Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MUGOT - DEMENTIA CONCEPT MAP - Page 3
MUGOT - DEMENTIA CONCEPT MAP - Page 3
Uploaded by
MICHELLIN VAN MUGOTOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MUGOT - DEMENTIA CONCEPT MAP - Page 3
MUGOT - DEMENTIA CONCEPT MAP - Page 3
Uploaded by
MICHELLIN VAN MUGOTCopyright:
Available Formats
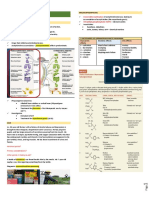
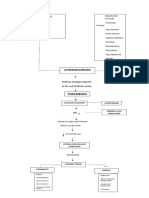
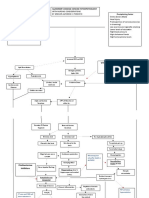
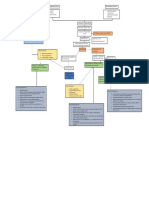
PREDISPOSING DEMENTI A PRECIPITATING
FACTORS: General term for the impaired ability FACTORS:
- Advancing Age to remember, think, or make - Smoking
- Genetics decisions that interferes with doing - Alcohol Use
everyday activities. - Hypertension- Vascular
- Sex- Women have
higher risk dementia
- Mild cognitive - Diabetes Mellitus
impairment Etiology - Obesity
- Neurotransmitter - Lack of physical
changes- Acetylcholine activity and poor diet
- Vascular abnormalities - Low levels of cognitive
- Stress hormones PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF engagement
- Circadian changes ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE (AD) VASCULAR DEMENTIA - Depression
- Seizure disorders - Traumatic brain injury
- Social isolation
Vascular insuficiency/ Vessel
Abnormal processing of pathology
amyloid precursor protein
- Reduction in Choline
Ischemic injury/ Vascular
Acetyltransferase
Hyperphosphorylation brain injury
(ChAT)
Aggregation of of
Inflammation - Reduction in
amyloid-ß microtubule-stabilizing Acetylcholinesterase Secondary
tau protein (AChE) neurodegeneration
- Extracellular deposition of
beta-amyloid (Aß) Formation of Decline in acetylcholine
- Extracellular neuritic/senile intracellular neurotransmitter SUBTYPES OF
Neuronal Dysfunction
plaques (amyloid-ß core neurofibrillary tangles VASCULAR DEMENTIA:
surruounded by activated (NFT) composed of - Muti infarct dementia
microglia and reactive hyperphosphorylated - Stroke induced
astrocytes) tau dementia
- Sub-cortical vascular
VASCULAR DEMENTIA dementia
- Disruption of Ca2+ - Mixed Dementia
homeostasis
- Free radical production Clinical
- Excitotoxicity Manifestations Behavioral Locomotor Loss of executive
- Inflammation Symptoms: Problems: function:
- Memory Loss - Gait - Problem solving
- Slowed disturbance - Working memory
- Neuronal Loss Impairments in nerve thinking - Dysarthia - Judgement
- Atrophy in temporofrontal cortex impulse transmission - Depression - Autonomic - Rasoning
- Anxiety dysfunction
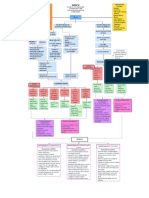
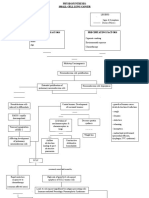
Clinical ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE
- Mental Health - Mental Health - Mental Health
Manifestations Status Status Status
assesment assesment assesment
Lack of Deficit in Executive Motor Neuropsychiatric: - Health history - Health history - Health history
Inattention and
orientation to episodic and planning Dysfunction: Delusions, - Physical exam - Physical exam - Physical exam
lack of
person, time, semantic dysfunction: Myoclonic apathy,
concentration
and place memory visouspatial seizure, irritability,
abnormalities, primitive aggression
anosgosia reflexes,
- Physical - Physical PHARMACOLOGICAL MEDICAL MANAGEMENT:
incontinence,
Examination Examination - Mental Health MANAGEMENT:
- Mental Health apraxia - Mental Health
- Mental Health - Mental Health Status - Cholinesterase inhibitors-
Status Therapies to manage include:
Status Status Status assesment
assesment enhance acetylcholine uptake - Music Therapy
assessment assessment assesment - Health history - Physical
- Health history in the brain - Reminiscence therapy
- Health History - Health History Examination
- Antipsychotic agents - Cognitive stimulation therapy
- Mental Health
- Anticonvulsant (CST)
Status assessment
- Antidepressant; Selective
- Health History
serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- CT Scan, MRI
- Treatment of underlying cause:
Antihypertensives, -Statins,
anticoagulants, Antidiabetic
PHARMACOLOGICAL MEDICAL MANAGEMENT: medications
MANAGEMENT:
- Cholinesterase inhibitors- Therapies to manage include:
enhance acetylcholine uptake - Music Therapy
