Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sewing Tools and Equipment
Sewing Tools and Equipment
Uploaded by
MarthaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sewing Tools and Equipment
Sewing Tools and Equipment
Uploaded by
MarthaCopyright:
Available Formats
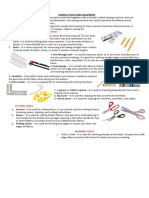
Sewing Tools and Equipment Marking Tools
Different sewing tools used in garment construction. The skillful use of Chalk Pencil/Dressmaking Pencil – this is available in white or pastel
the different sewing tools will help take body measurement and drafting pattern shades.
with accuracy and speed Liquid Marking Pen – comes in two types. One that washes out and on
that fades after 48 hours.
Tailors Chalk – this is essential as a marker use on materials.
Measuring Tools Wax Chalk – this available in black or white and is used for woolen fabrics.
Tracing Wheel – a wheel that produce a dot on the fabric and is suitable
Tape Measure – a flexible measuring device used in taking body
for most type of fabric.
measurements.
Dressmaker’s Carbon Paper – also called dressmaker tracing paper is a
Sewing Gauge – a small ruler with a sliding guide and is about six inches
specially waxed carbon paper that transfer’s the tracing wheel’s markings
long.
to the fabric.
Ruler – measuring instrument 12 inches or even 18 inches, either clear or
solid. Pinning and Sewing Tools
Yard Stick – it is made of smooth, shellack hardwood or metal.
Pincushion – holds the straight pins and needles while working to
L-square – the tailor square is used to transfer measurement to the draft
prevent accidents.
pattern.
Hand Needles – used in making temporary stiches and buttonholes.
Cutting Tools – an instrument that serve well if properly maintained.
Sizes of 7 to 10 are for general hand sewing.
Pinking Shears – this is popular in zigzagging or scalloped edge or for
Sewing Needle Threader – it aids in putting the thread in the needle.
seam finishes,
Thimble – a small hard pitted cup worn for protection on the finger
Cutting Scissors that pushes the needle in sewing.
a. Trimming Scissors – it is 3-4 inches long. It is used for trimmings, Materials
clipping threads and snipping slashes.
Fabric – is the clothing in making garments.
b. Embroidery Scissors – it has 4-5 inches finely tapered blades. Both
Thread – is used in assembling or constructing the parts of the garments.
points are sharp for use in working with the details.
c. Buttonhole Scissors – this is intended for making buttonholes. Types of Sewing Machines
Thread Clippers Lockstitch Sewing Machine – this is usually used in homes and sometimes
in school. This is also called ‘Domestic Sewing Machine’.
Seam Ripper – are specifically designed for ripping stiches seams, either
Hi-speed Sewing Machine – this is sometimes called =,’Straight Stitching
because of an error or during alteration.
Machine’.
Rotary Cutter and Mat – it is an adaption of the giant rotary used by the
Over Edging Machine – other companies call it ‘small machine’. It finishes
garment industry.
the raw edges of the pattern for construction.
Embroidery Machines – this is used in making fancy stiches and in making 13. Belt – connects the balance wheel to drive wheel.
different kinds of embroidery stiches on fabrics. 14. Stop Motion Screw – hinders moving when loosened and starts.
Buttonhole Machine – this is used in making buttonholes on garments.
Parts of Sewing Machine:
Button Attachment Machine – this is used in attaching buttons to the
garments. Parts of the sewing machine under the bed
Double Needle Machine – this is used in the construction of different
1. Feed Dog – moves the fabric while sewing.
kinds of clothing especially for the inseam, out seam, and side seam.
2. Throat Plate – is the windows of the feed dog and it is where the
Bar tacking Machine – this is used in reinforcing the opening and closing
bobbin thread come out.
pockets.
3. Slide Plate – is a movable plate that covers the shuttle and bobbin
Two Major Parts of the Lockstitch Sewing Machine case.
4. Shuttle – holds the bobbin case while sewing.
The two major parts of sewing machine are the upper and the lower parts.
5. Bobbin – is a metal spool for winding thread.
The upper parts are composed of. 6. Bobbin Case – holds the bobbin.
1. Head – is the complete sewing machine without the cabinet stand. Lower Parts of Sewing Machine
2. Arm – is the curve part of the head containing mechanism for operating
The lower parts of the sewing machine are the cabinet and the stand. The
the needle.
cabinet has drawers and screw on the hinges for the attachment of the head. The
3. Bed – is the flat portion of the machine and beneath is the feed dog
following are the lower parts of the sewing machine and their uses:
where it is mounted.
1. Band Wheel – leads the balance wheel through the belt connection.
Parts of the Sewing Machine in the Arm
2. Band Wheel Cranks – moves the band wheel.
Upper parts of sewing machine 3. Pitman Rod – holds the treadle to band wheel crank.
