osteoporosis is caused by decreased bone mass leading to fragile bones, gouty arthritis results from uric acid crystal deposition in joints causing inflammation, osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease common in weight-bearing joints, and rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder causing symmetrical inflammation of small joints. Diagnostics include x-rays, lab tests, and physical exams while management focuses on lifestyle changes, medications, exercise and joint protection.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
⮚ DIAGNOSTICS:
We MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS 1) X-RAY (Checks deformities & fractures)
2) DEXA (Dual Energy X-Ray Absorption)
BONE ✔ Checks the decreased bone mass
⮚ 99% calcium are inside the bone (To make the ✔ CONFIRMATORY TEST for
bone strong) Osteoporosis
⮚ 1% calcium are in the blood ⮚ MANAGEMENT:
1) AVOID Smoking
CALCIUM RESPORPTION (Bone-Blood) 2) DECREASED alcohol consumption
⮚ The calcium goes out from the bone to the 3) Increase Ca Intake
blood. a) Milk products
⮚ PROBLEM: the bone will be weak b) Green-leafy vegetables
4) Calcium supplementation
CALCIUM REABSORPTION (Blood-Bone) ✔ S/E: Constipation
⮚ The calcium goes back from the blood to the ✔ EXAMPLES:
bone a) Caltrate
5) Regular Exercise (Weight-bearing
OSTEOPOROSIS exercises)
⮚ Increased Calcium Resorption making the ✔ Stresses the bone to promote
bones weak. calcium absorption
⮚ CAUSES: ✔ E.g. walking, cycling,
1) AGE (>40 y.o.) 6) MEDICATION:
2) SEX (Common in FEMALES) a) BISPHOSPHONATE
✔ Postmenopausal women (d/t − MOA: Prevents Ca Resorption
decreased estrogen levels) − E.g. Alendronate (Fosamax)
3) LIFESTYLE (Sedentary) − S/E: Esophageal ulcer
4) DIET (Low calcium intake) (regurgitation of acids)
5) DECREASED VITAMIN D INTAKE (for − POSITION: High Fowler’s
Calcium Absorption) − Given EARLY MORNING
6) SMOKING (Increased Ca Resporption) b) ESTROGEN REPLACEMENT
7) ALCOHOLISM (Increased Ca Resporption) THERAPY (for FEMALES)
⮚ S/SX: − LAST option (can cause
1) INITIALLY: ASYMPTOMATIC breast cancer)
2) Deformity: KYPHOSIS (Dowager’s Hump) − S/E: Breast Cancer
✔ If a kyphotic patient is having a 7) BEDSIDE: Donut Pillow
cardiac arrest:
a) Position: SUPINE GOUTY ARTHRITIS
b) Place a donut pillow at the ⮚ Metabolic disorder that causes inflammation
back of the patient of the joints d/t increased uric acid in the
c) Then Start CPR blood.
✔ If at the beach, a kyphotic person is ⮚ CAUSES:
having a cardiac arrest: 1) AGE (>30 y.o.)