in the brain - Reminiscence therapy
- Antipsychotic agents - Cognitive stimulation therapy
- Anticonvulsant (CST)
- Antidepressant; Selective
serotonin reuptake inhibitors
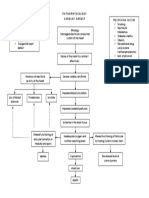
DEMENTIA
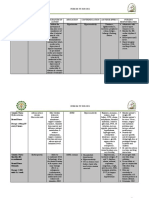
Nursing Diagnosis 1: Impaired Memory Nursing Diagnosis 2: Disturbed thought Nursing Diagnosis 3: Risk for Injury
process
Nursing Responsibilities:
Nursing Responsibilities: Nursing Responsibilities:
- Assess the patient?s overall cognitive
- Assess the patient?s ability for thought - Assess the degree of impaired ability of
function and memory.
processing every shift. competence, the emergence of impulsive
- Assess the patient for sensory
- Assess the level of cognitive impairment behavior, and a decrease in visual
deprivation, concurrent use of CNS drugs,
- Assess the patient?s ability to cope with perception.
poor nutrition, dehydration, infection, or
events, interests in surroundings and - Assess the patient?s surroundings for
other concurrent disease processes.
activity, motivation, and changes in hazards and remove them.
- Orient the patient to the environment as
memory pattern. - Eliminate or minimize sources of hazards
needed if the patient?s short-term memory
- Maintain a regular daily routine to prevent in the environment.
is intact. The use of calendars, radio,
problems resulting from thirst, hunger, - Instruct family to apply protective guard
newspapers, television, and so forth are
lack of sleep, or inadequate exercise. over electrical outlets, thermostats, and
also appropriate.
- Allow the patient the freedom to sit in a stove knobs.
- Encourage the use of complementary and
chair near the window, utilize books and - Instruct family to double lock doors and
alternative therapies such as exercises,
magazines as desired. windows, swimming pool areas, and
guided meditation, massage.
- Provide positive reinforcement and install pressure-sensitive buzzers on
feedback for positive behaviors doors.
- Limit decisions that the patient makes. - Maintain adequate lighting and clear
pathways.
You might also like
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2023: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BDocument21 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2023: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BBH 7mood0% (1)
- Skeletal System-Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesSkeletal System-Lecture Notesjcali06100% (5)
- Anticholinesterase: PHARMACOLOGY PPT by Dr. Geraldine CorporalDocument4 pagesAnticholinesterase: PHARMACOLOGY PPT by Dr. Geraldine Corporaltaco cat100% (1)
- Basic Guide To Anesthesia For Developing CountriesDocument242 pagesBasic Guide To Anesthesia For Developing Countriescltadams100% (4)
- MUGOT - DEMENTIA CONCEPT MAP - Page 3Document1 pageMUGOT - DEMENTIA CONCEPT MAP - Page 3MICHELLIN VAN MUGOTNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors - AGE 55 Yo - Gender - Race/ Ethnicity - HeredityDocument2 pagesPredisposing Factors - AGE 55 Yo - Gender - Race/ Ethnicity - HeredityGHANY mhar ginogaling atihNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Cardiac Arrest: Predisposingfactors Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology Cardiac Arrest: Predisposingfactors Precipitating FactorsAnnisa Mutmainnah ArifuddinNo ratings yet
- Viii. PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesViii. Pathophysiologymacedon145377No ratings yet
- Alzheimers DiseaseDocument11 pagesAlzheimers DiseaseCHRISTIAN RAY ALPAS PASILIAONo ratings yet
- Limos Drug-StudyDocument2 pagesLimos Drug-StudyClaire LimosNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke: The Normal Blood Supply To The Brain Is DisruptedDocument5 pagesIschemic Stroke: The Normal Blood Supply To The Brain Is DisruptedMelchora Lea Castro SorianoNo ratings yet
- Case On Intracranial HemorrhageDocument17 pagesCase On Intracranial HemorrhageLorebell100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Cardiac ArrestDocument1 pagePathophysiology Cardiac ArrestPATHOSHOPPE100% (2)
- Altered Mental StateDocument2 pagesAltered Mental Stateizzati94No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsTiger Knee100% (1)
