Professional Documents
Culture Documents
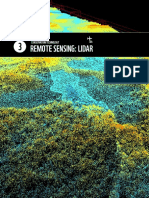
LIDAR
LIDAR
Uploaded by
Ola KhunOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LIDAR
LIDAR
Uploaded by
Ola KhunCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction:
In recent years, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology has emerged as a
powerful tool in the field of environmental assessment. With its ability to capture highly
accurate and detailed 3D information about landscapes and objects, LiDAR has
revolutionized the way we study and understand our natural environment. In this article,
we will explore the applications of LiDAR technology and its significant impact on
environmental assessment.
1. Understanding LiDAR Technology:
Briefly explain the principle behind LiDAR technology, which utilizes laser pulses
to measure distances and create precise 3D representations of objects and terrain.
Highlight the advantages of LiDAR, such as its ability to penetrate dense
vegetation, collect data at high speeds, and provide highly accurate measurements.
2. Mapping Terrain and Topography:
Discuss how LiDAR is transforming the way we map and analyze landscapes.
Explain how LiDAR data is used to create detailed digital elevation models
(DEMs) and high-resolution topographic maps.
Highlight the benefits of LiDAR in assessing landforms, including floodplains,
coastal areas, and mountainous regions, allowing for better understanding of
erosion, water flow, and land stability.
3. Vegetation Analysis and Forest Management:
Explore the applications of LiDAR in vegetation analysis and forest management.
Discuss how LiDAR data can be used to estimate tree height, density, biomass,
and species composition.
Explain how LiDAR assists in monitoring forest health, detecting changes in
vegetation patterns, and assessing the impact of natural disasters such as wildfires
or insect infestations.
4. Wetland and Coastal Zone Assessment:
Discuss how LiDAR technology is utilized in assessing wetland ecosystems and
coastal zones. Explain how LiDAR data helps identify wetland boundaries,
monitor changes in water levels, and study coastal erosion.
Highlight the importance of LiDAR in understanding the vulnerability of these
areas to climate change and aiding in the development of conservation and
management strategies.
5. Wildlife Monitoring and Habitat Assessment:
Explore the role of LiDAR in wildlife monitoring and habitat assessment. Explain
how LiDAR data can be used to identify and map animal habitats, such as nesting
sites, migration corridors, and breeding grounds.
Discuss how LiDAR assists in studying biodiversity, tracking population
dynamics, and aiding conservation efforts.
6. Challenges and Future Directions:
Address the challenges and limitations of LiDAR technology, such as cost, data
processing, and interpretation.
Discuss potential future advancements in LiDAR technology, including
miniaturization, increased data resolution, and integration with other remote
sensing technologies.
You might also like
- Imagery and GIS: Best Practices for Extracting Information from ImageryFrom EverandImagery and GIS: Best Practices for Extracting Information from ImageryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan Grade 9 Biology Biodiversity and EvolutionDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Grade 9 Biology Biodiversity and EvolutionLouise Meara Severo100% (2)
- Using Lidar in ArcGISDocument377 pagesUsing Lidar in ArcGISRomulo Soares100% (7)
- (Tự học SAT) - Khan academy Reading - Reading level 2 - Vol.2 PDFDocument22 pages(Tự học SAT) - Khan academy Reading - Reading level 2 - Vol.2 PDFTuan Nguyen100% (1)
- Modderfontein MasterPlan Progress UpdateDocument43 pagesModderfontein MasterPlan Progress Updaterodwellb100% (1)
- Remote SensingDocument8 pagesRemote SensinglsimnestNo ratings yet
- Forests 13 01743Document18 pagesForests 13 01743William Krista MahendraNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing: Forest Roads Mapped Using Lidar in Steep Forested TerrainDocument22 pagesRemote Sensing: Forest Roads Mapped Using Lidar in Steep Forested TerrainErvan Muktamar HendarnaNo ratings yet
- Methods Ecol Evol - 2022 - Silva - Treetop A Shiny Based Application and R Package For Extracting Forest Information FromDocument13 pagesMethods Ecol Evol - 2022 - Silva - Treetop A Shiny Based Application and R Package For Extracting Forest Information Frombrio rsmteNo ratings yet
- LIDAR TechnologyDocument9 pagesLIDAR TechnologyIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- International Encyclopedia of Geography - 2023 - Sharma - LiDARDocument12 pagesInternational Encyclopedia of Geography - 2023 - Sharma - LiDARrajashree naikNo ratings yet
- Application of LidarDocument1 pageApplication of Lidarfranchescamendez178No ratings yet
- Agronomy: Estimating Leaf Water Content Through Low-Cost LidarDocument12 pagesAgronomy: Estimating Leaf Water Content Through Low-Cost LidarVeera PrasadNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of LiDARDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of LiDARThierry NewtonNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing 6Document7 pagesRemote Sensing 6abheetpethe.scoe.entcNo ratings yet
- Theory Class 18 DecDocument4 pagesTheory Class 18 Decloveza lodhiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of UAV LiDAR For Mapping CoasDocument32 pagesEvaluation of UAV LiDAR For Mapping CoasTu Le VanNo ratings yet
- Meng 2010 Remotesensing-02-00833 PDFDocument28 pagesMeng 2010 Remotesensing-02-00833 PDFAnonymous cy0Ei0No ratings yet
- LiDAR Mapping A Remote Sensing TechnologyDocument3 pagesLiDAR Mapping A Remote Sensing Technologyvishwas sNo ratings yet
- Geomatic Field EssayDocument5 pagesGeomatic Field EssayKiran Raj100% (1)
- MG-2310 Application of Remote Sensing in ForestryDocument24 pagesMG-2310 Application of Remote Sensing in ForestryE19-115 Saitam KalekarNo ratings yet
- Review On Lidar Technology: Received: Date / Accepted: DateDocument9 pagesReview On Lidar Technology: Received: Date / Accepted: DateNUKONo ratings yet
- My Work Review Journal International About Remote Sensing To Mr. NurdinDocument3 pagesMy Work Review Journal International About Remote Sensing To Mr. NurdinelisauliwatitampubolNo ratings yet
- Lidar WWF Guidelines PDFDocument41 pagesLidar WWF Guidelines PDFHem BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- A Guide To LIDAR Data Acquisition and Processing For The Forests of The Pacific NorthwestDocument41 pagesA Guide To LIDAR Data Acquisition and Processing For The Forests of The Pacific NorthwestANGELRODNAHNo ratings yet
- LiDARSensor CBM September 2022 DebangshiDocument7 pagesLiDARSensor CBM September 2022 Debangshisampath nNo ratings yet
- Lidar Applications in Forestry - An Overview: Ward W. CarsonDocument9 pagesLidar Applications in Forestry - An Overview: Ward W. CarsonJelajah 3DNo ratings yet
- Airborne Light Detection and Ranging LiDAR For IndDocument35 pagesAirborne Light Detection and Ranging LiDAR For IndAdeliton DelkNo ratings yet
- Terra Point White PaperDocument10 pagesTerra Point White Paperobi SalamNo ratings yet
- Light Detection and Ranging LIDAR An Emerging ToolDocument8 pagesLight Detection and Ranging LIDAR An Emerging Toolzart123No ratings yet
- Light Detection and Ranging: March 2016Document29 pagesLight Detection and Ranging: March 2016Анастасія КачалубаNo ratings yet
- Applications of DronesDocument3 pagesApplications of Dronesbhanu.chaganti47No ratings yet
- LiDAR PrimerDocument1 pageLiDAR Primerد. سامي أبو جهادNo ratings yet
- Li DARDocument2 pagesLi DARlingmeiguo20102007No ratings yet
- The Evolution of Lidar and Its Application in High Precision MeasurementDocument12 pagesThe Evolution of Lidar and Its Application in High Precision MeasurementBadalNo ratings yet
- Remote SensingDocument8 pagesRemote SensingMaTheresa HabanaNo ratings yet
- Interim Report Group 01 PDFDocument20 pagesInterim Report Group 01 PDFRoshan KumarNo ratings yet
- Page - 1Document24 pagesPage - 1Rijy LoranceNo ratings yet
- ABRIL Radar and 3D Renderings Reveal Ancient Amazonian CitiesDocument3 pagesABRIL Radar and 3D Renderings Reveal Ancient Amazonian CitiesJumper086No ratings yet
- Web-LiDAR Forest Inventory: TreeExtractor ApplicationDocument12 pagesWeb-LiDAR Forest Inventory: TreeExtractor ApplicationCarlos Alberto Silva100% (1)
- CMRT05 Tiede Et AlDocument6 pagesCMRT05 Tiede Et AlJelajah 3DNo ratings yet
- LIDARDocument34 pagesLIDARVidya MoossNo ratings yet
- Article Costanza Et AlDocument14 pagesArticle Costanza Et AlluisNo ratings yet
- Remote SensingDocument3 pagesRemote SensingVinu JohnNo ratings yet
- Irjet V2i3352 PDFDocument4 pagesIrjet V2i3352 PDFPankaj RaibagkarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Lidar Technology: Presented By-Rahul Sarnagat M.TechDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Lidar Technology: Presented By-Rahul Sarnagat M.TechMandala pavan KalyanNo ratings yet
- LIDAR: Lighting The Way: BackgroundDocument6 pagesLIDAR: Lighting The Way: BackgroundMuhammad Art'DianNo ratings yet
- Pittmanetal2013 LidarApplications ChpterDocument31 pagesPittmanetal2013 LidarApplications ChpterIoana PavelNo ratings yet
- Applications of Digital Terrain Models in Environmental ManagementDocument3 pagesApplications of Digital Terrain Models in Environmental Managementmaulanaibrau2No ratings yet
- Lidar Exam PreparationDocument8 pagesLidar Exam Preparationsomnathmandal89100% (1)
- Light Detection and Ranging LIDAR An Emerging ToolDocument8 pagesLight Detection and Ranging LIDAR An Emerging ToolIoana PavelNo ratings yet
- 2012-Jaboyedoffetal Uzyte W LidarzeDocument25 pages2012-Jaboyedoffetal Uzyte W LidarzePiotr KiełbowiczNo ratings yet
- Applsci 12 06387 With CoverDocument36 pagesApplsci 12 06387 With Coversid202pkNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0034425720304752 MainDocument17 pages1 s2.0 S0034425720304752 MainVolodymyr TarnavskyyNo ratings yet
- RS Applications and Short Notes PDFDocument4 pagesRS Applications and Short Notes PDFEftikarNo ratings yet
- Random Forest Classification For Mangrove Land Cover Mapping Using Landsat 5 TM and Alos Palsar ImageriesDocument7 pagesRandom Forest Classification For Mangrove Land Cover Mapping Using Landsat 5 TM and Alos Palsar ImageriesIkki PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Lidar Dem Data For Flood Mapping and Assessment Opportunities Andchallenges A Review 2469 4134 1000211Document5 pagesLidar Dem Data For Flood Mapping and Assessment Opportunities Andchallenges A Review 2469 4134 1000211SamuelNo ratings yet
- ENC222-0375 - 2020 - BIKENDI - JUMA - HUDNUT - Final WriteUPDocument14 pagesENC222-0375 - 2020 - BIKENDI - JUMA - HUDNUT - Final WriteUPenochleshanNo ratings yet
- Presenation (Redefense)Document50 pagesPresenation (Redefense)Razel Corin ElegoresNo ratings yet
- C - 10 Integration of Bathymetric and Topographic Lidar - A Preliminary - InvestigationDocument6 pagesC - 10 Integration of Bathymetric and Topographic Lidar - A Preliminary - InvestigationZannatul NayemaNo ratings yet
- GIS Application in Watershed ManagementDocument7 pagesGIS Application in Watershed Managementjafar cad100% (1)
- 2006.LIDAR Forest Inventory With Single-TreeDocument8 pages2006.LIDAR Forest Inventory With Single-TreeIoana VizireanuNo ratings yet
- IRRI Annual Report 1993-1994Document104 pagesIRRI Annual Report 1993-1994CPS_IRRINo ratings yet
- Water Resources EngineeringDocument22 pagesWater Resources EngineeringBethel Princess Flores100% (1)
- Bengal Florican (Houbaropsis Bengalensis)Document19 pagesBengal Florican (Houbaropsis Bengalensis)effaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 1st Summativem1-M2Document2 pagesScience 7 1st Summativem1-M2Melannie MagalongNo ratings yet
- Lagerstroemia SpeciosaDocument3 pagesLagerstroemia SpeciosaslyothersNo ratings yet
- Periodic Reporting Exercise On The Application of The World Heritage Convention Section II: State of Conservation of Specific World Heritage PropertiesDocument27 pagesPeriodic Reporting Exercise On The Application of The World Heritage Convention Section II: State of Conservation of Specific World Heritage PropertiesAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Mohan, Et Al - Design and Construction Considerations For Wetland Restoration Using Dredged MaterialDocument14 pages5 - Mohan, Et Al - Design and Construction Considerations For Wetland Restoration Using Dredged MaterialsiskaapNo ratings yet
- BIO 105 Syllabus Fall 2008Document7 pagesBIO 105 Syllabus Fall 2008DrPearcy100% (1)
- Claremont Courier 7.5.13Document36 pagesClaremont Courier 7.5.13Claremont CourierNo ratings yet
- Running A MuseumTrainers ManualDocument91 pagesRunning A MuseumTrainers ManualvgoeckeNo ratings yet
- Gracel'S Enterprises: General SpecificationsDocument17 pagesGracel'S Enterprises: General SpecificationsRhanie Nitsuga GnoldubatNo ratings yet
- Brittany Turner ResumeDocument2 pagesBrittany Turner ResumeBrittany TurnerNo ratings yet
- Endangered Animals: by Sai Swananthra 8BDocument7 pagesEndangered Animals: by Sai Swananthra 8BswanNo ratings yet
- IFC GoodPracticeHandbook CumulativeImpactAssessment PDFDocument102 pagesIFC GoodPracticeHandbook CumulativeImpactAssessment PDFSiharath PhoummixayNo ratings yet
- DepEd K To 12 Education For Sustainable DevelopmentDocument29 pagesDepEd K To 12 Education For Sustainable DevelopmentLinda FranciaNo ratings yet
- Year 6 Week 7Document20 pagesYear 6 Week 7suhashini selva rajNo ratings yet
- 01 GoldammerDocument66 pages01 GoldammerGuilherme Moura FagundesNo ratings yet
- Assessing Functions of Movement in A Great Plains Endemic FishDocument21 pagesAssessing Functions of Movement in A Great Plains Endemic FishgagenahNo ratings yet
- Museum Collection Storage - UNESCODocument58 pagesMuseum Collection Storage - UNESCOKent WhiteNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Linear Momentum (Lab Report)Document5 pagesConservation of Linear Momentum (Lab Report)Arseniojakejr FloresNo ratings yet
- Menzies CR 2003 Traditional Ecological Knowledge and NAtural Resource Management University of Nebraska Press PDFDocument281 pagesMenzies CR 2003 Traditional Ecological Knowledge and NAtural Resource Management University of Nebraska Press PDFMara X Haro LunaNo ratings yet
- Environmental LawsDocument19 pagesEnvironmental LawsRichie GarciaNo ratings yet
- Musk DeerDocument1 pageMusk DeerAakansha ChauhanNo ratings yet
- EPA Sediment Remediation GuidanceDocument152 pagesEPA Sediment Remediation GuidanceflyingimamNo ratings yet
- Report Text - Comodo DragonDocument3 pagesReport Text - Comodo Dragonrahmattriatmojo95No ratings yet
- 3 AquaRAPCaura - Ingl S PDFDocument284 pages3 AquaRAPCaura - Ingl S PDFOliver HernadezNo ratings yet
- The Role of Corporation in Achieving Ecological SustainabilityDocument26 pagesThe Role of Corporation in Achieving Ecological Sustainabilityjoshua13110% (1)
- Environmental Law Tr3Document8 pagesEnvironmental Law Tr3rktrajNo ratings yet