Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Engineering Economics and Finacial Management (HUM 3051) Jul 2022
Engineering Economics and Finacial Management (HUM 3051) Jul 2022
Uploaded by
uday KiranCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- M&a Case Study SolutionDocument3 pagesM&a Case Study SolutionSoufiane EddianiNo ratings yet
- Test 14Document7 pagesTest 14Zoloft Zithromax ProzacNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment - 1Document2 pagesHome Assignment - 1Pankaj kumarNo ratings yet
- solution-CEL 779 Abid HasanDocument36 pagessolution-CEL 779 Abid HasanM M100% (2)
- Seem 2440A/B - Engineering Economics First Term (2011 - 2012)Document3 pagesSeem 2440A/B - Engineering Economics First Term (2011 - 2012)Sun KelvinNo ratings yet
- Quality Manager Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesQuality Manager Job DescriptionKhalid Mahmood100% (2)
- Engineering Economics and Finacial Management (HUM 3051)Document5 pagesEngineering Economics and Finacial Management (HUM 3051)uday KiranNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics Tutorial Chapter Five (1) - 2Document4 pagesEngineering Economics Tutorial Chapter Five (1) - 2saugat pandeyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy AssignmentDocument1 pageEngineering Economy Assignmentprateekagrawal812004No ratings yet
- Group AssignmentDocument5 pagesGroup AssignmentRoberaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics Assignment 2Document6 pagesEngineering Economics Assignment 2balkrishna7621No ratings yet
- 2nd Assignment 2021Document3 pages2nd Assignment 2021No NameNo ratings yet
- Break-Even Analysis and New Design Economics - Ii: (Draw Profit Volume Diagram)Document7 pagesBreak-Even Analysis and New Design Economics - Ii: (Draw Profit Volume Diagram)Garima PalNo ratings yet
- MEC210 Assignment#4 241Document3 pagesMEC210 Assignment#4 241Mohamed Gamal100% (1)
- Assignment 2 2015Document2 pagesAssignment 2 2015marryam nawazNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Problem SheetDocument9 pagesUnit 2 Problem SheetTejas ArgulewarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics: - Return. B.: Proceed. CDocument3 pagesEngineering Economics: - Return. B.: Proceed. CNSaiRohanNo ratings yet
- Previous Assignment 2Document2 pagesPrevious Assignment 2marryam nawazNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet-Ii: Dollar ($) Project A Project B Project CDocument5 pagesWork Sheet-Ii: Dollar ($) Project A Project B Project Crobel popNo ratings yet
- Groups Assignment EcoDocument4 pagesGroups Assignment Ecorobel pop100% (1)
- Tutorial 8 Time Value Money 2021Document8 pagesTutorial 8 Time Value Money 2021Hai Liang OngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Replacement AnalysisDocument29 pagesChapter 5 - Replacement AnalysisUpendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Terminal - FA17 Dr. FarihaDocument2 pagesTerminal - FA17 Dr. FarihaHashmi AshmalNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument9 pagesProblem SetJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- Economics Final Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesEconomics Final Exam SolutionsPower GirlsNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument5 pagesQuestion BankAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- MG2451 ModelDocument2 pagesMG2451 ModelchandrasekarcncetNo ratings yet
- Sheet 7Document2 pagesSheet 7Amany SobhyNo ratings yet
- Project Appraisal TutorialDocument4 pagesProject Appraisal TutorialRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Eefm ProblemsDocument4 pagesEefm ProblemsChitrala DhruvNo ratings yet
- WKT MFGDocument4 pagesWKT MFGGODNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy Jan 2014Document2 pagesEngineering Economy Jan 2014Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4sissy.he.7No ratings yet
- SM 300 Ee Semester Q&aDocument11 pagesSM 300 Ee Semester Q&aAnushka DasNo ratings yet
- Lease Demo SolutionDocument6 pagesLease Demo SolutionToufiqul IslamNo ratings yet
