Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen-Chem (Nature of Solids)
Gen-Chem (Nature of Solids)
Uploaded by
Jasmine Mary Issa Quezon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 pageThis document summarizes key concepts related to the nature and phases of solids. It defines crystallization as the process where atoms or molecules form a highly organized crystal structure. It describes different types of crystal structures including metallic, ionic, molecular, and covalent network crystals. It also defines and compares various phase changes that solids can undergo, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, and sublimation, as well as the corresponding phase transition temperatures and points.
Original Description:
Original Title
gen-chem (nature of solids)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes key concepts related to the nature and phases of solids. It defines crystallization as the process where atoms or molecules form a highly organized crystal structure. It describes different types of crystal structures including metallic, ionic, molecular, and covalent network crystals. It also defines and compares various phase changes that solids can undergo, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, and sublimation, as well as the corresponding phase transition temperatures and points.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 pageGen-Chem (Nature of Solids)
Gen-Chem (Nature of Solids)
Uploaded by
Jasmine Mary Issa QuezonThis document summarizes key concepts related to the nature and phases of solids. It defines crystallization as the process where atoms or molecules form a highly organized crystal structure. It describes different types of crystal structures including metallic, ionic, molecular, and covalent network crystals. It also defines and compares various phase changes that solids can undergo, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, and sublimation, as well as the corresponding phase transition temperatures and points.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
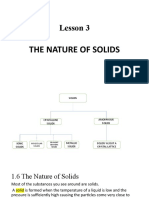
Nature of solids Melting- heating or adding solid state WITHOUT
Crystallization- the energy to a solid structure going through a liquid
process by which a solid to break down. (solid to state.
forms, where the atoms or liquid)
molecules are highly - Melting point- the Phase diagram- a
organized into a structure temperature at convenient way to
known as a crystal. which the solid represent graphical
melts to form the conditions at which stat is
Metallic crystals- liquid. stable
simplest type of structure
since single metallic atoms Freezing- removing heat
are the constituent units. or cooling a liquid, where it
- Cubic packing becomes unable to move.
- Hexagonal close- (liquid to solid)
packing - Freezing point-
the temperature at
Metallic solids- can be which the liquid
thought of as three- freezes into liquid.
dimensional arrays of Triple point- refers to the
metal cations embedded Vaporization/ temperature and pressure
into a matrix of negative evaporation- in which at which all three phases
charges. liquid particles escape the (solid, liquid, and gas)
- Copper surface of the liquid coexist.
- Zinc turning into vapors. (liquid Critical point- refers to
- Aluminum to gas) the critical temperature
- Iron - Boiling point- the and pressure together.
- Silver temperature at (in which, above these,
which the liquid kinetic energies are too
Ionic crystals- have ions boils. high, only gas phase can
as constituent particles. exist.
- Salt crystals Condensation- as where
particles in the vapor are ~ crystal lattice: highly
Molecular crystals- are cooled. (gas to liquid) ordered unit cells that form
those which have a repeated pattern
molecules as constituent Sublimation- where a ~endothermic process
particles as well as solid state goes to (absorb energy): melting,
structure units. Weal gaseous state WITHOUT evaporation, and
Waals forces of attraction going to a liquid state. sublimation
hold them together. (solid to gas) ~exothermic process
- They occur bear (release energy): freezing,
Covalent network volcanic vents condensation, and
crystals- are giant deposition.
molecules or Deposition- where a ~heating curve: plot of
macromolecules. gaseous state goes to a temperature versus heat
You might also like
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Document13 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Helene_mbbt100% (1)
- General ChemistryDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistrysilentchase332No ratings yet
- Notes Chem Enely 1Document11 pagesNotes Chem Enely 1rickyNo ratings yet
- Yr9 Particles RevisionDocument4 pagesYr9 Particles RevisionKung ThanyathornNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMDocument11 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 2 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMJay Bee83% (29)
- Lesson 5 MatterDocument39 pagesLesson 5 MatterJoly Mae Montejo ErmejeNo ratings yet
- 4 - State of Matter IiDocument91 pages4 - State of Matter IiHenry ChongNo ratings yet
- Matter Definition & The Five States of MatterDocument2 pagesMatter Definition & The Five States of MatterAceeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry O Level Notes 2022Document30 pagesChemistry O Level Notes 2022yessomegudstuffNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of Matter 2Document32 pagesThe Particulate Nature of Matter 2Pritam CainNo ratings yet