4. Belt Guide – hold the belt to its place.
1. Spoon Pin – is the thread holder. 5. Belt Shifter – removes the belt from the wheel.
2. Thread Guide – keeps the thread in position. 6. Dress Guard – protects the dress from the wheel.
3. Thread Take Up Lever – releases the thread and interlocks with the 7. Treadle – is where the feet are stationed to drive the band wheel through
bobbin thread. the pitman rod.
4. Presser Bar Lifter – moves the presser foot. 8. Legs – support the cabinet of the machine.
5. Tension – controls the looseness and tightness of stiches. 9. Cabinet – holds the head of the machine by interlocking screw on the
6. Needle Bar – holds the needle in place. hinges.
7. Needle Clamp – holds and tightens the needle.
8. Presser Foot – holds the fabric.
9. Needle – is a slander tool attached in the needle clamp used for sewing.
10. Bobbin Winder – controls the bobbin while winding thread.
11. Stitch Regulator – checks the length of the stitches.
12. Balance Wheel – sets the mechanism in motion.
You might also like
- Third Periodical Test in DressmakingDocument3 pagesThird Periodical Test in DressmakingJavan Ferry86% (22)
- Tailoring: Training ManualDocument42 pagesTailoring: Training ManualMuhammad Tayyab Lodhi100% (2)
- Different Types of StitchesDocument13 pagesDifferent Types of Stitcheshabibitltd100% (5)
- Pointers in Tle 7 - Q2Document3 pagesPointers in Tle 7 - Q2Margaret GonzalesNo ratings yet
- LessonDocument4 pagesLessonRonie CerinoNo ratings yet
- Sewing Tools and EquipmentDocument4 pagesSewing Tools and Equipmentcarlo100% (1)
- Project in TLE - 7Document15 pagesProject in TLE - 7Maria Angela DebuqueNo ratings yet
- TLE6.Sewing Tools and MaterialsDocument8 pagesTLE6.Sewing Tools and MaterialsEmiaj Mendoza LeunamNo ratings yet
- Students Notes - AFD - I Year - 02 - Tools & Equipment Used in Garment MakingDocument8 pagesStudents Notes - AFD - I Year - 02 - Tools & Equipment Used in Garment Makingmaya_muth100% (1)
- Sewing 2Document3 pagesSewing 2Hazel Joy BufeteNo ratings yet
- Dtressmaking Lesson 1.Document16 pagesDtressmaking Lesson 1.Angel FancobilaNo ratings yet
- Dressmaking Module 1 2Document11 pagesDressmaking Module 1 2glassy kimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Use of Sewing Tools: Learning OutcomesDocument11 pagesLesson 1: Use of Sewing Tools: Learning OutcomesMayaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 5Document8 pagesLesson Plan 5Lovely HerreraNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Sewing Tools and EquipmentDocument21 pagesWeek 1 Sewing Tools and EquipmentReynalyn LaderaNo ratings yet
- Tle-He-Dressmaking: Seven / Eight ThreeDocument4 pagesTle-He-Dressmaking: Seven / Eight ThreeCynthia TulopNo ratings yet
- 1.2 DressmakingDocument42 pages1.2 Dressmakinggundam100% (1)
- TLE 8 Q2 TLP1 Concept NotesDocument1 pageTLE 8 Q2 TLP1 Concept NotesnoonecaresaboutflochNo ratings yet
- Basic Sewing SuppliesDocument4 pagesBasic Sewing SuppliesFrancia LacruaNo ratings yet
- Technical Vocational Education Identifying Hand Tools and Parts of Sewing MachineDocument33 pagesTechnical Vocational Education Identifying Hand Tools and Parts of Sewing MachineJohn Carlo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- DRESSMAKINGDocument4 pagesDRESSMAKINGJasmine EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Sewing Tools and EquipmentDocument8 pagesSewing Tools and EquipmentChareLyn CaronggayNo ratings yet
- Dressmaking - JessaDocument28 pagesDressmaking - JessaJessa CañadaNo ratings yet
- DressmakingTAiloring8 Lecture P1Document43 pagesDressmakingTAiloring8 Lecture P1jhonruzzelqNo ratings yet
- Profee06 Chap4Document11 pagesProfee06 Chap4Angeline PaligsaNo ratings yet
- W2-Prepares Feasible and Practical BudgetDocument15 pagesW2-Prepares Feasible and Practical Budgetalfredo pintoNo ratings yet
- SEWING TOOLS and EQUIPMENTDocument4 pagesSEWING TOOLS and EQUIPMENTNeil Francis Yucot ValmoresNo ratings yet
