Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asthma - Patho, Signs & Symptoms
Asthma - Patho, Signs & Symptoms
Uploaded by
Baebee LouOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Asthma - Patho, Signs & Symptoms
Asthma - Patho, Signs & Symptoms
Uploaded by
Baebee LouCopyright:
Available Formats
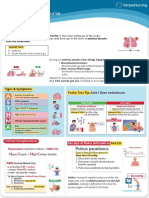
Asthma
Pediatrics: Respiratory
Pathophysiology
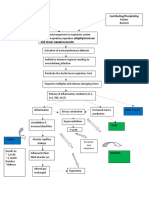
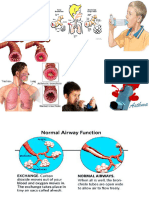
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder in the major pathways of the lungs:
Bronchi & Bronchioles. It comes & goes with flare-ups in the form of asthma attacks
that are reversible!
MEMORY TRICK During an asthma attack, 2 key things happen:
A - Asthma 1. Bronchoconstriction:
A - Acute Attacks that come & go Bronchi puff up with inflammation & get VERY tight.
2. Wet, mucus filled lungs:
Excessive mucus production from goblet cells that line the
#1 #2 respiratory tract.
Bronchoconstriction wet & mucus filled
PRIORITY! Since the respiratory tract is so constricted that oxygen cannot get
in & CO2 cannot get out, resulting in air trapping and making it hard to exhale.
Signs & Symptoms
Top Missed NCLEX Question:
A Accessory muscle use
Critical Sign: Paradoxical Breathing
S
Which child in the pediatric unit
SOB & dyspnea
should the nurse see first?
Critical Sign: Single word dyspnea
T
1. 8 year old with cystic fibrosis
Tight CHEST & Tachypnea presenting with fever &
green sputum
H
2. 10 year old with croup
presenting with a barking
High-pitched wheezing cough & tachypnea
3. 6 year old with acute asthma
M
exacerbation suddenly has
no wheezing
Minimal “diminished breath sounds”
4. 11 year old with new
A
tachycardia & anxiety after
albuterol nebulizer treatment
3 As 6 year old
Absent Breath Sounds (Silent Chest) PRIORITY
Acidosis (CO2 retention)
Air trapping - Prolonged exhalation
Critical Complications Key Sign of Status Asthmaticus Test Tip
Hypercapnic respiratory failure = HIGH CO2 Pulsus paradoxus 150
100
Pulsus paradoxus
Drop in systolic blood pressure
Hyper Capnic = High Carbon dioxide
50
More than 10 mmHg
1. Decrease in stroke volume
2. Decrease in systolic blood pressure
(systolic squeeze)
ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) 0₂
0₂
0₂
0₂ 3. Pulse wave amplitude during inspiration
pH less than 7.35 = Acidosis
PaCO2 - Over 45 = Acidosis
PaO2 - Less than 80! = Hypoxic
* 1st Sign of Hypoxia = Mental Status Change Patho: increased negative pressure > 10 mmHg
1. Agitation PRIORITY
within the lungs puts a lot of added 90
2. Restlessness NCLEX TIP
3. Drowsiness pressure on the left ventricle,
Status Asthmaticus NCLEX TIP making it difficult for the heart to
1. Endotracheal Intubation pump oxygen rich blood to the body.
You might also like
- Manual of Pediatric Cardiac Intensive CareDocument326 pagesManual of Pediatric Cardiac Intensive CareLeydi Baltazar T100% (4)
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Step 2 CK Uworld Pulmonary NotesDocument42 pagesStep 2 CK Uworld Pulmonary NotesMariyam Nauffer100% (8)
- ITLS 8e Advanced Pre-Test - Annotated Key PDFDocument10 pagesITLS 8e Advanced Pre-Test - Annotated Key PDFJohn E. Ibrahim100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Pneumonia Concept Map - KPoindexterDocument1 pagePneumonia Concept Map - KPoindexterKatie_Poindext_5154100% (2)
- Practical of Arterial Pulse For 1st Year Mbbs StudentsDocument7 pagesPractical of Arterial Pulse For 1st Year Mbbs StudentsMudassar Roomi33% (3)
- CMS Int. Med1 AnswersDocument15 pagesCMS Int. Med1 AnswersDiego Al Gutierrez50% (2)
- Asthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsDocument1 pageAsthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsVishalNo ratings yet
- Respiratory MedicineDocument49 pagesRespiratory MedicinemuhamedNo ratings yet
- Chronic CoughDocument6 pagesChronic CoughironNo ratings yet
- Chronic Bronchitis and EmphesemaDocument2 pagesChronic Bronchitis and Emphesemanursing concept maps100% (2)
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase StudyJA BerzabalNo ratings yet
- NCM 112-Mod3Document19 pagesNCM 112-Mod3Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- Chronic CoughDocument6 pagesChronic CoughironNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderBlessyl Mae EstenzoNo ratings yet
- 242 - Respiratory Pathology COPD - Clinical FeaturesDocument3 pages242 - Respiratory Pathology COPD - Clinical FeaturesPranav PunjabiNo ratings yet
- A Child Presenting With Breathing Difficulties (Asthma)Document54 pagesA Child Presenting With Breathing Difficulties (Asthma)Sindhu BabuNo ratings yet
- Copd - Midterm NotesDocument2 pagesCopd - Midterm NotesInday BertaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: 1. Pleural Effusion 3. Septic ShockDocument1 pagePneumonia: 1. Pleural Effusion 3. Septic ShockTrisha VergaraNo ratings yet
- Note GridDocument19 pagesNote Gridnesowav455No ratings yet
- Daniel P. Soriano BSN 4A Activity 3: Pediatric Nursing Health Assessment and Nursing Care Plan ObjectivesDocument6 pagesDaniel P. Soriano BSN 4A Activity 3: Pediatric Nursing Health Assessment and Nursing Care Plan ObjectivesChezka MendozaNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Respiratory Emergencies: Samuel HarminDocument41 pagesPediatrics Respiratory Emergencies: Samuel HarminUmbu ArnoldNo ratings yet
- 316 Revalida ReviewerDocument28 pages316 Revalida ReviewerSOPHIA PILLENANo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept Mapmild_tea100% (1)
- Acute Conditions of The NeonatesDocument8 pagesAcute Conditions of The Neonatesjillmonicadaquipil7No ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- NCP Acute BrochitisDocument5 pagesNCP Acute BrochitisFrancine kimberlyNo ratings yet
- High Risk Conditionof of NewbornDocument2 pagesHigh Risk Conditionof of NewbornstephanyNo ratings yet
- ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) : EarlyDocument1 pageARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) : EarlyDora Elena HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Tract DiseasesDocument4 pagesLower Respiratory Tract DiseasesJulia ManaloNo ratings yet
- Respiratory FailureDocument5 pagesRespiratory Failureta CNo ratings yet
- NCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T SecretionDocument3 pagesNCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T Secretionherscentasiascribd50% (8)
- Respiratory Review - 2022Document34 pagesRespiratory Review - 2022katerina ramajNo ratings yet
- Diana Kyla A. Punay Bsn-Dash-6: Subjective Data: Short Term: Short TermDocument3 pagesDiana Kyla A. Punay Bsn-Dash-6: Subjective Data: Short Term: Short TermZoè AshtrönNo ratings yet
- (NS) AsthmaCOPDPneumonia Tutorial QuestionsDocument25 pages(NS) AsthmaCOPDPneumonia Tutorial QuestionsJoei “Jojo” GohNo ratings yet
- NCP MontanoDocument7 pagesNCP MontanoKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- 04 Respiratory DistressDocument1 page04 Respiratory DistressAli BakNo ratings yet
- MS LEC Reviewer Oxygenation Problems 1Document4 pagesMS LEC Reviewer Oxygenation Problems 1Shekinah GeriosaNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument4 pagesCOPDitsmailbbkNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN About Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN About Ineffective Airway ClearanceJoji BaitNo ratings yet
- Upper Airway InfectionsDocument5 pagesUpper Airway InfectionsTreesa LouiseNo ratings yet
- 2022 Clinthera S1T4 Copd PDFDocument5 pages2022 Clinthera S1T4 Copd PDFmedicoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Study GuideDocument5 pagesPneumonia Study GuideMartha Marty BalintNo ratings yet
- Ventilatory Assistance Study GuideDocument9 pagesVentilatory Assistance Study GuideBrianna RorickNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of PneumoniaJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Lung Diseases Obstructive RestrictiveDocument3 pagesLung Diseases Obstructive RestrictiveJonathan PacunayenNo ratings yet
- Asthma 1Document79 pagesAsthma 1DanishMandiNo ratings yet
- Copd NotesDocument11 pagesCopd NotesAgnes Jeane EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationNichol John MalabananNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DisordersDocument8 pagesRespiratory DisordersDonna DayudayNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Sounds: by Oluwaseun OlaiyaDocument16 pagesRespiratory Sounds: by Oluwaseun OlaiyaOlaiya OluwaseunNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis On Aspiration Syndrome (MAS) : Pediatric Intensive Care UnitDocument11 pagesCase Analysis On Aspiration Syndrome (MAS) : Pediatric Intensive Care UnitArianne AlaveNo ratings yet
- PRIORITY 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Excessive or Thick Secretions Tree Secondary To PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPRIORITY 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Excessive or Thick Secretions Tree Secondary To PneumoniaElay Pedroso100% (1)
- COPD (D.E.P.C.I.T) : Done By: Miya WongDocument10 pagesCOPD (D.E.P.C.I.T) : Done By: Miya WongKyra KhalidNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeGabriel Tolentino70% (10)
- Pediatric Respiratory Anatomy: Course Tak 5 Dula Stephanie PDocument5 pagesPediatric Respiratory Anatomy: Course Tak 5 Dula Stephanie PSteph DulaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 NotesDocument6 pagesNCM 112 NotesKatrina Jhane MercadoNo ratings yet
- Encoded Notes Respi 1Document24 pagesEncoded Notes Respi 1Krizzia LaturnasNo ratings yet
- (PULMO) - ABG Interpretation PDFDocument7 pages(PULMO) - ABG Interpretation PDFKeith LajotNo ratings yet
- NCP AsthmaDocument6 pagesNCP AsthmaJohn Cyprian AbeloNo ratings yet
- The Complete Asthma Guide: An Asthma book for adults and children, that teaches how to be asthma free naturally with the right therapeutic diets, medications & alternative herbal therapiesFrom EverandThe Complete Asthma Guide: An Asthma book for adults and children, that teaches how to be asthma free naturally with the right therapeutic diets, medications & alternative herbal therapiesNo ratings yet
- Day 1. Mohd Sami 1Document67 pagesDay 1. Mohd Sami 1Baebee LouNo ratings yet
- Pancrelipase - EnzymesDocument1 pagePancrelipase - EnzymesBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Pals With Bls 2017cDocument53 pagesPals With Bls 2017cBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Abuse Assessment & SignsDocument1 pageAbuse Assessment & SignsBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Hypoglycaemia Low Blood SugarDocument4 pagesPediatric Hypoglycaemia Low Blood SugarBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Amblyopia, Astigmatism & HyperopiaDocument1 pageAmblyopia, Astigmatism & HyperopiaBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument1 pageIron Deficiency AnemiaBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Myopia & StrabismusDocument1 pageMyopia & StrabismusBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- CPR 2Document3 pagesCPR 2Baebee Lou100% (1)
- CoronavirusDocument3 pagesCoronavirusBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Saudi Nursing Licensure Examination Blueprint: (To Be Applied in January 2019)Document3 pagesSaudi Nursing Licensure Examination Blueprint: (To Be Applied in January 2019)Baebee LouNo ratings yet
- Hospital Admission Criteria For COVID-19 Patients: MODIFIED: MAY 8, 2020Document2 pagesHospital Admission Criteria For COVID-19 Patients: MODIFIED: MAY 8, 2020Baebee LouNo ratings yet
- ICU Criteria DuringDocument5 pagesICU Criteria DuringBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in ICU, CCU, OTDocument11 pagesDrugs Used in ICU, CCU, OTBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- AMI in Covid SCDC 1Document5 pagesAMI in Covid SCDC 1Baebee LouNo ratings yet
- Airway ManagementDocument8 pagesAirway ManagementBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Pulsus ParadoxusDocument2 pagesPulsus ParadoxusHassan.shehriNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade and ManagementDocument42 pagesCardiac Tamponade and ManagementRezwanul Hoque Bulbul100% (2)
- Cardiac Tamponade: Squeezing The Heart Until It StopsDocument4 pagesCardiac Tamponade: Squeezing The Heart Until It StopsJesse FlingNo ratings yet
- Physical DiagnosisDocument42 pagesPhysical DiagnosisKhim Yalong100% (1)
- Davidson's McqsDocument145 pagesDavidson's McqsSekhons Akademy100% (3)
- Mcqs Pediatric Cardiology EmergencyDocument29 pagesMcqs Pediatric Cardiology EmergencyOmed M. AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade 2Document23 pagesCardiac Tamponade 2Jethro Floyd QuintoNo ratings yet
- Pericardial Disease 1Document100 pagesPericardial Disease 1Anab Mohamed Elhassan Abbas AlnowNo ratings yet
- Emergency traumaEMQ34Document34 pagesEmergency traumaEMQ34assssadfNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pericardial DiseaseDocument36 pagesPathophysiology of Pericardial DiseaseivaniNo ratings yet
- Teaching Rounds A Visual Aid To Teaching Internal Medicine Pearls On The Wards 1St Edition Navin Kumar Full ChapterDocument67 pagesTeaching Rounds A Visual Aid To Teaching Internal Medicine Pearls On The Wards 1St Edition Navin Kumar Full Chapterbertha.commings489100% (8)
- Cardiovascular ExaminationDocument127 pagesCardiovascular Examinationwakemeup143No ratings yet
- List of Paradoxes - WikipediaDocument28 pagesList of Paradoxes - WikipediaBenedettoBoccuzziNo ratings yet
- Sunandan Sikdar - Handbook of Cardiac Critical Care and Anaesthesia-CRC Press (2023)Document332 pagesSunandan Sikdar - Handbook of Cardiac Critical Care and Anaesthesia-CRC Press (2023)orlovacz.katusNo ratings yet
- Lesson9 Cardiovascular AssessmentDocument21 pagesLesson9 Cardiovascular AssessmentDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- AEMT - Trauma Exam PracticeDocument26 pagesAEMT - Trauma Exam PracticeEMS DirectorNo ratings yet
- Cardiac TamponadeDocument3 pagesCardiac TamponadeKimberly SolisNo ratings yet
- Medical Skills Physical ExamDocument150 pagesMedical Skills Physical Examsholay100% (1)
- Diseases of The PericardiumDocument68 pagesDiseases of The PericardiumBana Remy WilsonNo ratings yet
- Emergency EchocardiographyDocument62 pagesEmergency Echocardiographyansarijaved100% (1)
- EscardioDocument9 pagesEscardioMYMANo ratings yet
- 1.2.1 Cardio History Taking and Physical Examination Part 1Document53 pages1.2.1 Cardio History Taking and Physical Examination Part 1Abanoub AwadallaNo ratings yet
- Status Asthmaticus in ChildrenDocument76 pagesStatus Asthmaticus in ChildrenJesterCruzNo ratings yet
- JBLNPairwayDocument39 pagesJBLNPairwayjmscribblerNo ratings yet
- Case Report Kardiologi TamponadeDocument13 pagesCase Report Kardiologi TamponadeMuhammad HidayatNo ratings yet
- Bedside Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument26 pagesBedside Hemodynamic MonitoringBrad F LeeNo ratings yet