- Changes in Matter/Phase Change: Phase Transition Liquid GasDocument1 pageChanges in Matter/Phase Change: Phase Transition Liquid GasMARISTELA MACARANASNo ratings yet
- 1GP - Chemistry NotesDocument12 pages1GP - Chemistry NoteseriannenabazengNo ratings yet
- The Nature of SolidsDocument11 pagesThe Nature of SolidsnsuperticiosoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ch.1: Keywords and End of Chapter QuestionsDocument2 pagesChemistry Ch.1: Keywords and End of Chapter QuestionsarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 0620 NotesDocument192 pagesChemistry 0620 Notesmohammed mahdyNo ratings yet
- Notes Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument4 pagesNotes Kinetic Molecular TheoryGino Carlos MiguelNo ratings yet
- Qr. 3 Science 8 MatterDocument3 pagesQr. 3 Science 8 MatterHezekiah GatesNo ratings yet
- PHSA - Science 11 - Q1 - Lecture 5 - Endogenic Processes - Heat in The Interior of The Earth and MagmatismDocument43 pagesPHSA - Science 11 - Q1 - Lecture 5 - Endogenic Processes - Heat in The Interior of The Earth and MagmatismFranz AndraNo ratings yet
- States of Matter - Solids, Liquids, Gases & Plasma - ChemistryDocument8 pagesStates of Matter - Solids, Liquids, Gases & Plasma - Chemistryjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument8 pagesChem Reviewerkaye arcedeNo ratings yet
- The Four Fundamental States. 14 JulioDocument7 pagesThe Four Fundamental States. 14 Juliodionisiojose14No ratings yet
- 3.1rev.4 Nature of MaterialsDocument41 pages3.1rev.4 Nature of MaterialsNguyễn Xuân NamNo ratings yet
- 13-Crystallization-I-Concepts and Homogeneous Nucleation-21-08-2023Document22 pages13-Crystallization-I-Concepts and Homogeneous Nucleation-21-08-2023NandiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Matter and The Atomic StructureDocument80 pagesChapter 2 - Matter and The Atomic StructurePUNITHA A/P NARAYANASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Hi GwynDocument3 pagesHi GwynUtopia CeballoNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy DefinintionsDocument1 pageMetallurgy Definintionsnasermohamed023457No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer q3Document4 pagesScience Reviewer q3Jaye Zielle Angela B. CosinasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lesson 3Document38 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 3PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Carmen - Dup Notes - NSW 700 - First 3 Days of Class UpdatedDocument48 pagesCarmen - Dup Notes - NSW 700 - First 3 Days of Class UpdatedNduP78No ratings yet
- KMT ImfaDocument44 pagesKMT Imfaellajazelle75No ratings yet
- Y9keywords AtomDocument5 pagesY9keywords AtomfugzieNo ratings yet
- Matter Study Guide For TurboquestDocument3 pagesMatter Study Guide For Turboquestapi-267947714No ratings yet
- LESSON 4-Solidification of Metals and Alloys PDFDocument19 pagesLESSON 4-Solidification of Metals and Alloys PDFmerooney desanchesNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument15 pagesStates of MatterMOHAMMAD DANISHNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Y3IP Chemistry Notes (2023) .Docx - Y3IP Chemistry Notes (2023) - 1Document43 pagesMicrosoft Word - Y3IP Chemistry Notes (2023) .Docx - Y3IP Chemistry Notes (2023) - 1biriginpeterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Matter and The Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concept of MatterDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Matter and The Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concept of Matterforyourhonour wongNo ratings yet
- VOLCANOES AbdelSalam2024Document19 pagesVOLCANOES AbdelSalam2024ab4943409No ratings yet
- Structure and Properties of WaterDocument6 pagesStructure and Properties of WaterBrendan Lewis DelgadoNo ratings yet
- State of MatterDocument13 pagesState of MatterKofoworola MikailNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Solid Liquid and GasesDocument36 pagesChapter 6 Solid Liquid and Gasestashnee pillayNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryatipriya choudharyNo ratings yet
- U1 PN Mod 2Document16 pagesU1 PN Mod 2Puja DhawanNo ratings yet
- 2 States of MatterDocument32 pages2 States of MatterB R YNo ratings yet
- ST - Xaviers Cathedral School, Amravati: ROLL No - 32 Subject-Science Topic - Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument16 pagesST - Xaviers Cathedral School, Amravati: ROLL No - 32 Subject-Science Topic - Matter in Our SurroundingsParth SonkhaskarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lesson #1 - The Kinetic Particle Theory Pre-Test!Document6 pagesChemistry Lesson #1 - The Kinetic Particle Theory Pre-Test!estherlimrhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Lecture 2-SolidsDocument16 pagesLecture 9 Lecture 2-SolidswaustavaiqiaNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument26 pagesRevisionAbisan ArulananthamNo ratings yet
- Sublimation Deposition Condensation VaporisationDocument2 pagesSublimation Deposition Condensation Vaporisationjoenediath9345No ratings yet
- LESSON 4-Solidification of Metals and AlloysDocument19 pagesLESSON 4-Solidification of Metals and Alloysmichael-education KNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 A NotesDocument67 pagesChemistry Form 4 A NotesJia En TanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument4 pagesSCIENCEirenecalaboNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 2A - Nature of Solids and Phase Changes 1Document34 pagesQ3 Module 2A - Nature of Solids and Phase Changes 1Rance BobadillaNo ratings yet
