Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EOYE Reinforcement 2022 23.
EOYE Reinforcement 2022 23.
Uploaded by
Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Statement On Understanding Earthing - Earthing InstituteDocument8 pagesStatement On Understanding Earthing - Earthing InstituteMaynaNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Electrico de Camion Cat 777DDocument2 pagesDiagrama Electrico de Camion Cat 777DPedro Ruiz100% (2)
- Sistema Electrico 930h DHCDocument4 pagesSistema Electrico 930h DHCricardo100% (1)
- Oro551 Renewable Energy Sources 2019-2020Document12 pagesOro551 Renewable Energy Sources 2019-2020SreejithNo ratings yet
- Basic Sources of Light: Mary Lenilie C. Vengano Bsa-3BDocument9 pagesBasic Sources of Light: Mary Lenilie C. Vengano Bsa-3BArthur VenganoNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Resource GuideDocument25 pagesLIGHT Resource Guidecourtney_fernan8968No ratings yet
- Darkside of Light Pollution EssayDocument4 pagesDarkside of Light Pollution EssayAchmad Zainur Rozzykin100% (1)
- Use of Solar Cells in 1000 Watts Power Plants: Keywords - Solar Panels, Battery Charge Controller, Battery, InverterDocument11 pagesUse of Solar Cells in 1000 Watts Power Plants: Keywords - Solar Panels, Battery Charge Controller, Battery, InverterBrian FerNo ratings yet
- Q 2 Week 3 Day 1 2 Properties of LightDocument24 pagesQ 2 Week 3 Day 1 2 Properties of LightNeil Joseph LandinginNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture 1 Safety Electron TheoryDocument20 pagesModule 1 Lecture 1 Safety Electron TheoryChona ANo ratings yet
- BaboDocument13 pagesBaboZezo EdrisNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Mary School of Clarin, IncDocument25 pagesPresentation of Mary School of Clarin, IncjuicymayNo ratings yet
- Science11 Q4 Module 4 SENDDocument23 pagesScience11 Q4 Module 4 SENDcyrilgoliat3No ratings yet
- Overview: How To Turn Water Into Fuels On A Sunny Day: Nikolle Alejandra Laguado Uribe 1103178 8 Noviembre de 2017Document2 pagesOverview: How To Turn Water Into Fuels On A Sunny Day: Nikolle Alejandra Laguado Uribe 1103178 8 Noviembre de 2017DANIEL ESPINOSA ROCHANo ratings yet
- Exploring Energy From Sunlight To Electricity Learning Books For Kids Teens Shah Rukh Full ChapterDocument67 pagesExploring Energy From Sunlight To Electricity Learning Books For Kids Teens Shah Rukh Full Chapterthaddeus.shields888100% (6)
- Research On Light Pollution: Xiaomei ZhouDocument3 pagesResearch On Light Pollution: Xiaomei Zhoubaotramlehuynh2k4No ratings yet
- Liters of Light - Engineering A New Soda Bottle Solar LightDocument15 pagesLiters of Light - Engineering A New Soda Bottle Solar LightOhm BuildNo ratings yet
- ExposéDocument5 pagesExposéFouad MihoubNo ratings yet
- LightDocument2 pagesLightTyba314No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Worksheets CbseDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Science Worksheets CbseHeidiNo ratings yet
- Poles Responded To Many Who Disagreed Because of Their Superficial UnderstandingDocument4 pagesPoles Responded To Many Who Disagreed Because of Their Superficial UnderstandingSiti Nur IndahsariNo ratings yet
- How To Power Your Home For Free - EbookDocument41 pagesHow To Power Your Home For Free - Ebooksupport5051100% (1)
- DSSC Ip Chapter 2Document8 pagesDSSC Ip Chapter 2Alyana RamirezNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell - MIKEDocument14 pagesSolar Cell - MIKEMichalis AltousNo ratings yet
- Physics B Type QuestionDocument17 pagesPhysics B Type QuestionHappy RoyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: General Physics 2Document8 pagesWorksheet: General Physics 2Abdul Raffih AdapunNo ratings yet
- 300-Word Essay Expressing Your Opinions and Assertion On The Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation On Living Things and The EnvironmentDocument1 page300-Word Essay Expressing Your Opinions and Assertion On The Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation On Living Things and The EnvironmentELISHA RUTH BARAOIDANNo ratings yet
- !!!!!RESEARCHDocument17 pages!!!!!RESEARCHjado07No ratings yet
- Concise Dictionary Of Physics: Terms frequently used in Physics and their accurate explanationFrom EverandConcise Dictionary Of Physics: Terms frequently used in Physics and their accurate explanationRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Experiment Final: Ms. PugoyDocument6 pagesExperiment Final: Ms. PugoyrobinNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Sem 2Document7 pagesGrade 8 Sem 2govindvyas4444No ratings yet
- The Water Case: Your Uanet IdDocument2 pagesThe Water Case: Your Uanet IdLoraNo ratings yet
