Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 Solutions
5 Solutions
Uploaded by
JimenaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5 Solutions
5 Solutions
Uploaded by
JimenaCopyright:
Available Formats
4.
The geological action of water
Water is the main agent that shapes relief on the continents.
Liquid water acts in different ways: rivers, surface runoff or flood waters, streams, torrents and groundwater. There is also the
action of waves that shapes costal relief.
4.1 Fluvial shaping
Rivers are currents of water that flow on a fixed riverbed.
We can distinguish three zones:
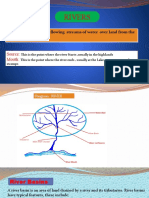
In the upper course: the erosive action makes the riverbed deeper. This is where we find ____ _____________ .
There are many rapids and waterfalls.
In the middle course: meanders are common
In the lower course: sediments are deposited. There are two types of river mouth.
o A delta is body of sediment at the river mouth as the river enters the sea.
o An esturary is where the sea enters the river at the river mouth, with less sediment.
Complete the following box
Upper course: waterfalls Middle course: meanders Lower course: Ebro delta Lower course: Tajo estuary
4.2 Groundwater
Ground water forms part of the water cycle. It comes from infiltration of water from _______, ________ or _______ into the
ground.
Aquifers are layers of rocks or sediments that contain and circulate groundwater.
Complete: Aquifer balance = - = variation of _______________
Overexploitation and contamination are the main risks connected with the exploitation of aquifers.
Explain it:
Overexploitation happens if the volume of water discharged is higher than the amount naturally recharged.As a result, the
quantity of water in the saturated zone decrease an the water table goes down.
Contamination happens when contaminated water can reach aquifers from different sources: agriculture and intensive
livestock farming industry, urban residues or salt water from marine intrusion.
Complete the following diagram and study the diagram.
This is a overexplotation of coastal aquifers.
As the water table goes down, due the increased usage, salt water from the sea infiltrates the aquifer to occupy the space that is
left by the fresh water.
4.3 Karst
Karst is a spectacular landscape formed by the action of surface water and groundwater on rocks such as salt, gypsum-, and
limestone rocks
Karst landscapes are very important in ´Spain due to the abundance of limestone in the east of the peninsula and Balearic Islands.
Complete.
4.4 Shaping from surface runoff and torrents
Surface runoff or flood waters flow without a fixed course. Their action is intense in sub-desert zones where there are sporadic
precipitations. This accelerated soil erosion causes desertification.
Torrents are sporadic bodies of water with a fixed course, where there is a big break in the slope between mountainous area
and a flat area. .
Parts
Water basin: area where rainwater collects.
Drainage channel: narrow course of water that evacuates and sediments.
Alluvial cone: situated at at the foot of the mountainous area where the torrent
loses energy and deposits its sediments.
4.5 Coastal shaping
The geological action of the sea is seen especially on the coast. Here we can see. :
The movements of the sea: waves, currents and tides.
Differential erosion of different types of rock.
Sediments from rivers that the sea extends
Intense human action.
Recent changes in the sea level due to glaciations.
The erosive action of the sea is carried out by waves, particularly waves formed in storms. Erosion is intensified when the direct
action of the waves is combined with abrasion caused by the impact of materials carried in the waves.
Why is not advisable to build on a cliff.
Due to the impact of materials carried in the waves the base of cliffs is undercut. Therefore, the cliffs collapse and recede,
leaving behind a wave-cut platform.
Costal landforms
Like other agents, the sea creates landforms from erosion and deposit.
Erosion landforms:
Deposit landforms:
+ Beaches:marine deposit landforms. Depending on the size of the sediments, there are Sandy beaches, whic are the
most common, and beaches with gravel or pebbles, rounded by the continous movement of the wáter.
