Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aqa Mechanisms Summary As
Aqa Mechanisms Summary As
Uploaded by
RS JOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aqa Mechanisms Summary As
Aqa Mechanisms Summary As
Uploaded by
RS JCopyright:
Available Formats
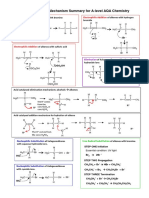
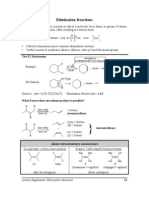
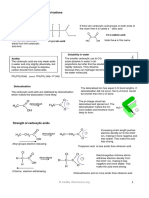
Mechanism Summary for AS AQA Chemistry
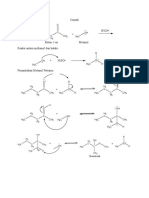
Nucleophilic Substitution of halogenoalkanes Nucleophilic Substitution of halogenoalkanes
with aqueous hydroxide ions. with cyanide ions.
H H H H
δ+
δ- δ+ δ- -
H3C C Br H3C C OH + :Br - H 3C C Br H 3C C CN + :Br
- -
NC:
HO: H
H H H
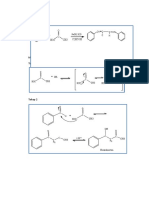
Nucleophilic Substitution of halogenoalkanes with ammonia
Elimination of halogenoalkanes with ethanolic
H H H :Br -
hydroxide ions
δ+ δ- +
CH3 CH2 C Br CH3 CH2 C N H H H H H
3HN:
H H CH3 C C H CH3 C C H
H
:NH3
+ Br - + H2O
Br H
H :OH-
CH3 CH2 C NH2 + NH Br
4
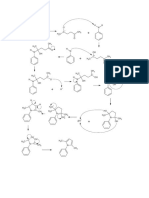
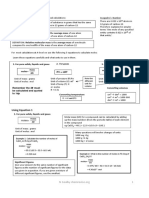
Electrophilic Addition of alkenes with bromine Electrophilic Addition of alkenes with hydrogen
bromide
H H H H H H H H
H H
+
C C H C C H H C C H H3C C C CH3 +
H3C C C CH3
H H Br Br Br δ+
Br δ+ H H
:Br - δ- :Br -
Br
Br δ-
H H
Electrophilic Addition of alkenes with sulfuric acid H3C C C CH3
H H Br H
H H
+
H3C C C H H3C C C H
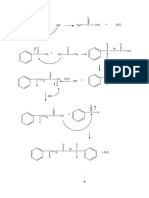
δ+ H Free Radical Substitution of alkanes with bromine
H -
:OSO2OH
OSO 2OH STEP ONE Initiation
δ- Essential condition: UV light
H H
Br2 2Br
.
H3C C C H
H STEP TWO Propagation
OSO 2OH .
CH3CH3 + Br HBr + CH3CH2
.
.
CH3CH2 + Br2 CH3CH2Br + Br
.
STEP THREE Termination
.
CH3CH2 + Br CH3CH2Br
.
.
CH3CH2 + CH3CH2 CH3CH2CH2CH3
.
