Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eng Reviewer
Eng Reviewer
Uploaded by
IBN-RASIR II PANDANGAN,0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThis document provides information about project proposals, types of letters, and resume structure and components. It discusses the explicit and implicit information typically included in a project proposal to convince sponsors. It also outlines the typical parts of formal, semi-formal, and informal letters, including salutation, title, body, and complimentary close. Finally, it summarizes the common sections of a resume, such as name, contact information, work history presented chronologically or functionally, education, and references.
Original Description:
Original Title
ENG-REVIEWER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about project proposals, types of letters, and resume structure and components. It discusses the explicit and implicit information typically included in a project proposal to convince sponsors. It also outlines the typical parts of formal, semi-formal, and informal letters, including salutation, title, body, and complimentary close. Finally, it summarizes the common sections of a resume, such as name, contact information, work history presented chronologically or functionally, education, and references.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesEng Reviewer
Eng Reviewer
Uploaded by
IBN-RASIR II PANDANGAN,This document provides information about project proposals, types of letters, and resume structure and components. It discusses the explicit and implicit information typically included in a project proposal to convince sponsors. It also outlines the typical parts of formal, semi-formal, and informal letters, including salutation, title, body, and complimentary close. Finally, it summarizes the common sections of a resume, such as name, contact information, work history presented chronologically or functionally, education, and references.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
EXPLICIT INFORMATION (direct)
directly stated in the text project proposal
fully revealed or expressed
used to convince a sponsor
IMPLICIT INFORMATION (assume) purpose: to solve particular problem or
ideas you need to infer to introduce an opportunity
not openly stated describes how the project is going to be
commenced
Types of claim 2 - 4 pages
to serve as a guide, to get funding, to
CLAIM OF FACT convince people to participate, to serve
assert a piece of legitimate as reference for evaluation
information.
statement is either proved or SOLICITED
disproved requested by business and government
provide evidence agencies
true or false
states main argument supported UNSOLICITED
with sufficient and accurate infos. submitted voluntarily
CLAIM OF VALUE GRANTS
some things are more desirable than asking for financial solicitation
others.
based on judgement and evaluation parts
qualitative assertion
good or bad, beneficial or PROJECT NAME
detrimental catchy name
questions about qualities and values
are usually asked. PROJECT TYPE
general type or kind of project
CLAIM OF POLICY May be INDUSTRIAL,
present a solution to problems ENVIRONMENTAL, INFORMATIVE,
a response to claims of fact TRAINING, SEMINARS
states solutions and plans that are
procedural and organized RATIONALE AND OBJECTIVES
begins with words like should, must, clear what is the problem
and ought to reason why the project must commence
take course of action principles
circumstances and reasons are what you want to accomplish (obj)
clearly stated.
PROJECT OUTLINE
provides an overview.
blueprint or draft of the product
step-by-step procedures
BUDGET PLAN SEMI-FORMAL LETTER
includes the needed materials, between formal and informal letter
budget needed and the source of familiarity and condescending tones
funding. are absent
mood control, politeness, courtesy, and
MONITORING AND EVALUATION deference are expected
determine the realization or success a letter on personal subjects
of the project's objectives.
tools: survey and evaluation forms INFORMAL LETTER
written to relatives, friends, and close
VArious forms of pals.
office correspondence intimacies are shared
slang, abbreviation, colloquial
umbrella word to denote expressions can be accommodated
communication
letters we receive and we send. parts
in formal letters
TYPES: formal, semi-formal, and
SALUTATION - Dear Sir/Madam,
informal letters
TITLE - an idea about the content. Written
in UPPERCASE all or in initial letters only
FORMAL LETTER
BODY - must be orderly presented. Proper
relationship is impersonal
organization and should be strictly formal.
tone is usually very polite
Let your language be direct and precise.
written for official or formal
COMPLIMENTARY CLOSE - Yours truly,
purposes
Sincerely yours, or Truly yours,
basic rules and conventions must be
followed by name and signature of sender.
observed
distinguishing feature: carry two College admission letter
address: sender and recipient
letter of intent
may be indented, modified, fully-
one-page letter required for college and
blocked style
university admission.
briefly discuss his/her intention
STRUCTURE OF FORMAL LETTERS
sender's address
a. PRE-WRITING
Date of origination
determine the program you want to
recipient's designation and address
take and research about it.
salutation
reflect on your purpose, achievements,
title
future goals
message or the body
complimentary close decide on a format (full-block,
signature indented, etc)
sender's name
Designation (if need) b. WRITING
Heading, date, and inside address
complete address + zip code
Date (should be spelled out)
inside address CHRONOLOGICAL
-name of college/university admission emphasizes work experiences
head starts with work experiences then
-job title educational background.