+ spits: sand bars when they are joined to the coast on one side
+ tombolo: when they connect an island with the mainland
+ Lagoons:_if they isolate a bay from the open sea
You might also like
- Bottled Mineral Waters PDFDocument4 pagesBottled Mineral Waters PDFsl7789No ratings yet
- Major Landforms of The EarthDocument25 pagesMajor Landforms of The Earthiamfavoured457No ratings yet
- Water Action and River ProcessesDocument2 pagesWater Action and River ProcesseschikwambaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - The Hydrosphere and Water PollutionDocument8 pagesModule 7 - The Hydrosphere and Water Pollutionjuliaroxas100% (1)
- Geo Term-2 Denudation 1Document11 pagesGeo Term-2 Denudation 1Tvisha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- RiversDocument32 pagesRiversmadzivirejayNo ratings yet
- Transport and Deposition of Sediments: N. Madhavan 942 872 9914Document39 pagesTransport and Deposition of Sediments: N. Madhavan 942 872 9914dkbunhaNo ratings yet
- DAN Inland EstuarineDocument28 pagesDAN Inland EstuarinejoshigautaNo ratings yet
- Ground Water and HydrologyDocument11 pagesGround Water and Hydrologyammigalla swethaNo ratings yet
- Earth'S Water: - Started As A Combination of Gasses Which Were Carried by Meteor That Collided WithDocument5 pagesEarth'S Water: - Started As A Combination of Gasses Which Were Carried by Meteor That Collided WithEim NellaNo ratings yet
- Hydrosphere - Course NotesDocument21 pagesHydrosphere - Course NotesChandrasekar ChandruNo ratings yet
- Estuarine EcologyDocument96 pagesEstuarine EcologyNayeema Ferdausy Hoque100% (1)
- Flood Plains 2Document13 pagesFlood Plains 2amosadjartey42No ratings yet
- Rivers (Drainage Basin and Hydrological Cycle)Document9 pagesRivers (Drainage Basin and Hydrological Cycle)zoeNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument2 pagesWater ResourcesGonzales, Erica Jeallean C.No ratings yet
- Sedimentary EnvironmentsDocument21 pagesSedimentary EnvironmentsAmr AesNo ratings yet
- Unit-I-Physical Geology Action of Running Water Why Study Running Water?Document25 pagesUnit-I-Physical Geology Action of Running Water Why Study Running Water?Rubel RanaNo ratings yet
- Erosion and Deposition Action of Running Water and GroundwaterDocument12 pagesErosion and Deposition Action of Running Water and GroundwaterDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument8 pagesHydrologyBhanu Prakash100% (2)
- Quiz 2 GeologyDocument5 pagesQuiz 2 Geologyhaha xdNo ratings yet
- Rivers Year SixDocument16 pagesRivers Year Sixhussain korirNo ratings yet
- 2 2riversDocument12 pages2 2riversLK chanellNo ratings yet
- Terminology For The Study of RiversDocument7 pagesTerminology For The Study of Riversrishipatel96No ratings yet
- Marine Ecosystems Estuary and Coastal WetlandsDocument20 pagesMarine Ecosystems Estuary and Coastal WetlandsTime NextNo ratings yet
- CSEC GeographyDocument11 pagesCSEC GeographyJadynn Sookhan-DassNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Ecosystem: I. LakesDocument6 pagesAquatic Ecosystem: I. LakesJohn Paul Espiña CandoNo ratings yet
- Geography RiverDocument6 pagesGeography RiverTik TokNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledBB KivinesNo ratings yet
- River and CoastDocument153 pagesRiver and CoastDhiya DassaniNo ratings yet
- Group PresentationDocument32 pagesGroup PresentationJulimar CabayaNo ratings yet
- 11 Geography Notes 07 Landforms and Their EvolutionDocument12 pages11 Geography Notes 07 Landforms and Their EvolutionPrateek Sharma50% (2)
- Pot Hydro Assignment 4 FinishedDocument5 pagesPot Hydro Assignment 4 FinishedMAP BNSNo ratings yet
- Geography NotesDocument7 pagesGeography NotesVenus MitchellNo ratings yet
- GroundwaterDocument7 pagesGroundwaterJJG ABVNo ratings yet
- River Processes - Erosion, Transport, DepositionDocument8 pagesRiver Processes - Erosion, Transport, DepositionF A L L E NNo ratings yet
- Geography Exam NotesDocument10 pagesGeography Exam Noteslajoneee :pNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document46 pagesCH 5Bersisa TolaNo ratings yet
- RiversDocument16 pagesRiversrihanna.chicotNo ratings yet
- Geography-River Landscapes and Processes: Water CycleDocument22 pagesGeography-River Landscapes and Processes: Water CycleJack LinsteadNo ratings yet
- Aquatic EnvironmentDocument32 pagesAquatic EnvironmentChhavi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Pot Hydro Assignment 4 FinishedDocument6 pagesPot Hydro Assignment 4 FinishedMAP BNSNo ratings yet
- Rivers Year SixDocument13 pagesRivers Year Sixhussain korirNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. Schematic of EstuaryDocument7 pagesFigure 1. Schematic of EstuaryasyhanggrainiNo ratings yet
- River Engineering Chapter-IDocument30 pagesRiver Engineering Chapter-ITigst Tigst YzachewNo ratings yet
- Sea Level Changes or EustatismDocument6 pagesSea Level Changes or Eustatismkalule elvisNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Landforms and Their Evolution 13Document16 pagesChap 5 Landforms and Their Evolution 13abhaykumarkans054No ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Ater CeansDocument9 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Ater Ceansurs4everrrNo ratings yet
- Streams and Floods: The Geology of Running WaterDocument8 pagesStreams and Floods: The Geology of Running WaterSerena KnightNo ratings yet
- Oceanic Crust Continental Shelf Continental Slope Continental Rise Tectonics Sea Level Rivers Energy Waves CurrentsDocument6 pagesOceanic Crust Continental Shelf Continental Slope Continental Rise Tectonics Sea Level Rivers Energy Waves CurrentsYadah AlindayoNo ratings yet
- Running Water)Document8 pagesRunning Water)Kayraine Mae Edillor CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Keybook Geography Sun Seven (t3)Document34 pagesKeybook Geography Sun Seven (t3)Abdus SaeedNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 GMDocument22 pagesUnit - 5 GMa80143200No ratings yet
- Geography Chapter No - 3Document14 pagesGeography Chapter No - 3ANJALI RAWATNo ratings yet
- A Levee Is A Raised Riverbed Found Alongside A River in ItDocument3 pagesA Levee Is A Raised Riverbed Found Alongside A River in Itderaw11557No ratings yet
- MathScieTech Report ModuleDocument3 pagesMathScieTech Report ModuleClarisse Allyza CabasanNo ratings yet
- Students Hydrosphere2Document54 pagesStudents Hydrosphere2Nikola MarinovNo ratings yet
- Delta and EstuariesDocument21 pagesDelta and Estuariesjawad100% (2)
- L - 5 - River - CEE 551 - GMMDocument19 pagesL - 5 - River - CEE 551 - GMMudayNo ratings yet
- Aquifers and Groundwater Movemen1Document8 pagesAquifers and Groundwater Movemen1patmarys247No ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesLokesh OriginalsNo ratings yet
- Design of Portable Hybrid Constructed Wetland Reactor For The Treatment of WastewaterDocument8 pagesDesign of Portable Hybrid Constructed Wetland Reactor For The Treatment of WastewaterIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Slum Case Study: - Vidyadhar Nagar Sector 4Document10 pagesSlum Case Study: - Vidyadhar Nagar Sector 4Mallika SinghNo ratings yet
- Electricity Bill FebDocument24 pagesElectricity Bill FebJayanath Nuwan SameeraNo ratings yet
- Naic Water Supply Corporation Deep Well: Financial RequirementsDocument2 pagesNaic Water Supply Corporation Deep Well: Financial RequirementsSarahNo ratings yet
- State of The Art Hydrological Models and Application of The HEC HMS Model: A ReviewDocument23 pagesState of The Art Hydrological Models and Application of The HEC HMS Model: A ReviewThiago GomesNo ratings yet
- Penawaran Pak YokoDocument1 pagePenawaran Pak YokoBudhi HartantyoNo ratings yet
- Book Depurazione LHesDocument63 pagesBook Depurazione LHesنيرمين احمدNo ratings yet
- Environmental Problems in AlicanteDocument12 pagesEnvironmental Problems in Alicantealebro2No ratings yet
- Tanzania Water Supply Design Manual 2020Document331 pagesTanzania Water Supply Design Manual 2020Benson MahengeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument14 pagesChemistry ProjectRELAXATION MUSICNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 5 - Q2 - W8Document8 pagesDLL - Science 5 - Q2 - W8Garneth OrantoyNo ratings yet
- MR - Arun-Lakhani Projects ShowcaseDocument5 pagesMR - Arun-Lakhani Projects ShowcaseArun LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Development Oman: P.O. Box: 81, Muscat Postal Code: 118 Sultanate of OmanDocument51 pagesPetroleum Development Oman: P.O. Box: 81, Muscat Postal Code: 118 Sultanate of OmanJose Angelo JunioNo ratings yet
- Physico-Chemical and Microbiological Analysis of Borehole Water Sources in E-One Estate Lemna, Calabar, Cross River State, NigeriaDocument6 pagesPhysico-Chemical and Microbiological Analysis of Borehole Water Sources in E-One Estate Lemna, Calabar, Cross River State, NigeriaVelumani sNo ratings yet
- Civil HydrologyDocument17 pagesCivil Hydrologysachin guptaNo ratings yet
- LAB: Environmental Engineering Experiment: Biochemical Oxygen Demand (Bod) 5.0 Result and CalculationDocument3 pagesLAB: Environmental Engineering Experiment: Biochemical Oxygen Demand (Bod) 5.0 Result and CalculationNadhirah LilyNo ratings yet
- 6 DONE What Is Water PollutionDocument3 pages6 DONE What Is Water PollutionSumaiya ImamNo ratings yet
- Kigali Centralised Sewage SystemDocument3 pagesKigali Centralised Sewage SystemGloria KAMWEZINo ratings yet
- CH-9 Public FacilityDocument1 pageCH-9 Public FacilityRG GamingNo ratings yet
- Figs. 1Document7 pagesFigs. 1abhay deep ashish kujurNo ratings yet
- Civ CH 9Document16 pagesCiv CH 9Sayan SinhaNo ratings yet
- Economy of Kanpur: Master PlanDocument1 pageEconomy of Kanpur: Master PlanPooja Aradhana PradhanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Further 04: PhoneticsDocument5 pagesAnswer Key: Further 04: PhoneticsAbby NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Vol 05.Baras-SBDocument11 pagesVol 05.Baras-SBMark MartinezNo ratings yet
- GREAT Workshop ReportDocument45 pagesGREAT Workshop ReportRoy Perez SalazarNo ratings yet
- Cooks Beach Project 2007-2022 - SummaryDocument1 pageCooks Beach Project 2007-2022 - Summaryapi-355774141No ratings yet
- Water Resources of Pakistan An AnalysisDocument4 pagesWater Resources of Pakistan An Analysisayyanfarhan656No ratings yet
- Hydrologic Losses: Infiltration, Evaporation and TranspirationDocument45 pagesHydrologic Losses: Infiltration, Evaporation and TranspirationdigdoNo ratings yet
- Penelitian Penggunaan Eceng Gondok Dan Teratai Untuk IrigasiDocument12 pagesPenelitian Penggunaan Eceng Gondok Dan Teratai Untuk Irigasiaryadi_18No ratings yet