a) Position: SUPINE 2) SEX (Common in MALES)
b) Place an inflatable donut at 3) DIET (Increased PURINE diet)
the back. ✔ E.g. organ meats, beans, anchovies
c) Start CPR (dilis), alcohol intake
d) If no inflatable donut, dig a ⮚ PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
small hole that fits the hump 1) Increased Purine diet
of the patient. 2) It increases Uric Acid
e) Start CPR. 3) Uric Acid travels in the blood
3) DECREASED HEIGHT 4) It can cause HYPERURICEMIA
✔ Measuring for Height: TAPE MEASURE 5) It travels to the synovial joints
4) LOWER BACK PAIN 6) It causes inflammation of joints
5) VERTEBRAL COLLAPSE (Risk for (arthritis)
fractures)
⮚ S/SX: 3)
Unilateral localized
1) Joint inflammation (arthritis) 4)
Asymmetrical
2) Joint Pains (arthralgia) 5)
Joint pain
3) Tophi (pathognomic sign of Gouty 6)
Joint stiffness (less than 30 minutes)
arthritis) 7)
Crepitus heard on the affected joints
✔ Large, visible bump made of urate 8)
DEFORMITIES:
crystals that form in joints, bone a) HEBERDEN’S NODE (Distal)
and cartilages (in the ear). − Bony bumps on the finger joints
4) Podagra (Big Toe enlargement) closest to the fingernails
✔ FIRST joint to be affected! b) BOUCHARD NODE (Proximal)
✔ Enlargement of the big toe − Bony bumps on the middle
containing urate crystals joints of the fingers
5) Pruritus (itching) ⮚ DIAGNOSTICS
✔ The urate crystals precipitate, 1) X-RAY (Visualization of narrowed joint
causing itching. spaces)
6) Risk for Renal calculi (made of urate ⮚ MANAGEMENT
crystals) 1) Relieve Pain:
⮚ DIAGNOSTICS: a) Rest & Exercise
1) X-RAY (visualization of uric deposits b) Warm & Cold Compress
–WHITE color) − Put Warm Compress in joint
2) SERUM URIC ACID (Increased uric acid) stiffness
3) ARTHROCENTESIS (aspiration of synovial − Put Cold Compress in joint
fluid of joints) inflammation
✔ CONFIRMATORY TEST for Gouty 2) Maintain joint mobility
Arthritis a) ROM
⮚ MANAGEMENT: b) Non-weight bearing exercises
1) LOW PURINE diet (Swimming)
2) Increase oral fluid intake 3) MEDICATIONS
3) MEDICATIONS: CAP a) NSAIDs (pain relief)
a) COLCHICIN b) Corticosteroids
− For pain
b) ALLOPURINOL RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA)
− Prevents formation of uric acids ⮚ CAUSE:
c) PROBENECID 1) AUTOIMMUNE (produces antibodies that
− Excretion of uric acids destroys the joints)
⮚ RISK FACTORS:
OSTEOARTHRITIS 1) Common in FEMALES
⮚ Inflammation of the bones and joints ⮚ PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
⮚ RISK FACTORS: 1) Antibodies are produced
1) Degenerative (slowly progresses) 2) Antibodies attacks the joints
2) Idiopathic (unknown cause) 3) Resulting inflammation of joints
3) Repetitive use of joints ⮚ S/SX:
4) Trauma 1) Inflammatory
5) Common in FEMALES 2) Small joints
⮚ PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 3) Bilateral systemic
1) Repetitive use of joints 4) Symmetrical
2) Frequent friction of two separate joints, 5) Joint pain
resulting wearing out of joints 6) Joint stiffness (more than 30 minutes)
3) It can now affect the bones d/t the worn 7) Fever
out joints, 8) DEFORMITIES:
4) Friction of bones then occurs, resulting a) Swan-neck
pain − Flexion of the base of the
⮚ S/SX: finger.