- TLE G 78 - Module 2.dressmaking Week 2 USE OF SEWING TOOLSDocument17 pagesTLE G 78 - Module 2.dressmaking Week 2 USE OF SEWING TOOLSKathlyne JhayneNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Tools and Materials Needed in SewingDocument8 pagesModule 1 Tools and Materials Needed in SewingMayeth Silva Gonzales100% (1)
- MODULE1 G7-8 DRESSMAKING ManaoagNHSDocument10 pagesMODULE1 G7-8 DRESSMAKING ManaoagNHSmichael segundoNo ratings yet
- SewingDocument8 pagesSewingRyan Jeffrey Quinto FabilaneNo ratings yet
- CLMD4A DressmakingG7 8Document23 pagesCLMD4A DressmakingG7 8Ana Marie Frane LptNo ratings yet
- Use of Sewing ToolsDocument85 pagesUse of Sewing ToolsReymond G. Balilu100% (1)
- DressmakingDocument40 pagesDressmakingMarian Valdez FernandoNo ratings yet
- CLMD4A DressmakingG8 FinalDocument30 pagesCLMD4A DressmakingG8 FinalHJ HJNo ratings yet
- Pre TestDocument13 pagesPre TestVince AzaresNo ratings yet
- Dressmaking 7 - 8 CompleteDocument25 pagesDressmaking 7 - 8 CompleteGina de OcampoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Use of Sewing Tools: Learning OutcomesDocument52 pagesLesson 1: Use of Sewing Tools: Learning OutcomesSophie De VillaNo ratings yet
- Sewing Tools and Equipment: Let's DefineDocument7 pagesSewing Tools and Equipment: Let's DefineluisaNo ratings yet
- DRESSMAKING LearnersDocument10 pagesDRESSMAKING LearnerspurisophiamarieNo ratings yet
- Use of Sewing ToolsDocument13 pagesUse of Sewing ToolsBoncodin ElaineNo ratings yet
- Common Competency - LO 1Document12 pagesCommon Competency - LO 1Michelle B. DelmonteNo ratings yet
- Tools and Materials in SewingDocument30 pagesTools and Materials in SewingMariel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Grade 7/8 Dressmaking Tools & MaterialsDocument107 pagesGrade 7/8 Dressmaking Tools & MaterialsMari Flor OrnidoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Dressmaking 8Document20 pagesWeek 1 Dressmaking 8Lovely JavierNo ratings yet
- Use of Sewing ToolsDocument68 pagesUse of Sewing ToolsAnimeLover ChannelNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Sewing Tools and EquipmentDocument12 pagesModule 6 Sewing Tools and EquipmentMichelle DoctorNo ratings yet
- GFD 1 NotesDocument17 pagesGFD 1 NotesLorebelle HinloNo ratings yet
- GFD 1 - Notes Familiarizing Dressmaking ToolsDocument7 pagesGFD 1 - Notes Familiarizing Dressmaking ToolsLorebelle HinloNo ratings yet
- SewingtoolsandequipmentsDocument3 pagesSewingtoolsandequipmentsapi-247772348No ratings yet
- Tailoring Tools and Equipment Use in Actual WorkDocument13 pagesTailoring Tools and Equipment Use in Actual Workcaseyjuliet20No ratings yet
- Basic Clothing Construction ToolsDocument8 pagesBasic Clothing Construction ToolsjessicadimailigNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Sewing MachineDocument13 pagesDifferent Types of Sewing MachineLeny Marie Tena ParcoNo ratings yet
- Dressmaking Module 1Document10 pagesDressmaking Module 1Jessica VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Sewing ToolsDocument40 pagesSewing ToolsCARMELLET LALASNo ratings yet
- Textiles EquipmeDocument4 pagesTextiles Equipme21ap040410No ratings yet
- Sewing Tools TLE 7and 8Document12 pagesSewing Tools TLE 7and 8Naris MarinoNo ratings yet
- Sewing Tools and Equipment and Their UsesDocument48 pagesSewing Tools and Equipment and Their Usesirene gniloNo ratings yet
- Lo1 DressmakingDocument51 pagesLo1 DressmakingRachel Hershe Israel-Flororita SerranoNo ratings yet
- Project IN T.L.E: Name:Keivn Bryan C. Malana Grade/Section:VII-J.G Villa Teacher:Mrs. Daisy VillafuerteDocument11 pagesProject IN T.L.E: Name:Keivn Bryan C. Malana Grade/Section:VII-J.G Villa Teacher:Mrs. Daisy VillafuerteKevin MalanaNo ratings yet
- 3 Beautiful Bags: Exclusive extract from the forthcoming A Bag for All ReasonsFrom Everand3 Beautiful Bags: Exclusive extract from the forthcoming A Bag for All ReasonsNo ratings yet
- Nautical Quilts: 12 Stitched and Quilted Projects Celebrating the SeaFrom EverandNautical Quilts: 12 Stitched and Quilted Projects Celebrating the SeaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- England Birthplace of Shakespeare and The Beatles Is A Country Bordering The British Isles Bordering Scotland and WalesDocument4 pagesEngland Birthplace of Shakespeare and The Beatles Is A Country Bordering The British Isles Bordering Scotland and WalesMarthaNo ratings yet
- Sewing Tools and Equipment 2Document1 pageSewing Tools and Equipment 2MarthaNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesPlate TectonicsMarthaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Finance and Financial ManagementDocument1 pageFundamentals of Finance and Financial ManagementMarthaNo ratings yet
- Principles of DesignDocument3 pagesPrinciples of DesignMarthaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document2 pagesModule 1MarthaNo ratings yet
- The Marketing Plan and The Marketing MixDocument5 pagesThe Marketing Plan and The Marketing MixMarthaNo ratings yet
- Famous Business People With Different Kinds of InvestmentDocument1 pageFamous Business People With Different Kinds of InvestmentMarthaNo ratings yet
- TOR - Sewing Machine MaintenanceDocument3 pagesTOR - Sewing Machine MaintenanceJe-ann H. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- SIRUBADocument2 pagesSIRUBAJorge CastelonNo ratings yet
- Singer 591D200, D300, C200, C300 Operator's GuideDocument19 pagesSinger 591D200, D300, C200, C300 Operator's GuideHilene Camacho-PhillipsNo ratings yet
- PT Crevis Tex Jaya Profile 2019 (2019.02.19)Document11 pagesPT Crevis Tex Jaya Profile 2019 (2019.02.19)Yandi RaifaNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLesson PlanAlejandra TorrenuevaNo ratings yet
- Pfaff Select Line 2.0 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument44 pagesPfaff Select Line 2.0 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Garment Manufacturing (TE-2114)Document67 pagesIntroduction To Garment Manufacturing (TE-2114)Hammad MustafaNo ratings yet
- Footwear Engineering-I: CuttingDocument20 pagesFootwear Engineering-I: CuttingBrishtyNo ratings yet
- Elect ConsumptionDocument20 pagesElect ConsumptionSupriya NandaNo ratings yet
- Kenmore 1203 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument34 pagesKenmore 1203 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- 7 8 DressmakingDocument3 pages7 8 DressmakingDulce Mea CueNo ratings yet
- Single Needle Lock Stitch MachineDocument8 pagesSingle Needle Lock Stitch Machinereyadonly123No ratings yet
- Semi DetailedDocument17 pagesSemi DetailedNathalie Jane Tabigne CincoNo ratings yet
- Singer 29K InstructionsDocument13 pagesSinger 29K Instructionsjokin mendiolaNo ratings yet
- 4th Exam Tle DressmakingDocument2 pages4th Exam Tle DressmakingCashmir Mabaquiao JoquinoNo ratings yet
- GRADE 9 HANDICRAFT Module 5Document10 pagesGRADE 9 HANDICRAFT Module 5Van ImperialNo ratings yet
- Seam Puckering and Its Types: Submitted By: Prakriti Gorai (B F T / 1 9 / 7 5) Semester 4Document9 pagesSeam Puckering and Its Types: Submitted By: Prakriti Gorai (B F T / 1 9 / 7 5) Semester 4PrakritiNo ratings yet
- Pre Test: Accomplishment Report June 2, 2020Document4 pagesPre Test: Accomplishment Report June 2, 2020JeffreyNo ratings yet
- Operation Breakdown & Operation Bullettin of Various Styles of Garments.....Document22 pagesOperation Breakdown & Operation Bullettin of Various Styles of Garments.....Sundhar Avinaash100% (1)
- Q4 - W1 W2 DressmakingDocument8 pagesQ4 - W1 W2 DressmakingShiela Mae ABELLONNo ratings yet
- Parts List: Ool Ssso-7Document32 pagesParts List: Ool Ssso-7Chooper BikeNo ratings yet
- EuroPro Intelli Sew 9136C Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument68 pagesEuroPro Intelli Sew 9136C Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- Manuel PFAFF 114Document36 pagesManuel PFAFF 114renardnathanNo ratings yet
- MBA Internship ReportDocument47 pagesMBA Internship Reportডক্টর স্ট্রেইঞ্জ100% (1)
- Usha Janome Dream Maker 30 ManualDocument44 pagesUsha Janome Dream Maker 30 ManualprinceejNo ratings yet
- Final Module Grade 8 T L e DressmakingDocument50 pagesFinal Module Grade 8 T L e DressmakingZahara SantiNo ratings yet
- Husqvarna/Viking Victoria Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument42 pagesHusqvarna/Viking Victoria Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet