Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing CS Acute-Kidney-Injury 04
Nursing CS Acute-Kidney-Injury 04
Uploaded by
Mahdia akterOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing CS Acute-Kidney-Injury 04
Nursing CS Acute-Kidney-Injury 04
Uploaded by
Mahdia akterCopyright:
Available Formats
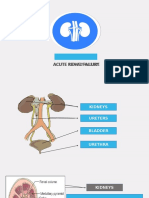
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI):
Characteristics
• Sudden trauma to the body can cause a build-up of waste
products in the blood and fluid imbalances in the body,
leading to AKI.
• AKI is usually reversible.
• Without prompt treatment, AKI can lead to chronic kidney
disease (CKD) or renal failure. Healty kidney Injured kidney
• AKI is a sudden instance of kidney failure or kidney damage. appearance appearance
Signs and Symptoms Risk Factors Assessment
• Peripheral edema • Injury • Monitoring for changes in vital signs,
(swelling all over the body) • Burns
intake and output, mood, edema,
and blood loss
• Fatigue or tiredness • Dehydration
• Observing the patient‘s mental state
• Confusion • Hemorrhage (blood loss)
• Obtaining labs regarding kidney
• Shortness of breath • Sepsis function, e.g. creatinine, glomerular
• Nausea • Surgery filtration rate (GFR) and overall health,
• Chest pain or pressure e.g. a complete blood count (CBC)
• Pregnancy
Acute Kidney Injury
Criteria
Rise in serum creatinine Reduction in urine output NURSING NOTE:
The
expected range
• > 0.3 mg/dL increase • < 0.5 mL/kg/h for more
for creatinine is
or than 6 hours
0.5–1.1 mg/dL.
• > 50% increase
• Restore fluid balance
Nursing Interventions for • Prevent infection
Clients with AKI Include • Improve nutritional intake
NOTES
www.lecturio.com/nursing Watch Video
You might also like
- 2023 Psgs Guidelines For Accreditation of Residency Training ProgramDocument121 pages2023 Psgs Guidelines For Accreditation of Residency Training ProgramJobelle0% (1)
- 12a Diabetic Emergencies DKA Case StudiesDocument13 pages12a Diabetic Emergencies DKA Case StudiesAnonymous yTdBi7100% (1)
- An Overview Of: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki: Hasan BasriDocument22 pagesAn Overview Of: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki: Hasan BasriDz PutraNo ratings yet
- Clinical Therapeutics Oral Revalida Review Notes: CASE 1: Dr. Abraham Daniel C. CruzDocument31 pagesClinical Therapeutics Oral Revalida Review Notes: CASE 1: Dr. Abraham Daniel C. CruzNoreenNo ratings yet
- AKI Vs CKD Lecture Latest 3rd Dec 2018Document51 pagesAKI Vs CKD Lecture Latest 3rd Dec 2018mugilessNo ratings yet
- 15-Acute Kidney InjuryDocument18 pages15-Acute Kidney Injuryمصطفى محمد جواد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury DR Moses KazevuDocument52 pagesAcute Kidney Injury DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Kidney FunctionDocument29 pagesEvaluation of Kidney FunctionAoiNo ratings yet
- Renal Function Tests: Dr. Arisha Sohail Dep. of Biochemistry DimcDocument28 pagesRenal Function Tests: Dr. Arisha Sohail Dep. of Biochemistry DimcArisha SohailNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury:: A Brief OutlineDocument48 pagesAcute Kidney Injury:: A Brief OutlinehanaNo ratings yet
- Kidney Injury Report by ZK MendozaDocument39 pagesKidney Injury Report by ZK MendozaZillah Korren MendozaNo ratings yet
- Report 5-8 in ProviDocument5 pagesReport 5-8 in ProviWilson AgustinNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Urinary SystemDocument47 pagesAn Introduction To The Urinary Systemسمير هزاعNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease in ChildrenDocument29 pagesChronic Kidney Disease in ChildrenAlvin OmondiNo ratings yet
- AKI MBCHB VDocument64 pagesAKI MBCHB VSsenyonga DominicNo ratings yet
- Gagal Ginjal Akut & Gagal Ginjal KronikDocument63 pagesGagal Ginjal Akut & Gagal Ginjal KronikSuf YusufNo ratings yet
- DKA NICE GuidelinesDocument6 pagesDKA NICE GuidelinestheonlinegeekhubNo ratings yet
- AKIDocument23 pagesAKInadddNo ratings yet
- Renal Skills LabDocument77 pagesRenal Skills LabDacillo GailleNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With Acute Kidney InjuryDocument70 pagesApproach To A Patient With Acute Kidney InjuryShivamNo ratings yet
- Aki App ContentDocument6 pagesAki App ContentmimoNo ratings yet
- Normal SCR 0.5 - 1 MG/DL: TopicDocument3 pagesNormal SCR 0.5 - 1 MG/DL: TopicLNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Understanding Progression and Clinical ConsequencesDocument30 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Understanding Progression and Clinical ConsequencesTry Wahyudi Jeremi LoLyNo ratings yet