1) Non-inflammatory
2) Weight-bearing joints
b) Ulnar deviation
− A hand condition where
the fingers bend
abnormally towards the
little finger
⮚ DIAGNOSTICS:
1) ERYTHROCYTE SEDIMENTATION RATE
(detects systemic inflammation)
2) ANTINUCLEAR ANTIBODIES
✔ Detects (+) RA
3) RHEUMATOID FACTOR TITER
✔ Detects (+) RA
⮚ MANAGEMENT
1) Relieve Pain:
a) Rest & Exercise
b) Warm & Cold Compress
− Put Warm Compress in joint
stiffness
− Put Cold Compress in joint
inflammation
2) Maintain joint mobility
a) ROM
b) Non-weight bearing exercises
(Swimming)
3) MEDICATIONS
a) NSAIDs (pain relief)
b) Corticosteroids
c) DMARDS (Disease Modifying
Anti-Rheumatoid Drugs)
− Decreases the antibodies of RA
− SLOW acting (the therapeutic
effect will show 3-6 months)
− Examples:
1. GOLD SALTS
2. HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE
(anti-malarial)
3. IMURAN (most EFFECTIVE)
You might also like
- Cardiac Arrest QuestionsDocument2 pagesCardiac Arrest Questionsmine251580% (5)
- Patho Physiology Bible: Over 70 Concept MapsDocument139 pagesPatho Physiology Bible: Over 70 Concept Mapslauramphs79100% (5)
- History TakingDocument130 pagesHistory Takingvwpwh86gfhNo ratings yet
- ORTHOPEDICSDocument8 pagesORTHOPEDICSjsreyes.402No ratings yet
- Unit 9 Osteoarthritis-19167Document11 pagesUnit 9 Osteoarthritis-19167Emma CebanNo ratings yet
- Neurosensory Disorders 22306Document13 pagesNeurosensory Disorders 22306Teresa TorreonNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: A. Components B. FunctionsDocument19 pagesThe Skeletal System: A. Components B. FunctionsVivek NairNo ratings yet
- The Foot and Ankle Complex Day 2Document39 pagesThe Foot and Ankle Complex Day 2Arun StalinNo ratings yet
- DISTURBANCES IN ABSORPTION AND ELIMINATION NotesDocument7 pagesDISTURBANCES IN ABSORPTION AND ELIMINATION NotesHoneylette DarundayNo ratings yet
- Calcaneus SpurDocument21 pagesCalcaneus SpurekoNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Practice Exam X 50 ItemsDocument15 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Practice Exam X 50 ItemsclobregasNo ratings yet
- Gouty ArthritisDocument8 pagesGouty ArthritisC.a. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Anand SirDocument16 pagesAnand Sirayurvedicpulse22No ratings yet
- Presentasi MODUL 9 LengkapDocument29 pagesPresentasi MODUL 9 Lengkapdimas oktoferryNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Osteoarthritis-19167Document12 pagesUnit 9 Osteoarthritis-19167Emma CebanNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument9 pagesOsteoporosisnc4440493No ratings yet
- Nur 149 p3w3 Fri Part1 Session 22 Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument55 pagesNur 149 p3w3 Fri Part1 Session 22 Musculoskeletal DisordersAlliah Marie CababarosNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis & Osteoarthritis in TCM TherapyDocument8 pagesOsteoporosis & Osteoarthritis in TCM TherapyPathway solusio plasentaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument5 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemAdriane VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Gouty ArthritisDocument12 pagesGouty ArthritisGreen MarlNo ratings yet
- Askep OsteoporosisDocument6 pagesAskep OsteoporosisMuhammad NurmanNo ratings yet
- ORTHOPEDICSDocument6 pagesORTHOPEDICSJAY-AR DAITNo ratings yet
- 11 - 13 - Day 1 - 01 PSBIM Review 2017 - Lecture - RheumatologyDocument220 pages11 - 13 - Day 1 - 01 PSBIM Review 2017 - Lecture - RheumatologyRye CalderonNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Assessment: Sequence of ExamDocument7 pagesAbdominal Assessment: Sequence of ExamCristine SyNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: The Commonest Disease of JointsDocument7 pagesOsteoarthritis: The Commonest Disease of JointsDr Gautam PalNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Bone: Growth Hormone: Sex Hormones (Estrogen/testosterone) Thyroid Hormones (PTH & Calcitonin)Document7 pagesPhysiology of Bone: Growth Hormone: Sex Hormones (Estrogen/testosterone) Thyroid Hormones (PTH & Calcitonin)Ayuub AbdirizakNo ratings yet
- 1-19 Diagnosis and Risk Factors of Osteoporosis 2004Document53 pages1-19 Diagnosis and Risk Factors of Osteoporosis 2004tarikeopsNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument10 pagesOrthopedic NursingZayne Lucas Gabrielle TadiamonNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DISORDERSDocument6 pagesMusculoskeletal DISORDERSJoe Stewart100% (1)
- Patho FinalDocument25 pagesPatho FinalSarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Etio:Autoimmune: Patho:associated Wit Hashimoto's Thyroiditis, Hyperthyroidism, Hypothyroidism, HypopanthyroidismDocument30 pagesEtio:Autoimmune: Patho:associated Wit Hashimoto's Thyroiditis, Hyperthyroidism, Hypothyroidism, HypopanthyroidismCavinpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Medicine-I RIT-3Document2 pagesMedicine-I RIT-3Amazing and News TVNo ratings yet
- MS Lec Ibs and MSDocument3 pagesMS Lec Ibs and MSTrishia Camille GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Day 5 (Constipation)Document4 pagesConcept Map Day 5 (Constipation)Matt McKinleyNo ratings yet
- Long Case DysphagiaDocument3 pagesLong Case DysphagiaNadia SalwaniNo ratings yet
- Bone and Cartilage ReviewDocument14 pagesBone and Cartilage ReviewCatchetatNo ratings yet
- Viêm D DàyDocument40 pagesViêm D DàyMai NamNo ratings yet
- Ch26 Ortho 1Document132 pagesCh26 Ortho 1Louis FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems ReviewDocument3 pagesHuman Body Systems ReviewDiana Mariela Martinez YepezNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument4 pagesGoutapi-3822433100% (1)
- Internal Diagnostic Ii Examination Procedures: Patient EvaluationDocument76 pagesInternal Diagnostic Ii Examination Procedures: Patient EvaluationbjpalmerNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument21 pagesOrthopedic NursingCris Constantino San JuanNo ratings yet
- 8758 - PPT AchondroplasiaDocument33 pages8758 - PPT AchondroplasiaFidesha Nurganiah SiregarNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 WorksheetDocument5 pagesLab 3 Worksheetjose.lruiz0916No ratings yet
- Achilles Tendonitis and Rupture: DR Carl ClintonDocument20 pagesAchilles Tendonitis and Rupture: DR Carl ClintonHilda YusufNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy, Medical Terminology, BA Week 5. 2Document27 pagesPharmacy, Medical Terminology, BA Week 5. 2Noor FarhanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Hip for Functional Diagnosis - CopyDocument61 pagesAssessment of Hip for Functional Diagnosis - Copyanushka13sherikarNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology (4) 2015Document59 pagesRheumatology (4) 2015MUHAMMAD BAGIR ALJUFRINo ratings yet
- MusculoSensory - TCA #3 - Osteoporosis Osteoarthritis DDDDocument8 pagesMusculoSensory - TCA #3 - Osteoporosis Osteoarthritis DDDapi-3822433No ratings yet
- MUSCULO-SKELETAL - NursingDocument82 pagesMUSCULO-SKELETAL - NursingJan Clarisse RamosNo ratings yet
- Neurosensory Disorders 22306Document14 pagesNeurosensory Disorders 22306bekbekk cabahugNo ratings yet
- Talar Cyst: JSM Foot and AnkleDocument2 pagesTalar Cyst: JSM Foot and Anklenpr00No ratings yet
- Orthopedics: Extra Notes 2Document35 pagesOrthopedics: Extra Notes 2Sayyidah NafisahNo ratings yet
- Ortho Fracture Notes 3Document32 pagesOrtho Fracture Notes 3Umar AzlanNo ratings yet
- Heel Pain: Lecture 2: Plantar FasciitisDocument10 pagesHeel Pain: Lecture 2: Plantar FasciitispinakingNo ratings yet
- CASE REPORT On OsteomyelitisDocument30 pagesCASE REPORT On OsteomyelitisNirbhay KatiyarNo ratings yet
- 1-Hematoma and Inflammation Cartilage FormationDocument3 pages1-Hematoma and Inflammation Cartilage FormationAfif Al BaalbakiNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument34 pagesOsteoarthritisLaiba KhanNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet AgentsDocument4 pagesAnticoagulants and Antiplatelet AgentsMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrilliation Part 1 Pathophysiology C CottrellDocument5 pagesAtrial Fibrilliation Part 1 Pathophysiology C CottrellA Farid WajdyNo ratings yet
- Ob2rle Sas 8Document9 pagesOb2rle Sas 8Aira Mae R. AndradaNo ratings yet
- First Aid PPT - DR GhaziDocument22 pagesFirst Aid PPT - DR GhaziMands_KLP100% (1)
- Complications of PuerperiumDocument45 pagesComplications of PuerperiumsubashikNo ratings yet
- A Look at Your Child's NutritionDocument2 pagesA Look at Your Child's NutritionAslul KhitanNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland An Diseases of Thyroid D Gland: Omc LectureDocument59 pagesThyroid Gland An Diseases of Thyroid D Gland: Omc LectureEdward MakemboNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration Form D02Document1 pageHealth Declaration Form D02Hizwani ZainalNo ratings yet
- Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (Mers) : Causative AgentDocument6 pagesMiddle East Respiratory Syndrome (Mers) : Causative AgentEmbrmrie ParkNo ratings yet
- Medsurg AdhdDocument3 pagesMedsurg AdhdminniprkNo ratings yet
- BD TTM Neuro Brochure Update Feb 2020 - v1Document2 pagesBD TTM Neuro Brochure Update Feb 2020 - v1Hanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Sore Throat Acute in Adults Antimicrobial Prescribing Visual SummaryDocument3 pagesSore Throat Acute in Adults Antimicrobial Prescribing Visual Summaryzobi2020No ratings yet
- Sompo PAStar Brochure Oct 2021Document8 pagesSompo PAStar Brochure Oct 2021priscillasooNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Acute BronchitisDocument28 pagesCase Study: Acute BronchitisMarco AlabanzaNo ratings yet
- ASSESSING SHOCK RESUSCITATION STRATEGIES BY OXYGEN DEBT REPAYMENT Robert Wayne Barbee 2010Document10 pagesASSESSING SHOCK RESUSCITATION STRATEGIES BY OXYGEN DEBT REPAYMENT Robert Wayne Barbee 2010Mara TorrealbaNo ratings yet
- Pathology AIIMSDocument26 pagesPathology AIIMSvkNo ratings yet
- ATI Fundamentals Protored Exam - Concept Guide, Study MaterialDocument2 pagesATI Fundamentals Protored Exam - Concept Guide, Study Materialzezoconan6No ratings yet
- Contoh Format SKDocument12 pagesContoh Format SKIrfan SetiawanNo ratings yet
- RNTCPDocument43 pagesRNTCPSanket AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Tonsil: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesTonsil: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAQis AQishNo ratings yet
- Edh SDHDocument6 pagesEdh SDHArdian RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Compendium Dermatologie RomanaDocument207 pagesCompendium Dermatologie RomanaRusu Bianca Elena67% (3)
- 30 Years of Vagus NerveDocument5 pages30 Years of Vagus NerveErnesto Ochoa MonroyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Congenital Bone DisorderDocument100 pagesLecture 6 Congenital Bone DisorderWilson HalimNo ratings yet
- USMLE STEP 2 MCQsDocument1 pageUSMLE STEP 2 MCQsAhmad Waleed0% (2)
- History Taking in Clinical Practice 2023Document164 pagesHistory Taking in Clinical Practice 2023imran karimNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Case StudyDocument5 pagesActivity 2 - Case StudyGrace MendozaNo ratings yet
- Referral Form Jessa 2021Document1 pageReferral Form Jessa 2021Jessa MaeNo ratings yet