Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 2 - Inventory Control Models
Tutorial 2 - Inventory Control Models
Uploaded by
MUSA AHMED ABDULLAHI ALIOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 2 - Inventory Control Models
Tutorial 2 - Inventory Control Models
Uploaded by
MUSA AHMED ABDULLAHI ALICopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 2 – Inventory Control Models
1. Lisa has determined that the annual demand for number 6 screws is 100,000 screws. She
estimates that it costs $10 every time an order is placed. Furthermore, she estimates that the cost
of carrying one screw in inventory for a year is one-half of 1 cent. Assume that the demand is
constant throughout the year.
a) How many number 6 screws should Lisa order at a time if she wishes to minimize total
inventory cost?
b) How many orders per year should be placed? What would the annual ordering cost be?
c) What would the average inventory be? What would the annual holding cost be?
2. The CariKomputer Dot Com Store sells a printer for RM 200. Demand for this is constant during
the year, and annual demand is forecasted to be 600 units. The holding cost is RM 20 per unit per
year, while the cost of ordering is RM 60 per order. Currently, the company is ordering 12 times
per year (50 units each time). There are 250 working days per year and the lead-time is 10 days.
a) Given the current policy of ordering 50 units at a time, what is the total of the annual ordering
cost and the annual holding cost?
b) If the company used the absolute best inventory policy, what would the total of ordering and
holding cost be?
c) What is the reorder point?
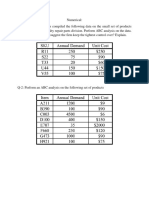
3. The following table shows that price schedule for purchasing a product.
Order Size 0-99 100-199 200-499 500 or more
Price per Unit $20.00 $19.50 $19.00 $18.75
A company who buys the products estimates the holding cost at 10% of purchase price per year
and ordering costs at $40 per order. The company’s annual demand is 460 units.
a) Determine the size of each order.
b) Determine how often the company should order.
c) Determine the price that company should order.
You might also like
- Chicagoland Sweets (Questions 3 and 4) Chicagoland Sweets, A Commercial Baker, UsesDocument5 pagesChicagoland Sweets (Questions 3 and 4) Chicagoland Sweets, A Commercial Baker, UsesIpsita RathNo ratings yet
- C7,8 - ExercisesDocument31 pagesC7,8 - ExercisesTÂM MAI0% (1)
- Inventory Models ExercisesDocument3 pagesInventory Models ExercisesIncubus100% (1)
- Inventory NumericalDocument2 pagesInventory NumericaljehadNo ratings yet
- QANT520 Problems 0706 CH 6Document6 pagesQANT520 Problems 0706 CH 6Rahil VermaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Homework Template - 13thDocument11 pagesWeek 7 Homework Template - 13thalgadilan0% (2)
- C10 12ed Quantitative DataDocument9 pagesC10 12ed Quantitative DataAdam LoNo ratings yet
- Inventory Control Subject To Known DemandDocument4 pagesInventory Control Subject To Known DemandHello WorldNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 QuestionDocument8 pagesAssignment 2 QuestionJanarthanan Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7Document5 pagesTutorial 7sbb anbwNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (BBA & BBIS) SUB: OM Inventory Management: EOQ 200 Units & ROL 40 L, L Lead TimeDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 (BBA & BBIS) SUB: OM Inventory Management: EOQ 200 Units & ROL 40 L, L Lead Timesajal koiralaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Puvithera A/P GunasegaranNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 1Document5 pagesPractice Problems 1Murtaza PoonawalaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 OM PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 OM PDFSuman ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management CasesDocument3 pagesInventory Management Caseszk984975No ratings yet
- MT 378 TS3Document2 pagesMT 378 TS3Mike NdalamaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management - ExercisesDocument2 pagesInventory Management - ExercisesmeriemNo ratings yet
- SCM Numerical 2011Document13 pagesSCM Numerical 2011arvindpmNo ratings yet
- Total Relevant Cost (TRC)Document7 pagesTotal Relevant Cost (TRC)LinhThùyNo ratings yet
- Inventory Control Practice Problems (To Be Submitted As Assignment On or Before 02-12-2019)Document2 pagesInventory Control Practice Problems (To Be Submitted As Assignment On or Before 02-12-2019)syedqutub16No ratings yet
- Production and Operations Management - HandoutsDocument4 pagesProduction and Operations Management - HandoutsGhilman HabibNo ratings yet
- Inventory ControlDocument3 pagesInventory Controlहुमागाँई शिशिर0% (3)