- What Is: Acute Renal Failure Acute Kidney InjuryDocument32 pagesWhat Is: Acute Renal Failure Acute Kidney InjuryCiedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- 8 - Chronic Kidney Disease Clinical Pathway - Final - Nov.20.2014Document56 pages8 - Chronic Kidney Disease Clinical Pathway - Final - Nov.20.2014As RifahNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Dari: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki) : Dr. Hasan BasriDocument22 pagesGambaran Dari: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki) : Dr. Hasan BasriLiana Ika SuwandyNo ratings yet
- Renal MNTDocument58 pagesRenal MNTMARIA TARIQNo ratings yet
- Sheffield Hospital Surgical Care Guidelines For AKIDocument53 pagesSheffield Hospital Surgical Care Guidelines For AKIWael N Sh GadallaNo ratings yet
- Aki PregnancyDocument35 pagesAki PregnancyAhmed Ra'fatNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury (AkiDocument23 pagesAcute Kidney Injury (AkiHyunna 15No ratings yet
- Kidney Emergency: M. Syamsul BakhriDocument30 pagesKidney Emergency: M. Syamsul BakhrierahadeNo ratings yet
- DRUGs FOR KIDNEYDocument33 pagesDRUGs FOR KIDNEYaNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument45 pagesAcute Kidney Injuryajusdabo95No ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Case Presentation GRP 3Document60 pagesAcute Renal Failure Case Presentation GRP 3varish100% (1)
- Care of The Patient With Renal and Urinary Disorders - HandoutDocument52 pagesCare of The Patient With Renal and Urinary Disorders - HandoutAaron Ramirez LuNo ratings yet
- FLG 332 Renal - 3 (2023)Document19 pagesFLG 332 Renal - 3 (2023)c6d5hggz6dNo ratings yet
- Blood Urea Blood Creatinine Creatinine Clearance Uric Acid: Laboratory TrainingDocument44 pagesBlood Urea Blood Creatinine Creatinine Clearance Uric Acid: Laboratory Trainingعلي عبيد العتابيNo ratings yet
- 17-Acute Kidney InjuryDocument38 pages17-Acute Kidney InjuryChamindraNo ratings yet
- PolyuriaDocument49 pagesPolyuriasky rainNo ratings yet
- AKI Developing Critical Thinking Through Understanding Pathophysiology-1-6Document5 pagesAKI Developing Critical Thinking Through Understanding Pathophysiology-1-6Anonymous StudentNo ratings yet
- المحاطرة الاولة كيمياء سريريةDocument35 pagesالمحاطرة الاولة كيمياء سريريةMohamedErrmaliNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury Etd Nov-Dec HPSF Sem 6 2022Document22 pagesAcute Kidney Injury Etd Nov-Dec HPSF Sem 6 2022Harry James Potter James PotterNo ratings yet
- How To Bring Down High Creatinine LevelsDocument30 pagesHow To Bring Down High Creatinine Levelskavitha_vk76No ratings yet
- Diabetes Related CKD 2Document1 pageDiabetes Related CKD 2Jia-PeiWuNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Assignment (Kidney Function Test) - 3Document26 pagesBiochemistry Assignment (Kidney Function Test) - 3deerecover715No ratings yet
- Surgery Acute Kidney Injury 10-06-21Document49 pagesSurgery Acute Kidney Injury 10-06-21Muhammad ArsalNo ratings yet
- Surgery Acute Kidney Injury 10-06-21Document49 pagesSurgery Acute Kidney Injury 10-06-21Muhammad ArsalNo ratings yet
- Renal IiDocument24 pagesRenal Iijacobcw2003No ratings yet
- GFRDocument28 pagesGFRStar CruiseNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument27 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseRegina EstherNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument16 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryPutrii Rahayu Sriikandi100% (1)
- AKIDocument22 pagesAKISatyabrata SinghNo ratings yet
- Penampilan Minggu 3Document130 pagesPenampilan Minggu 3riski anugrahNo ratings yet
- Kidney and Liver FunctionDocument6 pagesKidney and Liver FunctionAhmad Ripani Musyaffa AhdanLabNo ratings yet
- Canine Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Diagnostic Tree /ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument3 pagesCanine Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Diagnostic Tree /ENDOCRINOLOGYPetrisor GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- Diet Penyakit Ginjal Dan Saluran KemihDocument73 pagesDiet Penyakit Ginjal Dan Saluran KemihNurul AlfatarisyaNo ratings yet
- Renal Nutrition (For Non-Renal Dietitians)Document41 pagesRenal Nutrition (For Non-Renal Dietitians)Vaidehi UlaganathanNo ratings yet
- Creatinine Clearance Test-1Document17 pagesCreatinine Clearance Test-1wanderer_1010No ratings yet
- The Perfect Insulin Resistance Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Losing Weight, Reversing Insulin Resistant And And Preventing Pre-Diabetes With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Insulin Resistance Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Losing Weight, Reversing Insulin Resistant And And Preventing Pre-Diabetes With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia, (High Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypercalcemia, (High Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics PharmacologyDocument10 pagesAntibiotics PharmacologyMahdia akterNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Angina PectorisDocument1 pageNursing CS Angina PectorisMahdia akterNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Abnormal Lung SoundsDocument1 pageNursing CS Abnormal Lung SoundsMahdia akterNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Angina-Pectoris-medications 03Document1 pageNursing CS Angina-Pectoris-medications 03Mahdia akterNo ratings yet
- NS 302 AnatomyDocument8 pagesNS 302 AnatomydhonaNo ratings yet
- Lung Ultrasound For Critically Ill Patients - Mojoli F, Bouhemad B, Mongodi S, Lichtenstein D. (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019)Document53 pagesLung Ultrasound For Critically Ill Patients - Mojoli F, Bouhemad B, Mongodi S, Lichtenstein D. (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019)Mr. IncognitoNo ratings yet
- Kennesaw State DissertationDocument6 pagesKennesaw State DissertationOnlinePaperWriterFargo100% (1)
- Pain Assessment & MGTDocument16 pagesPain Assessment & MGTSitti Mardiya SariolNo ratings yet
- Roles and Responsibilities of A Guidance CounselorDocument5 pagesRoles and Responsibilities of A Guidance CounselorDan NavarroNo ratings yet
- Mass Media and Pulse Polio Awareness CamDocument7 pagesMass Media and Pulse Polio Awareness CamRajeev RaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Activities AssessmentDocument6 pagesChapter 7 Activities AssessmentKYLE GOMEZNo ratings yet
- HRM610 Final SlideDocument19 pagesHRM610 Final SlideArju LubnaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. IdentificationDocument12 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1. Identificationraja duraiNo ratings yet
- Competency-Based Curriculum A. Course Design: TESDA-OP-CO-01-F11Document44 pagesCompetency-Based Curriculum A. Course Design: TESDA-OP-CO-01-F11RYDENNo ratings yet
- AlprazolamDocument3 pagesAlprazolamapi-3797941100% (1)
- Qualification Handbook v1-1Document92 pagesQualification Handbook v1-1rafael espinosa semperNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard AnalysisDocument9 pagesJob Hazard AnalysisMohammad HadoumiNo ratings yet
- Internet Addiction TG UpdatedDocument12 pagesInternet Addiction TG UpdatedLamberto Pilatan Jr.No ratings yet
- Research Essay 1Document10 pagesResearch Essay 1api-582788002No ratings yet
- Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development: By: Sean Sanko T/TH 11:00-12:15Document15 pagesErikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development: By: Sean Sanko T/TH 11:00-12:15sivakumarNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Self Experienced and Perceived HIV AIDS Stigma Using Parallel Scales in Chennai IndiaDocument11 pagesMeasurement of Self Experienced and Perceived HIV AIDS Stigma Using Parallel Scales in Chennai IndiaAshik RahamanNo ratings yet
- The Politics of Depression: Diverging Trends in Internalizing Symptoms Among US Adolescents by Political BeliefsDocument25 pagesThe Politics of Depression: Diverging Trends in Internalizing Symptoms Among US Adolescents by Political BeliefsJuan PeNo ratings yet
- K. Sesha Kumar - WNC 2021Document34 pagesK. Sesha Kumar - WNC 2021K Sesha KumarNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Unworthy of Your Love A Dark Stalker Forbidden Romance Sasha RC Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pages(Download PDF) Unworthy of Your Love A Dark Stalker Forbidden Romance Sasha RC Full Chapter PDFmamosailiw4100% (9)
- Growth Prediction IiDocument29 pagesGrowth Prediction IiSurabhi SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Medi 99 E20541Document3 pagesMedi 99 E20541wlNo ratings yet
- Guardian Brand Book - 042019Document15 pagesGuardian Brand Book - 042019FTU.CS2 Nguyễn Việt HưngNo ratings yet
- Target 2021 Government Schemes I WWW - Iasparliament.com2Document264 pagesTarget 2021 Government Schemes I WWW - Iasparliament.com2Himanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- COVID and The Great Reset - Is The Motive An Imminent Cataclysm?Document9 pagesCOVID and The Great Reset - Is The Motive An Imminent Cataclysm?CK_2023No ratings yet
- Step 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) : Sample Test QuestionsDocument55 pagesStep 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) : Sample Test QuestionsAlfredo JaureguiNo ratings yet
- Latest Additions - Books June, 2018: SL - No Sub Code Author Title Ed Year 1Document1 pageLatest Additions - Books June, 2018: SL - No Sub Code Author Title Ed Year 1pavans25No ratings yet
- How Well Conventional Therapy and Mirror Therapy Work For StrokeDocument4 pagesHow Well Conventional Therapy and Mirror Therapy Work For Strokeh4henryNo ratings yet
- Scherer, A. K., 2016. Bioarchaeology and The Skeletons of Pre-Columbian MayaDocument53 pagesScherer, A. K., 2016. Bioarchaeology and The Skeletons of Pre-Columbian MayaĐani NovakovićNo ratings yet