- Capital Expenditure DecisionsDocument2 pagesCapital Expenditure DecisionsSundarNo ratings yet
- Decisions.: Examination Control Division M/IiDocument20 pagesDecisions.: Examination Control Division M/IiPrabin123No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Economic Evaluation of AlternativesDocument21 pagesChapter 3 - Economic Evaluation of Alternativessam guptNo ratings yet
- Sums On Project AnalysisDocument26 pagesSums On Project AnalysisAlbert Thomas80% (5)
- ABPL90030: Project Evaluation Worksheet 2 - EUAC Model For Project EvaluationDocument1 pageABPL90030: Project Evaluation Worksheet 2 - EUAC Model For Project EvaluationMohamed MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document2 pagesAssignment 5Chalermchai New KawinNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Economics For EngineersDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank - Economics For EngineersAnurag AnandNo ratings yet
- Week 12 HomeworkDocument2 pagesWeek 12 HomeworkMichael Clark0% (1)
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Parth ShahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 1 (UNIT-1)Document5 pagesTutorial Sheet - 1 (UNIT-1)Frederick DugayNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument3 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (Economics Exercises)Document5 pagesAssignment 5 (Economics Exercises)OlyvianurmaharaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 CB Problems - IDocument11 pagesChapter 4 CB Problems - IRoy YadavNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentPrashanthRameshNo ratings yet
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2016 Semester End Main ExaminationsDocument3 pagesBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2016 Semester End Main Examinationshemavathi jayNo ratings yet
- Session 8 & 9 HWDocument9 pagesSession 8 & 9 HWElisten DabreoNo ratings yet
- Documents - MX - FM Questions MsDocument7 pagesDocuments - MX - FM Questions MsgopalNo ratings yet
- Skkk4173 Assignment #4 2016Document4 pagesSkkk4173 Assignment #4 2016Fhairna BaharulraziNo ratings yet
- Pteroleum Economy Exercise - DepreciationDocument31 pagesPteroleum Economy Exercise - Depreciationshaziera omarNo ratings yet
- CH 13b BASICS OF CAPITAL BUDGETINGDocument2 pagesCH 13b BASICS OF CAPITAL BUDGETINGSadia YasmeenNo ratings yet
- Mba Executive - I Year 2 Semester / January 2021Document2 pagesMba Executive - I Year 2 Semester / January 2021gaurav jainNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting PAPERDocument7 pagesManagement Accounting PAPERtemailggNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-Income Statement - Break-Even Modified PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial 2-Income Statement - Break-Even Modified PDFKhiren MenonNo ratings yet
- Or Au QP 60 Pages-1-10Document1 pageOr Au QP 60 Pages-1-10_hrithik_rkNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Equipment EconomicsDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 Equipment EconomicsJohnny LimNo ratings yet
- 11CH8DHSS2Document4 pages11CH8DHSS2Pranit SonthaliaNo ratings yet
- HTV International Pvt. Ltd.Document1 pageHTV International Pvt. Ltd.Raj GuptaNo ratings yet
- State Energy Efficiency Index 2022Document114 pagesState Energy Efficiency Index 2022satyamsantoshmajhiNo ratings yet
- Anas Aly - Translator - Content WriterDocument2 pagesAnas Aly - Translator - Content WriterAnas EbrahimNo ratings yet
- ONGC MM - Manual+28 - 04 - 2015Document359 pagesONGC MM - Manual+28 - 04 - 2015raviNo ratings yet
- Economics of Strategy: Sixth EditionDocument45 pagesEconomics of Strategy: Sixth EditionVanessa HartonoNo ratings yet
- Satain Bhat: Equipment & Stores Manager (Hospital Operations) Profile SummaryDocument2 pagesSatain Bhat: Equipment & Stores Manager (Hospital Operations) Profile SummarytinkuNo ratings yet
- BCM Through BRFDocument35 pagesBCM Through BRFkunariefNo ratings yet
- Flight Invoice A2308021216350Document2 pagesFlight Invoice A2308021216350helmy ahmedNo ratings yet
