Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eatapas Desarrollo de La Mama en Ingles
Eatapas Desarrollo de La Mama en Ingles
Uploaded by
jose perezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Assessment of Learning On Module: 3A Activity No. 1Document6 pagesAssessment of Learning On Module: 3A Activity No. 1Rujiyana P. UliNo ratings yet
- A New Life - Pregnancy and Baby DevelopmentDocument36 pagesA New Life - Pregnancy and Baby DevelopmentMiss FraterNo ratings yet
- 3 - Anatomy Presentation NotesDocument43 pages3 - Anatomy Presentation Notesonezwa1992No ratings yet
- Kelompok 6Document13 pagesKelompok 6betty gindiNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 AnswerDocument20 pagesNCM 109 AnswerBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Breast FeedingDocument5 pagesBreast FeedingClareen JuanicoNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding - The Essential PrinciplesDocument11 pagesBreastfeeding - The Essential PrinciplesJavier Gutiérrez CastilloNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 27 Mar 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 27 Mar 2023shjjhhejdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 11: Biomedical Perspective in Gendur Tand SexualityDocument1 pageUnit 11: Biomedical Perspective in Gendur Tand SexualityAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction PortfolioDocument19 pagesHuman Reproduction PortfolioIgnacio FelicityNo ratings yet
- Der To Properly Care About The Offspring and Keep It Safe.: ImplantationDocument2 pagesDer To Properly Care About The Offspring and Keep It Safe.: ImplantationChristine AguilarNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction 2 Menstrual CycleDocument19 pagesHuman Reproduction 2 Menstrual CyclepaballorandomaccNo ratings yet
- B. Menstrual CycleDocument5 pagesB. Menstrual CycleJulio NazarethNo ratings yet
- 4 1Document265 pages4 1sillypoloNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge of LactationDocument27 pagesBasic Knowledge of Lactationedward_chiNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 AnswerDocument23 pagesNCM 109 AnswerBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Breast: Mammary GlandsDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Breast: Mammary GlandsAlmira GamaoNo ratings yet
- Ovary CycleDocument2 pagesOvary CyclemarckharoldensanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lactation NewDocument15 pagesChapter 3 Lactation NewJassyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching On Breast Feeding 3Document19 pagesClinical Teaching On Breast Feeding 3Devuchandana RNo ratings yet
- VictorDocument12 pagesVictorTanya SierraNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Lactation 2023Document34 pagesPhysiology of Lactation 2023liu goedy fernadezNo ratings yet
- Concepts of LactationDocument26 pagesConcepts of LactationKeerthi AnbazhaganNo ratings yet
- Managemente of Cardiovascular Disease Diseases During PregnancyDocument14 pagesManagemente of Cardiovascular Disease Diseases During PregnancyHillary AchachNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document9 pagesModule 4Angelica MadronaNo ratings yet
- MATERNAL RLE Second WeekDocument6 pagesMATERNAL RLE Second WeekEma HibayaNo ratings yet
- Human Milk: Composition and Health Benefits: Fabio Mosca, Maria Lorella GiannìDocument6 pagesHuman Milk: Composition and Health Benefits: Fabio Mosca, Maria Lorella GiannìJuanZotelo09No ratings yet
- Module 1 PrenatalDocument3 pagesModule 1 PrenatalCherry BobierNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Organs, Menstrual Cycles, and FertilizationDocument13 pagesFemale Reproductive Organs, Menstrual Cycles, and FertilizationNurinnisa ShiddiqiyahNo ratings yet
- NSVDDocument32 pagesNSVDChris Oliver Kevin Ledesma100% (3)
- Placental HormoneDocument3 pagesPlacental Hormonealok nayakNo ratings yet
- Book No 2Document43 pagesBook No 2shwetaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Lactation: Prepared By: Fy MSC NursingDocument32 pagesPhysiology of Lactation: Prepared By: Fy MSC NursingSùjâl PätídàrNo ratings yet
- NFDN 2004 - Unit 2 - Student JLBDocument62 pagesNFDN 2004 - Unit 2 - Student JLBRumkee chyNo ratings yet
- Human Milk Composition and Health BenefitsDocument6 pagesHuman Milk Composition and Health BenefitsAshok KarnamNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology of The CowDocument4 pagesReproductive Anatomy and Physiology of The CowDiahNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument6 pagesFertilizationKristine Castillo100% (1)
- Breastfeeding Med 2020 - Factors Affecting The Composition of Expressed Fresh Human MilkDocument8 pagesBreastfeeding Med 2020 - Factors Affecting The Composition of Expressed Fresh Human MilkJosé CharcapeNo ratings yet
- Fertilization, Pregnancy, and Fetal Development: Paul F. Terranova, PH.DDocument23 pagesFertilization, Pregnancy, and Fetal Development: Paul F. Terranova, PH.DriswanfebriantoNo ratings yet
- Module 2-The-Scientific-SelfDocument15 pagesModule 2-The-Scientific-Selfmardigonzaga2No ratings yet
- HormonesDocument2 pagesHormonesAngeline NacarioNo ratings yet
- U9W6 - Physiology of LactationDocument2 pagesU9W6 - Physiology of LactationSuh KhaNo ratings yet
- Breast Development PDFDocument26 pagesBreast Development PDFgiant nitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document26 pagesLesson 2jen jen calsonaNo ratings yet
- MCN LectureDocument8 pagesMCN LectureEmily BernatNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Breast Milk ProductionDocument17 pagesPhysiology of Breast Milk ProductionOlivia TegliaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Mammary GlandsDocument2 pagesHistology of Mammary GlandsAlifah SyarafinaNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding and Nutritional Requirements in ChildrenDocument64 pagesBreastfeeding and Nutritional Requirements in Childrenapule geraldhumble100% (1)
- Approach To Breast FeedingDocument13 pagesApproach To Breast FeedingsmokaNo ratings yet
- NUT 565 Lecture 3 IYCN LactationDocument73 pagesNUT 565 Lecture 3 IYCN Lactationppknmd7pjnNo ratings yet
- LactationDocument8 pagesLactationDevuchandana RNo ratings yet
- Reproduction 2Document9 pagesReproduction 218118No ratings yet
- Colostrum 1Document57 pagesColostrum 1Light CareNo ratings yet
- MCHN 3RD LectDocument9 pagesMCHN 3RD LectZahNo ratings yet
- Anatomia y Fisiologuia General Libro-1351-1400Document50 pagesAnatomia y Fisiologuia General Libro-1351-1400Felipe Aguirre CórdovaNo ratings yet
- BREASTFEEDINGDocument49 pagesBREASTFEEDINGAurora Doris BatagaNo ratings yet
- Protein and Programming PDFDocument8 pagesProtein and Programming PDFAnnie RealNo ratings yet
- Fetal Development: Ms - Virgina Varghese and DR - SoniyaDocument37 pagesFetal Development: Ms - Virgina Varghese and DR - Soniyaalmayasa2002No ratings yet
- How To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornFrom EverandHow To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Practical Workbook: CH 7 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument31 pagesSuggested Answers To Practical Workbook: CH 7 Gas Exchange in HumansCharmine HolmesNo ratings yet
- The FEBS Journal - 2021 - Karamanos - A Guide To The Composition and Functions of The Extracellular MatrixDocument63 pagesThe FEBS Journal - 2021 - Karamanos - A Guide To The Composition and Functions of The Extracellular MatrixEduardo MullerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 727: Table 727-3 Abbreviations For Specimens inDocument9 pagesChapter 727: Table 727-3 Abbreviations For Specimens inGab ByNo ratings yet
- One Mark FMDocument4 pagesOne Mark FMragulraj6699No ratings yet
- 9.2 Exam Questions - Mark SchemeDocument2 pages9.2 Exam Questions - Mark SchemeSangidaNo ratings yet
- MLS305 Hema Lec PrelimsDocument16 pagesMLS305 Hema Lec PrelimsEvanka BaguistanNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment TaskDocument11 pagesSummative Assessment Taskapi-296545639No ratings yet
- 4 Tutorial Biocatalysis 2021 - SkemaDocument4 pages4 Tutorial Biocatalysis 2021 - SkemaM Syarifuddin Mohd AminNo ratings yet
- Bio 20 Unit C Topic 3 - Biogeochemical CyclesDocument18 pagesBio 20 Unit C Topic 3 - Biogeochemical CyclesUnzal FatehullahNo ratings yet
- Body Asymmetries: Incidence, Etiology and Clinical ImplicationsDocument35 pagesBody Asymmetries: Incidence, Etiology and Clinical Implicationsok okNo ratings yet
- Revision SB025 Set 1 AnswerDocument12 pagesRevision SB025 Set 1 Answerewine0529No ratings yet
- Revista CienciaDocument126 pagesRevista CienciaMario SantayanaNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument93 pagesPreviewpdfjaime luque lopezNo ratings yet
- DiplopodaDocument3 pagesDiplopodaLara Lirc100% (1)
- Module - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of BehaviorDocument11 pagesModule - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of Behavioraudree d. aldayNo ratings yet
- l4 Cell Injury, Cell Death & AdaptationsDocument22 pagesl4 Cell Injury, Cell Death & AdaptationsGeethanjali SivakumarNo ratings yet
- The Natural Horse and Unnatural BehaviourDocument7 pagesThe Natural Horse and Unnatural BehaviourOngki RadjaNo ratings yet
- ProcreationDocument55 pagesProcreationRoshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Homeostasis and ExcretionDocument15 pagesChapter 8: Homeostasis and ExcretionZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Scientia Horticulturae: Md. Fuad Mondal, Md. Asaduzzaman, Hideyuki Tanaka, Toshiki AsaoDocument7 pagesScientia Horticulturae: Md. Fuad Mondal, Md. Asaduzzaman, Hideyuki Tanaka, Toshiki AsaoYeya MarNo ratings yet
- Injury Incidence Between Barefoot and Shod RunnersDocument92 pagesInjury Incidence Between Barefoot and Shod Runnersxuuu0702No ratings yet
- Summary Book Abnormal Psychology Barlow Durand PDFDocument58 pagesSummary Book Abnormal Psychology Barlow Durand PDFLee DonghyuckNo ratings yet
- 2.1.2 WS ReusableDocument2 pages2.1.2 WS Reusableharittha.param33No ratings yet
- Case Presentation On Respiratory Track InfectionDocument22 pagesCase Presentation On Respiratory Track InfectionNewtan DebNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Architecture That BuildingsDocument39 pagesCognitive Architecture That BuildingsLilims LilithNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 9 (Muscles)Document21 pagesAnatomy Lec 9 (Muscles)HumrazNo ratings yet
- SeminarskiDocument17 pagesSeminarskiKadric Nagla UtokaNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument21 pagesBiochemistryRahul HalderNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Rino DoctNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukemia - Multiple Choice Questions - Laboratory HubDocument14 pagesAcute Leukemia - Multiple Choice Questions - Laboratory HubAssssssNo ratings yet
Eatapas Desarrollo de La Mama en Ingles
Eatapas Desarrollo de La Mama en Ingles
Uploaded by
jose perezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eatapas Desarrollo de La Mama en Ingles
Eatapas Desarrollo de La Mama en Ingles
Uploaded by
jose perezCopyright:
Available Formats
STAGES of
DEVELOPMENT THE
mother
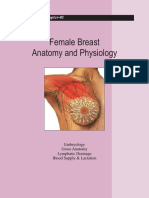
BREAST DEVELOPMENT
The development of the breast during a woman's life is characterized by different
phases.
ELC-induced growth regression begins when the infant is initiated on complementary
feeding and ends when the breast has involuted to the resting state. The full
development of the breast during lactation is essential to provide the adequate
volume and composition of breast milk for the growth, protection and development of
the infant.
development fetal
Embryonic development of the breast begins before the sixth week of gestation from a thickening of the
ectodermal ridge that extends from the groin to the axilla on the anterior surface of the embryo. The
appearance of the mammary buds does not change significantly until 13-20 weeks, when a depression forms on
their surface and the proliferation of different populations of epithelial progenitor cells causes the formation
and branching of secondary buds. In the last 8 weeks of gestation, the density of the periductal stroma
increases along with limited lobulo-alveolar development.
Neonatal and prepubertal
development
Until early childhood, the mammary gland remains in an
immature quiescent state, with minimal development and
virtually identical structure in males and females .
Puberty
Puberty induces rapid breast growth, fueled by ovulation and the establishment of regular
menstrual cycles. The increase in the size of the breasts is mainly due to a greater deposition of
adipose tissue inside the gland. Review of the anatomy of the female breast 5 groups called
lobules. Normally, the mini breast remodeling that occurs with each menstrual cycle does not
completely subside by the end of the cycle. Lobe 1, consisting of about 11 ductules;
Lobe 2, of about 47 ductules; and Lobe 3, of approximately 80 ductules.
Pregnancy
Although a mini-remodeling of the breast occurs with each menstrual cycle, it is not until the cycle of pregnancy and
lactation that a complete remodeling of the breast occurs, gradually transforming it into a mature and fully functional
organ. This remodeling works through changes in circulating hormonal complexes that activate populations of The
maturation phases are directly regulated by the increase in circulating lactogenic hormonal complex that induces ductal
branching, alveolar morphogenesis, and secretory differentiation.
Lactation
Secretory activation allows a rapid upregulation of milk synthesis and normally occurs 48-72 hours after calving, triggered by a decrease in blood progesterone and an
increase in prolactin levels. For example, it is well established that the clotting rate in the baby's stomach of infant formulas made from cow's milk, higher than that of
breast milk, is associated with slower gastric emptying and different colonization of the stomach. intestine compared to breastfed babies. Some studies with cattle
suggest that there is a relationship with increased plasma estrogen levels. The possibility can be raised that the increase in factors that induce proliferation during
pregnancy counteracts the factors that induce milk synthesis, since both exert antagonistic effects.
REFERENCIAS
"McPherson, K., Steel, C. M., & Dixon, J. M. (2000). Breast cancer—epidemiology, risk
factors, and genetics. BMJ : British Medical Journal, 321(7261), 624–628.
Sánchez Basurto, C. (2010). Tratado de las enfermedades de la glándula mamaria. Volúmen
1. Editorial Alfil, S. A. de C. V.UNAD
Paola Quintana Torrado
You might also like
- Assessment of Learning On Module: 3A Activity No. 1Document6 pagesAssessment of Learning On Module: 3A Activity No. 1Rujiyana P. UliNo ratings yet
- A New Life - Pregnancy and Baby DevelopmentDocument36 pagesA New Life - Pregnancy and Baby DevelopmentMiss FraterNo ratings yet
- 3 - Anatomy Presentation NotesDocument43 pages3 - Anatomy Presentation Notesonezwa1992No ratings yet
- Kelompok 6Document13 pagesKelompok 6betty gindiNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 AnswerDocument20 pagesNCM 109 AnswerBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Breast FeedingDocument5 pagesBreast FeedingClareen JuanicoNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding - The Essential PrinciplesDocument11 pagesBreastfeeding - The Essential PrinciplesJavier Gutiérrez CastilloNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 27 Mar 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 27 Mar 2023shjjhhejdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 11: Biomedical Perspective in Gendur Tand SexualityDocument1 pageUnit 11: Biomedical Perspective in Gendur Tand SexualityAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction PortfolioDocument19 pagesHuman Reproduction PortfolioIgnacio FelicityNo ratings yet
- Der To Properly Care About The Offspring and Keep It Safe.: ImplantationDocument2 pagesDer To Properly Care About The Offspring and Keep It Safe.: ImplantationChristine AguilarNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction 2 Menstrual CycleDocument19 pagesHuman Reproduction 2 Menstrual CyclepaballorandomaccNo ratings yet
- B. Menstrual CycleDocument5 pagesB. Menstrual CycleJulio NazarethNo ratings yet
- 4 1Document265 pages4 1sillypoloNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge of LactationDocument27 pagesBasic Knowledge of Lactationedward_chiNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 AnswerDocument23 pagesNCM 109 AnswerBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Breast: Mammary GlandsDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Breast: Mammary GlandsAlmira GamaoNo ratings yet
- Ovary CycleDocument2 pagesOvary CyclemarckharoldensanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lactation NewDocument15 pagesChapter 3 Lactation NewJassyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching On Breast Feeding 3Document19 pagesClinical Teaching On Breast Feeding 3Devuchandana RNo ratings yet
- VictorDocument12 pagesVictorTanya SierraNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Lactation 2023Document34 pagesPhysiology of Lactation 2023liu goedy fernadezNo ratings yet
- Concepts of LactationDocument26 pagesConcepts of LactationKeerthi AnbazhaganNo ratings yet
- Managemente of Cardiovascular Disease Diseases During PregnancyDocument14 pagesManagemente of Cardiovascular Disease Diseases During PregnancyHillary AchachNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document9 pagesModule 4Angelica MadronaNo ratings yet
- MATERNAL RLE Second WeekDocument6 pagesMATERNAL RLE Second WeekEma HibayaNo ratings yet
- Human Milk: Composition and Health Benefits: Fabio Mosca, Maria Lorella GiannìDocument6 pagesHuman Milk: Composition and Health Benefits: Fabio Mosca, Maria Lorella GiannìJuanZotelo09No ratings yet
- Module 1 PrenatalDocument3 pagesModule 1 PrenatalCherry BobierNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Organs, Menstrual Cycles, and FertilizationDocument13 pagesFemale Reproductive Organs, Menstrual Cycles, and FertilizationNurinnisa ShiddiqiyahNo ratings yet
- NSVDDocument32 pagesNSVDChris Oliver Kevin Ledesma100% (3)
- Placental HormoneDocument3 pagesPlacental Hormonealok nayakNo ratings yet
- Book No 2Document43 pagesBook No 2shwetaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Lactation: Prepared By: Fy MSC NursingDocument32 pagesPhysiology of Lactation: Prepared By: Fy MSC NursingSùjâl PätídàrNo ratings yet
- NFDN 2004 - Unit 2 - Student JLBDocument62 pagesNFDN 2004 - Unit 2 - Student JLBRumkee chyNo ratings yet
- Human Milk Composition and Health BenefitsDocument6 pagesHuman Milk Composition and Health BenefitsAshok KarnamNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology of The CowDocument4 pagesReproductive Anatomy and Physiology of The CowDiahNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument6 pagesFertilizationKristine Castillo100% (1)
- Breastfeeding Med 2020 - Factors Affecting The Composition of Expressed Fresh Human MilkDocument8 pagesBreastfeeding Med 2020 - Factors Affecting The Composition of Expressed Fresh Human MilkJosé CharcapeNo ratings yet
- Fertilization, Pregnancy, and Fetal Development: Paul F. Terranova, PH.DDocument23 pagesFertilization, Pregnancy, and Fetal Development: Paul F. Terranova, PH.DriswanfebriantoNo ratings yet
- Module 2-The-Scientific-SelfDocument15 pagesModule 2-The-Scientific-Selfmardigonzaga2No ratings yet
- HormonesDocument2 pagesHormonesAngeline NacarioNo ratings yet
- U9W6 - Physiology of LactationDocument2 pagesU9W6 - Physiology of LactationSuh KhaNo ratings yet
- Breast Development PDFDocument26 pagesBreast Development PDFgiant nitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document26 pagesLesson 2jen jen calsonaNo ratings yet
- MCN LectureDocument8 pagesMCN LectureEmily BernatNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Breast Milk ProductionDocument17 pagesPhysiology of Breast Milk ProductionOlivia TegliaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Mammary GlandsDocument2 pagesHistology of Mammary GlandsAlifah SyarafinaNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding and Nutritional Requirements in ChildrenDocument64 pagesBreastfeeding and Nutritional Requirements in Childrenapule geraldhumble100% (1)
- Approach To Breast FeedingDocument13 pagesApproach To Breast FeedingsmokaNo ratings yet
- NUT 565 Lecture 3 IYCN LactationDocument73 pagesNUT 565 Lecture 3 IYCN Lactationppknmd7pjnNo ratings yet
- LactationDocument8 pagesLactationDevuchandana RNo ratings yet
- Reproduction 2Document9 pagesReproduction 218118No ratings yet
- Colostrum 1Document57 pagesColostrum 1Light CareNo ratings yet
- MCHN 3RD LectDocument9 pagesMCHN 3RD LectZahNo ratings yet
- Anatomia y Fisiologuia General Libro-1351-1400Document50 pagesAnatomia y Fisiologuia General Libro-1351-1400Felipe Aguirre CórdovaNo ratings yet
- BREASTFEEDINGDocument49 pagesBREASTFEEDINGAurora Doris BatagaNo ratings yet
- Protein and Programming PDFDocument8 pagesProtein and Programming PDFAnnie RealNo ratings yet
- Fetal Development: Ms - Virgina Varghese and DR - SoniyaDocument37 pagesFetal Development: Ms - Virgina Varghese and DR - Soniyaalmayasa2002No ratings yet
- How To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornFrom EverandHow To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Practical Workbook: CH 7 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument31 pagesSuggested Answers To Practical Workbook: CH 7 Gas Exchange in HumansCharmine HolmesNo ratings yet
- The FEBS Journal - 2021 - Karamanos - A Guide To The Composition and Functions of The Extracellular MatrixDocument63 pagesThe FEBS Journal - 2021 - Karamanos - A Guide To The Composition and Functions of The Extracellular MatrixEduardo MullerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 727: Table 727-3 Abbreviations For Specimens inDocument9 pagesChapter 727: Table 727-3 Abbreviations For Specimens inGab ByNo ratings yet
- One Mark FMDocument4 pagesOne Mark FMragulraj6699No ratings yet
- 9.2 Exam Questions - Mark SchemeDocument2 pages9.2 Exam Questions - Mark SchemeSangidaNo ratings yet
- MLS305 Hema Lec PrelimsDocument16 pagesMLS305 Hema Lec PrelimsEvanka BaguistanNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment TaskDocument11 pagesSummative Assessment Taskapi-296545639No ratings yet
- 4 Tutorial Biocatalysis 2021 - SkemaDocument4 pages4 Tutorial Biocatalysis 2021 - SkemaM Syarifuddin Mohd AminNo ratings yet
- Bio 20 Unit C Topic 3 - Biogeochemical CyclesDocument18 pagesBio 20 Unit C Topic 3 - Biogeochemical CyclesUnzal FatehullahNo ratings yet
- Body Asymmetries: Incidence, Etiology and Clinical ImplicationsDocument35 pagesBody Asymmetries: Incidence, Etiology and Clinical Implicationsok okNo ratings yet
- Revision SB025 Set 1 AnswerDocument12 pagesRevision SB025 Set 1 Answerewine0529No ratings yet
- Revista CienciaDocument126 pagesRevista CienciaMario SantayanaNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument93 pagesPreviewpdfjaime luque lopezNo ratings yet
- DiplopodaDocument3 pagesDiplopodaLara Lirc100% (1)
- Module - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of BehaviorDocument11 pagesModule - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of Behavioraudree d. aldayNo ratings yet
- l4 Cell Injury, Cell Death & AdaptationsDocument22 pagesl4 Cell Injury, Cell Death & AdaptationsGeethanjali SivakumarNo ratings yet
- The Natural Horse and Unnatural BehaviourDocument7 pagesThe Natural Horse and Unnatural BehaviourOngki RadjaNo ratings yet
- ProcreationDocument55 pagesProcreationRoshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Homeostasis and ExcretionDocument15 pagesChapter 8: Homeostasis and ExcretionZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Scientia Horticulturae: Md. Fuad Mondal, Md. Asaduzzaman, Hideyuki Tanaka, Toshiki AsaoDocument7 pagesScientia Horticulturae: Md. Fuad Mondal, Md. Asaduzzaman, Hideyuki Tanaka, Toshiki AsaoYeya MarNo ratings yet
- Injury Incidence Between Barefoot and Shod RunnersDocument92 pagesInjury Incidence Between Barefoot and Shod Runnersxuuu0702No ratings yet
- Summary Book Abnormal Psychology Barlow Durand PDFDocument58 pagesSummary Book Abnormal Psychology Barlow Durand PDFLee DonghyuckNo ratings yet
- 2.1.2 WS ReusableDocument2 pages2.1.2 WS Reusableharittha.param33No ratings yet
- Case Presentation On Respiratory Track InfectionDocument22 pagesCase Presentation On Respiratory Track InfectionNewtan DebNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Architecture That BuildingsDocument39 pagesCognitive Architecture That BuildingsLilims LilithNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 9 (Muscles)Document21 pagesAnatomy Lec 9 (Muscles)HumrazNo ratings yet
- SeminarskiDocument17 pagesSeminarskiKadric Nagla UtokaNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument21 pagesBiochemistryRahul HalderNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Rino DoctNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukemia - Multiple Choice Questions - Laboratory HubDocument14 pagesAcute Leukemia - Multiple Choice Questions - Laboratory HubAssssssNo ratings yet