-address of the university best if the applicant has 10-15 years of
skip a line between heading, date, and work experiences
inside address
FUNCTIONAL
GREETING OR SALUTATION focuses on the skills.
mostly starts with "Dear" and ends best if the applicant changed career or
with a colon (:) re-entered the industry
If name is not stated use "Ma'am/Sir" also used by high school or college
students
THE BODY
main part of the letter COMBINATION or HYBRID
course you are interested, the reason works best if the applicant is aiming
for choosing the university, for a career change
description of academic interest, basis present both skills and
for consideration, and plans. accomplishment.
Last part will include your request to
consider your application.
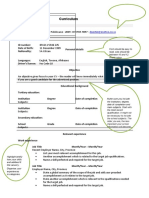
parts
PHOTO
must be recent, formal with plain
COMPLIMENTARY CLOSE
background.
polite way of finishing the letter
always ends with comma (,)
HEADING
complete name, current address,
Signature and Sender's Indentification
contact details
last part of the letter
formatting style must be formal
name (1st line)
your title (if applicable) (2nd line)
ACADEMIC EXPERIENCES
sign above the first line
includes clubs and position, activities
joined or initiated, etc.
resume writing
ACADEMIC QUALIFICATION
formal document that serves to show
schools you attended and year you
a person's career background and
graduated.
skills.
To help a candidate to land a new job
ACADEMIC SUMMARY
consists of a professional summary,
showcase knowledge and abilities
work history, and education sections.
summary of soft skills
three types of resume:
CHRONOLOGICAL, FUNCTIONAL,
CHARACTER REFERENCE
COMBINATION or HYBRID.
character and interpersonal abilities
name of someone who knows you well
except family member/relatives.
You might also like
- Diagnostic Test Practical Research 2Document4 pagesDiagnostic Test Practical Research 2Lubeth Cabatu88% (8)
- Mind Body TechniquesDocument31 pagesMind Body Techniquesveldman100% (3)
- Family TiesDocument3 pagesFamily TiesKm Jml100% (1)
- 2Document3 pages2Christian CaliguidNo ratings yet
- Resume Writing Tips & Hints - Goldman SachsDocument1 pageResume Writing Tips & Hints - Goldman Sachssayantan07.sarkarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (TechWriting) : PRELIMDocument4 pagesReviewer (TechWriting) : PRELIMHazel GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Bpa 112 - Prelim Coverage Part 1Document7 pagesBpa 112 - Prelim Coverage Part 1Trq AlmounaimNo ratings yet
- Writing ResumeDocument17 pagesWriting Resumekapoorayush365No ratings yet
- Work Imm ReviewerDocument12 pagesWork Imm ReviewerLawrence Angelo Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Job Interview Part 1Document2 pagesJob Interview Part 1Hassen AmmNo ratings yet
- Personal Statement Writing: 303 MARTIN HALL - (334) 844-4744 - CAREER - AUBURN.EDUDocument2 pagesPersonal Statement Writing: 303 MARTIN HALL - (334) 844-4744 - CAREER - AUBURN.EDUmosarrufNo ratings yet
- Resume and Application LetterDocument27 pagesResume and Application LetterCharlyn DavidNo ratings yet
- Finals First SemDocument22 pagesFinals First Sems.hanruthmjNo ratings yet
- Resume and Application LetterDocument27 pagesResume and Application LetterRicardo DoroNo ratings yet
- Career ServiceDocument2 pagesCareer ServiceKemala Putri AyundaNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 3Document2 pagesLearning Task 3Bautista NikNo ratings yet
- Resume & Cover Letter WorkshopDocument35 pagesResume & Cover Letter Workshopapi-25885198No ratings yet
- RNW ReviewerDocument6 pagesRNW ReviewerKristine AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Effective CV Writing Skills Presenation 2023 - GraduatesDocument37 pagesEffective CV Writing Skills Presenation 2023 - GraduatesLaura MindeNo ratings yet
- Chronological Resume Template Download PDFDocument1 pageChronological Resume Template Download PDFMarion Shanne Pastor Corpuz100% (1)
- Group 5 PC - 20240320 - 075145 - 0000Document60 pagesGroup 5 PC - 20240320 - 075145 - 0000cortezjoeykateNo ratings yet
- Professional Documents GuideDocument21 pagesProfessional Documents Guide208322 Popoola Ibrahim INDUSTRIALNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Personal InformationVidhya MohanrajNo ratings yet
- Relative Pronouns: Defining ClauseDocument7 pagesRelative Pronouns: Defining Clauseallen c.No ratings yet
- Resume Lesson DocumentsDocument9 pagesResume Lesson Documentsapi-534095936No ratings yet
- Basic ResumeDocument1 pageBasic ResumeChrissy Greenan ArchackiNo ratings yet
- Handout For Reading and Writing SkillDocument7 pagesHandout For Reading and Writing SkillSerina CajelesNo ratings yet
- Resume and Cover Letter 18 Accessible2019 PDFDocument17 pagesResume and Cover Letter 18 Accessible2019 PDFJaegerNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion Lesson 2Document4 pagesWork Immersion Lesson 2rharpienNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument64 pagesUntitledArrent Chrislyn ReyesNo ratings yet
- WRCC 3RDQTR ReviewerDocument21 pagesWRCC 3RDQTR RevieweraziNo ratings yet
- Bcom Resume Template 2Document2 pagesBcom Resume Template 2cowlingericNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter Assignment (CW1) S2 2022-2023 ++ 2Document8 pagesCover Letter Assignment (CW1) S2 2022-2023 ++ 2aq27aqaqaqNo ratings yet
- AAU Career ToolKitDocument27 pagesAAU Career ToolKitwsangrattanamaneeNo ratings yet
- Romeo S. Grande JR., Claveria Sat DLLDocument9 pagesRomeo S. Grande JR., Claveria Sat DLLRomy Sales Grande Jr.No ratings yet
- Purposive Reviewer 1Document3 pagesPurposive Reviewer 1Marianne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Concordia Resume GuideDocument18 pagesConcordia Resume GuideKile MatersonNo ratings yet
- RCC ResumeCoverLetterChecklistDocument1 pageRCC ResumeCoverLetterChecklist01-13-07 G.No ratings yet
- L12 Writing A Resume, An Application Letter, and Office Correspondence (RAWS)Document15 pagesL12 Writing A Resume, An Application Letter, and Office Correspondence (RAWS)Monica Pendel CastroNo ratings yet
- Eng 102 Rev MayDocument2 pagesEng 102 Rev MayLysa Antonette R. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Personal Statement PreparationDocument2 pagesPersonal Statement PreparationjeetmadNo ratings yet
- Professional and Business Correspondence HandoutDocument6 pagesProfessional and Business Correspondence HandoutlucilNo ratings yet
- Learn To Write A Cover Letter Js 5Document7 pagesLearn To Write A Cover Letter Js 5Rahma Ben KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Resumes, References, and Cover Letters: A Helpful Guide For Entering The Job MarketDocument20 pagesResumes, References, and Cover Letters: A Helpful Guide For Entering The Job MarketVijaysinh KambleNo ratings yet
- EAPP Finals ReviewerDocument9 pagesEAPP Finals ReviewerArgueza, John Ryan V.No ratings yet
- PPT 9Document25 pagesPPT 9Gunawan WibisonoNo ratings yet
- Eapp ReviewerDocument2 pagesEapp Revieweramorakatherine0No ratings yet
- The Basic Principles of Technical WritingDocument36 pagesThe Basic Principles of Technical WritingHazel GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Revise Your DocumentsDocument2 pagesRevise Your DocumentssammyNo ratings yet
- Curriculum: Ds Unter@onetwo - Co.zaDocument2 pagesCurriculum: Ds Unter@onetwo - Co.zaTELECOM BRANCHNo ratings yet
- Resumes and Job Letters 3Document24 pagesResumes and Job Letters 3api-325274340No ratings yet
- SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL-Reading and Writing SkillsDocument8 pagesSENIOR HIGH SCHOOL-Reading and Writing SkillsADONIS & CherylNo ratings yet
- Resume CoverLetterDocument36 pagesResume CoverLetterRosalyn NazarioNo ratings yet
- Letter - How To WriteDocument47 pagesLetter - How To WriteSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- CV Packet With CompetenciesDocument7 pagesCV Packet With CompetenciesNoe GNo ratings yet
- ISU PortfolioDocument11 pagesISU PortfoliomilanaNo ratings yet