- Frugal Resources Testimonials - DocDocument5 pagesFrugal Resources Testimonials - DocØmïïNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Planning - AwitinDocument2 pagesLesson 6 Planning - AwitinRio AwitinNo ratings yet
- Trường Đại Học Kinh Tế - Đại Học Đà Nẵng Khoa Quản Trị Kinh DoanhDocument42 pagesTrường Đại Học Kinh Tế - Đại Học Đà Nẵng Khoa Quản Trị Kinh DoanhBach NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bypassing Safety Control Safety MomentsDocument10 pagesBypassing Safety Control Safety MomentsCHRISTOPHER WEALTHNo ratings yet
- Afework ProposalDocument33 pagesAfework ProposalchuchuNo ratings yet
- 1 ACI Philippines, Inc. vs. Coquia - UnlockedDocument14 pages1 ACI Philippines, Inc. vs. Coquia - Unlockedmartin vincentNo ratings yet
- SDE-Individual AssignmentDocument3 pagesSDE-Individual AssignmentParagNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Dealing With Management and Operation IssuesDocument17 pagesStrategic Management: Dealing With Management and Operation IssuesSHARMAINE CORPUZ MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Accounting For Decision Making: Unit-Iii Accounting Principles & ConventionsDocument24 pagesAccounting For Decision Making: Unit-Iii Accounting Principles & ConventionsVishal ChandakNo ratings yet
- Perforaciones para Las 5 Celdas en ShelterDocument19 pagesPerforaciones para Las 5 Celdas en Sheltermichael carpinteroNo ratings yet
- How To Refine Order BlockDocument20 pagesHow To Refine Order Blockriteshthakur3690No ratings yet
- Pnjdent: Prudent Advisory Services LTDDocument20 pagesPnjdent: Prudent Advisory Services LTDDasari PrabodhNo ratings yet
- Uy 154429Document2 pagesUy 154429Matheus MassuiaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Corporate Objectives, Strategy and StructureDocument28 pagesTopic 1 - Corporate Objectives, Strategy and StructureJoseph VillartaNo ratings yet
- Module I - Ratio Proportion & Percentgae Question SheetDocument2 pagesModule I - Ratio Proportion & Percentgae Question SheetyashNo ratings yet
- Case Study #9 - Bruner 31 Debt PoliciesDocument6 pagesCase Study #9 - Bruner 31 Debt PoliciesMarie CuvNo ratings yet
- Environmental Audit Manual EDITED 29 Nov 2010Document79 pagesEnvironmental Audit Manual EDITED 29 Nov 2010JocelynKongSingCheah100% (1)
- The Dow Theory (Part 1) : Technical AnalysisDocument24 pagesThe Dow Theory (Part 1) : Technical AnalysisHarsh MisraNo ratings yet
- 04.theories of SupplyDocument10 pages04.theories of SupplyYusril Izha MahendraNo ratings yet
- Evolution of ManagementDocument17 pagesEvolution of ManagementJesta ZillaNo ratings yet
Engineering Economics and Finacial Management (HUM 3051) Jul 2022
Engineering Economics and Finacial Management (HUM 3051) Jul 2022
Uploaded by
uday KiranOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Economics and Finacial Management (HUM 3051) Jul 2022
Engineering Economics and Finacial Management (HUM 3051) Jul 2022
Uploaded by
uday KiranCopyright:
Available Formats
Reg. No.
VI SEMESTER B.TECH. (COMMON TO ALL)
END SEMESTER MAKE-UP EXAMINATIONS- JULY 2022
SUBJECT: ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND FINANCIAL
MANAGEMENT [HUM 3051]
REVISED CREDIT SYSTEM
Time: 3 hours MAX. MARKS: 50
Instructions to Candidates:
Answer ALL the questions.
Missing data may be suitably assumed.
Interest factor table is provided in the last page (else use formulae).
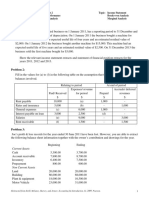
1. Calculate the Current ratio and Quick asset ratio from the following parameters. (04)
Particulars Amount
Sundry debtors 400000
Stock 1600000
Marketable security 80000
Cash 12000
Prepaid expenses 40000
Bills payable 80000
Debenture 200000
Outstanding expenses 260000
2. A blast furnace for a metallurgical operation was purchased for Rs. 300,000. An amount of Rs. (03)
50,000 more was spent on its installation and commissioning. The estimated residual value after
10 years was Rs. 70,000
(a) Calculate the Depreciation charge
(b) Determine the amount of Depreciation at the end of 6 years after the purchase of the furnace.