- Matter: Definition & The Five States of Matter: AtomsDocument10 pagesMatter: Definition & The Five States of Matter: AtomsJeonila Margarette RapadaNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy (GZ) 2017Document20 pagesHeat Energy (GZ) 2017kaviNo ratings yet
- Solids, Liquids and GasesDocument9 pagesSolids, Liquids and GasesBassel ZeitouniNo ratings yet
- 5 CH 2 Sec 2 Changes in State and Energy - UploadDocument74 pages5 CH 2 Sec 2 Changes in State and Energy - Uploadapi-270861823No ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document3 pagesChapter 06zahidNo ratings yet
- Space Plasma Physics Lecture-1Document71 pagesSpace Plasma Physics Lecture-1Furqan Ali CheemaNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument5 pagesProjectile MotionJasmine Mary Issa QuezonNo ratings yet
- Abm WannabeDocument13 pagesAbm WannabeJasmine Mary Issa QuezonNo ratings yet
- OUTLINE - Reactions & Molecular CollisionsDocument2 pagesOUTLINE - Reactions & Molecular CollisionsJasmine Mary Issa QuezonNo ratings yet
- KMT - Properties of LiquidDocument8 pagesKMT - Properties of LiquidJasmine Mary Issa QuezonNo ratings yet
- ReligionDocument2 pagesReligionJasmine Mary Issa QuezonNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Outline - GeneticsDocument2 pagesGen Bio Outline - GeneticsJasmine Mary Issa QuezonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chapter Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding: Chapter Practice ProblemsHairy Balls2No ratings yet
- 50 Top Semiconductors - PN Junction Theory Questions and Answers PDF Semiconductors - PN Junction Theory Interview Questions and AnswersDocument5 pages50 Top Semiconductors - PN Junction Theory Questions and Answers PDF Semiconductors - PN Junction Theory Interview Questions and Answersjilanlucky2220% (1)
- EEE 221: Physical Electronics: Engr. Dr. H. O. Ohize April 28, 2021Document24 pagesEEE 221: Physical Electronics: Engr. Dr. H. O. Ohize April 28, 2021Quantum BoyNo ratings yet
- Absolute Electronegativity and Absolute Hardness Lewis Acids and BasesDocument1 pageAbsolute Electronegativity and Absolute Hardness Lewis Acids and Basesleizar_death64No ratings yet
- Said DissertationDocument129 pagesSaid DissertationSaeed AzarNo ratings yet
- MSCCH 501Document204 pagesMSCCH 50120tamilselvi-ugcheNo ratings yet
- Chapt 03 PDFDocument37 pagesChapt 03 PDFpuceiroaleNo ratings yet
- Graphene FET On Diamond For High-Frequency ElectronicsDocument4 pagesGraphene FET On Diamond For High-Frequency Electronicsh20230136No ratings yet
- Syllabus NANOTECH Detail PDFDocument15 pagesSyllabus NANOTECH Detail PDFOshi_TweetyNo ratings yet
- Electronic and Device - Lecture NotesDocument39 pagesElectronic and Device - Lecture Notesxinyu guoNo ratings yet
- Transparent ElectronicsDocument11 pagesTransparent ElectronicsanshulNo ratings yet
- CH 06 Binary PhaseDocument62 pagesCH 06 Binary PhaseUltrichNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry CHEMHACKDocument9 pagesSurface Chemistry CHEMHACKSonu Kr safiNo ratings yet
- Mot 1 10Document10 pagesMot 1 10Nupur ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 1.1 D Landau Level EigenstatesDocument8 pages1.1 D Landau Level EigenstatesahsbonNo ratings yet
- Glass - Wikipedia 21Document1 pageGlass - Wikipedia 21A-ReaderNo ratings yet
- Anomalous Expansion of WaterDocument2 pagesAnomalous Expansion of WaterDiana BuisNo ratings yet
- Crystal Imperfections, Plastic Deformation ... : BME, Department of Materials Science and EngineeringDocument30 pagesCrystal Imperfections, Plastic Deformation ... : BME, Department of Materials Science and EngineeringParijat MitraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Course ContentDocument5 pagesChemistry Course ContentEfrem Hirko GufiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Electron-Hole Puddles On The Performance of Graphene Antidot Field Effect TransistorDocument12 pagesEffect of Electron-Hole Puddles On The Performance of Graphene Antidot Field Effect TransistorAtul YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Atomic Structure and BondingDocument27 pagesChapter Two: Atomic Structure and Bondingdawit gashuNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Ic Fabrication ProcessDocument172 pagesTopic 2-Ic Fabrication Processfir100% (1)
- Introduction of Quantum MechanicsDocument2 pagesIntroduction of Quantum MechanicsAnand Verma0% (1)
- Chemical BondingDocument7 pagesChemical BondingSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Drift CurrentDocument9 pagesDrift CurrentDeepanwita SarNo ratings yet
- Nanomaterials 12 01058 PDFDocument33 pagesNanomaterials 12 01058 PDFmuraliNo ratings yet
- Quantum Field Theory Notes by JaffeDocument17 pagesQuantum Field Theory Notes by JaffedbranetensionNo ratings yet
- Charge Neutrality FinalDocument11 pagesCharge Neutrality FinalBern Michael VillenaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Co-Ordination CompoundsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Co-Ordination CompoundsAbid waniNo ratings yet
- DC Characteristics of A MOS Transistor (MOSFET) : Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.4Document22 pagesDC Characteristics of A MOS Transistor (MOSFET) : Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.4Cazimir BostanNo ratings yet