Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Hematology Section
The Hematology Section
Uploaded by
VENUS LIRIA PANTICopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Reversible and Irreversible Cell InjuryDocument55 pagesReversible and Irreversible Cell Injurygabb bbNo ratings yet
- Membrane BiochemistryDocument21 pagesMembrane BiochemistryAnna SafitriNo ratings yet
- Patho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Document34 pagesPatho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Sheryl Layne LaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesDocument26 pagesLecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics PerpetualDocument20 pagesPediatrics PerpetualHazel Fernandez VillarNo ratings yet
- Muscle BiopsyDocument48 pagesMuscle Biopsybusiness onlyyouNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AbscessDocument3 pagesAbdominal AbscessIchalAzNo ratings yet
- Stress and Coping Mechanisms Among Hemodialysis Patients in The Gulf and Neighboring Countries A Systematic ReviewDocument5 pagesStress and Coping Mechanisms Among Hemodialysis Patients in The Gulf and Neighboring Countries A Systematic ReviewMahalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Histology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesHistology of Male Reproductive SystemSanna Asila AkramNo ratings yet
- Intro To MycoDocument6 pagesIntro To Mycojohn hector regpalaNo ratings yet
- Lab Physiology Second Year PracticalDocument21 pagesLab Physiology Second Year PracticalNona NonicaaNo ratings yet
- 8 Extremity TraumaDocument10 pages8 Extremity TraumaMyrtle Yvonne RagubNo ratings yet
- (MT 57) PARA - Specimen CollectionDocument10 pages(MT 57) PARA - Specimen CollectionLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Blood CellDocument3 pagesKinds of Blood CellBalkis HumairohNo ratings yet
- Finals Week 10Document8 pagesFinals Week 10MARIE NELLIE MOSTRADONo ratings yet
- 1.06 General Pathology - Neoplasia (Part 1) - Dr. Annette SallilasDocument17 pages1.06 General Pathology - Neoplasia (Part 1) - Dr. Annette SallilasCherry RahimaNo ratings yet
- (Compre - 3itransteam) Mt6320 - Bacte Lec Unit 1.1-11Document244 pages(Compre - 3itransteam) Mt6320 - Bacte Lec Unit 1.1-11Ylia MastarsNo ratings yet
- Neuro Written III TablesDocument5 pagesNeuro Written III TablesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Medical Mycology Basic Fungal BiologyDocument6 pages1 - Introduction To Medical Mycology Basic Fungal BiologyMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- HmoDocument35 pagesHmoDiorVelasquezNo ratings yet
- Strasinger AUBFDocument44 pagesStrasinger AUBFangela tanteoNo ratings yet
- Vibrio, Campylobacter, and HelicobacterDocument7 pagesVibrio, Campylobacter, and HelicobacterRach ReyesNo ratings yet
- UROLOGY 2020 (Doc BarcenasDocument33 pagesUROLOGY 2020 (Doc BarcenasJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- Clinpara Finals LabDocument81 pagesClinpara Finals LabAnne CabreraNo ratings yet
- (MT 57) para - MidtermsDocument56 pages(MT 57) para - MidtermsLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- 4 - TissueDocument13 pages4 - TissueGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Resistance of The Body To Infection: II. Immunity and AllergyDocument34 pagesUnit 6: Resistance of The Body To Infection: II. Immunity and AllergyEsteban Tabares GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Para Compre 2Document17 pagesPara Compre 2serainie maiNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci TransDocument5 pagesGram Positive Cocci Transkerynne dyNo ratings yet
- General Pathology QuizDocument2 pagesGeneral Pathology QuizMatt DickoNo ratings yet
- Sputum Analysis and BalDocument41 pagesSputum Analysis and BalClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceace Part 1Document48 pagesEnterobacteriaceace Part 1Krenz CatiboNo ratings yet
- 18 Characteristics of Leukemias Lymphomas and MyelomasDocument9 pages18 Characteristics of Leukemias Lymphomas and MyelomasDaphne HernaezNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Morphology Myocardial InfarctionDocument10 pagesMicroscopic Morphology Myocardial InfarctionnathanielNo ratings yet
- ALaboratory Reportonthe Observed Parasitesinthe Gillsand Gutof Anabastestudineus Puyofrom Kabacan Cotabato PhilippinesDocument15 pagesALaboratory Reportonthe Observed Parasitesinthe Gillsand Gutof Anabastestudineus Puyofrom Kabacan Cotabato PhilippinesNicollo DadiavelliNo ratings yet