- Pathophysiology MaiaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Maiajia88No ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY (Schematic Diagram) : - Fever - LeukocytosisDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY (Schematic Diagram) : - Fever - Leukocytosisranee diane100% (1)
- Biochem B Midterm CBL 2020Document16 pagesBiochem B Midterm CBL 2020Lyan SamsonNo ratings yet
- WWW - Natures.Ir: More Free Usmle, Mccee, Mcqe and Amq FlashcardsDocument54 pagesWWW - Natures.Ir: More Free Usmle, Mccee, Mcqe and Amq FlashcardsNixon GoyalNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of CvaDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of CvaAngelica BrilloNo ratings yet
- Osms - It/alzheimers-Disease: Pathology & CausesDocument1 pageOsms - It/alzheimers-Disease: Pathology & Causesdysa ayu shalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Summary Drugs Table - MSK 1 BlockDocument2 pagesSummary Drugs Table - MSK 1 BlockRiley WestwoodNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument2 pagesStrokealambatinjrrNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument7 pagesPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Physiosynthesis of SCLCDocument4 pagesPhysiosynthesis of SCLCkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- DementiaDocument9 pagesDementiaSivabharathi SivanandamNo ratings yet
- Before: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide, P. 407Document2 pagesBefore: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide, P. 407SoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Therapeutics: Eximius 2021Document13 pagesPediatric Therapeutics: Eximius 2021Isabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Stroke PathophysioDocument3 pagesStroke PathophysioKrystele CangaNo ratings yet
- Encephalopathy HepaticumDocument2 pagesEncephalopathy Hepaticumtitis dwi tantiNo ratings yet
- Summary Drugs Table - NEURO BlockDocument6 pagesSummary Drugs Table - NEURO BlockRiley WestwoodNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Acute Non Traumatic WeaknessDocument55 pagesModule 2 - Acute Non Traumatic WeaknessRick RanitNo ratings yet
- Lipid Storage Disorders OverviewDocument1 pageLipid Storage Disorders OverviewprofesorpraveenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1-Ward1Document4 pagesDrug Study 1-Ward1Annaoj Esor DarasNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocument7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Drug Study 4Document9 pagesDrug Study 4bobo gamingNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapkyla.inoferioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyApril Sarol67% (3)
- Assessment & Specific Managements: Alcohol UseDocument34 pagesAssessment & Specific Managements: Alcohol UseChris Jardine LiNo ratings yet
- Case Study - ESRD (DS, NCP)Document8 pagesCase Study - ESRD (DS, NCP)Zhy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Section XIX - Lysosomal Storage Diseases: Disease Deficient Enzyme Accumulated Substrate Findings InheritanceDocument2 pagesSection XIX - Lysosomal Storage Diseases: Disease Deficient Enzyme Accumulated Substrate Findings InheritanceKatharine NervaNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid DsDocument2 pagesValproic Acid DsCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Pheochromocytoma DPDocument1 pagePheochromocytoma DPRosemarie HagnaNo ratings yet
- Pathway Stroke Non Hemoragik EngDocument1 pagePathway Stroke Non Hemoragik EngFitria NorkhalidaNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument2 pagesSubarachnoid Hemorrhagevfsqp9zxgqNo ratings yet
- Dopamine HCLDocument1 pageDopamine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- Approach To Altered Mental StatusDocument19 pagesApproach To Altered Mental StatusMudassar SattarNo ratings yet
- Chapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney DisordersDocument40 pagesChapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney Disordersjericho dinglasanNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Neuromuscular DisorderDocument3 pagesPEDIA Neuromuscular DisorderThakoon TtsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1-25Document52 pagesDrug Study 1-25WemslaiNo ratings yet