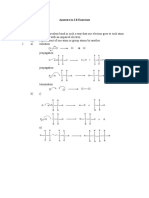
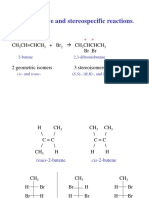
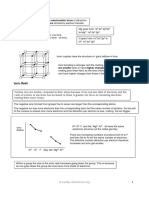
Acid catalysed elimination mechanism: alcohols alkenes
H
H H H H H
H3C C CH3 CH3 +
H3C C H C C CH3 H C C CH3
O H +
O H H H+
:
H+
H
The H+ comes from the conc H2SO4 or conc H3PO4
Acid catalysed addition mechanism for hydration of ethene
H H H H H H
H H
+
H C C H H C C H H C C H
C C
+
H
H H H H O H H O H+
O
H+ H H
H
The H+ comes from the conc H3PO4
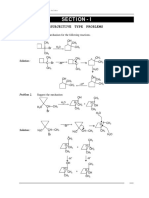
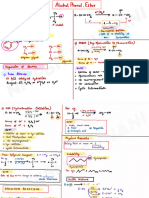
AS Reactions- Summary
diol
poly(alkene) KOH aqueous
heat under reflux
nucleophilic substitution
high pressure
catalyst
dihalogenoalkane
alkene
alkane
1 H2SO4
conc H2SO4 or 2 H2O warm
conc H3PO4 Electrophilic
Acid catalysed Br2, Cl2 UV light
Addition
Free radical
Elimination
Substitution
KOH aqueous
heat under reflux
alcohol nucleophilic substitution halogenoalkane
KCN in ethanol/ water Alcoholic NH3
mixture heat under reflux heat under pressure
nucleophilic substitution nucleophilic substitution
nitrile amine
aldehyde ketone
If primary alcohol or aldehyde
K2Cr2O7/H+
heat under reflux
+ excess oxidising agent
Oxidation
carboxylic acid
You might also like
- Mechanism Summary For AS AQA Chemistry: HO: NCDocument4 pagesMechanism Summary For AS AQA Chemistry: HO: NCjohn mNo ratings yet
- Aqa Mechanisms A21Document4 pagesAqa Mechanisms A21Sarah INo ratings yet
- Aqa Mechanisms A Level SummaryDocument5 pagesAqa Mechanisms A Level SummaryRS JNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Summary For A-Level AQA Chemistry: BR BRDocument5 pagesMechanism Summary For A-Level AQA Chemistry: BR BRamrhkmhNo ratings yet
- MechanismsDocument5 pagesMechanismsnajifaahmed223No ratings yet
- 102 Lecture Ch13Document36 pages102 Lecture Ch13macybnzNo ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers Chapter 18 Asal ChemistryDocument4 pagesCoursebook Answers Chapter 18 Asal ChemistryMarin PesicNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Organic Chemistry MechanismsDocument2 pagesChemistry - Organic Chemistry Mechanismshelixate100% (3)
- Reaction Mechanism: C C H H H O Hgso H SO CHO H CDocument6 pagesReaction Mechanism: C C H H H O Hgso H SO CHO H CFATHIMA THANHA T NNo ratings yet
- Cope EliminationDocument2 pagesCope EliminationArt Julius D. HallazgoNo ratings yet
- Reductions PPT 29-08-2020Document12 pagesReductions PPT 29-08-2020jkc collegeNo ratings yet
- Org Chem RxnsDocument4 pagesOrg Chem RxnsAkshit agarwalNo ratings yet
- Cyclohexane Cyclohexene Lab AnswersDocument6 pagesCyclohexane Cyclohexene Lab AnswersTingYuan HoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-Reactions of AlkenesDocument35 pagesChapter 8-Reactions of Alkenes張湧浩No ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-02 - Solved ProblemsDocument13 pagesAlkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-02 - Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Contoh: + Butan-2-On Metanol H SODocument2 pagesContoh: + Butan-2-On Metanol H SOElis TianiNo ratings yet
- Contoh: + Butan-2-On Metanol H SODocument2 pagesContoh: + Butan-2-On Metanol H SOElis TianiNo ratings yet
- OrganicChemistryChapter7 PDFDocument30 pagesOrganicChemistryChapter7 PDFSeanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Summary of Alkyne Reactions: H H C H H C BR HDocument1 pageSummary of Alkyne Reactions: H H C H H C BR HKamelNo ratings yet
- Pyrolytic Elimination - Syn EliminationsDocument3 pagesPyrolytic Elimination - Syn EliminationssaheedvkNo ratings yet
- Answers To AssignmentDocument1 pageAnswers To AssignmentIgbereyivwe TejiriNo ratings yet
- Exp 7 Preparation of AlkenesDocument14 pagesExp 7 Preparation of AlkenesGeorge PiliposyanNo ratings yet
- Alkene Preparation ReactionsDocument13 pagesAlkene Preparation ReactionsSaket ModiNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Alkynes 3Document13 pagesHydrocarbon Alkynes 3Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- CH2211 Mechanisms: NH + OHDocument5 pagesCH2211 Mechanisms: NH + OHneemNo ratings yet
- Adisi Elektrofilik Kimia OrganikDocument25 pagesAdisi Elektrofilik Kimia OrganikAcikaNo ratings yet
- Alquinos 13Document1 pageAlquinos 13Fernando EstradaNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 14Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 14Edna MaeNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de Química OrgánicaDocument1 pageTrabajo de Química OrgánicaPaulina Mota MacipNo ratings yet
- Alkenes Reactions NotesDocument14 pagesAlkenes Reactions NotesMartin AlvinNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme RX DibenzalasetonDocument2 pagesMekanisme RX DibenzalasetonWulan safitriNo ratings yet
- MechanismDocument2 pagesMechanismRyan BoodramlallNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes PDFDocument6 pagesHaloalkanes PDFthc8477No ratings yet
- Alkanes: Quicktime™ and A Tiff (Uncompressed) Decompressor Are Needed To See This PictureDocument30 pagesAlkanes: Quicktime™ and A Tiff (Uncompressed) Decompressor Are Needed To See This Pictureafreenbegum-0502No ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument80 pagesNomenclature of Organic CompoundsSajjad MiraniNo ratings yet
- RubberDocument29 pagesRubberabdullah2110154No ratings yet
- PirrolDocument1 pagePirrolabnerNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Axial EcuatorialDocument1 pageEjercicios Axial EcuatorialJulio Cesar Boada MartinezNo ratings yet
- Summary of All Reactions For Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesSummary of All Reactions For Organic Chemistryfoodytang91% (23)
- 314 Stereochem ProbsDocument14 pages314 Stereochem ProbsAtul SinghNo ratings yet
- Answers To 2.8 Exercises 2.8 Exercise 1: CL CL Cl. CLDocument3 pagesAnswers To 2.8 Exercises 2.8 Exercise 1: CL CL Cl. CLSsNo ratings yet
- Elimination Reactions: Elimination Reaction: A Reaction in Which A Molecule Loses Atoms or Groups of AtomsDocument8 pagesElimination Reactions: Elimination Reaction: A Reaction in Which A Molecule Loses Atoms or Groups of AtomsMohammed Adil ShareefNo ratings yet
- OrganicChemistryChapter5 PDFDocument19 pagesOrganicChemistryChapter5 PDFJuliet Tatiana CumbeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 (AK 1)Document44 pagesLecture 16 (AK 1)vipulugaleNo ratings yet
- Amines NotesDocument9 pagesAmines NotesMehlam AkbaraliNo ratings yet
- Aldol - Similar Name Reaction PDFDocument34 pagesAldol - Similar Name Reaction PDFSBNo ratings yet
- CH CH CH CH I: BRCH CH CH CCH BR CH CHDocument24 pagesCH CH CH CH I: BRCH CH CH CCH BR CH CHSam TabujaraNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme ORGANIC For Set 2Document2 pagesAnswer Scheme ORGANIC For Set 2Hafizah HalimNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Ch-6.Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument45 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Ch-6.Haloalkanes and Haloareneskarnan karupiahNo ratings yet
- New CHY3201 Chapter 9 Addition ReactionDocument31 pagesNew CHY3201 Chapter 9 Addition Reaction222418No ratings yet
- Stereochemistry of OrganicDocument35 pagesStereochemistry of OrganicRams ChanderNo ratings yet
- Elimination Reactions: E1, E2Document11 pagesElimination Reactions: E1, E2Susobhan ghoshNo ratings yet
- Che 91165 FlashcardsDocument5 pagesChe 91165 FlashcardsLê Minh DuyNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument30 pagesAcids and BasesSwagata SahaNo ratings yet