- Science10 ActivityDocument12 pagesScience10 ActivityTitanium NohorNo ratings yet
- Physics: Essential QuestionsDocument6 pagesPhysics: Essential QuestionsShiny NivolyaNo ratings yet
- ADM Physical Science Q2 Module 5 W5Document10 pagesADM Physical Science Q2 Module 5 W5johnfernanfernandez2No ratings yet
- GR 8 - Sample QP - ANSWER KEYDocument6 pagesGR 8 - Sample QP - ANSWER KEYJoseph JayakanthanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Explain - Ionizing RadiationDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Explain - Ionizing Radiationapi-344880038No ratings yet
- 02 Light PollutionDocument23 pages02 Light PollutionJothisha JothiNo ratings yet
- AnglaisDocument2 pagesAnglaisFouad MihoubNo ratings yet
- Waves in Everyday LifeDocument3 pagesWaves in Everyday LifeL1ghtedNo ratings yet
- To Study The Solar Cell and Its ProgressDocument5 pagesTo Study The Solar Cell and Its Progresssunnykumar13632No ratings yet
- Solarenergy Lesson AbcDocument4 pagesSolarenergy Lesson Abcapi-353690981No ratings yet
- Gen. Physics 2Document49 pagesGen. Physics 2Shelamae MangyaoNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2: Week 1 - 2Document10 pagesScience: Quarter 2: Week 1 - 2Khiel YumulNo ratings yet
- Solar Tree ReportDocument28 pagesSolar Tree ReportvijayNo ratings yet
- What Is Electroluminescence?Document4 pagesWhat Is Electroluminescence?Sumit Salunkhe Mtech2019No ratings yet
- Conductors and InsulatorsDocument5 pagesConductors and InsulatorsimanuelsukarnoNo ratings yet
- U.S. EPA Radiation Education Activities: Radiation Exposure Page 1 of 48Document48 pagesU.S. EPA Radiation Education Activities: Radiation Exposure Page 1 of 48Ariel Ybañez Edrada100% (1)
- Waves in Everyday LifeDocument3 pagesWaves in Everyday LifeL1ghtedNo ratings yet
- Science10 ActivityDocument12 pagesScience10 ActivityTitanium NohorNo ratings yet
- Nano Tech PaperDocument8 pagesNano Tech Paperapi-341656796No ratings yet
- Solar PhotovoltaicDocument17 pagesSolar PhotovoltaicAnshul KatiyarNo ratings yet
- What Is Light Pollution?Document4 pagesWhat Is Light Pollution?Redeemer ReeveNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Static Electricity PDFDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Static Electricity PDFShin KazueNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science 5 Module 3Document22 pagesQ3 Science 5 Module 3Cecilia Guevarra Dumlao100% (2)
- Week 1 Physics 2Document4 pagesWeek 1 Physics 2Stephanie Gwynette Almirol LalasNo ratings yet
- Physics Journal 2023Document22 pagesPhysics Journal 2023ADO ZERNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Quarter 3 Module 6 LightDocument14 pagesScience 4 Quarter 3 Module 6 LightFrit Zie75% (4)
- Wilmer Nossa Pino Paso - 3Document7 pagesWilmer Nossa Pino Paso - 3Eder SolisNo ratings yet
- GEOG114Document5 pagesGEOG114samuel.w.calderNo ratings yet
- Visible Light: Presented By: Mark Dee, Danielle Ella, Shantal Gamboa, and Yuki Harada of 10 - MarawiDocument11 pagesVisible Light: Presented By: Mark Dee, Danielle Ella, Shantal Gamboa, and Yuki Harada of 10 - MarawiYuki Marie HaradaNo ratings yet
- OpenSciEd High School Scope Sequence September 2021 PDFDocument22 pagesOpenSciEd High School Scope Sequence September 2021 PDFSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
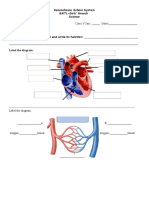
- Week 6. Lesson#2 - Term2 - Human Body System - ReinforcementDocument1 pageWeek 6. Lesson#2 - Term2 - Human Body System - ReinforcementSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Matter Energy Flow VideoDocument3 pagesMatter Energy Flow VideoSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- What Is Ecology?: Studying Our Living PlanetDocument4 pagesWhat Is Ecology?: Studying Our Living PlanetSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Science Class-V - Week2-4keeping Healthy AUGUST 2017-18Document63 pagesScience Class-V - Week2-4keeping Healthy AUGUST 2017-18Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Week 16 - Grade V - November 22, 2021, To November 26, 2021.Document2 pagesWeek 16 - Grade V - November 22, 2021, To November 26, 2021.Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Scales of Ecosystems: Mathayom 3 Date: Science in English 2019-2020Document4 pagesScales of Ecosystems: Mathayom 3 Date: Science in English 2019-2020Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Carbon in The Biosphere WsDocument3 pagesCarbon in The Biosphere WsSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Food Webs: Part 1 Complete The Following Food Web Then Use It To Answer The Questions That FollowDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Science Food Webs: Part 1 Complete The Following Food Web Then Use It To Answer The Questions That FollowSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Producer ConsumerDocument2 pagesProducer ConsumerSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1-State changes-Heating-cooling-curves-Set-1-msDocument2 pages1.2.1-State changes-Heating-cooling-curves-Set-1-msSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Desert Food Web: Cut Out The Animals and Paste Them Below To Create A Food WebDocument1 pageDesert Food Web: Cut Out The Animals and Paste Them Below To Create A Food WebSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- 110140224282116Document1 page110140224282116Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Desert Food Chain: Cut Out The Animals and Paste Them Below To Create A Food ChainsDocument1 pageDesert Food Chain: Cut Out The Animals and Paste Them Below To Create A Food ChainsSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Answer 2022Document1 pageAnswer 2022Rashida ParveenNo ratings yet
- December Checkpoints Grade6Document5 pagesDecember Checkpoints Grade6Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Rockets and Artificial Satellites With AnswersDocument2 pagesRockets and Artificial Satellites With AnswersSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- "Living or Nonliving" WorksheetDocument1 page"Living or Nonliving" WorksheetSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Science Paper Section B and C Class VII 2019-10Document1 pageScience Paper Section B and C Class VII 2019-10Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Mark Scheme: Science Exams SortedDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure Mark Scheme: Science Exams SortedSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Beaconhouse School System L1Document2 pagesBeaconhouse School System L1Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Class V Science 2nd EOUADocument5 pagesClass V Science 2nd EOUASaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Term Ii, Week 10 Lesson 1&2Document2 pagesTerm Ii, Week 10 Lesson 1&2Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- 1st&2nd TERM CAT DATA aNALYSIS CAT 5A 2022-23 - 4th CATDocument1 page1st&2nd TERM CAT DATA aNALYSIS CAT 5A 2022-23 - 4th CATSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Light Povert Nad ReinforcementDocument3 pagesLight Povert Nad ReinforcementSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Final Grade 5 Paper ScienceDocument13 pagesFinal Grade 5 Paper ScienceSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Week 14-Grade V - November 15, 2021, To November 19, 2021.Document4 pagesWeek 14-Grade V - November 15, 2021, To November 19, 2021.Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Students Will Be Able To Describe Parts of The Eye.Document3 pagesStudents Will Be Able To Describe Parts of The Eye.Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- 2019 Physics CheckpointDocument10 pages2019 Physics CheckpointSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- AWE U10Document3 pagesAWE U10Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current: Class - X ScienceDocument18 pagesChapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current: Class - X ScienceGovind DabralNo ratings yet
- Exploring Parallel Path Magnetic Technology - Overunity in DisguiseDocument7 pagesExploring Parallel Path Magnetic Technology - Overunity in DisguiseTomislav JovanovicNo ratings yet
- C 15Document2 pagesC 15mohanNo ratings yet
- Module 8 ElectromagnetismDocument36 pagesModule 8 ElectromagnetismDiana Dealino-SabandalNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Schematic D5R Uenr13680001Document13 pagesHydraulic Schematic D5R Uenr13680001Dwi100% (1)
- Esquema Eléctrico C9 Motor MarinoDocument8 pagesEsquema Eléctrico C9 Motor MarinoLuis Angel Culqui VasquezNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetDocument4 pagesElectromagnetftplevel1No ratings yet
- c4.4 Sistema ElectricoDocument7 pagesc4.4 Sistema ElectricoAngelica VergaraNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project of Physics 3Document25 pagesInvestigatory Project of Physics 3Rahul MeenaNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Eléctrico 420f2Document34 pagesDiagrama Eléctrico 420f2Angel Heber Diestra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Project Camelot - Ralph Ring and Otis CarrDocument32 pagesProject Camelot - Ralph Ring and Otis CarrjlcdiNo ratings yet
- D9N Electrical SystemDocument2 pagesD9N Electrical Systemwtn2013100% (1)
- Sbe Elec PDFDocument17 pagesSbe Elec PDFRajan Mullappilly100% (1)
- Solenoid EngineDocument13 pagesSolenoid EngineLohitNo ratings yet
- KENR82260001 Plano Electrico D11R-84Document11 pagesKENR82260001 Plano Electrico D11R-84Frank Mc GyverNo ratings yet
- Left Hand Console: Electrical System 313 and 313 GC ExcavatorDocument6 pagesLeft Hand Console: Electrical System 313 and 313 GC ExcavatorHenry Sergio HuayhuaNo ratings yet
- 1st - Magnetism & ElectromagnetismDocument47 pages1st - Magnetism & Electromagnetisming_manceraNo ratings yet
- Marwan K. Abbadi Advisor: Dr. Winfred AnakwaDocument35 pagesMarwan K. Abbadi Advisor: Dr. Winfred AnakwaAniruddha NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- Describing Magnetic FieldsDocument19 pagesDescribing Magnetic FieldsFabio LayneNo ratings yet
- Edi Meow Exp 1Document6 pagesEdi Meow Exp 1Jay Romar PabianiaNo ratings yet
- Analisis K3 BHG B Fizik SPM (2003-2016)Document3 pagesAnalisis K3 BHG B Fizik SPM (2003-2016)Red KiteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document16 pagesChapter 9wallacec1017No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument14 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentREHANNo ratings yet
- G-7 CT On Magnetism, 23Document4 pagesG-7 CT On Magnetism, 23Jitu MohammadNo ratings yet
- 320c Electrical System 1Document10 pages320c Electrical System 1yoga_jpbmbmNo ratings yet
- Tehandler KatoDocument15 pagesTehandler KatoWalterNo ratings yet
EOYE Reinforcement 2022 23.
EOYE Reinforcement 2022 23.
Uploaded by
Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EOYE Reinforcement 2022 23.
EOYE Reinforcement 2022 23.
Uploaded by
Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBCopyright:
Available Formats
EOYE--Reinforcement--2022-23.
Differentiating between biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials and explaining their impact on pollution in
water, air, and land:
1. What is the difference between biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials?
1. Give three examples of biodegradable materials.
2. Give three examples of non-biodegradable materials.
3. What happens when biodegradable materials are left in the environment?
4. What happens when non-biodegradable materials are left in the environment?
Answer Key:
1. Biodegradable materials can be broken down and decomposed by natural processes, such as bacteria and
fungi, over time. Non-biodegradable materials cannot be broken down by natural processes and can remain
in the environment for a long time.
1. Examples of biodegradable materials include food waste, paper, and plant materials.
2. Examples of non-biodegradable materials include plastics, metals, and glass.
3. When biodegradable materials are left in the environment, they are broken down by microorganisms and
decompose into natural materials, such as water and carbon dioxide.
4. When non-biodegradable materials are left in the environment, they can accumulate and persist for years,
causing environmental pollution and harming wildlife.
How solar eclipses occur:
1. What is a solar eclipse?
2. What are the two types of solar eclipses?
3. Why is it not safe to look directly at a solar eclipse?
4. How often do solar eclipses occur?
Answer Key:
1. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, blocking the Sun's light and
casting a shadow on the Earth's surface.
2. The two types of solar eclipses are a total solar eclipse, where the Moon completely covers the Sun, and a
partial solar eclipse, where the Moon only partially covers the Sun.
3. It is not safe to look directly at a solar eclipse because the Sun's rays can cause permanent eye damage or
blindness.
4. Solar eclipses occur a few times a year, but they are not visible from all parts of the world. Total solar
eclipses are rare and occur about once every 18 months.
Describe what light poverty is and its consequences.
Explore the advantages of solar-powered lighting solutions.
What is light poverty?
A: Light poverty is a situation where people lack access to adequate and reliable lighting, particularly in their homes,
workplaces, or public spaces.
What are the consequences of light poverty?
A: The consequences of light poverty can include limited educational and economic opportunities, increased health
risks due to poor lighting and air quality, and reduced safety and security, particularly for women and children.
What are the advantages of solar-powered lighting solutions?
A: Solar-powered lighting solutions have several advantages, including:
They are cost-effective and require no electricity from the grid
They are environmentally friendly and sustainable
They are easy to install and maintain
They can improve the quality of life and safety of people in areas with light poverty
They can promote economic growth and development by providing opportunities for entrepreneurship and education.