- 0304 ConsultantoncallDocument4 pages0304 Consultantoncallnessimmounir1173No ratings yet
- Achondroplasia: Genetic Disorder Dominant/Recessive Malfunctioning Protein General Effects/SymptomsDocument2 pagesAchondroplasia: Genetic Disorder Dominant/Recessive Malfunctioning Protein General Effects/SymptomsMatt FerrariNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Document7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Tiger Knee100% (3)
- NCM 104 (DUTY) - Risperidone Drug StudyDocument1 pageNCM 104 (DUTY) - Risperidone Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Atenolol TenorminDocument3 pagesAtenolol TenorminLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Clinical Autonomic and Mitochondrial Disorders: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment for Mind-Body WellnessFrom EverandClinical Autonomic and Mitochondrial Disorders: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment for Mind-Body WellnessNo ratings yet
- Bangor Biology Unit 1 2018Document69 pagesBangor Biology Unit 1 2018Daishaadil DilNo ratings yet
- Daftar Barang Ecatalog Dan LinkDocument3 pagesDaftar Barang Ecatalog Dan LinkHeni DiesNo ratings yet
- CPRDocument23 pagesCPRsangita patil50% (2)
- Shoulder MuscleDocument52 pagesShoulder Muscleshahirah770% (1)
- Biology Ecology Revision NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Ecology Revision NotesGeorge ArgyrouNo ratings yet
- Biology 30 - Assign 4Document31 pagesBiology 30 - Assign 4maryam nurain apendiNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Cellular Respiration (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument12 pagesRegulation of Cellular Respiration (Article) - Khan Academydeepali_nih9585No ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document35 pagesChapter 18serenaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Sutures: Monofilament MultifilamentDocument17 pagesClassification of Sutures: Monofilament Multifilamentlina_m354No ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Document3 pagesAnimal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Amor Panopio MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Neu 2013 3197Document8 pagesNeu 2013 3197Sri MarniantiNo ratings yet
- HUN 1201 Blue Zones - TM 0920Document9 pagesHUN 1201 Blue Zones - TM 0920tmanareNo ratings yet
- Neuromodulation Industry Report - Medical Alley PDFDocument49 pagesNeuromodulation Industry Report - Medical Alley PDFElizabeth KrusemarkNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With DizzinessDocument5 pagesApproach To The Patient With DizzinessHuda HamoudaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 PDFDocument10 pagesLecture 8 PDFaaa rrNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Human BrainDocument2 pagesAnatomy of Human BrainIan Rhadel RaganasNo ratings yet
- Cell ComponentsDocument2 pagesCell ComponentsJuliana RiveraNo ratings yet
- Tantric Sexual YogaDocument6 pagesTantric Sexual YogaFan Hasiru100% (1)
- 5 Integumentary System PDFDocument3 pages5 Integumentary System PDFKenneth ResideNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument5 pagesMCQAmjad AlmousawiNo ratings yet
- Discharge Summary JAGONOYDocument6 pagesDischarge Summary JAGONOYKirstie de LunaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System DisordersDocument74 pagesEndocrine System DisordersFaith Levi Alecha AlferezNo ratings yet
- Final Notes INT3007Document26 pagesFinal Notes INT3007Nina FischerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lecture 02 - Anatomic Topograhic Regions - HeadDocument94 pagesAnatomy Lecture 02 - Anatomic Topograhic Regions - HeadNikita Prasad100% (1)
- Esophageal Carcinoma A. Anatomy of The EsophagusDocument5 pagesEsophageal Carcinoma A. Anatomy of The EsophagusChiu ChunNo ratings yet
- Larynx Anatomy WriteDocument5 pagesLarynx Anatomy Write060 GAYATHRI BNo ratings yet
- Head (Skull, Scalp, Hair) : Head-To-Toe Assessment (C. Eyebrows, Eyes and Eyelashes)Document15 pagesHead (Skull, Scalp, Hair) : Head-To-Toe Assessment (C. Eyebrows, Eyes and Eyelashes)anne002No ratings yet