- Operations Management Pactice QuestionsDocument8 pagesOperations Management Pactice QuestionsHumphrey OsaigbeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 320G062 NALVETHA BNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions-Deterministic Inventory ModelsDocument3 pagesPractice Questions-Deterministic Inventory ModelsSabir Ali0% (2)
- Tutorial 5 Supply Chain and InventoryDocument4 pagesTutorial 5 Supply Chain and InventoryHai Liang OngNo ratings yet
- Inventory 1Document5 pagesInventory 1Kim Ivy May FabunanNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Material ControlDocument2 pagesAssignment - Material Controlkevin75108No ratings yet
- IE323 Study Set 2Document5 pagesIE323 Study Set 2Mehmet ŞahinNo ratings yet
- Üretim Servis Çalışma SorularıDocument10 pagesÜretim Servis Çalışma SorularıEzgi Su KilitNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 - Mar 2014Document2 pagesQuiz 3 - Mar 2014manojboaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions Operations Management (Iet204)Document3 pagesTutorial Questions Operations Management (Iet204)Jagajith Sathis Chandran NairNo ratings yet
- Assignment Inventory Management 12.7Document2 pagesAssignment Inventory Management 12.7meriemNo ratings yet
- Inventory NumericalsDocument2 pagesInventory NumericalssushmaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management QuesDocument4 pagesInventory Management QuesDisha Commerce AcademyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1mayen DauNo ratings yet
- Working CapitalDocument5 pagesWorking Capitalchanchal shahiNo ratings yet
- Asignment Financial Management IIDocument1 pageAsignment Financial Management IItame kibruNo ratings yet
- EOQ QuestionDocument8 pagesEOQ QuestionSaurav ShawNo ratings yet
- MS29P TutorialQuestionsInventory JITDocument2 pagesMS29P TutorialQuestionsInventory JITSolar ProNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument5 pagesProblem SetKUMRNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Inventory Management BUSI2603U Fall 2015Document5 pagesChapter 4: Inventory Management BUSI2603U Fall 2015Jharr699No ratings yet
- Operations Management 712116822Document41 pagesOperations Management 712116822Arun HariharanNo ratings yet
- In Class Work Examples 3Document2 pagesIn Class Work Examples 3CemileNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 - Inventory Control: (Order Quantity 100 Units, TC RM5137.50)Document2 pagesTutorial 5 - Inventory Control: (Order Quantity 100 Units, TC RM5137.50)Nik Nur Azmina AzharNo ratings yet
- Operations Research Tutorial ProblemDocument4 pagesOperations Research Tutorial ProblemAjitsingh JagtapNo ratings yet
- Practice of Material ManagementDocument8 pagesPractice of Material ManagementBilal AliNo ratings yet
- 1 TutorDocument7 pages1 TutorHero StrikesNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management Classroom ProblemsDocument1 pageInventory Management Classroom ProblemsApril Grace BonaobraNo ratings yet
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT Problems Only For Class Nov 2014Document2 pagesINVENTORY MANAGEMENT Problems Only For Class Nov 2014swaroop666No ratings yet
- Exercises of Inventory ManagementDocument3 pagesExercises of Inventory ManagementTâm ThuNo ratings yet
- SCM ProbDocument6 pagesSCM ProbRhoel YadaoNo ratings yet
- Deterministic Inventory Control Model Formulas RushabhDocument6 pagesDeterministic Inventory Control Model Formulas RushabhVijay ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Inventory NMDocument15 pagesInventory NMAashish BistaNo ratings yet
- Fixed-OrderQuantity and Fixed-TimePeriod ExercisesDocument1 pageFixed-OrderQuantity and Fixed-TimePeriod ExercisesIris Descent0% (1)
- Practice Set EOQ ModelDocument1 pagePractice Set EOQ ModelBhaswar ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Inventory NumericalsDocument4 pagesInventory Numericalsalizasajid50No ratings yet
- Relevant Costing Problems FA05Document3 pagesRelevant Costing Problems FA05Cy HicarteNo ratings yet
- Cost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsFrom EverandCost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Tutorial 3 - Project Network ModelDocument1 pageTutorial 3 - Project Network ModelMUSA AHMED ABDULLAHI ALINo ratings yet
- Predicting The Term Deposit SubscriptionDocument38 pagesPredicting The Term Deposit SubscriptionMUSA AHMED ABDULLAHI ALINo ratings yet
- Behavioral Finance Modern Portfolio Theory and The Efficient Market HypothesisDocument11 pagesBehavioral Finance Modern Portfolio Theory and The Efficient Market HypothesisMUSA AHMED ABDULLAHI ALINo ratings yet
- 0001Document1 page0001MUSA AHMED ABDULLAHI ALINo ratings yet