How does solar-powered lighting work?
A: Solar-powered lighting works by harnessing the energy of the sun through solar panels, which convert the sunlight
into electricity. This electricity is stored in batteries and used to power LED lights when the sun sets.
What are some examples of solar-powered lighting solutions?
A: Examples of solar-powered lighting solutions include solar lanterns, solar street lights, and solar home systems.
These solutions are particularly useful in areas with no or unreliable electricity access.
Describe what happens when light meets an opaque object.
What is an opaque object?
A: An opaque object is an object that does not allow light to pass through it.
What happens when light meets an opaque object?
A: When light meets an opaque object, the light is either absorbed, reflected, or scattered by the surface of the object.
The amount of light absorbed, reflected, or scattered depends on the properties of the surface of the object, such as
its color, texture, and shape.
What is absorption of light?
A: Absorption of light is the process by which an object takes in some or all of the light that falls on it.
A: Reflection of light is the process by which an object bounces back some or all of the light that falls on it, without
absorbing it.
What is scattering of light?
A: Scattering of light is the process by which light is redirected in different directions as it passes through a material,
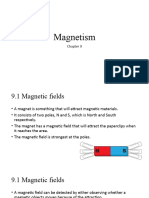
Differentiate between the properties of permanent magnets and electro-magnets and research their use in everyday
objects/ appliances.
What is an electric current?
A: An electric current is a flow of electric charge through a conductor, such as a wire.
How does an electric current produce a magnetic field?
A: An electric current produces a magnetic field around it because the moving electric charges (electrons) create a
magnetic field.
How can you use a magnetic compass to detect a magnetic field?
A: A magnetic compass aligns itself with the direction of a magnetic field, so if you place a magnetic compass near a
current-carrying wire, the compass needle will move and align itself with the magnetic field around the wire.
What is a permanent magnet?
A: A permanent magnet is a magnet that produces its own magnetic field and retains its magnetism without the need
for an external magnetic field.
What is an electromagnet?
A: An electromagnet is a magnet that produces a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through a wire
wrapped around a magnetic core.
What is the difference between permanent magnets and electromagnets?
A: Permanent magnets produce their own magnetic field without the need for an external source of electricity, while
electromagnets require an electric current to produce a magnetic field. Additionally, the strength of an electromagnet
can be controlled by varying the amount of electric current, while the strength of a permanent magnet cannot be
easily changed.
What are some everyday objects or appliances that use magnets?
A: Some examples of everyday objects or appliances that use magnets include refrigerator magnets, speakers, electric
motors, and MRI machines.
You might also like
- Statement On Understanding Earthing - Earthing InstituteDocument8 pagesStatement On Understanding Earthing - Earthing InstituteMaynaNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Electrico de Camion Cat 777DDocument2 pagesDiagrama Electrico de Camion Cat 777DPedro Ruiz100% (2)
- Sistema Electrico 930h DHCDocument4 pagesSistema Electrico 930h DHCricardo100% (1)
- Oro551 Renewable Energy Sources 2019-2020Document12 pagesOro551 Renewable Energy Sources 2019-2020SreejithNo ratings yet
- Basic Sources of Light: Mary Lenilie C. Vengano Bsa-3BDocument9 pagesBasic Sources of Light: Mary Lenilie C. Vengano Bsa-3BArthur VenganoNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Resource GuideDocument25 pagesLIGHT Resource Guidecourtney_fernan8968No ratings yet
- Darkside of Light Pollution EssayDocument4 pagesDarkside of Light Pollution EssayAchmad Zainur Rozzykin100% (1)
- Use of Solar Cells in 1000 Watts Power Plants: Keywords - Solar Panels, Battery Charge Controller, Battery, InverterDocument11 pagesUse of Solar Cells in 1000 Watts Power Plants: Keywords - Solar Panels, Battery Charge Controller, Battery, InverterBrian FerNo ratings yet
- Q 2 Week 3 Day 1 2 Properties of LightDocument24 pagesQ 2 Week 3 Day 1 2 Properties of LightNeil Joseph LandinginNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lecture 1 Safety Electron TheoryDocument20 pagesModule 1 Lecture 1 Safety Electron TheoryChona ANo ratings yet
- BaboDocument13 pagesBaboZezo EdrisNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Mary School of Clarin, IncDocument25 pagesPresentation of Mary School of Clarin, IncjuicymayNo ratings yet
- Science11 Q4 Module 4 SENDDocument23 pagesScience11 Q4 Module 4 SENDcyrilgoliat3No ratings yet
- Overview: How To Turn Water Into Fuels On A Sunny Day: Nikolle Alejandra Laguado Uribe 1103178 8 Noviembre de 2017Document2 pagesOverview: How To Turn Water Into Fuels On A Sunny Day: Nikolle Alejandra Laguado Uribe 1103178 8 Noviembre de 2017DANIEL ESPINOSA ROCHANo ratings yet
- Exploring Energy From Sunlight To Electricity Learning Books For Kids Teens Shah Rukh Full ChapterDocument67 pagesExploring Energy From Sunlight To Electricity Learning Books For Kids Teens Shah Rukh Full Chapterthaddeus.shields888100% (6)
- Research On Light Pollution: Xiaomei ZhouDocument3 pagesResearch On Light Pollution: Xiaomei Zhoubaotramlehuynh2k4No ratings yet
- Liters of Light - Engineering A New Soda Bottle Solar LightDocument15 pagesLiters of Light - Engineering A New Soda Bottle Solar LightOhm BuildNo ratings yet
- ExposéDocument5 pagesExposéFouad MihoubNo ratings yet
- LightDocument2 pagesLightTyba314No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Worksheets CbseDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Science Worksheets CbseHeidiNo ratings yet
- Poles Responded To Many Who Disagreed Because of Their Superficial UnderstandingDocument4 pagesPoles Responded To Many Who Disagreed Because of Their Superficial UnderstandingSiti Nur IndahsariNo ratings yet
- How To Power Your Home For Free - EbookDocument41 pagesHow To Power Your Home For Free - Ebooksupport5051100% (1)
- DSSC Ip Chapter 2Document8 pagesDSSC Ip Chapter 2Alyana RamirezNo ratings yet
- Solar Cell - MIKEDocument14 pagesSolar Cell - MIKEMichalis AltousNo ratings yet
- Physics B Type QuestionDocument17 pagesPhysics B Type QuestionHappy RoyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: General Physics 2Document8 pagesWorksheet: General Physics 2Abdul Raffih AdapunNo ratings yet
- 300-Word Essay Expressing Your Opinions and Assertion On The Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation On Living Things and The EnvironmentDocument1 page300-Word Essay Expressing Your Opinions and Assertion On The Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation On Living Things and The EnvironmentELISHA RUTH BARAOIDANNo ratings yet
- !!!!!RESEARCHDocument17 pages!!!!!RESEARCHjado07No ratings yet
- Concise Dictionary Of Physics: Terms frequently used in Physics and their accurate explanationFrom EverandConcise Dictionary Of Physics: Terms frequently used in Physics and their accurate explanationRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Experiment Final: Ms. PugoyDocument6 pagesExperiment Final: Ms. PugoyrobinNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Sem 2Document7 pagesGrade 8 Sem 2govindvyas4444No ratings yet
- The Water Case: Your Uanet IdDocument2 pagesThe Water Case: Your Uanet IdLoraNo ratings yet
- Science10 ActivityDocument12 pagesScience10 ActivityTitanium NohorNo ratings yet
- Physics: Essential QuestionsDocument6 pagesPhysics: Essential QuestionsShiny NivolyaNo ratings yet
- ADM Physical Science Q2 Module 5 W5Document10 pagesADM Physical Science Q2 Module 5 W5johnfernanfernandez2No ratings yet
- GR 8 - Sample QP - ANSWER KEYDocument6 pagesGR 8 - Sample QP - ANSWER KEYJoseph JayakanthanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Explain - Ionizing RadiationDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Explain - Ionizing Radiationapi-344880038No ratings yet
- 02 Light PollutionDocument23 pages02 Light PollutionJothisha JothiNo ratings yet
- AnglaisDocument2 pagesAnglaisFouad MihoubNo ratings yet
- Waves in Everyday LifeDocument3 pagesWaves in Everyday LifeL1ghtedNo ratings yet
- To Study The Solar Cell and Its ProgressDocument5 pagesTo Study The Solar Cell and Its Progresssunnykumar13632No ratings yet
- Solarenergy Lesson AbcDocument4 pagesSolarenergy Lesson Abcapi-353690981No ratings yet
- Gen. Physics 2Document49 pagesGen. Physics 2Shelamae MangyaoNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2: Week 1 - 2Document10 pagesScience: Quarter 2: Week 1 - 2Khiel YumulNo ratings yet
- Solar Tree ReportDocument28 pagesSolar Tree ReportvijayNo ratings yet
- What Is Electroluminescence?Document4 pagesWhat Is Electroluminescence?Sumit Salunkhe Mtech2019No ratings yet
- Conductors and InsulatorsDocument5 pagesConductors and InsulatorsimanuelsukarnoNo ratings yet