3. A person buys a machine by making a down payment of Rs.10,000 and the balance in (03)
payments of Rs.8,000 per year for five years starting three years from now at an interest
rate of 10% per annum. Determine the Cost of the machine.
4. A person is planning to withdraw Rs.5,000 in the tenth year from now and then onwards (04)
he increases his withdrawal amount by Rs.250 per year till the end of 15th year. For these
expenses, he is planning to invest an equal amount for eight years starting from the end
(HUM 3051) Page 1 of 6
of first year. Find the equal amounts that he has to save using an interest rate of 10% per
annum.
5. A company is planning to expand its present business activity. It has two alternatives for the (03)
expansion programme and the corresponding cash flows are tabulated below. At MARR = 10%,
suggest the best alternative to the company. Use ROR method.
n E1 E2
0 -$ 2,000 -$ 3,000
1 1,000 4,000
2 1,000
3 1,000
6. An 8-year-old asset may be replaced with either of the two new assets. Current data for each (03)
alternative are given below, using the Cash flow approach and interest rate of 12% per year.
Determine the best course of action.
Course of action Current asset (Rs) Challenger 1 (Rs) Challenger 2
(Rs)
First cost - 30000 54000
Defender trade - 10500 7500
Annual cost 9000 4500 3600
Salvage value 1500 3000 1500
Life, years 5 yr 5 yr 5 yr
7. A plant engineer is considering two types of solar water heating systems: (04)
Model A Model B
Initial cost $7000 $10000
Annual savings $700 $1000
Annual Maintenance $100 $50
Expected life 20 years 20 years
Salvage value $ 400 $ 500
a. Find ROR of each system.
(HUM 3051) Page 2 of 6
b. If MARR is 12%, what will be your recommendation?
8. A sheltered workshop requires a lift truck to handle pallets for a new contract. A lift truck can be (03)
purchased for Rs.270,000. Annual insurance costs are 3% of the purchase price, payable on the
first of each year. An equivalent truck can be rented Rs. 15,000 per month payable at the end of
each month. Operating costs are same for both alternatives. For what minimum number of months
must a purchased truck be used on the contract to make purchasing more attractive than leasing?
Interest rate is 12% compounded monthly. Assume that the purchased truck has no salvage value.
9. Find the value of C for the data given below at i=12%, assuming equivalence between (03)
Deposits and Withdrawals.
Period (n) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Deposits (Rs) 1000 800 600 400 200
Withdrawals(Rs) C 2C 3C 4C 5C
10. For equipment that has a first cost of $10,000 and the estimated operating costs and (04)
year-end salvage values are shown below. Determine the Economic service life at 10%
per year.
Year Operating Cost $(Year) Salvage Value $
1 -1,000 7,000
2 -1,200 5,000
3 -1,300 4,500
4 -2,000 3,000
5 -3,000 2,000
11. A low-cost non-contact temperature measuring tool may be able to identify rail road car wheels (03)
that are in need of repair long before a costly structural failure occurs. If the tool is bought the
railways would save $25,000 per quarter in the years 1 through 5 and this savings is expected to
increase by $2,500 every quarter in the years 6 through 20. What is the annual savings over the 20
years? Interest rate is 10% per annum compounded quarterly.
12. A series of ten quarterly payments of $1,500 at the rate of 12% per annum compounded (03)
quarterly is equivalent to three semi-annual withdrawals. The withdrawals will start
immediately after the last payment is done. What is the amount of these three payments?
If the three withdrawals are annual from the fourth year, recalculate the amount.
13. A railway track will be used for 15 years. During the construction of the railway track line, either (04)
type A or type B ties may be used. Type A ties have an installed cost of $6 and a 10-year life;
type B will cost $4.50 with a 6-year life. If at the end of 15 years the ties used have a remaining
useful life of at least 4 years they will be used elsewhere for a different project and can fetch a
salvage value of $3 each. Any ties that are taken off after the end of their life or if it is very near
(HUM 3051) Page 3 of 6
to the end of its life to be used elsewhere, then, it can be sold for $0.50 each. Give the most cost
effective plan for the 15 year analysis period using NPW method at 10% interest.