- MEKANISMEDocument2 pagesMEKANISMEEry NourikaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol Ether (1) 6Document9 pagesAlcohol Phenol Ether (1) 6sdnishacNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol Ether (1) 4Document9 pagesAlcohol Phenol Ether (1) 4subhashitamurapakaNo ratings yet
- Dia orDocument8 pagesDia orNaman MahawarNo ratings yet
- DK Maths Year5 Percentages 2Document2 pagesDK Maths Year5 Percentages 2RS JNo ratings yet
- Regulation 3 AwardsDocument8 pagesRegulation 3 AwardsRS JNo ratings yet
- Level 4 Sats Questions Co OrdinatesDocument12 pagesLevel 4 Sats Questions Co OrdinatesRS JNo ratings yet
- Risk Review 2021 AraDocument97 pagesRisk Review 2021 AraRS JNo ratings yet
- Diploma FullStack Software Development Specialization Uk Brochure-1Document19 pagesDiploma FullStack Software Development Specialization Uk Brochure-1RS JNo ratings yet
- Diploma FullStack Software Development Specialization Europe Brochure-1Document19 pagesDiploma FullStack Software Development Specialization Europe Brochure-1RS JNo ratings yet
- Full-Stack Scientific PythonDocument3 pagesFull-Stack Scientific PythonRS JNo ratings yet
- SEC Strategic Plan v4.0 GREENDocument23 pagesSEC Strategic Plan v4.0 GREENRS JNo ratings yet
- 616d97f4ee41ee7aa48cabcb - Software Development Bootcamp SyllabusDocument8 pages616d97f4ee41ee7aa48cabcb - Software Development Bootcamp SyllabusRS JNo ratings yet
- Task A - Administer UserprofilesDocument21 pagesTask A - Administer UserprofilesRS JNo ratings yet
- Onsite Course PacketDocument9 pagesOnsite Course PacketRS JNo ratings yet
- L&Q Behavioural FrameworkDocument1 pageL&Q Behavioural FrameworkRS JNo ratings yet
- Day+01 +Unit+030+Knowledge+OverviewDocument82 pagesDay+01 +Unit+030+Knowledge+OverviewRS JNo ratings yet
- Security Advisory Services Brochure For CandidatesDocument8 pagesSecurity Advisory Services Brochure For CandidatesRS JNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - Creating An Answer FileDocument40 pagesTask 1 - Creating An Answer FileRS JNo ratings yet
- Paper5 Details PhysicsDocument2 pagesPaper5 Details PhysicsRS JNo ratings yet
- SEC Panel Members 2023Document1 pageSEC Panel Members 2023RS JNo ratings yet
- Biorevise Notes MAINDocument34 pagesBiorevise Notes MAINRS JNo ratings yet
- Paper DetailsDocument2 pagesPaper DetailsRS JNo ratings yet
- Paper1 Details ZoologyDocument2 pagesPaper1 Details ZoologyRS JNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology 2019 2020Document27 pagesA Level Biology 2019 2020RS JNo ratings yet
- Alevel 2017 Paper 1 Model AnswerDocument28 pagesAlevel 2017 Paper 1 Model AnswerRS JNo ratings yet
- 3.9 Revision Guide Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives AqaDocument8 pages3.9 Revision Guide Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- Alevel Chemistry Paper 2Document28 pagesAlevel Chemistry Paper 2RS JNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Revision Guide Calculations AqaDocument14 pages1.2 Revision Guide Calculations AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- Alevel Chem Paper 3 Model AnswerDocument30 pagesAlevel Chem Paper 3 Model AnswerRS JNo ratings yet
- 3.16 Revision Guide Chromatography AqaDocument3 pages3.16 Revision Guide Chromatography AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- 1.9 Revision Guide Rate Equations AqaDocument8 pages1.9 Revision Guide Rate Equations AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- 3.11 Revision Guide Amines AqaDocument4 pages3.11 Revision Guide Amines AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaDocument8 pages1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaRS JNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument7 pagesChemical KineticsdineshnpNo ratings yet
- 1 Soal Kenetika 2Document1 page1 Soal Kenetika 2Zelia MartinsNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Chemistry: 1,4 Diazabicyclo (2.2.2) Octane (DABCO) As A Useful Catalyst in Organic SynthesisDocument7 pagesEuropean Journal of Chemistry: 1,4 Diazabicyclo (2.2.2) Octane (DABCO) As A Useful Catalyst in Organic SynthesisVladimirNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Enzyme ActivityDocument10 pagesFactors Affecting Enzyme ActivitygauravpriyaNo ratings yet
- Si OrganometallicsDocument47 pagesSi OrganometallicsfarshadNo ratings yet
- Mevalonic Acid PathwayDocument4 pagesMevalonic Acid PathwayChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- 311 Pinacol Pinacolone RearrangementDocument9 pages311 Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangementayesha sana100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics DPP 03 (Of Lecture 05)Document4 pagesChemical Kinetics DPP 03 (Of Lecture 05)socialworker561No ratings yet
- Total Synthesis of (+) - Acutiphycin: Ryan M. Moslin and Timothy F. JamisonDocument10 pagesTotal Synthesis of (+) - Acutiphycin: Ryan M. Moslin and Timothy F. JamisonTạ Đình TrungNo ratings yet
- Gold-Catalyzed Synthesis of Icetexane Cores: Short Synthesis of Taxamairin B and RosmaridiphenolDocument4 pagesGold-Catalyzed Synthesis of Icetexane Cores: Short Synthesis of Taxamairin B and RosmaridiphenolabcdefNo ratings yet
- CMC Chapter 16 (1) - 1Document84 pagesCMC Chapter 16 (1) - 1Raghad AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Oppenauer OxidationDocument38 pagesOppenauer OxidationHarumi Nabila RidzkiNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms-II APSP PDFDocument20 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanisms-II APSP PDFGOURISH AGRAWAL100% (1)
- ABC 1 (Theory Exercise)Document17 pagesABC 1 (Theory Exercise)Mayank GoyalNo ratings yet
- Quiz Organic 1Document6 pagesQuiz Organic 1ronakgupta332005No ratings yet
- Fischer-Tropsh Energy Balance IMCCRE (2904)Document2 pagesFischer-Tropsh Energy Balance IMCCRE (2904)chuertaNo ratings yet
- Aldol Condensation and Synthesis of DibenzalacetoneDocument8 pagesAldol Condensation and Synthesis of DibenzalacetoneArturo CamañoNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Terang Dan Gelap: Dua Tahapan Fotosintesis Tanaman: Pendidikan Fisika, Universitas Negeri Jakarta EmailDocument10 pagesReaksi Terang Dan Gelap: Dua Tahapan Fotosintesis Tanaman: Pendidikan Fisika, Universitas Negeri Jakarta Emailpuryati puryaNo ratings yet
- Maillard ReactionDocument81 pagesMaillard ReactionklicksNo ratings yet
- Sintesis Zyegler de AlcoholesDocument5 pagesSintesis Zyegler de AlcoholesJuan Carlos VillotaNo ratings yet
- CHT305 SyllabusDocument8 pagesCHT305 SyllabusYuxin CasioNo ratings yet
- CHE 430 Fa21 - HW#1 (27-August-2021)Document2 pagesCHE 430 Fa21 - HW#1 (27-August-2021)Charity QuinnNo ratings yet
- BIOC 215 Lecture 12-Enzyme RegulationDocument10 pagesBIOC 215 Lecture 12-Enzyme RegulationEkram FadhelNo ratings yet
- CSTR ReportDocument26 pagesCSTR ReportMohamad Samer KansouNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2 (CHEM 30) For Bolero Final Exam PDFDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2 (CHEM 30) For Bolero Final Exam PDFKhangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 FACTORS AFFECTING ENZYMEDocument27 pagesLesson 12 FACTORS AFFECTING ENZYMEAera Kapurihan100% (1)
- Sad PDFDocument1 pageSad PDFrisrizNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Reactions of Organic HalidesDocument4 pagesCharacteristic Reactions of Organic HalidesDANIEL CARLOS SALIPSIPNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Reaction Kinetics McqsDocument7 pagesChapter 11 Reaction Kinetics McqsshahidkakaNo ratings yet
- Adichemistry Online Coaching Sample 1 PDFDocument13 pagesAdichemistry Online Coaching Sample 1 PDFMeenakshi GaurNo ratings yet