- U.S. EPA Radiation Education Activities: Radiation Exposure Page 1 of 48Document48 pagesU.S. EPA Radiation Education Activities: Radiation Exposure Page 1 of 48Ariel Ybañez Edrada100% (1)
- Waves in Everyday LifeDocument3 pagesWaves in Everyday LifeL1ghtedNo ratings yet
- Science10 ActivityDocument12 pagesScience10 ActivityTitanium NohorNo ratings yet
- Nano Tech PaperDocument8 pagesNano Tech Paperapi-341656796No ratings yet
- Solar PhotovoltaicDocument17 pagesSolar PhotovoltaicAnshul KatiyarNo ratings yet
- What Is Light Pollution?Document4 pagesWhat Is Light Pollution?Redeemer ReeveNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Static Electricity PDFDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Static Electricity PDFShin KazueNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science 5 Module 3Document22 pagesQ3 Science 5 Module 3Cecilia Guevarra Dumlao100% (2)
- Week 1 Physics 2Document4 pagesWeek 1 Physics 2Stephanie Gwynette Almirol LalasNo ratings yet
- Physics Journal 2023Document22 pagesPhysics Journal 2023ADO ZERNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Quarter 3 Module 6 LightDocument14 pagesScience 4 Quarter 3 Module 6 LightFrit Zie75% (4)
- Wilmer Nossa Pino Paso - 3Document7 pagesWilmer Nossa Pino Paso - 3Eder SolisNo ratings yet
- GEOG114Document5 pagesGEOG114samuel.w.calderNo ratings yet
- Visible Light: Presented By: Mark Dee, Danielle Ella, Shantal Gamboa, and Yuki Harada of 10 - MarawiDocument11 pagesVisible Light: Presented By: Mark Dee, Danielle Ella, Shantal Gamboa, and Yuki Harada of 10 - MarawiYuki Marie HaradaNo ratings yet
- OpenSciEd High School Scope Sequence September 2021 PDFDocument22 pagesOpenSciEd High School Scope Sequence September 2021 PDFSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Week 6. Lesson#2 - Term2 - Human Body System - ReinforcementDocument1 pageWeek 6. Lesson#2 - Term2 - Human Body System - ReinforcementSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Matter Energy Flow VideoDocument3 pagesMatter Energy Flow VideoSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- What Is Ecology?: Studying Our Living PlanetDocument4 pagesWhat Is Ecology?: Studying Our Living PlanetSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Science Class-V - Week2-4keeping Healthy AUGUST 2017-18Document63 pagesScience Class-V - Week2-4keeping Healthy AUGUST 2017-18Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Week 16 - Grade V - November 22, 2021, To November 26, 2021.Document2 pagesWeek 16 - Grade V - November 22, 2021, To November 26, 2021.Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Scales of Ecosystems: Mathayom 3 Date: Science in English 2019-2020Document4 pagesScales of Ecosystems: Mathayom 3 Date: Science in English 2019-2020Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Carbon in The Biosphere WsDocument3 pagesCarbon in The Biosphere WsSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Food Webs: Part 1 Complete The Following Food Web Then Use It To Answer The Questions That FollowDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Science Food Webs: Part 1 Complete The Following Food Web Then Use It To Answer The Questions That FollowSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Producer ConsumerDocument2 pagesProducer ConsumerSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1-State changes-Heating-cooling-curves-Set-1-msDocument2 pages1.2.1-State changes-Heating-cooling-curves-Set-1-msSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Desert Food Web: Cut Out The Animals and Paste Them Below To Create A Food WebDocument1 pageDesert Food Web: Cut Out The Animals and Paste Them Below To Create A Food WebSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- 110140224282116Document1 page110140224282116Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Desert Food Chain: Cut Out The Animals and Paste Them Below To Create A Food ChainsDocument1 pageDesert Food Chain: Cut Out The Animals and Paste Them Below To Create A Food ChainsSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Answer 2022Document1 pageAnswer 2022Rashida ParveenNo ratings yet
- December Checkpoints Grade6Document5 pagesDecember Checkpoints Grade6Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Rockets and Artificial Satellites With AnswersDocument2 pagesRockets and Artificial Satellites With AnswersSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- "Living or Nonliving" WorksheetDocument1 page"Living or Nonliving" WorksheetSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Science Paper Section B and C Class VII 2019-10Document1 pageScience Paper Section B and C Class VII 2019-10Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Mark Scheme: Science Exams SortedDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure Mark Scheme: Science Exams SortedSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Beaconhouse School System L1Document2 pagesBeaconhouse School System L1Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Class V Science 2nd EOUADocument5 pagesClass V Science 2nd EOUASaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Term Ii, Week 10 Lesson 1&2Document2 pagesTerm Ii, Week 10 Lesson 1&2Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- 1st&2nd TERM CAT DATA aNALYSIS CAT 5A 2022-23 - 4th CATDocument1 page1st&2nd TERM CAT DATA aNALYSIS CAT 5A 2022-23 - 4th CATSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Light Povert Nad ReinforcementDocument3 pagesLight Povert Nad ReinforcementSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Final Grade 5 Paper ScienceDocument13 pagesFinal Grade 5 Paper ScienceSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Week 14-Grade V - November 15, 2021, To November 19, 2021.Document4 pagesWeek 14-Grade V - November 15, 2021, To November 19, 2021.Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
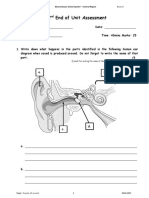
- Students Will Be Able To Describe Parts of The Eye.Document3 pagesStudents Will Be Able To Describe Parts of The Eye.Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- 2019 Physics CheckpointDocument10 pages2019 Physics CheckpointSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- AWE U10Document3 pagesAWE U10Saima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current: Class - X ScienceDocument18 pagesChapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current: Class - X ScienceGovind DabralNo ratings yet
- Exploring Parallel Path Magnetic Technology - Overunity in DisguiseDocument7 pagesExploring Parallel Path Magnetic Technology - Overunity in DisguiseTomislav JovanovicNo ratings yet
- C 15Document2 pagesC 15mohanNo ratings yet
- Module 8 ElectromagnetismDocument36 pagesModule 8 ElectromagnetismDiana Dealino-SabandalNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Schematic D5R Uenr13680001Document13 pagesHydraulic Schematic D5R Uenr13680001Dwi100% (1)
- Esquema Eléctrico C9 Motor MarinoDocument8 pagesEsquema Eléctrico C9 Motor MarinoLuis Angel Culqui VasquezNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetDocument4 pagesElectromagnetftplevel1No ratings yet
- c4.4 Sistema ElectricoDocument7 pagesc4.4 Sistema ElectricoAngelica VergaraNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project of Physics 3Document25 pagesInvestigatory Project of Physics 3Rahul MeenaNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Eléctrico 420f2Document34 pagesDiagrama Eléctrico 420f2Angel Heber Diestra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Project Camelot - Ralph Ring and Otis CarrDocument32 pagesProject Camelot - Ralph Ring and Otis CarrjlcdiNo ratings yet
- D9N Electrical SystemDocument2 pagesD9N Electrical Systemwtn2013100% (1)
- Sbe Elec PDFDocument17 pagesSbe Elec PDFRajan Mullappilly100% (1)
- Solenoid EngineDocument13 pagesSolenoid EngineLohitNo ratings yet
- KENR82260001 Plano Electrico D11R-84Document11 pagesKENR82260001 Plano Electrico D11R-84Frank Mc GyverNo ratings yet
- Left Hand Console: Electrical System 313 and 313 GC ExcavatorDocument6 pagesLeft Hand Console: Electrical System 313 and 313 GC ExcavatorHenry Sergio HuayhuaNo ratings yet
- 1st - Magnetism & ElectromagnetismDocument47 pages1st - Magnetism & Electromagnetisming_manceraNo ratings yet
- Marwan K. Abbadi Advisor: Dr. Winfred AnakwaDocument35 pagesMarwan K. Abbadi Advisor: Dr. Winfred AnakwaAniruddha NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- Describing Magnetic FieldsDocument19 pagesDescribing Magnetic FieldsFabio LayneNo ratings yet
- Edi Meow Exp 1Document6 pagesEdi Meow Exp 1Jay Romar PabianiaNo ratings yet
- Analisis K3 BHG B Fizik SPM (2003-2016)Document3 pagesAnalisis K3 BHG B Fizik SPM (2003-2016)Red KiteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document16 pagesChapter 9wallacec1017No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument14 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentREHANNo ratings yet
- G-7 CT On Magnetism, 23Document4 pagesG-7 CT On Magnetism, 23Jitu MohammadNo ratings yet
- 320c Electrical System 1Document10 pages320c Electrical System 1yoga_jpbmbmNo ratings yet
- Tehandler KatoDocument15 pagesTehandler KatoWalterNo ratings yet