- Resume Writing Handbook: The Career Development Center Edison Building, Suite 1120 (215) 503-5805Document7 pagesResume Writing Handbook: The Career Development Center Edison Building, Suite 1120 (215) 503-5805karthickNo ratings yet
- Resume Checklist Cover Letter Checklist: Heading YES NO YES NODocument1 pageResume Checklist Cover Letter Checklist: Heading YES NO YES NOjim nunezNo ratings yet
- Writing An Effective ResumeDocument5 pagesWriting An Effective ResumeMichelle RangesNo ratings yet
- 6-A Introduction To FormsDocument5 pages6-A Introduction To FormsWaleed Barakat MariaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English12Document8 pagesLesson Plan in English12Maria ZhoyNo ratings yet
- Graduate School Letter of ReferenceDocument2 pagesGraduate School Letter of ReferenceMaika Alex CalunodNo ratings yet
- Writing Skills for Business: How to communicate clearly to get your message acrossFrom EverandWriting Skills for Business: How to communicate clearly to get your message acrossNo ratings yet
- Case Digests On Liberty of Abode and TravelDocument4 pagesCase Digests On Liberty of Abode and TravelonlineonrandomdaysNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For AMCATDocument4 pagesSyllabus For AMCATmmrafizNo ratings yet
- Reply To Shakespeare Bites BackDocument6 pagesReply To Shakespeare Bites BackJOHN HUDSON100% (3)
- Human Person in The Environment NoteDocument3 pagesHuman Person in The Environment NoteMaleficent Idea100% (1)
- WK 2 - Writing (Part 2 - Informal Letter)Document18 pagesWK 2 - Writing (Part 2 - Informal Letter)Shiu RashydNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmentDocument9 pagesRisk AssessmentAshley Levy San PedroNo ratings yet
- Weiner - The Therapeutic RelationshipDocument169 pagesWeiner - The Therapeutic Relationshipdianapenati100% (5)
- Queer AppalachiaDocument1 pageQueer AppalachiaLiv StoffelNo ratings yet
- Critical Discourse Analysis: Norman FaircloughDocument28 pagesCritical Discourse Analysis: Norman Faircloughemo_transNo ratings yet
- How To Write Architectural Thesis BookDocument7 pagesHow To Write Architectural Thesis Booklob1vesuzov2100% (1)
- Rev. Dr. Colton Smith Sermon 7-14-2106Document6 pagesRev. Dr. Colton Smith Sermon 7-14-2106Anonymous xb3jRqVYNo ratings yet
- Śrī Harināma Mahā-MantraDocument136 pagesŚrī Harināma Mahā-Mantraanon98No ratings yet
- Glossary of Art Terms and First Few LessonsDocument80 pagesGlossary of Art Terms and First Few LessonsVeraaryans83% (6)
- The Automated Children's Book GeneratorDocument4 pagesThe Automated Children's Book Generatorwuzziwug100% (1)
- Seven Arcana of The Emerald TabletDocument2 pagesSeven Arcana of The Emerald TabletChazMichaelmichaels100% (3)
- History Book L15Document18 pagesHistory Book L15Arvind Sanu MisraNo ratings yet
- The Age of Metternich and RomanticismDocument14 pagesThe Age of Metternich and RomanticismHarry SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Practice of BodhicittaDocument10 pagesPractice of BodhicittaMin Bahadur ShakyaNo ratings yet
- English 6 Quarter 3 Week 3Document1 pageEnglish 6 Quarter 3 Week 3odessa pabellanoNo ratings yet
- Sociology 2: Class 14: World-System Theory: Do Not Copy or Distribute Without PermissionDocument31 pagesSociology 2: Class 14: World-System Theory: Do Not Copy or Distribute Without PermissionСілвестер НосенкоNo ratings yet
- Richard Polt Heideggers Being and Time Critical EssaysDocument256 pagesRichard Polt Heideggers Being and Time Critical Essaysweltfremdheit100% (1)
- What's Left of Descartes? by Roger KimballDocument8 pagesWhat's Left of Descartes? by Roger Kimballj9z83fNo ratings yet
- Praying The Names of Jesus SampleDocument23 pagesPraying The Names of Jesus SampleZondervan100% (1)
- Pfeffer 2008Document23 pagesPfeffer 2008MaybelineNo ratings yet
- SM Unit2Document20 pagesSM Unit2Sudip ParajuliNo ratings yet
- MinimalismDocument8 pagesMinimalismkgaviolaNo ratings yet
- PVL101Q Unit6Document17 pagesPVL101Q Unit6Pulkit PareekNo ratings yet