14. To decrease the costs of operating a lock in a large river, a new system of operation is proposed. (03)
The system will cost $650,000 to design and build. It is estimated that it will have to be reworked
every 10 years at a cost of $100,000. In addition, an expenditure of $50,000 will have to be
made at the end of the fifth year for a new type of gear that will not be available until then.
Annual operating costs are expected to be $30,000 for the first 15 years and $35,000 a year
thereafter. Also, there are cyclical maintenance costs, the cycle repeating every 4 years; $1000
End of Year (EOY) 1, $2000 EOY2, $2500 EOY3 and $3000 EOY 4. Compute the capitalized
cost of perpetual service at 10% interest.
15. A machine with 6 years of life was purchased two years ago for Rs.10, 000. Its annual (03)
maintenance cost is Rs.750 and salvage value at the end of its life is Rs.1, 000. Now, a company
is offering a new machine at a cost of Rs.10, 000. Its life is 5 years and its salvage value at the
end of its life is Rs.4, 000. The annual maintenance cost of the new machine is Rs.500. The
company which is supplying the new machine is willing to take the old machine for Rs.6, 500 if
it is replaced by the new machine. Assuming interest rate of 12%, compounded annually, perform
a replacement analysis, and suggest the best course of action.
**************
(HUM 3051) Page 4 of 6
(HUM 3051) Page 5 of 6
(HUM 3051) Page 6 of 6
You might also like
- M&a Case Study SolutionDocument3 pagesM&a Case Study SolutionSoufiane EddianiNo ratings yet
- Test 14Document7 pagesTest 14Zoloft Zithromax ProzacNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment - 1Document2 pagesHome Assignment - 1Pankaj kumarNo ratings yet
- solution-CEL 779 Abid HasanDocument36 pagessolution-CEL 779 Abid HasanM M100% (2)
- Seem 2440A/B - Engineering Economics First Term (2011 - 2012)Document3 pagesSeem 2440A/B - Engineering Economics First Term (2011 - 2012)Sun KelvinNo ratings yet
- Quality Manager Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesQuality Manager Job DescriptionKhalid Mahmood100% (2)
- Engineering Economics and Finacial Management (HUM 3051)Document5 pagesEngineering Economics and Finacial Management (HUM 3051)uday KiranNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics Tutorial Chapter Five (1) - 2Document4 pagesEngineering Economics Tutorial Chapter Five (1) - 2saugat pandeyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy AssignmentDocument1 pageEngineering Economy Assignmentprateekagrawal812004No ratings yet
- Group AssignmentDocument5 pagesGroup AssignmentRoberaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics Assignment 2Document6 pagesEngineering Economics Assignment 2balkrishna7621No ratings yet
- 2nd Assignment 2021Document3 pages2nd Assignment 2021No NameNo ratings yet
- Break-Even Analysis and New Design Economics - Ii: (Draw Profit Volume Diagram)Document7 pagesBreak-Even Analysis and New Design Economics - Ii: (Draw Profit Volume Diagram)Garima PalNo ratings yet
- MEC210 Assignment#4 241Document3 pagesMEC210 Assignment#4 241Mohamed Gamal100% (1)
- Assignment 2 2015Document2 pagesAssignment 2 2015marryam nawazNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Problem SheetDocument9 pagesUnit 2 Problem SheetTejas ArgulewarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics: - Return. B.: Proceed. CDocument3 pagesEngineering Economics: - Return. B.: Proceed. CNSaiRohanNo ratings yet
- Previous Assignment 2Document2 pagesPrevious Assignment 2marryam nawazNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet-Ii: Dollar ($) Project A Project B Project CDocument5 pagesWork Sheet-Ii: Dollar ($) Project A Project B Project Crobel popNo ratings yet
- Groups Assignment EcoDocument4 pagesGroups Assignment Ecorobel pop100% (1)
- Tutorial 8 Time Value Money 2021Document8 pagesTutorial 8 Time Value Money 2021Hai Liang OngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Replacement AnalysisDocument29 pagesChapter 5 - Replacement AnalysisUpendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Terminal - FA17 Dr. FarihaDocument2 pagesTerminal - FA17 Dr. FarihaHashmi AshmalNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument9 pagesProblem SetJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- Economics Final Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesEconomics Final Exam SolutionsPower GirlsNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument5 pagesQuestion BankAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- MG2451 ModelDocument2 pagesMG2451 ModelchandrasekarcncetNo ratings yet
- Sheet 7Document2 pagesSheet 7Amany SobhyNo ratings yet
- Project Appraisal TutorialDocument4 pagesProject Appraisal TutorialRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Eefm ProblemsDocument4 pagesEefm ProblemsChitrala DhruvNo ratings yet
- WKT MFGDocument4 pagesWKT MFGGODNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy Jan 2014Document2 pagesEngineering Economy Jan 2014Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4sissy.he.7No ratings yet
- SM 300 Ee Semester Q&aDocument11 pagesSM 300 Ee Semester Q&aAnushka DasNo ratings yet
- Lease Demo SolutionDocument6 pagesLease Demo SolutionToufiqul IslamNo ratings yet
- Capital Expenditure DecisionsDocument2 pagesCapital Expenditure DecisionsSundarNo ratings yet
- Decisions.: Examination Control Division M/IiDocument20 pagesDecisions.: Examination Control Division M/IiPrabin123No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Economic Evaluation of AlternativesDocument21 pagesChapter 3 - Economic Evaluation of Alternativessam guptNo ratings yet
- Sums On Project AnalysisDocument26 pagesSums On Project AnalysisAlbert Thomas80% (5)
- ABPL90030: Project Evaluation Worksheet 2 - EUAC Model For Project EvaluationDocument1 pageABPL90030: Project Evaluation Worksheet 2 - EUAC Model For Project EvaluationMohamed MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document2 pagesAssignment 5Chalermchai New KawinNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Economics For EngineersDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank - Economics For EngineersAnurag AnandNo ratings yet
- Week 12 HomeworkDocument2 pagesWeek 12 HomeworkMichael Clark0% (1)
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Parth ShahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 1 (UNIT-1)Document5 pagesTutorial Sheet - 1 (UNIT-1)Frederick DugayNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument3 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (Economics Exercises)Document5 pagesAssignment 5 (Economics Exercises)OlyvianurmaharaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 CB Problems - IDocument11 pagesChapter 4 CB Problems - IRoy YadavNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentPrashanthRameshNo ratings yet
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2016 Semester End Main ExaminationsDocument3 pagesBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2016 Semester End Main Examinationshemavathi jayNo ratings yet
- Session 8 & 9 HWDocument9 pagesSession 8 & 9 HWElisten DabreoNo ratings yet
- Documents - MX - FM Questions MsDocument7 pagesDocuments - MX - FM Questions MsgopalNo ratings yet
- Skkk4173 Assignment #4 2016Document4 pagesSkkk4173 Assignment #4 2016Fhairna BaharulraziNo ratings yet
- Pteroleum Economy Exercise - DepreciationDocument31 pagesPteroleum Economy Exercise - Depreciationshaziera omarNo ratings yet
- CH 13b BASICS OF CAPITAL BUDGETINGDocument2 pagesCH 13b BASICS OF CAPITAL BUDGETINGSadia YasmeenNo ratings yet
- Mba Executive - I Year 2 Semester / January 2021Document2 pagesMba Executive - I Year 2 Semester / January 2021gaurav jainNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting PAPERDocument7 pagesManagement Accounting PAPERtemailggNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-Income Statement - Break-Even Modified PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial 2-Income Statement - Break-Even Modified PDFKhiren MenonNo ratings yet
- Or Au QP 60 Pages-1-10Document1 pageOr Au QP 60 Pages-1-10_hrithik_rkNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Equipment EconomicsDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 Equipment EconomicsJohnny LimNo ratings yet
- 11CH8DHSS2Document4 pages11CH8DHSS2Pranit SonthaliaNo ratings yet
- HTV International Pvt. Ltd.Document1 pageHTV International Pvt. Ltd.Raj GuptaNo ratings yet
- State Energy Efficiency Index 2022Document114 pagesState Energy Efficiency Index 2022satyamsantoshmajhiNo ratings yet
- Anas Aly - Translator - Content WriterDocument2 pagesAnas Aly - Translator - Content WriterAnas EbrahimNo ratings yet
- ONGC MM - Manual+28 - 04 - 2015Document359 pagesONGC MM - Manual+28 - 04 - 2015raviNo ratings yet
- Economics of Strategy: Sixth EditionDocument45 pagesEconomics of Strategy: Sixth EditionVanessa HartonoNo ratings yet
- Satain Bhat: Equipment & Stores Manager (Hospital Operations) Profile SummaryDocument2 pagesSatain Bhat: Equipment & Stores Manager (Hospital Operations) Profile SummarytinkuNo ratings yet
- BCM Through BRFDocument35 pagesBCM Through BRFkunariefNo ratings yet
- Flight Invoice A2308021216350Document2 pagesFlight Invoice A2308021216350helmy ahmedNo ratings yet
- Frugal Resources Testimonials - DocDocument5 pagesFrugal Resources Testimonials - DocØmïïNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Planning - AwitinDocument2 pagesLesson 6 Planning - AwitinRio AwitinNo ratings yet
- Trường Đại Học Kinh Tế - Đại Học Đà Nẵng Khoa Quản Trị Kinh DoanhDocument42 pagesTrường Đại Học Kinh Tế - Đại Học Đà Nẵng Khoa Quản Trị Kinh DoanhBach NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bypassing Safety Control Safety MomentsDocument10 pagesBypassing Safety Control Safety MomentsCHRISTOPHER WEALTHNo ratings yet
- Afework ProposalDocument33 pagesAfework ProposalchuchuNo ratings yet
- 1 ACI Philippines, Inc. vs. Coquia - UnlockedDocument14 pages1 ACI Philippines, Inc. vs. Coquia - Unlockedmartin vincentNo ratings yet
- SDE-Individual AssignmentDocument3 pagesSDE-Individual AssignmentParagNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Dealing With Management and Operation IssuesDocument17 pagesStrategic Management: Dealing With Management and Operation IssuesSHARMAINE CORPUZ MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Accounting For Decision Making: Unit-Iii Accounting Principles & ConventionsDocument24 pagesAccounting For Decision Making: Unit-Iii Accounting Principles & ConventionsVishal ChandakNo ratings yet
- Perforaciones para Las 5 Celdas en ShelterDocument19 pagesPerforaciones para Las 5 Celdas en Sheltermichael carpinteroNo ratings yet
- How To Refine Order BlockDocument20 pagesHow To Refine Order Blockriteshthakur3690No ratings yet
- Pnjdent: Prudent Advisory Services LTDDocument20 pagesPnjdent: Prudent Advisory Services LTDDasari PrabodhNo ratings yet
- Uy 154429Document2 pagesUy 154429Matheus MassuiaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Corporate Objectives, Strategy and StructureDocument28 pagesTopic 1 - Corporate Objectives, Strategy and StructureJoseph VillartaNo ratings yet
- Module I - Ratio Proportion & Percentgae Question SheetDocument2 pagesModule I - Ratio Proportion & Percentgae Question SheetyashNo ratings yet
- Case Study #9 - Bruner 31 Debt PoliciesDocument6 pagesCase Study #9 - Bruner 31 Debt PoliciesMarie CuvNo ratings yet
- Environmental Audit Manual EDITED 29 Nov 2010Document79 pagesEnvironmental Audit Manual EDITED 29 Nov 2010JocelynKongSingCheah100% (1)
- The Dow Theory (Part 1) : Technical AnalysisDocument24 pagesThe Dow Theory (Part 1) : Technical AnalysisHarsh MisraNo ratings yet
- 04.theories of SupplyDocument10 pages04.theories of SupplyYusril Izha MahendraNo ratings yet
- Evolution of ManagementDocument17 pagesEvolution of ManagementJesta ZillaNo ratings yet