Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chole Reporting
Chole Reporting
Uploaded by
MarcieOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chole Reporting
Chole Reporting
Uploaded by
MarcieCopyright:
Available Formats
Your body needs healthy fats for energy and other THIASIS
functions. But too much saturated fat can cause Occurs when gallbladder doesn't empty correctly. If
cholesterol to build up in your arteries (blood your gallbladder doesn't empty completely or often
vessels). enough, bile may become very concentrated,
contributing to the formation of gallstones.
CHOLECYSTITIS Your bile contains too much cholesterol. Normally,
Overview of the Existing Health Problem your bile contains enough chemicals to dissolve the
Cholecystitis (is a redness and swelling cholesterol excreted by your liver. But if your liver
(inflammation)of the gallbladder. excretes more cholesterol than your bile can
It happens when a digestive juice called bile gets dissolve, the excess cholesterol may form into
trapped in your gallbladder. crystals and eventually into stones
Cholecystitis, or gallbladder inflammation, occurs Signs & Symptoms
when bile can’t circulate out of the gallbladder as it severe and sudden pain in the upper right part of
normally does. the abdomen
When bile builds up, it causes the gallbladder to Pain that spreads to your right shoulder or back
thicken, harden, swell, and become irritated. may last for 30 mins to 1 hr
When your gallbladder is inflamed and swollen, it
When gallstones block this tube, bile builds up in irritates your phrenic nerve. Your phrenic nerve
your gallbladder. This causes irritation and pressure stretches from the abdomen, through the chest, and
in the gallbladder. It can cause swelling and into your neck. Each time you eat a fatty meal, it
infection. aggravates the nerve and causes referred pain in
your right shoulder blade.
CHOLELITHIASIS
Cholelithiasis or gallstones are hardened deposits of Pain after eating a meal
digestive fluid that can form in your gallbladder The gallbladder may hurt after eating because the
body secretes more bile after large or high fat
Gallstones are usually made up of cholesterol or meals. Bile works to break down fats we eat so the
bilirubin that collect at the bottom of your body can absorb them. When fats are ingested, the
gallbladder until they harden into “stones.” gallbladder contracts significantly in response, and
combined with blocked ducts, this pressure can
cause pain.
Etiology/Causes CYTS
The gallbladder stores bile. Gallstones are formed in An abdomen that’s tender to the touch
your gallbladder. They are made from bile. Biliary colic is defined as pain in the abdomen,
due to obstruction usually by stones in the cystic
Cholecystitis happens when a digestive juice called duct or common bile duct of the biliary tree. It
bile gets trapped in your gallbladder. typically occurs after eating a large, fatty meal that
causes contraction of the gallbladder.
In most cases, this happens because lumps of solid Nausea
material (gallstones) are blocking a tube that drains Vomiting
bile from the gallbladder. Fever
Due to inflammation
When gallstones block this tube, bile builds up in
your gallbladder. This causes irritation and pressure 4 f’s
in the gallbladder. It can cause swelling and The incidence of gallstones had been thought to be
infection. more common in Females over Forty as they were
reaching perimenopause. Women who were
Bacterial infection in the bile duct system. The bile Fertile, meaning that they had one or more
duct system is the drainage system that carries bile children, were thought to be at higher risk due to
from your liver and gallbladder into the first part of higher estrogen levels and the association of
your small intestine (the duodenum). gallstones with pregnancy. Fat was included
because being “overweight” or “obese” was linked
Cholecystitis most frequently occurs when to increased levels of cholesterol that could cause
gallstones (stones that form within the bile coming gallstones.
down from the liver) block the tube leading out of
the gallbladder. This results in a build-up of bile, Anatomy and Physiology
which causes inflammation.
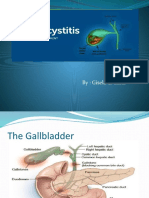
gallbladder is a pear-shaped, hollow structure
located under the liver and on the right side of the
abdomen
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped hollow
organ. It is approximately an inch wide and 3 inches
long,1 and is tapered at one end where it connects to
the cystic duct. It can store approximately 30 to 50 Cholesterol stones are usually yellow-green in color
cubic centimeters (cc) of bile.q and are made of mostly hardened cholesterol. In
The gallbladder's main function is to store bile, a some countries, cholesterol stones make up about
fluid that helps with digestion 75 percent of gallstones.
The gallbladder is a small organ that holds bile from Pigment stones are dark in color and are made of
the liver and releases it into the small intestine to bilirubin. Some people have a mix of both kinds of
help with digestion. stones. Made of a yellowish pigment called
bilirubin
Pathophysiology
Laboratory Study or Confirmatory tests
Predisposing factors:
40y/o and older Complete blood count: A high white blood cell
Female count may indicate an infection. High levels of
Diabetes meilltus bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and serum
aminotransferase may also help the doctor make a
Precipitating factors” diagnosis
Diet: CT scans or ultrasound: Images of the gallbladder
Increased cholesterol intake may reveal signs of cholecystitis.
Calculous cholecystitis Surgical Management
Calculous cholecystitis is the most common, and
usually less serious, type of acute cholecystitis. It A cholecystectomy is surgery to remove your
accounts for around 95% of all cases. gallbladder.
Calculous cholecystitis develops when the main There are 2 types of surgery to remove the
opening to the gallbladder, the cystic duct, gets gallbladder:
blocked by a gallstone or a substance known as
biliary sludge. Open (traditional) method. In this method, 1 cut
(incision) about 4 to 6 inches long is made in the
Biliary sludge is a mixture of bile, a liquid produced upper right-hand side of your belly. The surgeon
by the liver that helps digest fats, and small finds the gallbladder and takes it out through the
cholesterol and salt crystals. incision.
The blockage in the cystic duct causes bile to build Laparoscopic method. This method uses 3 to 4 very
up in the gallbladder, increasing the pressure inside small incisions. It uses a long, thin tube called a
it and causing it to become inflamed. An inflamed laparoscope. The tube has a tiny video camera and
gallbladder can sometimes become infected by surgical tools. The tube, camera and tools are put in
bacteria. through the incisions. The surgeon does the surgery
while looking at a TV monitor. The gallbladder is
Acalculous cholecystitis removed through 1 of the incisions.
Acalculous cholecystitis is gallbladder
inflammation without gallstones. It's less common,
but usually more serious, than calculous Nursing Management
cholecystitis. - Assess vital signs
-Provide adequate nutrition by Assessing nutritional
The exact cause of acalculous cholecystitis is not status. Encourage a low salt low fat diet
known, but it's usually a complication of a serious -Observe and document location, severity (0-10
illness, infection or injury that damages the scale), and character of pain.
gallbladder. - Relieve pain and promote rest.
- Activity. Promote bedrest, allowing the patient to
A combination of risk factors may lead to assume a position of comfort.
acalculous cholecystitis, including accidental - Administer IV fluids, monitor intake and output
damage to the gallbladder during major surgery,
serious injuries
or burns, sepsis,severe malnutrition or dehydration. Drug Study
Cholesterol gallstones: This most common type of CHOLELITHIASIS
gallstone often appears yellow in color and is
composed mainly of undissolved cholesterol. Cholelithiasis or gallstones are hardened deposits of
digestive fluid that can form in your gallbladder
Pigment gallstones: These dark brown or black
stones form when bile contains too much bilirubin Gallstones are usually made up of cholesterol or
(a brownish yellow substance produced when the bilirubin that collect at the bottom of your
liver breaks down red blood cells). gallbladder until they harden into “stones.”
Cholesterol gallstones: This most common type of The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped hollow
gallstone often appears yellow in color and is organ. It is approximately an inch wide and 3 inches
composed mainly of undissolved cholesterol. long,1 and is tapered at one end where it connects to
the cystic duct.
Pigment gallstones: These dark brown or black
stones form when bile contains too much bilirubin It can store approximately 30 to 50 cubic
(a brownish yellow substance produced when the centimeters (cc) of bile.
liver breaks down red blood cells).
The gallbladder's main function is to store bile, a
Cholesterol stones are usually yellow-green in color fluid that helps with digestion
and are made of mostly hardened cholesterol. In
some countries, cholesterol stones make up about
75 percent of gallstones. Pathophysiology
Pigment stones are dark in color and are made of
bilirubin. Some people have a mix of both kinds of Calculous cholecystitis
stones. Made of a yellowish pigment called Calculous cholecystitis is the most common, and
bilirubin usually less serious, type of acute cholecystitis. It
accounts for around 95% of all cases.
Etiology/Causes Calculous cholecystitis develops when the main
opening to the gallbladder, the cystic duct, gets
Occurs when gallbladder doesn't empty correctly. If blocked by a gallstone or a substance known as
your gallbladder doesn't empty completely or often biliary sludge.
enough, bile may become very concentrated,
contributing to the formation of gallstones. Biliary sludge is a mixture of bile, a liquid produced
by the liver that helps digest fats, and small
Your bile contains too much cholesterol. Normally, cholesterol and salt crystals.
your bile contains enough chemicals to dissolve the
cholesterol excreted by your liver. But if your liver The blockage in the cystic duct causes bile to build
excretes more cholesterol than your bile can up in the gallbladder, increasing the pressure inside
dissolve, the excess cholesterol may form into it and causing it to become inflamed. An inflamed
crystals and eventually into stones gallbladder can sometimes become infected by
bacteria.
Types of gallstones Types of gallstones that can Acalculous cholecystitis
form in the gallbladder include: Cholesterol Acalculous cholecystitis is gallbladder
gallstones. The most common type of gallstone, inflammation without gallstones. It's less common,
called a cholesterol gallstone, often appears yellow but usually more serious, than calculous
in color. These gallstones are composed mainly of cholecystitis.
undissolved cholesterol, but may contain other
components. Pigment gallstones. These dark brown The exact cause of acalculous cholecystitis is not
or black stones form when your bile contains too known, but it's usually a complication of a serious
much bilirubin illness, infection or injury that damages the
gallbladder.
Signs & Symptoms
Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the upper A combination of risk factors may lead to
right portion of your abdomen acalculous cholecystitis, including accidental
damage to the gallbladder during major surgery,
Sudden and rapidly intensifying pain in the center serious injuries
of your abdomen, just below your breastbone or burns, sepsis,severe malnutrition or dehydration.
Back pain between your shoulder blades
Laboratory Study or Confirmatory tests
Pain in your right shoulder Complete blood count: A high white blood cell
count may indicate an infection. High levels of
Nausea or vomiting bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and serum
aminotransferase may also help the doctor make a
yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes diagnosis. However, these markers may notTrusted
(jaundice) Source be present in the chronic version.
Anatomy and Physiology CT scans or ultrasound: Images of the gallbladder
may reveal signs of cholecystitis.
gallbladder is a pear-shaped, hollow structure
located under the liver and on the right side of the Surgical Management
abdomen A cholecystectomy is surgery to remove your
gallbladder.
age; female--sex; fertile--fertility; fat--obesity) still
There are 2 types of surgery to remove the remains the basic canon among risk factors that
gallbladder: determine the development of cholecystolithiasis.
Open (traditional) method. In this method, 1 cut
(incision) about 4 to 6 inches long is made in the
upper right-hand side of your belly. The surgeon
finds the gallbladder and takes it out through the
incision.
Laparoscopic method. This method uses 3 to 4 very
small incisions. It uses a long, thin tube called a
laparoscope. The tube has a tiny video camera and
surgical tools. The tube, camera and tools are put in
through the incisions. The surgeon does the surgery
while looking at a TV monitor. The gallbladder is
removed through 1 of the incisions.
Which is better laparoscopy or open surgery for
gallbladder?
According to reports, a laparoscopic approach
generally causes less blood loss, less trauma, and
provides a faster recovery with reduced
hospitalization as compared to open surgery.
However, laparoscopic does require general
anesthesia, and it costs more than open surgery.
Nursing Management
Low salt low fat diet
Avoid fatty foods
Assess general condition of the patient
Closely monitor vital signgs
Provide a comfortable and restful environment.
Keep the patient on bed rest and assist in a position
of comfort such as low-Fowler’s, knee-to-chest, or
side-lying position.
Administer prescribed medications
Assess vital signs
-Provide adequate nutrition by Assessing nutritional
status. Encourage a low salt low fat diet
-Observe and document location, severity (0-10
scale), and character of pain.
- Relieve pain and promote rest.
- Activity. Promote bedrest, allowing the patient to
assume a position of comfort.
- Administer IV fluids, monitor intake and output
Your liver produces bile, which is mostly made of
cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin. Your
gallbladder stores the bile until it’s needed. When
you eat, your body signals your gallbladder to
empty bile into your duodenum to mix with food.
The bile ducts carry the bile from your gallbladder
to the duodenum.
What are the 4fs in cholecystitis?
It seemed appropriate to answer the question
whether 4 x F canon (forty--the age over 40 years of
You might also like
- SCID - Full InterviewDocument141 pagesSCID - Full InterviewCirtiu Dana92% (13)
- JF Nov 04 Web VersionDocument8 pagesJF Nov 04 Web VersionAndrew GrazianoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument122 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistryqwerty123100% (1)
- CholecystitisDocument60 pagesCholecystitistammycristobalmd100% (15)
- Cholecystitis With CholelithiasisDocument20 pagesCholecystitis With CholelithiasisrhyanneNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis And Gallstones, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCholecystitis And Gallstones, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Communicative II, Unit 2 QuestionsDocument2 pagesCommunicative II, Unit 2 QuestionsAddis VLOG100% (3)
- KDOQI Guidelines 2020 PDFDocument107 pagesKDOQI Guidelines 2020 PDFLorePalmaOrellanaNo ratings yet
- CHOLECYSTITISDocument4 pagesCHOLECYSTITISMarcieNo ratings yet
- Reporting CholeDocument4 pagesReporting CholeMarcieNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Full With EditDocument43 pagesCholecystitis Full With Editmustafalotfy01No ratings yet
- CHOLECYSTITIS With CHOLECYSTOLITHIASISDocument33 pagesCHOLECYSTITIS With CHOLECYSTOLITHIASISSherry100% (3)
- Cholelithiasis RLDocument29 pagesCholelithiasis RLPrincess Joanna Marie B DelfinoNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Gallbladder and BileDocument10 pagesUnderstanding The Gallbladder and BileAbirajanNo ratings yet
- GallbladderDocument6 pagesGallbladderShiri Michelle Lopez CaytonNo ratings yet
- LSPUDocument24 pagesLSPUNYSELL DELOS REYESNo ratings yet
- Chole CystitisDocument20 pagesChole CystitisAnjene BurgosNo ratings yet
- Acute Cholecystitis: What Are The Symptoms?Document3 pagesAcute Cholecystitis: What Are The Symptoms?Prince Jhessie L. AbellaNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis With CholecystolithiasisDocument33 pagesCholecystitis With CholecystolithiasisDino V EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Right Hypochondrium PainDocument34 pagesApproach To Right Hypochondrium PainkhansamrNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis Brief DiscussionDocument8 pagesCholelithiasis Brief Discussionriel100% (6)
- What Are GallstonesDocument15 pagesWhat Are GallstonesStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Chole Cyst IsDocument8 pagesChole Cyst IsJose Adrian Mendoza OrejuelaNo ratings yet
- CholecystitisDocument2 pagesCholecystitisCassandra James HaleyNo ratings yet
- B. Synthesis of The DiseaseDocument5 pagesB. Synthesis of The DiseaseQaz ZaqNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder Diseases Are Most Often Caused by GallstonesDocument8 pagesGallbladder Diseases Are Most Often Caused by GallstonesCharlie C. SanchezNo ratings yet
- The Diseases of GallbladderDocument27 pagesThe Diseases of GallbladderAroosha IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis IntroductionDocument4 pagesCholecystitis IntroductionJechelle Ann Pabustan Martin-BoniquitNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder HydropsDocument6 pagesGallbladder HydropsSaifulAnamNo ratings yet
- Dave Jay S. Manriquez RN. Acute CholecystitisDocument11 pagesDave Jay S. Manriquez RN. Acute CholecystitisChilleMaeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - GallbladderDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - GallbladderCHi NAiNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis: What Is It?Document6 pagesCholecystitis: What Is It?Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Litiasis EctomyDocument23 pagesCholecystitis Litiasis EctomyTimothy WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Gallstones: Session 4Document2 pagesGallstones: Session 4Valeria Casiano CelisNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy With Intraoperative CholangiogramDocument8 pagesCholecystectomy With Intraoperative CholangiogramLourd Andrew VillegasNo ratings yet
- CHOLECYSTITIS With CHOLECYSTOLITHIASISDocument2 pagesCHOLECYSTITIS With CHOLECYSTOLITHIASISkennice_nereaNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: (1) (2) (3) Go ToDocument6 pagesNtroduction: (1) (2) (3) Go ToretnaNo ratings yet
- What Are GallstonesDocument7 pagesWhat Are GallstonesImtiazAhmedNo ratings yet
- GALLBLADDERDocument17 pagesGALLBLADDERSnehaNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol Stone. People Are at Most Risk For Cholecystitis or Cholelithiasis Is Obese Women Who HaveDocument4 pagesCholesterol Stone. People Are at Most Risk For Cholecystitis or Cholelithiasis Is Obese Women Who HavePatriot DolorNo ratings yet
- CholecystitisDocument3 pagesCholecystitissaranya amuNo ratings yet
- What Are Gallstones?: Lemuel Jay A. Segovia Grade 8-Peace Science Q4M1Document4 pagesWhat Are Gallstones?: Lemuel Jay A. Segovia Grade 8-Peace Science Q4M1Zarah Joyce SegoviaNo ratings yet
- CholecystitisDocument10 pagesCholecystitisCris Pin BumatangNo ratings yet
- Progesterone Has Been Shown To Decrease Gall-Bladder Motility, WhichDocument9 pagesProgesterone Has Been Shown To Decrease Gall-Bladder Motility, WhichFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- Progesterone Has Been Shown To Decrease Gall-Bladder Motility, WhichDocument9 pagesProgesterone Has Been Shown To Decrease Gall-Bladder Motility, WhichFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- Case Stydy On CholithiasisDocument29 pagesCase Stydy On CholithiasisDaniel TalleyNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis - OverviewDocument2 pagesCholecystitis - OverviewValerie DelmundoNo ratings yet
- CholedocholithiasisDocument44 pagesCholedocholithiasisGerli Bismonte100% (6)
- Gallblader QuizletDocument10 pagesGallblader QuizletMaria Theresa BuscasNo ratings yet
- Foreign ObjectsDocument2 pagesForeign ObjectsSophia limNo ratings yet
- Case Study CholecystitisDocument27 pagesCase Study CholecystitisBandana RajpootNo ratings yet
- Pseudochist PancreaticDocument10 pagesPseudochist PancreaticArassikaNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis: Introduction: General Illness InformationDocument9 pagesCholelithiasis: Introduction: General Illness InformationJhangot Abad GabucoNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis and CholecystitisDocument10 pagesCholelithiasis and CholecystitisMaria Theresa BuscasNo ratings yet
- CHOLELITHIASIS Seminar-1Document10 pagesCHOLELITHIASIS Seminar-1Zihaan MohammadNo ratings yet
- CholedocholithiasisDocument3 pagesCholedocholithiasisPao AcelajadoNo ratings yet
- Diverticular DiseaseDocument8 pagesDiverticular Diseasenurse_enzo100% (1)
- CHOLECYSTITISDocument23 pagesCHOLECYSTITISR-JAY BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- CholecystitisDocument20 pagesCholecystitisMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Acalculous Cholecystopathy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Acalculous Cholecystopathy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Cholecystitis, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Cholecystitis, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fatty Liver Diet Cookbook: Triumph Over FLD and Hepatic Steatosis with Scrumptious Low-Fat Recipes, Harness Your Metabolism, and Embrace a Swell-Free Life Naturally [II EDITION]From EverandFatty Liver Diet Cookbook: Triumph Over FLD and Hepatic Steatosis with Scrumptious Low-Fat Recipes, Harness Your Metabolism, and Embrace a Swell-Free Life Naturally [II EDITION]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- Diverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandDiverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- CHOLECYSTITISDocument4 pagesCHOLECYSTITISMarcieNo ratings yet
- Revised NCP 1-3Document6 pagesRevised NCP 1-3MarcieNo ratings yet
- NCP Pre Term LaborDocument8 pagesNCP Pre Term LaborMarcieNo ratings yet
- KJJJDocument6 pagesKJJJMarcieNo ratings yet
- Cva NCP 1Document3 pagesCva NCP 1MarcieNo ratings yet
- CKD PathoDocument1 pageCKD PathoMarcieNo ratings yet
- CHN 113 Nursing Care of Community TO DO: My Community and OthersDocument4 pagesCHN 113 Nursing Care of Community TO DO: My Community and OthersMarcieNo ratings yet
- Movie Review Mood DisorderDocument1 pageMovie Review Mood DisorderMarcieNo ratings yet
- Documentary Gretchen John BarbDocument4 pagesDocumentary Gretchen John BarbMarcieNo ratings yet
- Representative Laboratory Reference Values: Blood, Plasma, and SerumDocument22 pagesRepresentative Laboratory Reference Values: Blood, Plasma, and SerumKubra ĖdrisNo ratings yet
- Lession 1Document99 pagesLession 1BHUKYA USHARANINo ratings yet
- Prevention of Pre-Eclampsia by Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin in Addition To Aspirin: A Meta-AnalysisDocument7 pagesPrevention of Pre-Eclampsia by Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin in Addition To Aspirin: A Meta-AnalysisAnonymous 9OHpuvNo ratings yet
- HAAD Exam 2018Document11 pagesHAAD Exam 2018midhun100% (1)
- Moral and Ethical Considerations For The Use of AnimalsDocument9 pagesMoral and Ethical Considerations For The Use of AnimalsDr Dart05No ratings yet
- SRS Kidney - 2016BDocument3 pagesSRS Kidney - 2016ByayayanizaNo ratings yet
- A Thing of Nothing. The Catastrophic Body in HamletDocument19 pagesA Thing of Nothing. The Catastrophic Body in HamletMarialena MarialenakiNo ratings yet
- DyspneaDocument2 pagesDyspneaDesya SilayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Food Preservation by High TemperatureDocument19 pagesChapter 2 Food Preservation by High TemperatureNaresh NNo ratings yet
- Gynecologic Oncology: Review ArticleDocument16 pagesGynecologic Oncology: Review ArticleElson TavaresNo ratings yet
- Analytical Study of Diagnosis For Angioplasty and Stents Patients Using Improved Classification TechniqueDocument4 pagesAnalytical Study of Diagnosis For Angioplasty and Stents Patients Using Improved Classification TechniqueEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Donor Health Check For New and Returning DonorsDocument1 pageDonor Health Check For New and Returning DonorsGaoudam NatarajanNo ratings yet
- 3rd YrMedical Surgical NursingDocument24 pages3rd YrMedical Surgical Nursingpunam todkarNo ratings yet
- Reduced Risk of AnxietyDocument7 pagesReduced Risk of AnxietySyaika Amelia ZahraNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Examination of UrineDocument17 pagesMicroscopic Examination of UrineBrent LagartoNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Exocrine PancreasDocument5 pagesPathology of The Exocrine PancreassatriayanuwardaniNo ratings yet
- Miasm and Susceptibility 1Document188 pagesMiasm and Susceptibility 1Yashas An100% (1)
- Geriatric Nursing: Theories of AgingDocument4 pagesGeriatric Nursing: Theories of AgingNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Pa16 01 00 00 00Document88 pagesPa16 01 00 00 00dikshaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Extended Essay SnickereensDocument28 pagesBiology - Extended Essay Snickereenshello helloNo ratings yet
- Health SystemsDocument37 pagesHealth SystemsKyle RicardoNo ratings yet
- Cpot ScoreDocument11 pagesCpot ScoreabdulkadirmunsyNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis PTDocument16 pagesAppendicitis PTDelia Soriano AlingayaoNo ratings yet
- Epigenetic SDocument19 pagesEpigenetic SNoor SabahNo ratings yet
- Tongue Thrusting Habit & Other Habits, Its Management 2Document20 pagesTongue Thrusting Habit & Other Habits, Its Management 2Madhu Sudan ReddyNo ratings yet



























































![Fatty Liver Diet Cookbook: Triumph Over FLD and Hepatic Steatosis with Scrumptious Low-Fat Recipes, Harness Your Metabolism, and Embrace a Swell-Free Life Naturally [II EDITION]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/598276019/149x198/1b7a1779c0/1711328726?v=1)