- Fixation ImpregnationDocument18 pagesFixation ImpregnationKarla Mae Tolelis - BurlatNo ratings yet
- (MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyDocument6 pages(MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyHenryboi CañasNo ratings yet
- DR Ara Khan Marwat: Join My Watssap Group For Part-1 Books, Papers and UpdatesDocument25 pagesDR Ara Khan Marwat: Join My Watssap Group For Part-1 Books, Papers and UpdatesmisdduaaNo ratings yet
- Neisse RiaDocument49 pagesNeisse RiaSubhada GosaviNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy TractsDocument7 pagesNeuroanatomy TractsLola PNo ratings yet
- 6 B&B CirrhosisDocument30 pages6 B&B CirrhosisSara Joseph100% (1)
- Virus ClassificationDocument5 pagesVirus ClassificationNUR AIN NADHIRAH SHAMSUL BADRINo ratings yet
- ImmunopathologyDocument21 pagesImmunopathologyapplesncoreNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Streptococcus: Propertie S Morpholo Gy Culture & Biochemi Cal ReactionsDocument3 pagesStaphylococcus Streptococcus: Propertie S Morpholo Gy Culture & Biochemi Cal ReactionsmadhuNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec 2nd SemDocument39 pagesHistopath Lec 2nd SemMark jay LlanoNo ratings yet
- CH10Document17 pagesCH10Kim BasicNo ratings yet
- IPD A Cardiovascular System Bates and and VideoDocument10 pagesIPD A Cardiovascular System Bates and and Videostar220498No ratings yet
- 11 Reticular Formation and Limbic SystemDocument15 pages11 Reticular Formation and Limbic SystemDavid KleinNo ratings yet
- Trans Savi Oto Lec 01 Head and Neck History and PE 1st SemesterDocument12 pagesTrans Savi Oto Lec 01 Head and Neck History and PE 1st SemesterJoherNo ratings yet
- PMLS ReviewerDocument10 pagesPMLS ReviewerHersheen MagaddatuNo ratings yet
- Compre MolbioDocument93 pagesCompre MolbioDeniebev'z OrillosNo ratings yet
- Approach To Anemia: - Reticulocyte Count Is Most Important TestDocument15 pagesApproach To Anemia: - Reticulocyte Count Is Most Important TestJanella SuerteNo ratings yet
- Aljane Rose Mae Q. Visto BSN 2A Pharmacology Thyroid and Parathyroid Agents Quiz (20 Items)Document2 pagesAljane Rose Mae Q. Visto BSN 2A Pharmacology Thyroid and Parathyroid Agents Quiz (20 Items)Erma VistoNo ratings yet
- Neuro Written II TablesDocument10 pagesNeuro Written II TablesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument45 pagesUrinalysisMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Endo Quizlet 1Document4 pagesEndo Quizlet 1Lycette CabantocNo ratings yet
- Benign WBC Disorders Third YaerDocument27 pagesBenign WBC Disorders Third YaerAisho KeyfNo ratings yet
- Edema Pathology by Asif AliDocument21 pagesEdema Pathology by Asif AliHassan AsifNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics SamplexDocument6 pagesPediatrics SamplexThea SansonNo ratings yet
- Understanding Haemolytic AnaemiaDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Haemolytic AnaemiaValeria Rudolph MartinezNo ratings yet
- MLS 123 MODULE 6 UNIT 5 Venipuncture Procedure Special Collection Procedure in POCTDocument16 pagesMLS 123 MODULE 6 UNIT 5 Venipuncture Procedure Special Collection Procedure in POCTVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- MLS 123 MODULE 6 UNIT 1 Venipuncture Procedure Syringe SystemDocument19 pagesMLS 123 MODULE 6 UNIT 1 Venipuncture Procedure Syringe SystemVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- Act. 6Document33 pagesAct. 6VENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- Act. 7Document23 pagesAct. 7VENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System Lec TransesDocument10 pagesThe Respiratory System Lec TransesVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument18 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- IMMUNOHEMATOLOGYDocument2 pagesIMMUNOHEMATOLOGYVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- PMLS 2Document1 pagePMLS 2VENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 Crossword Puzzle ModuleDocument1 pagePMLS 2 Crossword Puzzle ModuleVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
The Hematology Section
The Hematology Section
Uploaded by
VENUS LIRIA PANTIOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Hematology Section
The Hematology Section
Uploaded by
VENUS LIRIA PANTICopyright:
Available Formats
THE HEMATOLOGY SECTION WALLACE COULTER
HISTORY - developed cell counting by impedance measurement.
This method was based on the fact that cells are known
WILLIAM HEWSON for electrical conduction and that they manifest
electrical resistance as they pass through a small
- father of hematology aperture.
- discovery of wbc, lymphatic circulation, fibrinogen
BLOOD COMPONENTS
- coagulation fundamentals Glauber’s salt (1st anti-
coagulant) PLASMA
Preparation Blood sample is not
FRANZ ERNST CHRISTIAN NEUMANN (1868) allowed to clot prior to
- discovered the role of bone marrow in separation from cells
HEMATOPOIESIS Blood sample used for
collection is anti-
Production of cellular components of blood coagulated
and blood plasma Appearance after Pale cellular fluid
Also occur in the liver and yolk sac in fetal Separation separated from the blood
cells via centrifugation
hematopoiesis
Clotting factor Presence of fibrinogen
JAMES HOMER WRIGHT (1902) (Factor 1)
Presence of all clotting
- developed the WRIGHT STAIN and WRIGHT’S factors
ROMANOWSKY
Type of stain that remains the foundation of BLOOD (liquid extracellular matrix/plasma 55%)
blood cell
Fixative, sol I (eosin), sol II (crystal violet), (formed elements 45% RBC 44 WBC 1)
distilled water - composed of 91.5% water, 7% plasma protein, 1.5 %
An acidic solution/ low ph other solutes
Basic/alkaline solution/high ph
pH (power/potential of hydrogen) SERUM
Preparation Blood sample is allowed
KARL VIORORDT to clot before separation
from the clot
- the first to perform a blood count in 1852. His
Blood sample used for
method includes drawing blood into a capillary tube
collection is not anti-
and spreading a known volume of the collected blood coagulant
onto a slide followed by microscopic analysis. Appearance after Yellow fluid separation
GEORGE OLIVER separation from the blood clot via
centrifugation
- he provided an RBC count without the need for Clotting factor Absence of fibrinogen
manual counting of individual cells. His method was (Factor 1)
based on the VISUAL MEASUREMENT of light Absence of factor V, VIII,
loss by scattering and absorption in a test tube filled XIII, II)
with DILUTED BLOOD.
RED BLOOD CELLS
- Red Blood Cells are biconcave disc-shaped cells that
are anucleated
- RBCs contain the oxygen-carrying hemoglobin
which is a pigment that gives whole blood its red
HERCANDIER ET Al color. These cells are primarily responsible for
physiological gas exchange, specifically transporting
- utilized a PHOTODETECTOR for the
oxygen from the lungs to the different parts of the
measurement of light absorption instead of relying on
body and carry carbon dioxide back to the lungs.
unaided eyes.
- first description was by Van Leeunhook based on - comprises 1-3% of the total WBC population
the physiological gas exchange in the lungs which was
explained by William Henry.
BASOPHILS
Poikilocytosis refers to an increase in abnormal red
blood cells of any shape that makes up to 10% or
more of the total population. Poikilocytes can be flat,
elongated, teardrop-shaped, crescent-shaped, sickle-
shaped, or can have pointy or thorn-like projections, or
may have other abnormal feature
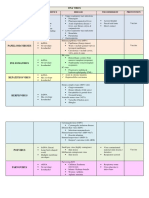
WHITE BLOOD CELLS
GRANULOCYTES (BEN)
NEUTROPHILS - nucleus has 2 lobes; nucleus is not easily observed
because it is often covered by large granules
- cytoplasm contains water soluble blue-black granules
with affinity for BASIC stains
- involved in allergic and hypersensitivity reactions
- comprises 0-2% of total WBC population
- nucleus has 2-5 lobes
- cytoplasm has fine; pale lilac granules with
NEUTRAL affinity for stains
- phagocytic; respond to bacterial infection
- comprises 50-70% of total WBC population
AGRANULOCYTE (ML)
MONOCYTE
EOSINOPHILS
- are converted to macrophages as they leave the
blood circulation and enter peripheral tissues
- macrophages are potent phagocytes which defend
- nucleus usually has 2 lobes connected by thick the body against mycobacterium species and other
chromatin strand bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses
- cytoplasm contains large, re-orange granules with - comprises 2-11% of total WBC population
affinity for ACIDIC stains
- nucleus is horseshoe or kidney-shaped often with
- responds to parasitic and helminthic infection and brain-like convolutions
allergy
- also characterized to have phagocytic activity
- cytoplasm is blue-gray colored and foamy and has a Hematocrit Determination
very fine azurophilic granules responsible for the RBC Count
characteristic “Ground glass” appearance WBC Count
LYMPHOCYTE WBC Differential Count
RBC Morphological Examination
Platelet Count
RBC Indices
H/H Test
(Hemoglobin Hematocrit Determination)
Hemoglobin Determination
- It is primarily used for the diagnosis of anemia.
Anemia is a condition in which the number of red
- round or slightly indented nucleus that occupies blood cells or their oxygen-carrying pigment
majority of the cell area hemoglobin is insufficient to meet physiologic needs.
- scanty cytoplasm with a characteristic “Robin’s egg Anemia is defined by the WHO as hemoglobin levels
blue coloration” of less than 12.0 g/dL in women and less than 13.0
g/dL in men.
- Immunocytes
Hematocrit Determination
- predominant WBC that responds to several viral
infections - It is also known as Packed Cell Volume (PCV) or
Erythrocyte Volume Fraction (EVF), is the volume
- comprises 18-42% of total WBC population percentage of RBCs in a whole blood sample.
WBC Count
- Is a clinically significant value. Leukocytosis/High
PLATELETS WBC count us often seen in infections, allergy, and
leukemic states. Leukopenia/Low WBC count on the
other hand, is observed in cases of viral infections that
temporarily disrupt bone marrow, autoimmune
disorders, and immunodeficiency.
Platelet Count
- It is the quantification of thrombocytes of the blood
samples.
WBC Differential Count
- platelets are cell fragments that play significant roles
in hemostasis. These cells contain many vesicles but - It is a routine procedure that involves observing a
have no nucleus. When your skin is injured puncturing total of 100 WBCs and simultaneously classifying
the vascular area, platelets clump together and form them as either neutrophil, lymphocytes, monocytes,
clots to stop bleeding. eosinophils, and basophils.
RBC Morphology Examination
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT (CBC) - It involves microscopic observation of the size and
shape of the red blood cell population of the sample.
- is a commonly performed blood test that is often
included as part of a routine checkup. CBC can be RBC Indices
used to help in the detection of a variety of disorders - It aids in morphological classification of anemia,
including infections, anemia, diseases of the immune MCV, MCH, and MCHC are commonly reported
system, and blood cancers. indices.
PANEL TESTS
Hemoglobin Determination
You might also like
- Reversible and Irreversible Cell InjuryDocument55 pagesReversible and Irreversible Cell Injurygabb bbNo ratings yet
- Membrane BiochemistryDocument21 pagesMembrane BiochemistryAnna SafitriNo ratings yet
- Patho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Document34 pagesPatho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Sheryl Layne LaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesDocument26 pagesLecture 2-Introduction To MicroscopesThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics PerpetualDocument20 pagesPediatrics PerpetualHazel Fernandez VillarNo ratings yet
- Muscle BiopsyDocument48 pagesMuscle Biopsybusiness onlyyouNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AbscessDocument3 pagesAbdominal AbscessIchalAzNo ratings yet
- Stress and Coping Mechanisms Among Hemodialysis Patients in The Gulf and Neighboring Countries A Systematic ReviewDocument5 pagesStress and Coping Mechanisms Among Hemodialysis Patients in The Gulf and Neighboring Countries A Systematic ReviewMahalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Histology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesHistology of Male Reproductive SystemSanna Asila AkramNo ratings yet
- Intro To MycoDocument6 pagesIntro To Mycojohn hector regpalaNo ratings yet
- Lab Physiology Second Year PracticalDocument21 pagesLab Physiology Second Year PracticalNona NonicaaNo ratings yet
- 8 Extremity TraumaDocument10 pages8 Extremity TraumaMyrtle Yvonne RagubNo ratings yet
- (MT 57) PARA - Specimen CollectionDocument10 pages(MT 57) PARA - Specimen CollectionLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Blood CellDocument3 pagesKinds of Blood CellBalkis HumairohNo ratings yet
- Finals Week 10Document8 pagesFinals Week 10MARIE NELLIE MOSTRADONo ratings yet
- 1.06 General Pathology - Neoplasia (Part 1) - Dr. Annette SallilasDocument17 pages1.06 General Pathology - Neoplasia (Part 1) - Dr. Annette SallilasCherry RahimaNo ratings yet
- (Compre - 3itransteam) Mt6320 - Bacte Lec Unit 1.1-11Document244 pages(Compre - 3itransteam) Mt6320 - Bacte Lec Unit 1.1-11Ylia MastarsNo ratings yet
- Neuro Written III TablesDocument5 pagesNeuro Written III TablesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Medical Mycology Basic Fungal BiologyDocument6 pages1 - Introduction To Medical Mycology Basic Fungal BiologyMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- HmoDocument35 pagesHmoDiorVelasquezNo ratings yet
- Strasinger AUBFDocument44 pagesStrasinger AUBFangela tanteoNo ratings yet
- Vibrio, Campylobacter, and HelicobacterDocument7 pagesVibrio, Campylobacter, and HelicobacterRach ReyesNo ratings yet
- UROLOGY 2020 (Doc BarcenasDocument33 pagesUROLOGY 2020 (Doc BarcenasJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- Clinpara Finals LabDocument81 pagesClinpara Finals LabAnne CabreraNo ratings yet
- (MT 57) para - MidtermsDocument56 pages(MT 57) para - MidtermsLiana JeonNo ratings yet
- 4 - TissueDocument13 pages4 - TissueGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Resistance of The Body To Infection: II. Immunity and AllergyDocument34 pagesUnit 6: Resistance of The Body To Infection: II. Immunity and AllergyEsteban Tabares GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Para Compre 2Document17 pagesPara Compre 2serainie maiNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci TransDocument5 pagesGram Positive Cocci Transkerynne dyNo ratings yet
- General Pathology QuizDocument2 pagesGeneral Pathology QuizMatt DickoNo ratings yet
- Sputum Analysis and BalDocument41 pagesSputum Analysis and BalClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceace Part 1Document48 pagesEnterobacteriaceace Part 1Krenz CatiboNo ratings yet
- 18 Characteristics of Leukemias Lymphomas and MyelomasDocument9 pages18 Characteristics of Leukemias Lymphomas and MyelomasDaphne HernaezNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Morphology Myocardial InfarctionDocument10 pagesMicroscopic Morphology Myocardial InfarctionnathanielNo ratings yet
- ALaboratory Reportonthe Observed Parasitesinthe Gillsand Gutof Anabastestudineus Puyofrom Kabacan Cotabato PhilippinesDocument15 pagesALaboratory Reportonthe Observed Parasitesinthe Gillsand Gutof Anabastestudineus Puyofrom Kabacan Cotabato PhilippinesNicollo DadiavelliNo ratings yet
- Fixation ImpregnationDocument18 pagesFixation ImpregnationKarla Mae Tolelis - BurlatNo ratings yet
- (MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyDocument6 pages(MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyHenryboi CañasNo ratings yet
- DR Ara Khan Marwat: Join My Watssap Group For Part-1 Books, Papers and UpdatesDocument25 pagesDR Ara Khan Marwat: Join My Watssap Group For Part-1 Books, Papers and UpdatesmisdduaaNo ratings yet
- Neisse RiaDocument49 pagesNeisse RiaSubhada GosaviNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy TractsDocument7 pagesNeuroanatomy TractsLola PNo ratings yet
- 6 B&B CirrhosisDocument30 pages6 B&B CirrhosisSara Joseph100% (1)
- Virus ClassificationDocument5 pagesVirus ClassificationNUR AIN NADHIRAH SHAMSUL BADRINo ratings yet
- ImmunopathologyDocument21 pagesImmunopathologyapplesncoreNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Streptococcus: Propertie S Morpholo Gy Culture & Biochemi Cal ReactionsDocument3 pagesStaphylococcus Streptococcus: Propertie S Morpholo Gy Culture & Biochemi Cal ReactionsmadhuNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec 2nd SemDocument39 pagesHistopath Lec 2nd SemMark jay LlanoNo ratings yet
- CH10Document17 pagesCH10Kim BasicNo ratings yet
- IPD A Cardiovascular System Bates and and VideoDocument10 pagesIPD A Cardiovascular System Bates and and Videostar220498No ratings yet
- 11 Reticular Formation and Limbic SystemDocument15 pages11 Reticular Formation and Limbic SystemDavid KleinNo ratings yet
- Trans Savi Oto Lec 01 Head and Neck History and PE 1st SemesterDocument12 pagesTrans Savi Oto Lec 01 Head and Neck History and PE 1st SemesterJoherNo ratings yet
- PMLS ReviewerDocument10 pagesPMLS ReviewerHersheen MagaddatuNo ratings yet
- Compre MolbioDocument93 pagesCompre MolbioDeniebev'z OrillosNo ratings yet
- Approach To Anemia: - Reticulocyte Count Is Most Important TestDocument15 pagesApproach To Anemia: - Reticulocyte Count Is Most Important TestJanella SuerteNo ratings yet
- Aljane Rose Mae Q. Visto BSN 2A Pharmacology Thyroid and Parathyroid Agents Quiz (20 Items)Document2 pagesAljane Rose Mae Q. Visto BSN 2A Pharmacology Thyroid and Parathyroid Agents Quiz (20 Items)Erma VistoNo ratings yet
- Neuro Written II TablesDocument10 pagesNeuro Written II TablesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument45 pagesUrinalysisMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Endo Quizlet 1Document4 pagesEndo Quizlet 1Lycette CabantocNo ratings yet
- Benign WBC Disorders Third YaerDocument27 pagesBenign WBC Disorders Third YaerAisho KeyfNo ratings yet
- Edema Pathology by Asif AliDocument21 pagesEdema Pathology by Asif AliHassan AsifNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics SamplexDocument6 pagesPediatrics SamplexThea SansonNo ratings yet
- Understanding Haemolytic AnaemiaDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Haemolytic AnaemiaValeria Rudolph MartinezNo ratings yet
- MLS 123 MODULE 6 UNIT 5 Venipuncture Procedure Special Collection Procedure in POCTDocument16 pagesMLS 123 MODULE 6 UNIT 5 Venipuncture Procedure Special Collection Procedure in POCTVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- MLS 123 MODULE 6 UNIT 1 Venipuncture Procedure Syringe SystemDocument19 pagesMLS 123 MODULE 6 UNIT 1 Venipuncture Procedure Syringe SystemVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- Act. 6Document33 pagesAct. 6VENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- Act. 7Document23 pagesAct. 7VENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System Lec TransesDocument10 pagesThe Respiratory System Lec TransesVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument18 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- IMMUNOHEMATOLOGYDocument2 pagesIMMUNOHEMATOLOGYVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- PMLS 2Document1 pagePMLS 2VENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 Crossword Puzzle ModuleDocument1 pagePMLS 2 Crossword Puzzle ModuleVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet